Bushong Chapter 4 finished Electricity, Magnetism, and Electromagnetism
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
what is the primary function of a x-ray imaging system?
to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy
the electric motor converts electric energy into what?
mechanical energy
the electric range converts electric energy into what?
thermal energy. ex toaster

define electrostatic
the study of stationary electric charges
an object is said to be electrified if it has _______ or ________ electrons
too few or too many
what are the 3 ways electrification can be created?
contact, friction, or induction
what is an example of contact?
touching a metal doorknob after walking across a carpet in winter, you get a shock

what is an example of friction?
when electrons are rubbed off the carpet onto your shoes

what is an example of induction?
when there is a thunderstorm, wind and cloud movement can remove electrons from one cloud and deposit them on another.

define electric ground
one object that is available to accept electric charges from an electrified object, acts like a reservoir. ex earth
where does lightning occur?
occurs between an electrified cloud and the earth. the discharge between clouds that is deposited in another (lightning)
what is the unit of electric charge?
the coulomb (C)
1C is equal to how many electron charges?
1C = 6.3 x 10*18 electron charges
what are the 4 laws of electrostatic?
1. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other.
2. Coulomb's law: The electrostatic force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of their quantities and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
3. Electric charge distribution is uniform throughout or on the surface.
4. Electric charge of a conductor Glossary is concentrated along the sharpest curvature of the surface.
what is Coulomb's law?
the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the electrostatic charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
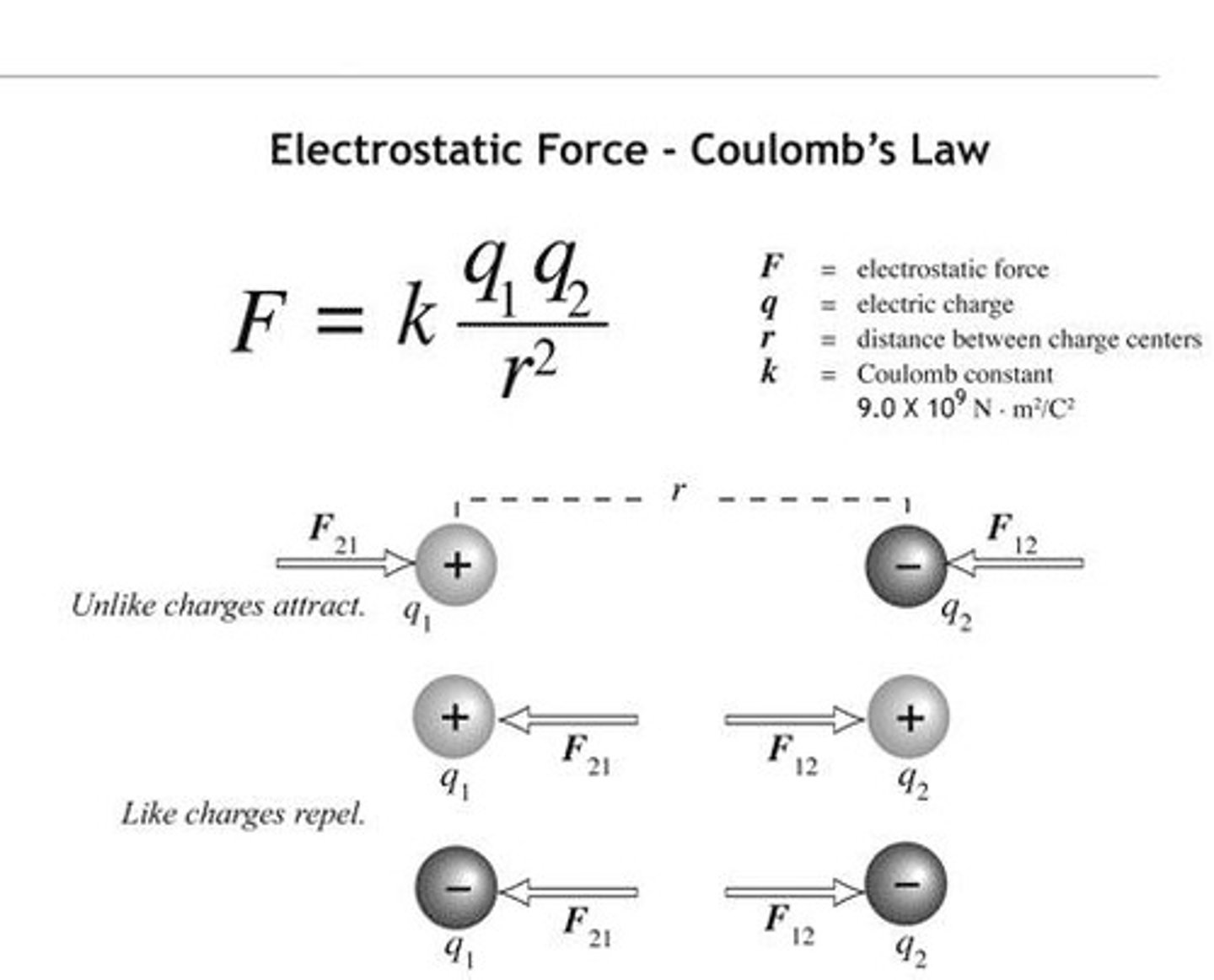
define electrostatic force
the force of attraction between unlike charges or repulsion between like charges is attributable to the electric filed.
electrostatic charges are concentrated on surfaces of sharpest or smoothest curvature?
sharpest
what is the unit of electric potential?
volt (V)
the higher the voltage, the greater the what?
the greater is the potential to do work
in the US the electric potential in homes and offices is what?
110V
Imaging systems usually require how much electric potential?
220V or higher
the volt is?
potential energy/unit charge or joule/coulomb (1V = 1J/C)
define electric current
when electric potential is applied to objects, like a copper wire, the electrons move along the wire
electrodynamics is the study of what?
the study of electric charges in motion
electric current is always opposite that of electron flow. T/F
True
what is a conductor?
any substance through which electrons flow easily
what are some examples of electric conductors?
metals and water

what is an insulator?
any material that does not allow electron flow
what are some examples of insulators?
glass, clay, and rubber
what is a semiconductor?
a material that under some conditions behaves as an insulator and in other conditions behaves as a conductor. ex silicon and germanium
what is superconductivity?
the property of some materials to exhibit no resistance below a critical temperature. ex niobium and titanium
at room temperature do all materials resist the flow of electricity?
yes
what is an electric circuit?
is a path in which electrons from a voltage or current source flow. The point where those electrons enter an electrical circuit is called the "source" of electrons.
electric current is measured in what?
Amperes (A) 1A = 1C
electron resistance is measured in what?
ohms

what is Ohm's law?
the voltage across the total circuit or any portion of the circuit is equal to the current times the resistance.

what is the function of the resistor in the circuit?
inhibits flow of electrons

what is the function of a battery in the circuit?
provides electric potential

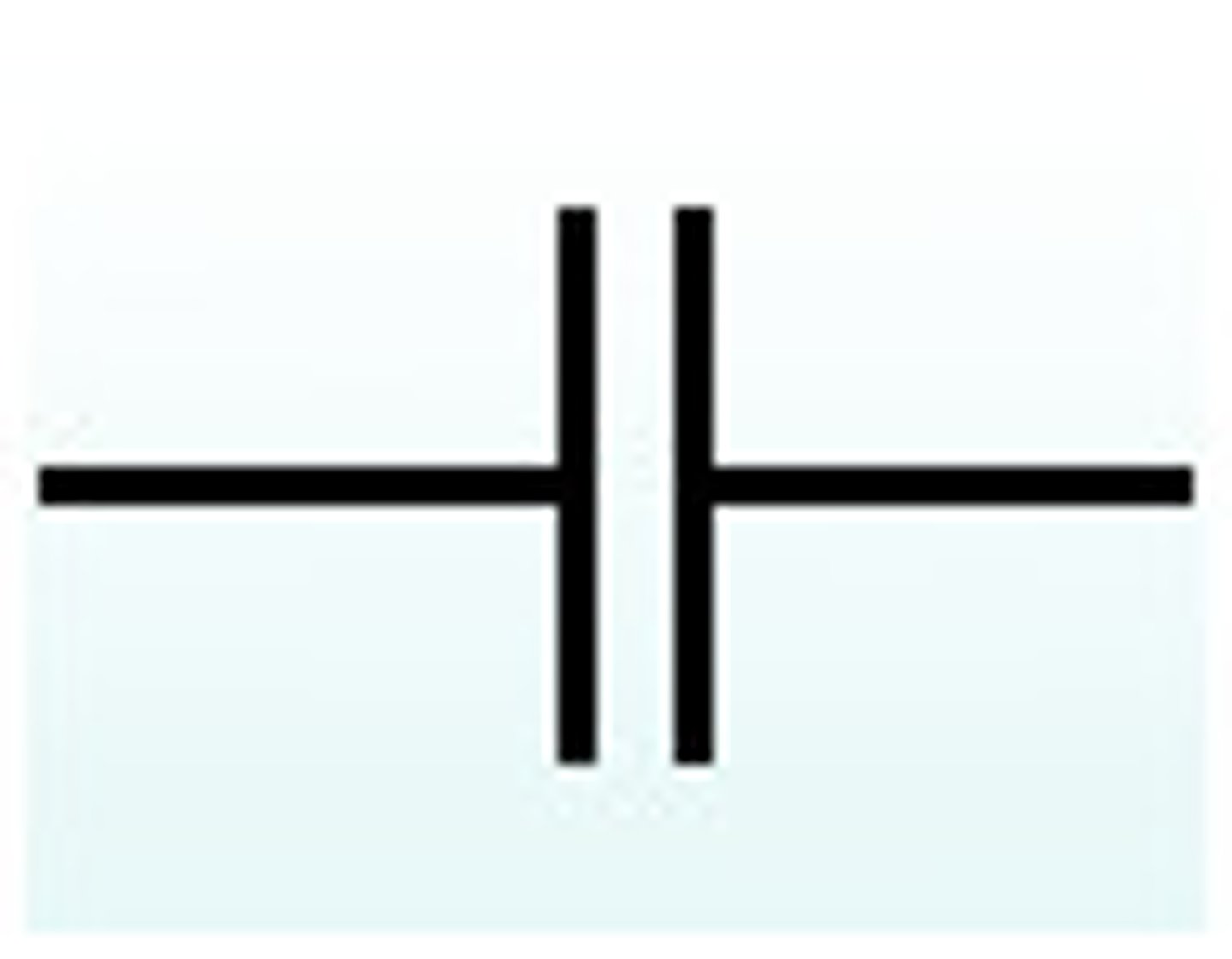
what is the function of the capacitor in the circuit?
momentarily stores electric charge
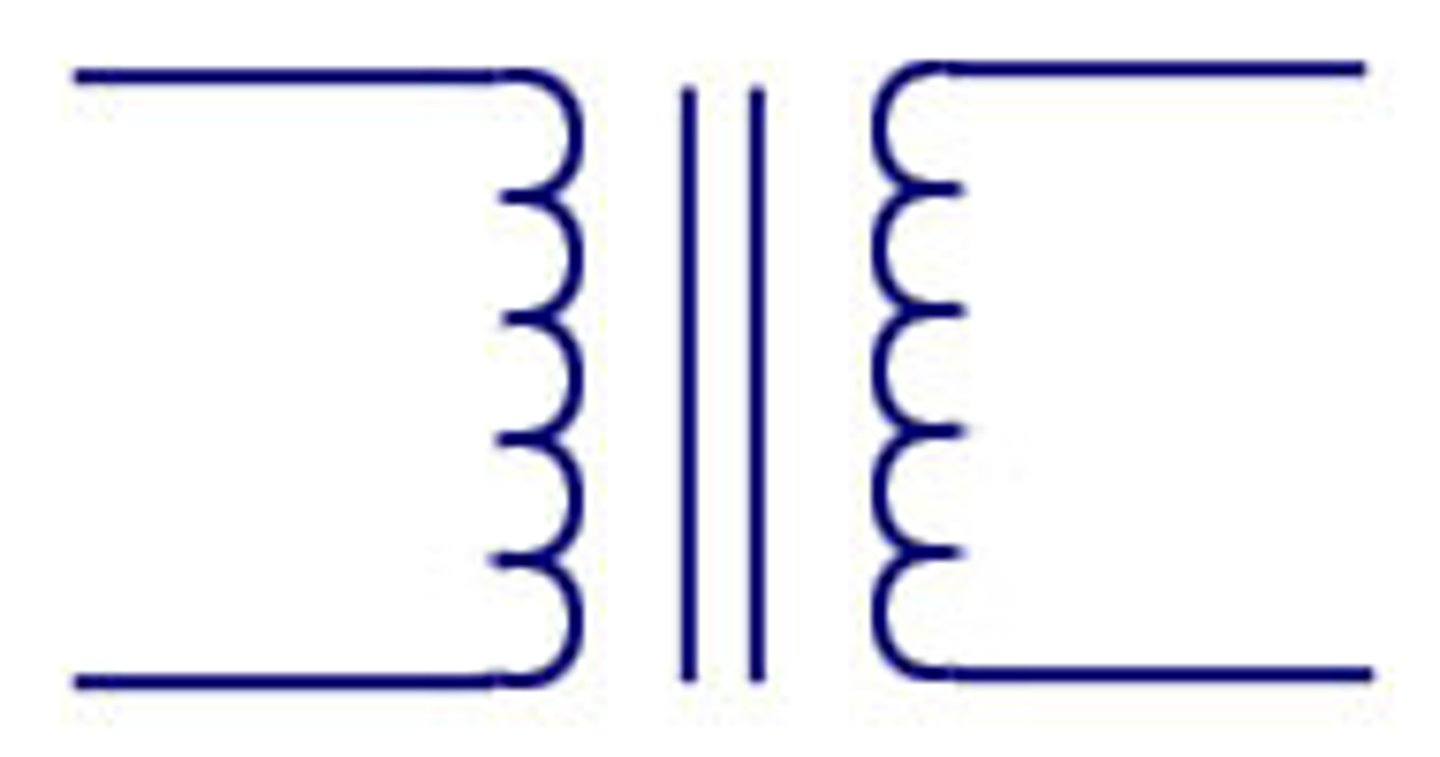
what is the function of the transformer in the circuit?
increases or decreases voltage by fixed amount (AC only)
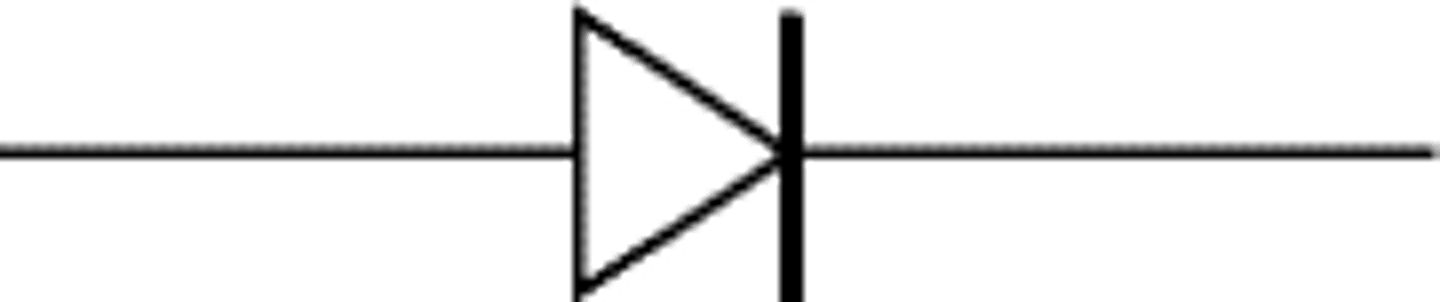
what is the function of the diode in the circuit?
allows electrons to flow in only one direction.
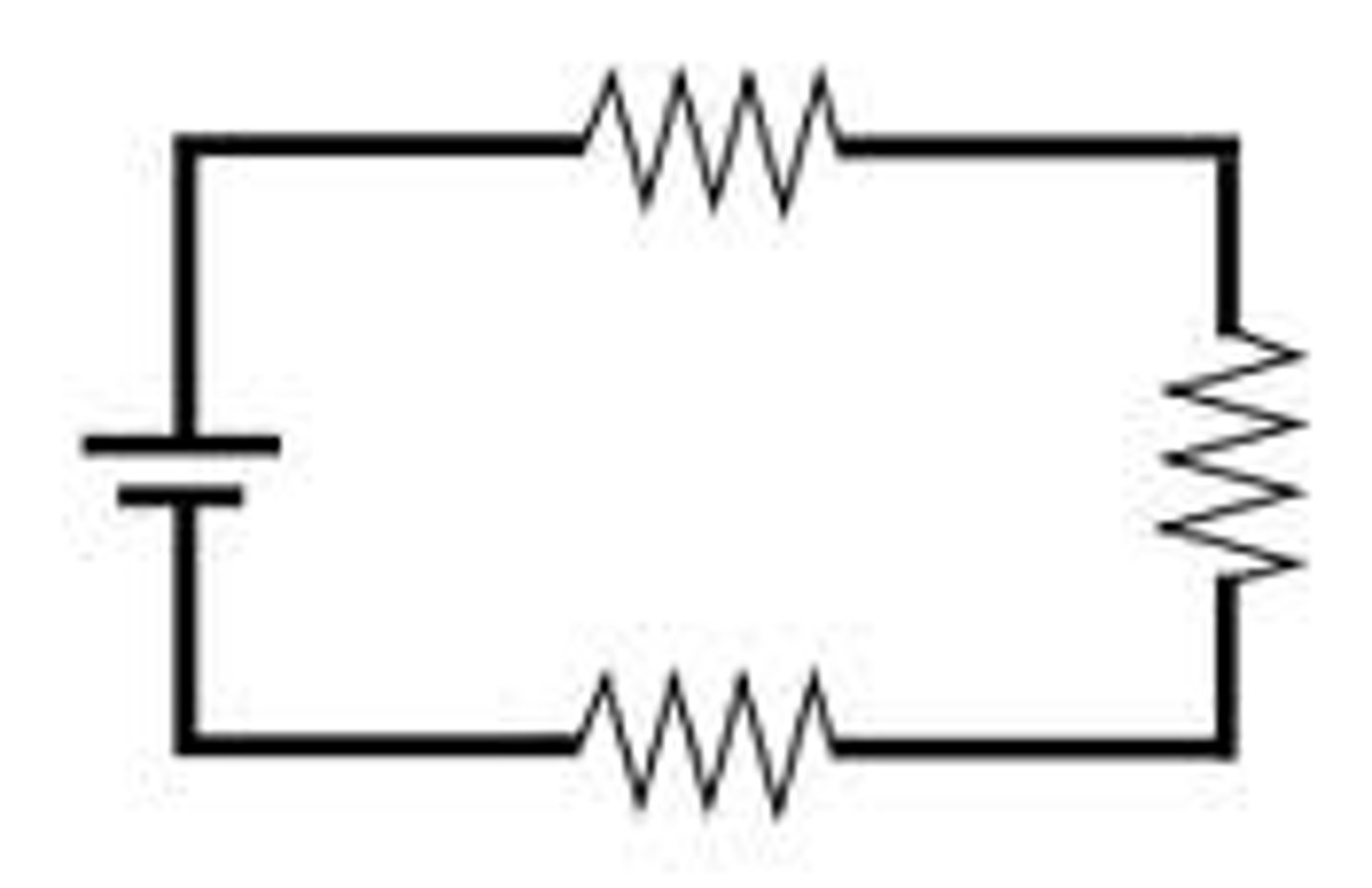
rules for series circuits
the total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
the current through each circuit element is the same and is equal to the total circuit current.
the sum of the voltages across each circuit element is equal to the total circuit voltage.
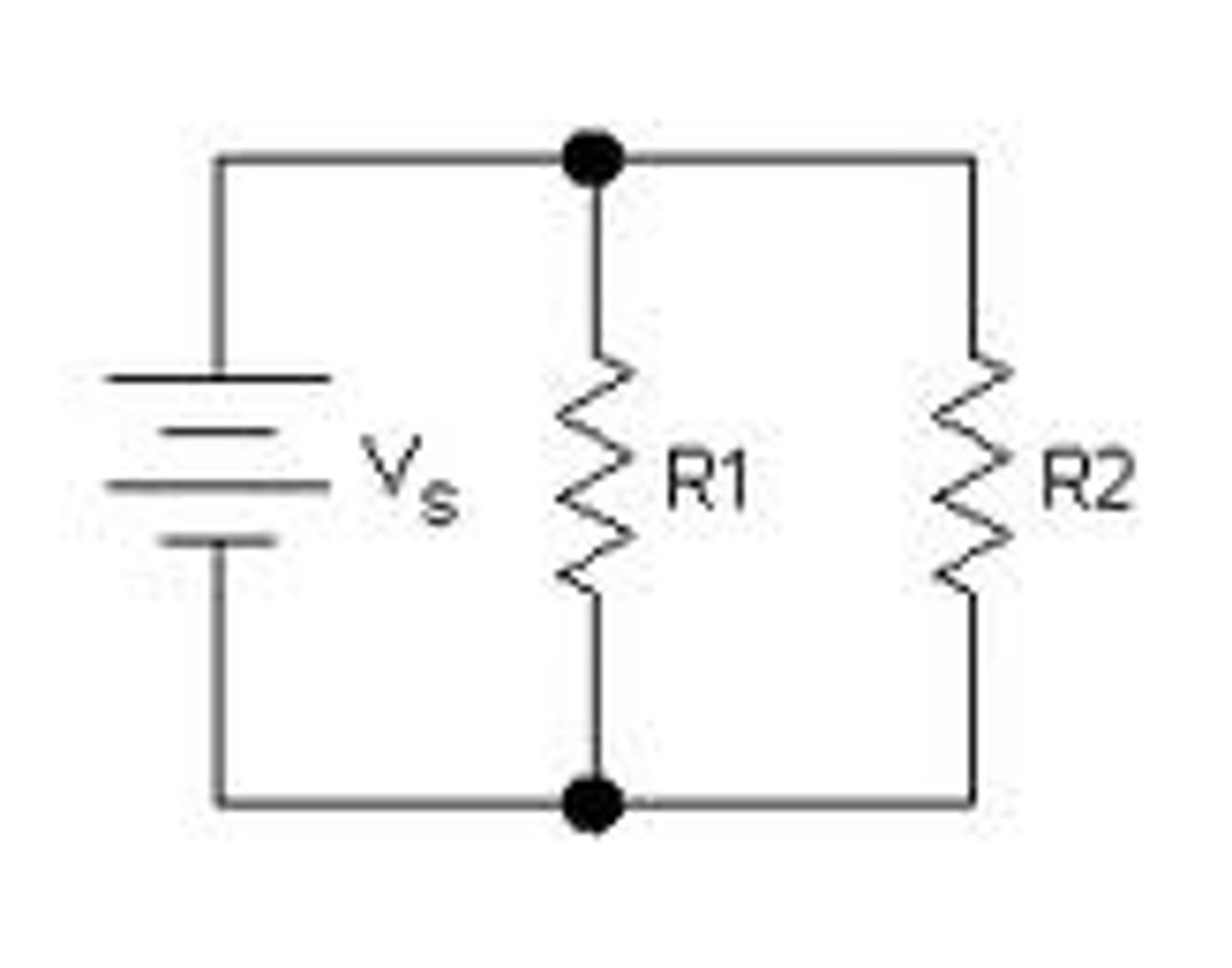
rules for a parallel circuit
the sum of the current through each circuit element is equal to the total circuit current.
the voltage across each circuit element is eh same and is equal to the total circuit voltage.
the total resistance is the inverse of the sum of the reciprocals of each individual resistance.
electric field
line of force exerted on charged ions
positive charge
point outwards
negative charge
point downwards
electrostatic force
force of attraction between like charges
electrodynamics
study of electric charges in motion
electrical engineer
works with electric current
physicist
works with electron flow
four states of matter
conductor, insulator, semiconductor,superconductor
conductor
electron flows easily
insulator
doesn't allow electron flow
semiconductor
behaves as insulator or conductor
superconductor
allows electron flow without resistance. Niobium, Titanium
William shockley 1946
demonstrated semiconduction
super conductivity 1911
no resistance within a critical temperature
electric circuit
path of electron flow through a conductor
1V
1J/C
electric resistance
measured in omhs
battery
provides electric potential
capacitor
momentarily stores electric charge
ammeter
measures electric charge
transformer
increase and decrease voltage
rheostat
variable resistor
diode
electron flow in one direction
direct current
electron flow in only one direction
alternating current
electron flows alternately. 60Hz current
wave form
graphic representation of wave
electric power
measured in watts
magnetite
oxide of iron Fe3O4
magnetism
fundamental property of some forms of matter
electron spin
a property created when electron behave as they rotate on its axis
magnetic moment
basis of MRI
bipolar
has two poles
poles
north and south pole
magnetic dipole
small magnet created by electron orbit
magnetic domain
accumulation of atomic magnets with dipoles aligned
magnetic permeability
ability of the material to attract lines of magnetic field
three types of magnet
naturally occuring magnets
permanent magnets
electromagnets
ferromagnetic
it can be strongly magnetized
nonmagnetic
unaffected By magnetic field
soft iron
an excellent temporary magnet
voltaic pile
precursor of modern battery
alessandro volta
contributed on the development of battery
magnetic field strength
Si unit: tesla
older unit: gauss
1T: 10,000G
natural magnet
a magnet that get its magnetism from the earth
magnetic induction
the process of Making ferromagnetic material magnetic
closed core transformer
a square core of ferromagnetic materials built up of laminated layers of iron. It reduces energy loss caused By Eddy current
source of electromagnetic force
any device that converts some form of energy directly into electric energy
Hans oersted
he demonstrated that electricity can be used to generate magnetic fields
electromagnetic devices
electric motor, electric generator and transformer
magnetic lines of induction
the imaginary magnetic field lines
solenoid
a coil of wire
electromagnetic
a coil or wire wrapped around an iron core that intensified the magnetic field
Eddy Current
a current that opposes the magnetic field that induced it, creating a loss of transformer efficiency.
step up transformer
turns ratio greater than 1
primary side: low voltage, high current
shell-type transformer
it confines more of magnet field lines of primary winding.
Advantage: more efficient than closed core transformer.
modern battery
carbon rod (+) and zinc cylindrical can (-)
faradays law
the first law of electromagnetic