Enzymes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
6 Classes of Enzymes
Oxidoreductases, Transferases, Hydrolases, Lyases, Isomerases, Ligases
Oxidoreductase Purpose
Oxidation-Reduction reaction
Transferases Purpose
Transfer of functional groups
Hydrolases Purpose
Hydrolysis reactions
Lyases purpose
group elimination to form double bonds
Isomerases Purpose
Isomerization reactions
Ligases Purpose
Bond formation coupled with ATP Hydrolysis
How is a Lineweaver-Burk plot effected with a competitive inhibitor
Km increases, Vmax is unchanged
How is a Lineweaver-Burk plot effected with an uncompetitive inhibitor
Km decreases, Vmax decreases
How is a Lineweaver-Burk plot effected with a noncompetitive inhibitor
km is unchanged, Vmax is decreased
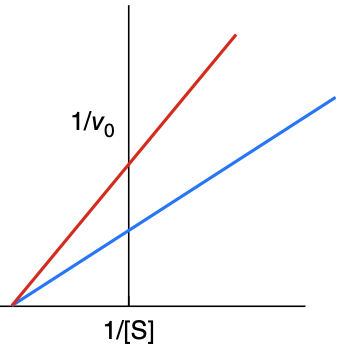
What type of inhibitor is this?
noncompetitive
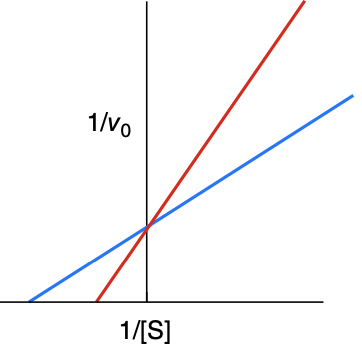
What type of inhibitor is this?
A competitive inhibitor
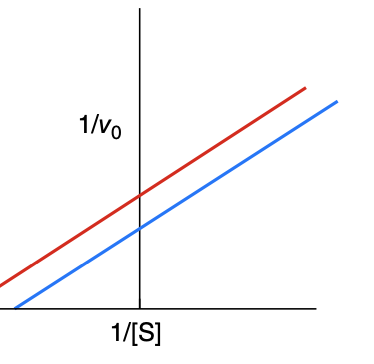
What type of inhibitor is this?
uncompetitive
What is a competitive inhibitor
A molecule that binds to an enzyme's active site, preventing the substrate from binding
What is a noncompetitive inhibitor
A molecule that binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, altering enzyme function and preventing substrate binding.
What is an uncompetitive inhibitor
A molecule that binds only to the enzyme-substrate complex, preventing conversion to the product.
Michaelis-Menten Equation
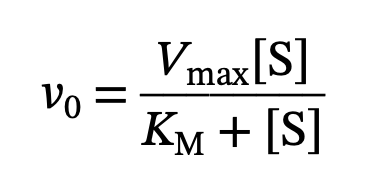
Km Equation
[E][S]/[ES]
Kcat equation
Vmax/[E]t
What is Km
the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of Vmax, indicating the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate.
What is kcat
the turnover number of an enzyme, representing the number of substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme molecule per unit time when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate.
Catalytic Efficiency Equation
kcat/Km
What is catalytic efficiency
A measure of how effectively an enzyme converts a substrate into product. Higher values indicate more efficient enzymes.
What is the equation of a Lineweaver-Burk Plot
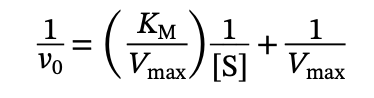
what is a suicide substrate
a substrate that goes to the enzymes active site but is unable to undergo the complete reaction and becomes “stuck” in the active site
Michealis-Menten equation for a competitive inhibitor
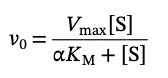
Why does Km seem larger with a competitive inhibitor
Because the inhibitor prevents some of the substrate from reaching the active site, the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate appears to decrease. However, because the inhibitor binds reversibly, it constantly dissociates from and re-associates with the enzyme, which allows a substrate molecule to occasionally enter the active site. It requires a higher substrate concentration to achieve the same enzyme activity, making it appear to have a larger Km.
equation for Ki
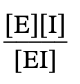
different mechanism of enzyme catalysis
Acid-base catalysis, covalent catalysis, metal ion catalysis