hydrogen NMR
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Predicting hydrogen environments

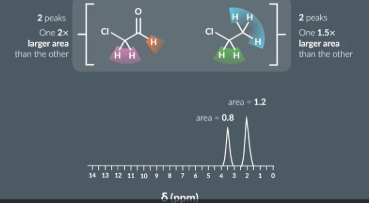
How to calculate the number of hydrogens in each environment
Both molecules have 2 hydrogen environments so we cant use the number of peaks in the spectra to tell them apart. However we can use the areas underneath the peaks
One molecule has 2 hydrogen in its hydrogen environment and 1 in the other so 1 peak should be 2X larger than the other
1 molecule has 3 hydrogen in it hydrogen environemtn and 2 in the other so one peak should be 1.5X larger than the other.
Looking at the spectrum produced the area under one peak is 1.5X smaller than the area under the other peak (1.2/0.8=1.5) so the 2nd molecule is responsible for the spectra
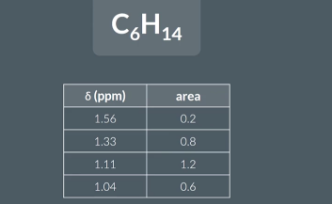
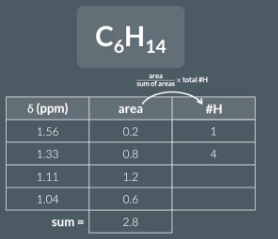
Sometimes a question will give us the molecular formula of a molecule as well as the areas under each peak in its hydrogen NMR and ask us to work out the number oh hydrogen atoms in each environment
area/ sum of areas x total number of hydorgens (in molecular formula)
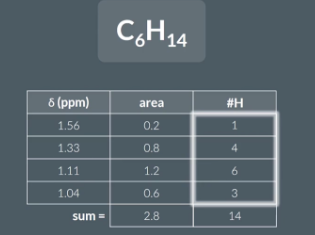
These values are all whole numbers and sum to 14.
in your exams, examiners won’t call the values you’ll use to determine the number of hydrogen atoms in each environment ‘the areas underneath each peak’, examiners will refer to ‘integration ratios’
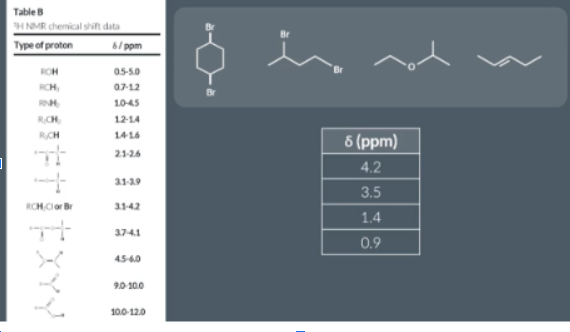
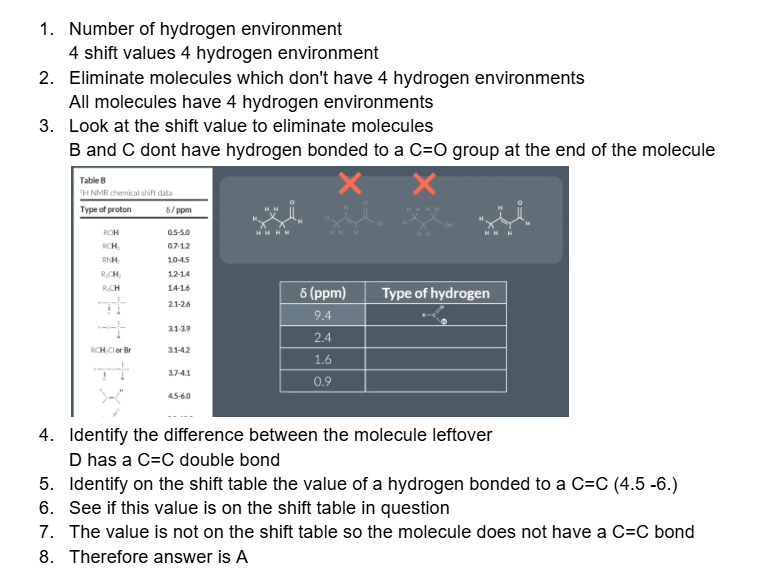
How to identify which molecule this is from shift values

double peaks, triple peaks and quartet peaks
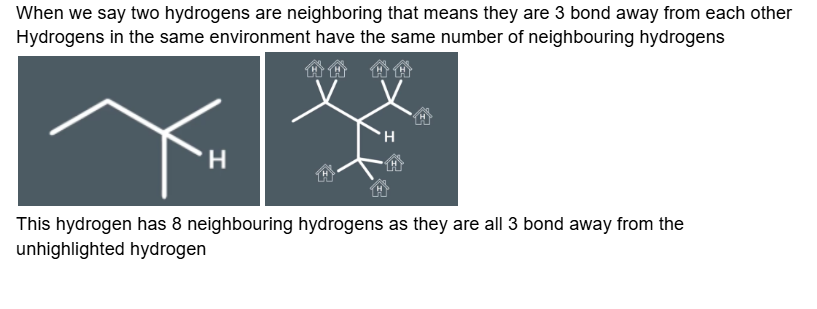
understanding splitting; neighbouring hydrogens
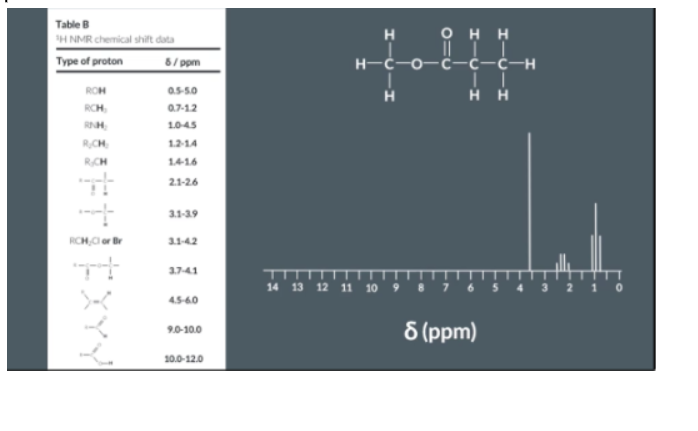
Understanding the spitting rule
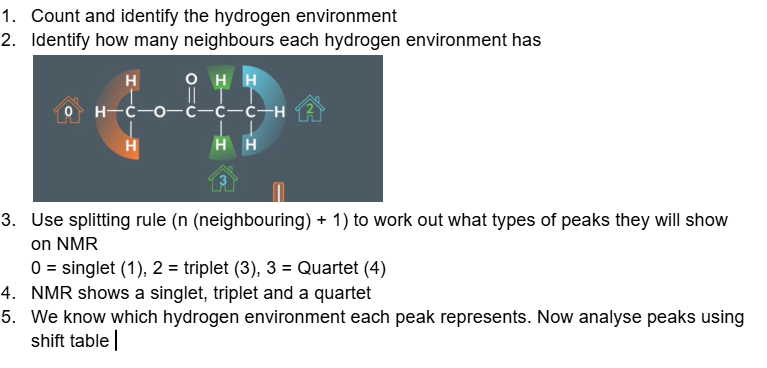
Equivalent hydrogens
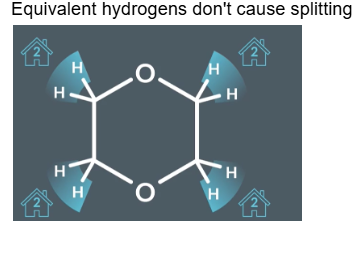
How many peak does this molecule produce
2 hydrogen environments
Orange hydrogen environment has 2 neighbouring hydrogens and are equal to produce 1 triplet
Green hydrogen environment has 3 neighbouring hydrogens and are equal to produce 1 quartet.
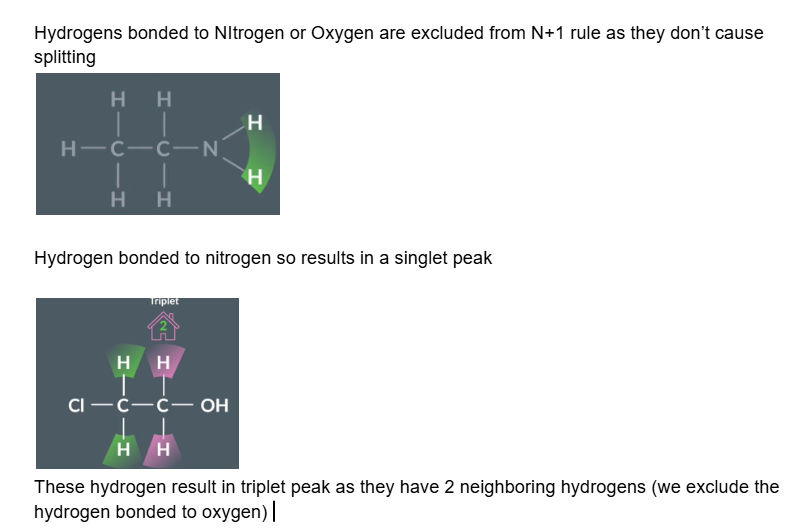
Hydrogens bonded to Nitrogen or Oxygen
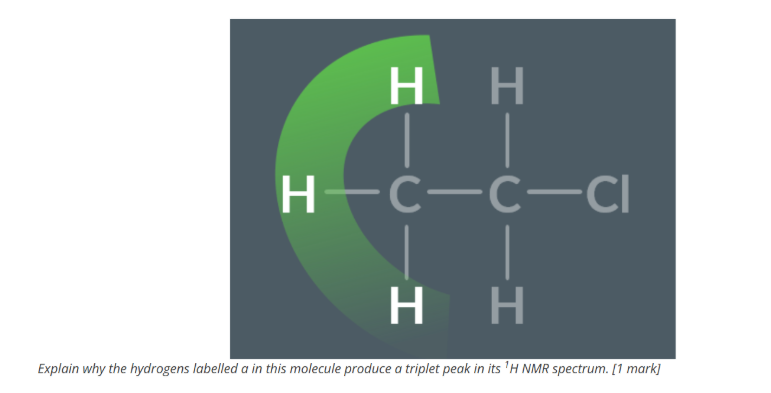
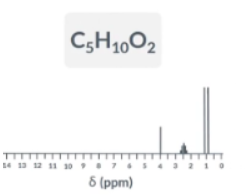
GIven the data draw the fulls structure of this molecule
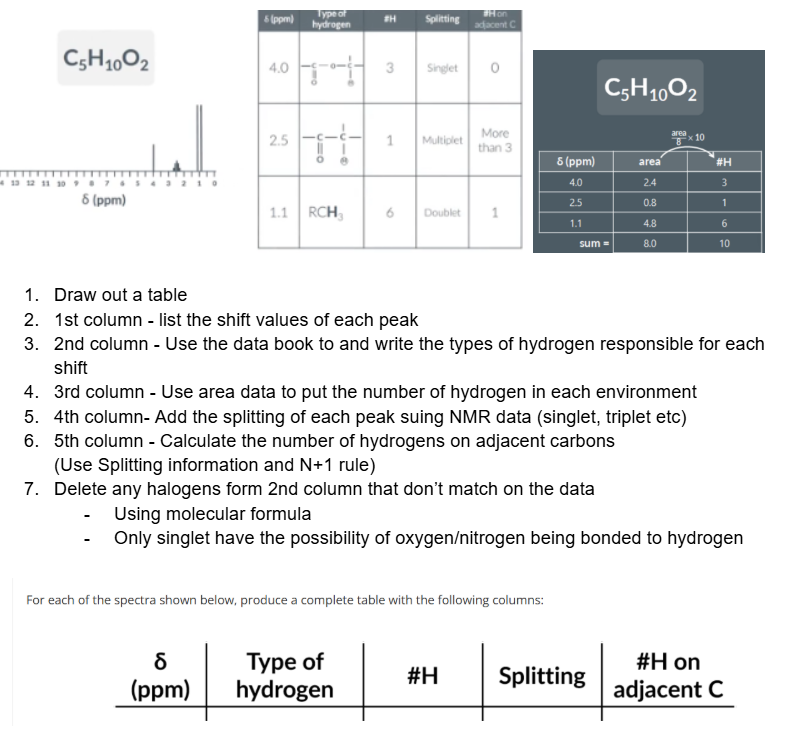
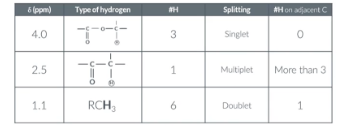
In the exam you may be given a table like this and asked to deduce the molecule
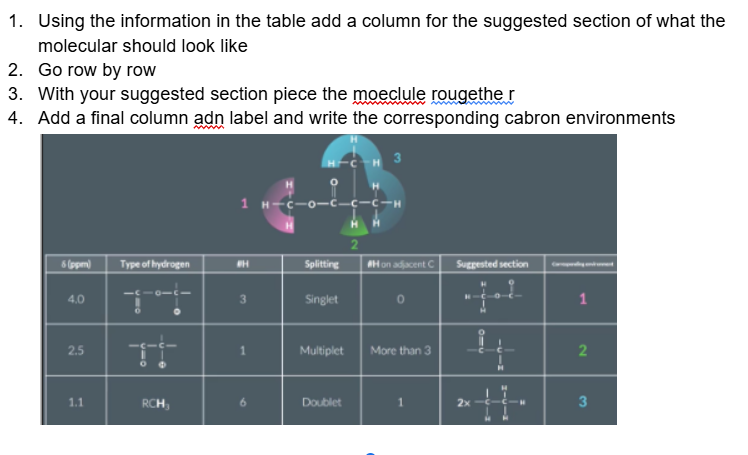
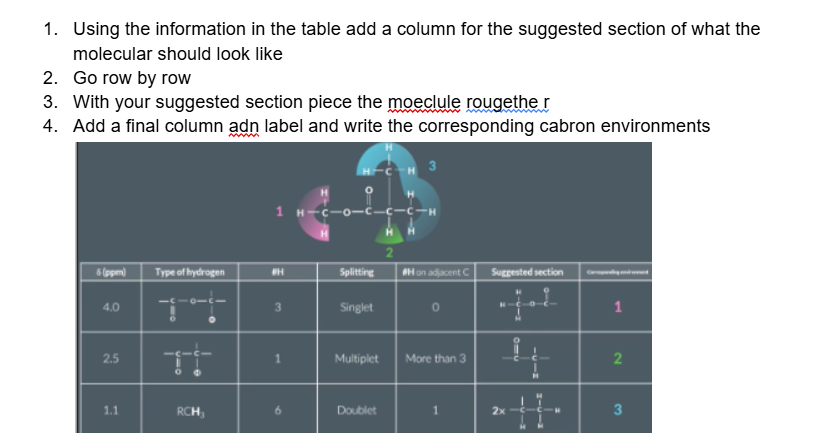

Some peaks crop up quite often in a level hydrogen NMR questions which are worth remembering

Groups 4 and 9
HNMR substances