BIOL 320 Lab 3
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
247 Terms
Senses
Means by which the brain receives information about the
environment and the body.
Special senses:
Sight (Visual)
Hearing (Auditory)
Taste (Gustatory)
Smell (Olfactory)
Touch (Tactile)
General senses:
Temperature
Pain
Vibration
Joint position
Proprioception
Retina
Light-sensitive receptors
innermost layer
Rods
Night vision
Cones
color vision
Taste
Chemical sense
Types of taste buds
Sweet
Salt
Sour
Bitter
Umami receptor:
meat, aging cheese, and artificial flavoring
Smell
Chemical sense
Olfactory receptors found on the roof of the nasal cavity
Touch
Sense of pressure perception
Nociception
perception of pain
Thermoception
sense of heat and cold
Proprioception
perception of body position
Stroop Test
Measures an individual’s ability to focus on the color of a word, while ignoring the meaning of the word.
Engagement of automatic and control processes
Stroop test four exercises
monochrome, rectangles, words, and colors
Stroop test measure
Number of errors
Peripheral skin temperature
heart rate
Cornea
light rays travel through where they undergo refraction
Ciliary body
alter lens shape for proper focus on the retina, predominantly controlled by parasympathetic fibers form the short ciliary nerves
Adaptation
refers to the process by which a sensory system becomes insensitive to a continuing source of stimulation
The visible range for humans is
380 nm to 750 nm
Sclera
tough fibrous outermost tunic of the eye, protects and shapes the eyeball and is continuous with the dura mater of the brain
Cornea
anteriorly the sclera forms the whites of our eyes and the becomes transparent as it changes
Choroid tunic
highly vascular and pigmented
Glaucoma
occurs when aqueous humor does not adequately drain and thus pressure increases in the eye until the retina and optic nerve can be compressed and damaged
Fovea centralis of the macula lutea
most of the non-photoreceptor portions of the retina are displaced to the sides leaving less tissue for the light to pass through before making it to the cones in this region, increases visual acuity
Detached retina
occurs when the neural components of the retina release from the pigmented layer of the retina and is often caused by a blow to the head or sudden stopping of the head
Cataracts
hardening and clouding over of the lens
Lacrimal caruncle
contains sebaceous and sweat glands, produces an oily secretion that helps lubricate and protect the eye, sometimes collect “sand” at night
Chalazion
infected tarsal glands form a cyst
Sty
an inflammation of one of the smaller glands
Pinkeye conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva when caused by bacteria or viral infection
main eye muscles not controlled by the oculomotor nerve
lateral rectus muscle and superior obliqye muscle
inferior oblique muscles
elevates the eye and turns it laterally
superior oblique muscle
depresses the eye and turns it laterally
Diplopia/strabismus
asymmetrical weakness or paralysis of the eye muscles
parasympathetic fibers
largely control close vision
Fovea
is located in the center of the macula and is responsible for sharp central vision
Optic disc
located where ganglion cell axons exit the eye and form the optic nerve
“blind spot”
Rhodopsin
which supplies us with a blueish grey vision in shades of grey based on the intensity of stimulation
564nm
red
534nm
green
420nm
blue
Tympanic membrane
boundary between the outer and middle ear
Crista ampullaris
collection of hair cells within a fluid-filled ampulla
Endolymph
movement of the head causes the cupula or crest of the ampulla to bend
Bony labyrinth
inner ear is imbedded in a small cavity of the temporal bone
Stereocilia
the “hairs” that give hair cells their name are actually microvilliEq
Equilibrioception
the perception of balance and is related to the vestibular system in the inner ear
vestibular nystagmus
describes the strange eye movements that occur reflexively in response to the events abive
Motion sickness
is caused when the brain receives sensory mismatch of information where the eyes send information
Deafness
defined as any degree of hearing loss
Conduction deafness
occurs when something decreases the ability of sound to conduct to the fluids of the inner ear
Sensorineural deafness
results from damage to neural components of hearing such as the hair cells, the cochlear nerve, or the auditory cortical cells
Tinutis
symptom of a buzzing, clicking, or ringing in theears without an actual auditory simulation
Mieniere’s syndrome
affects all aspects of the inner ear
Nociception
perception of pain
Thermoception
is the sense of heat and cold
Proprioception
is the perception of body position and is a sense that people rely on enormously
What does the Stroop test consist of
monochrome
rectangles
words
colors
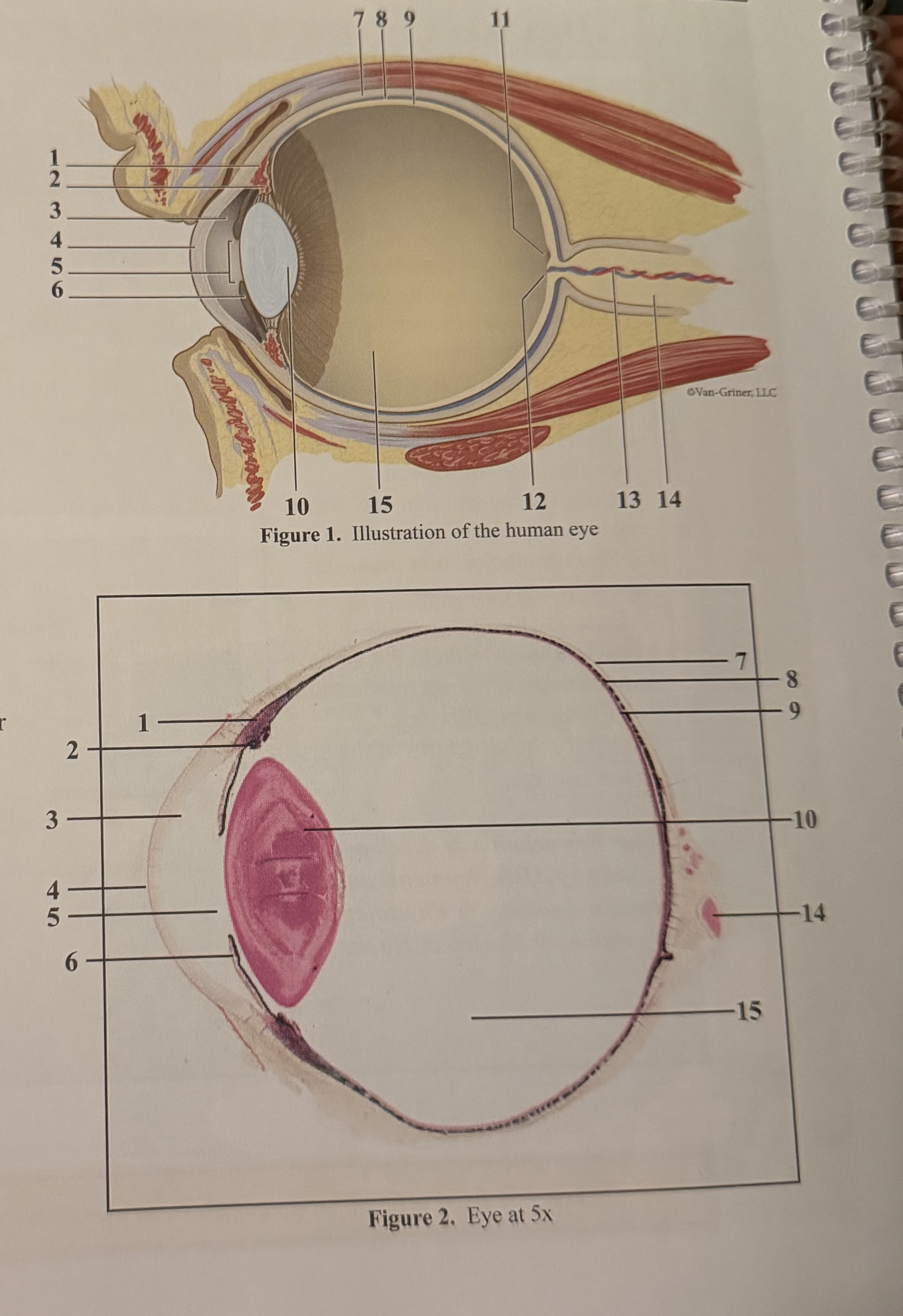
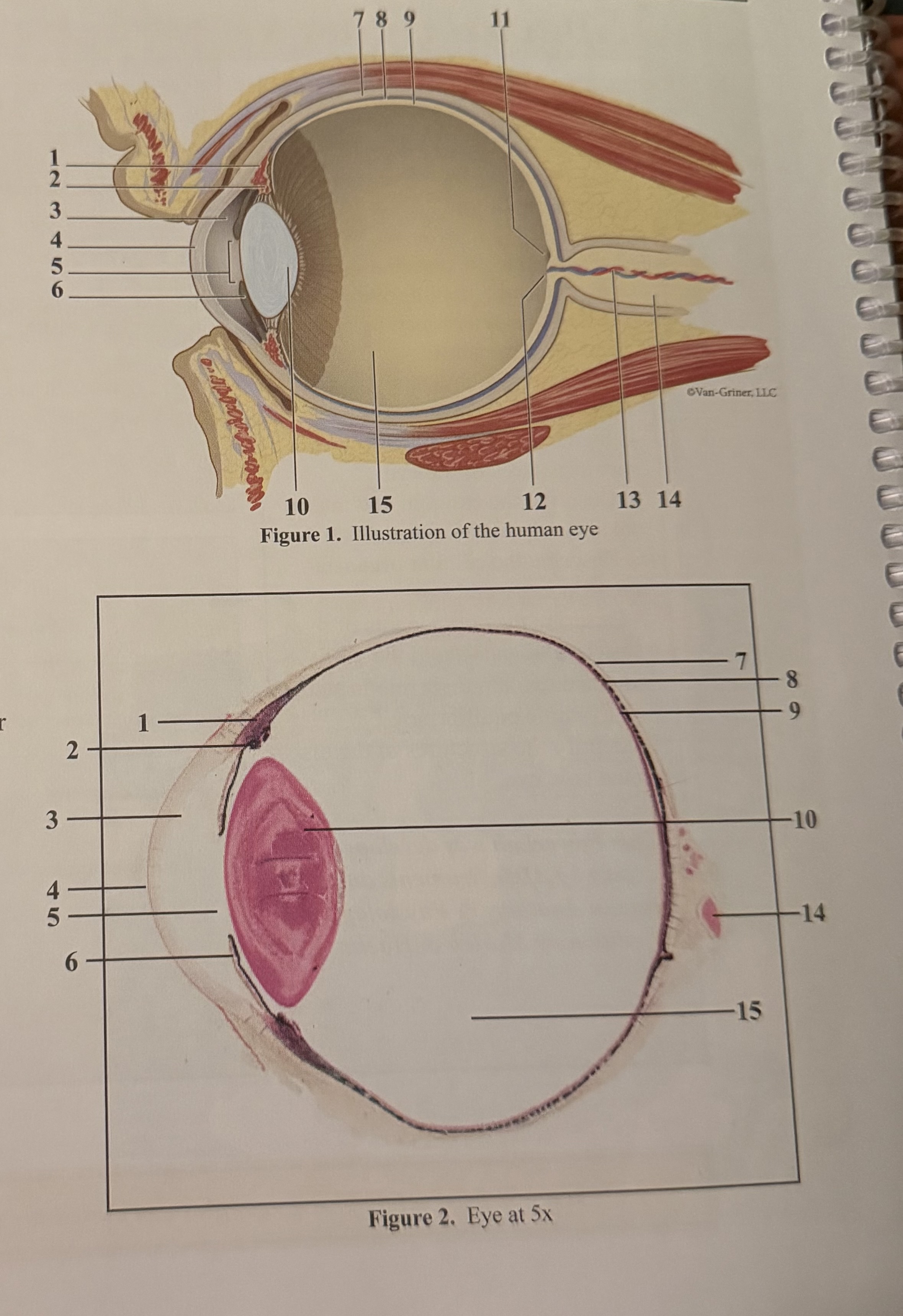
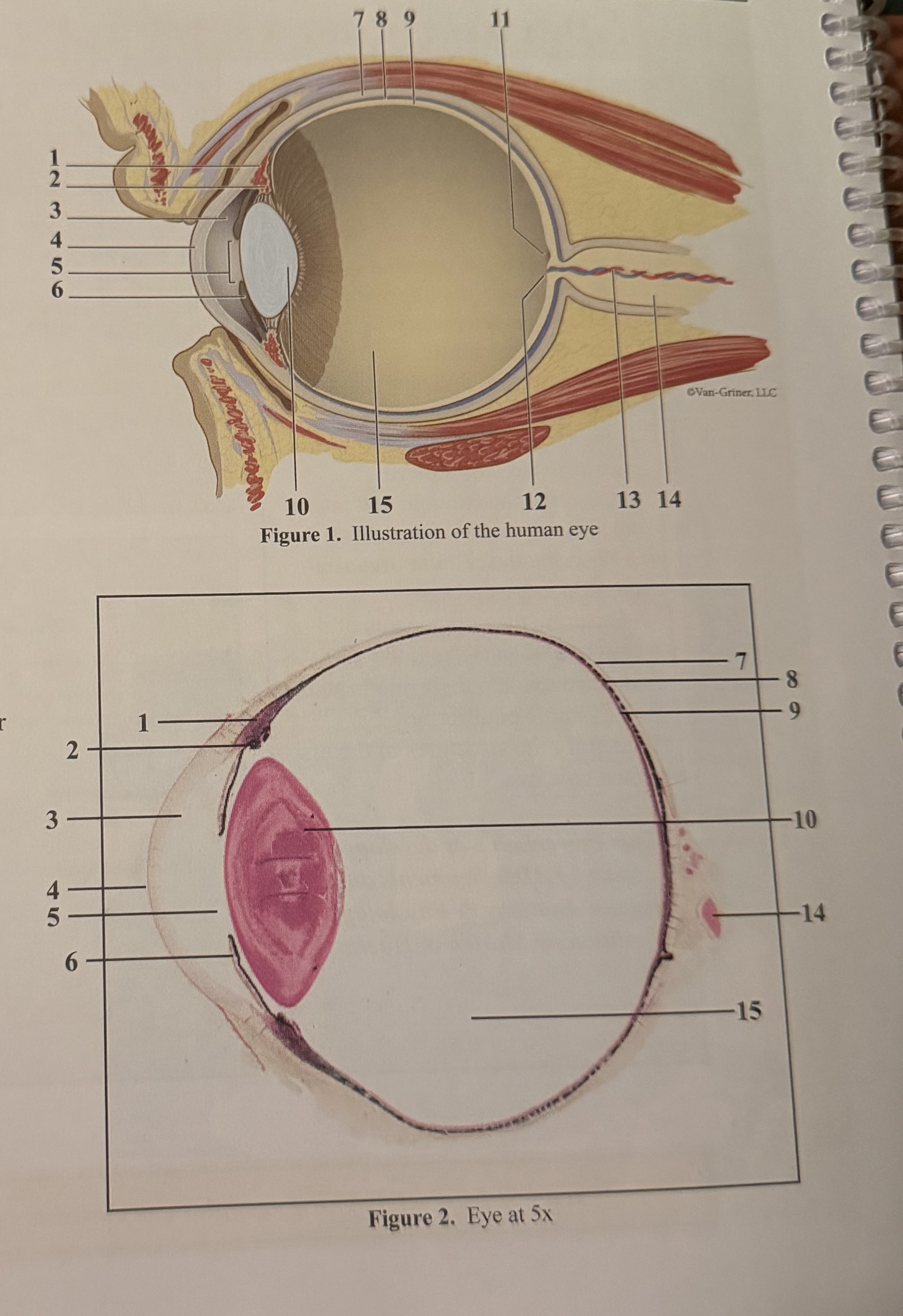
What is 1
Smooth muscle cells
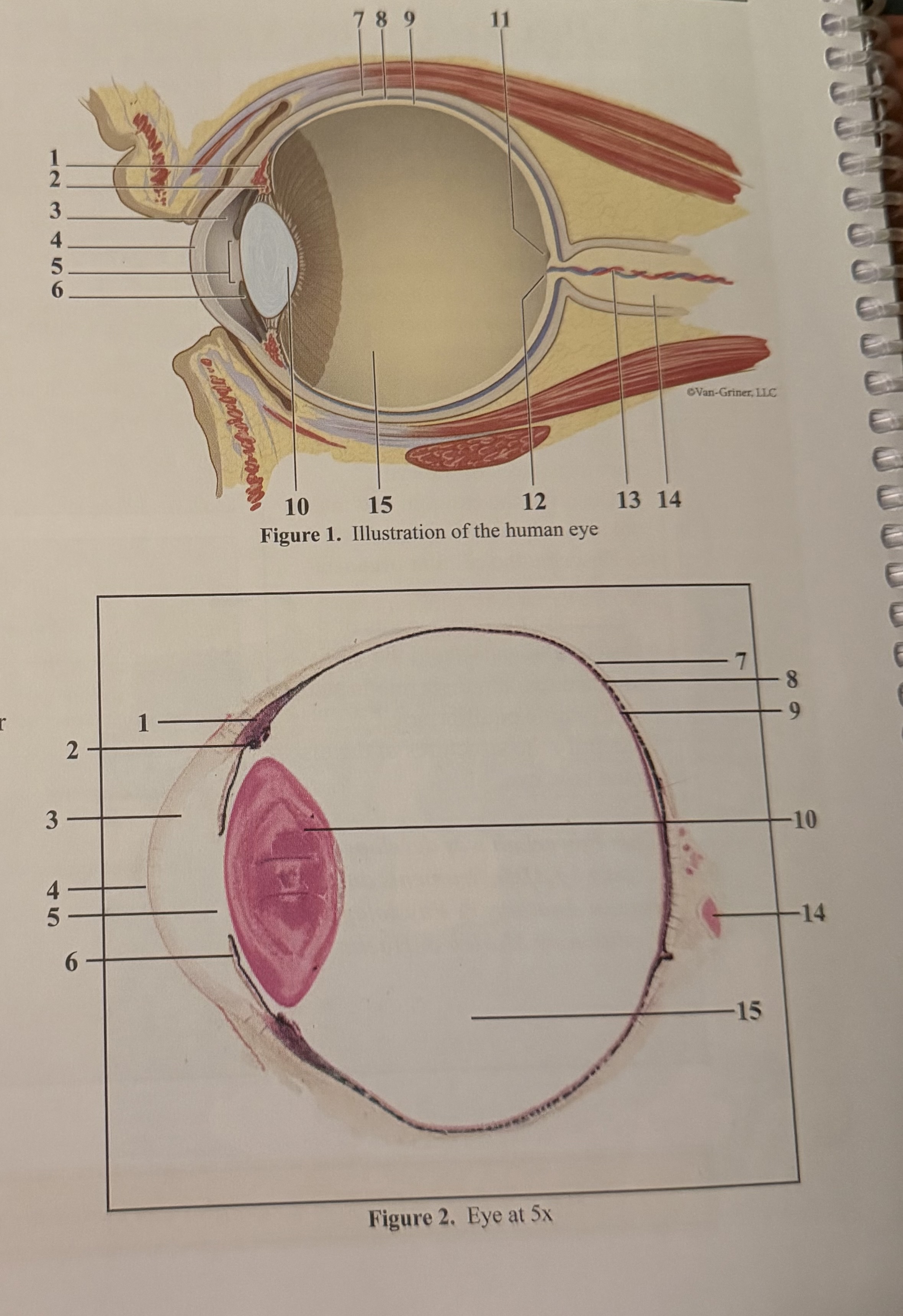
What is 2
Ciliary body
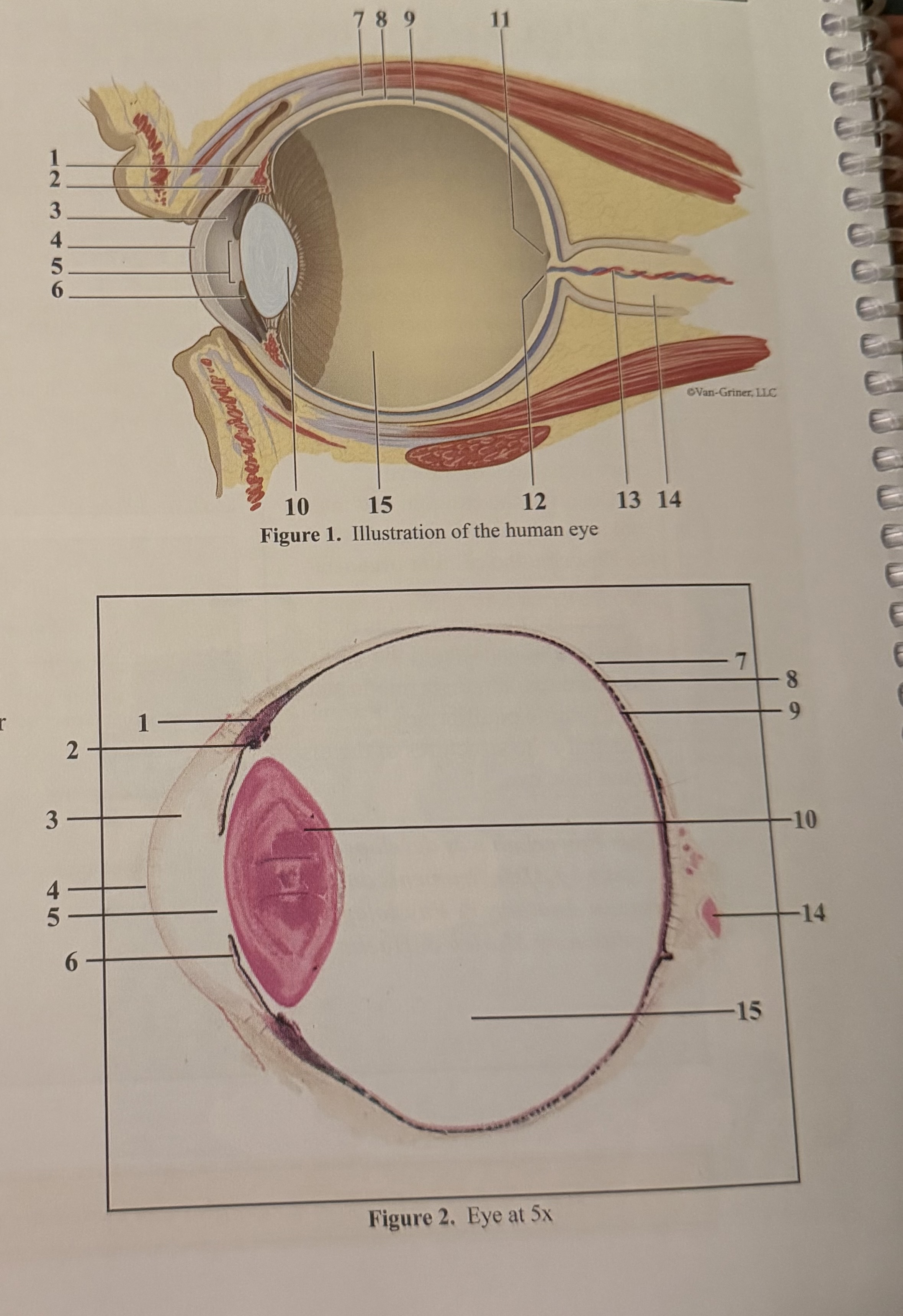
What is 3
Anterior aqueous chamber
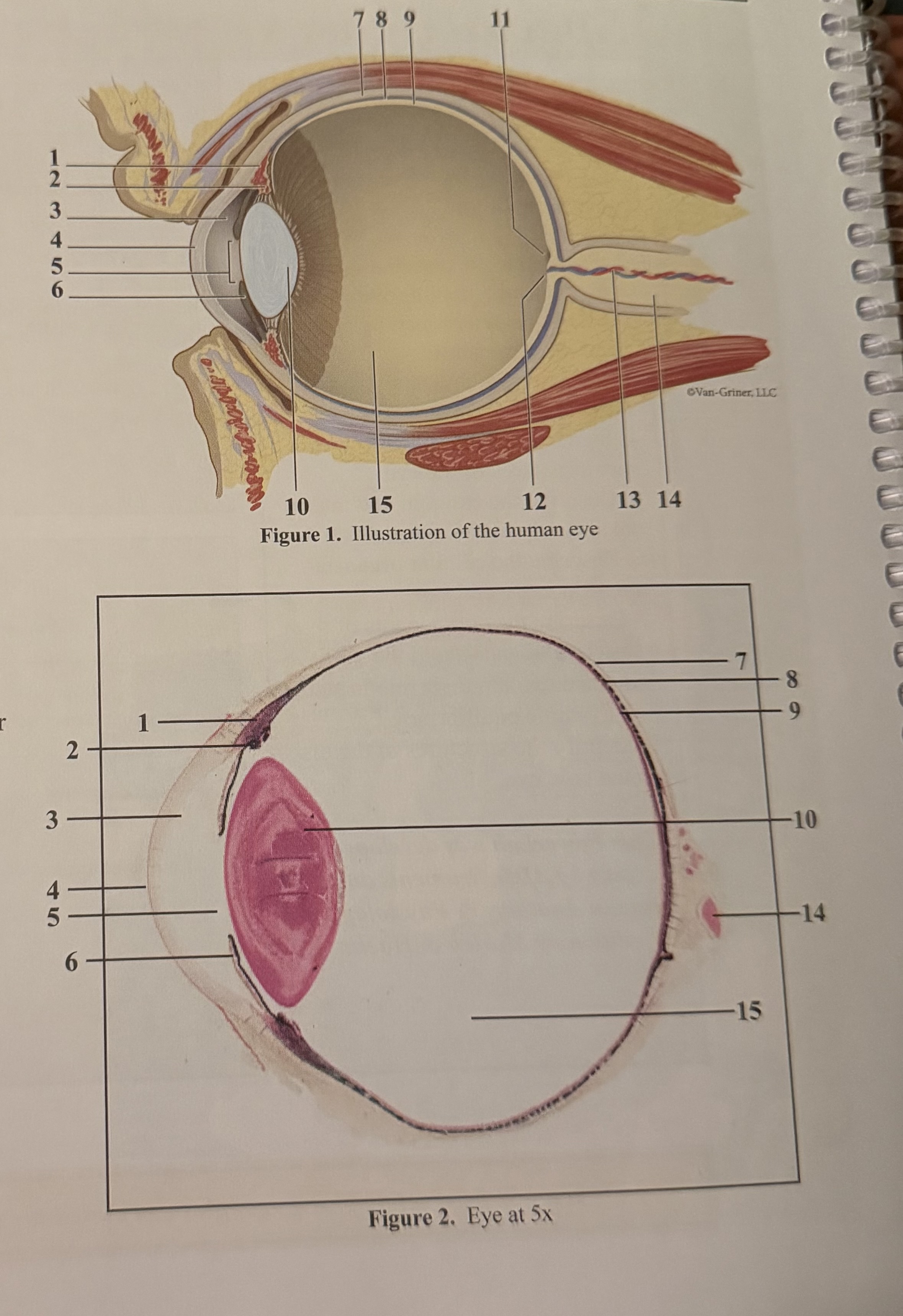
What is 4
Cornea
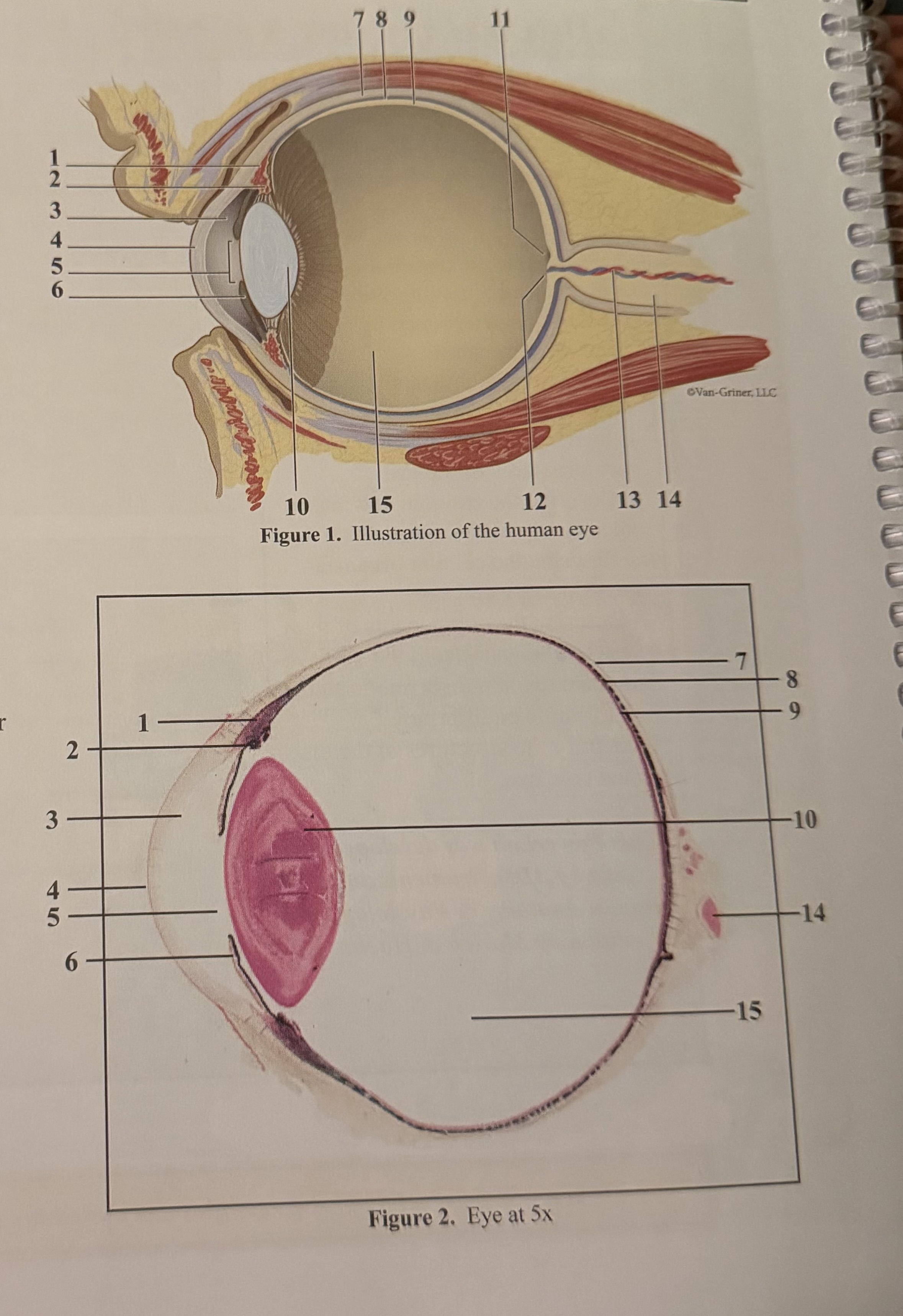
What is 5
Pupil
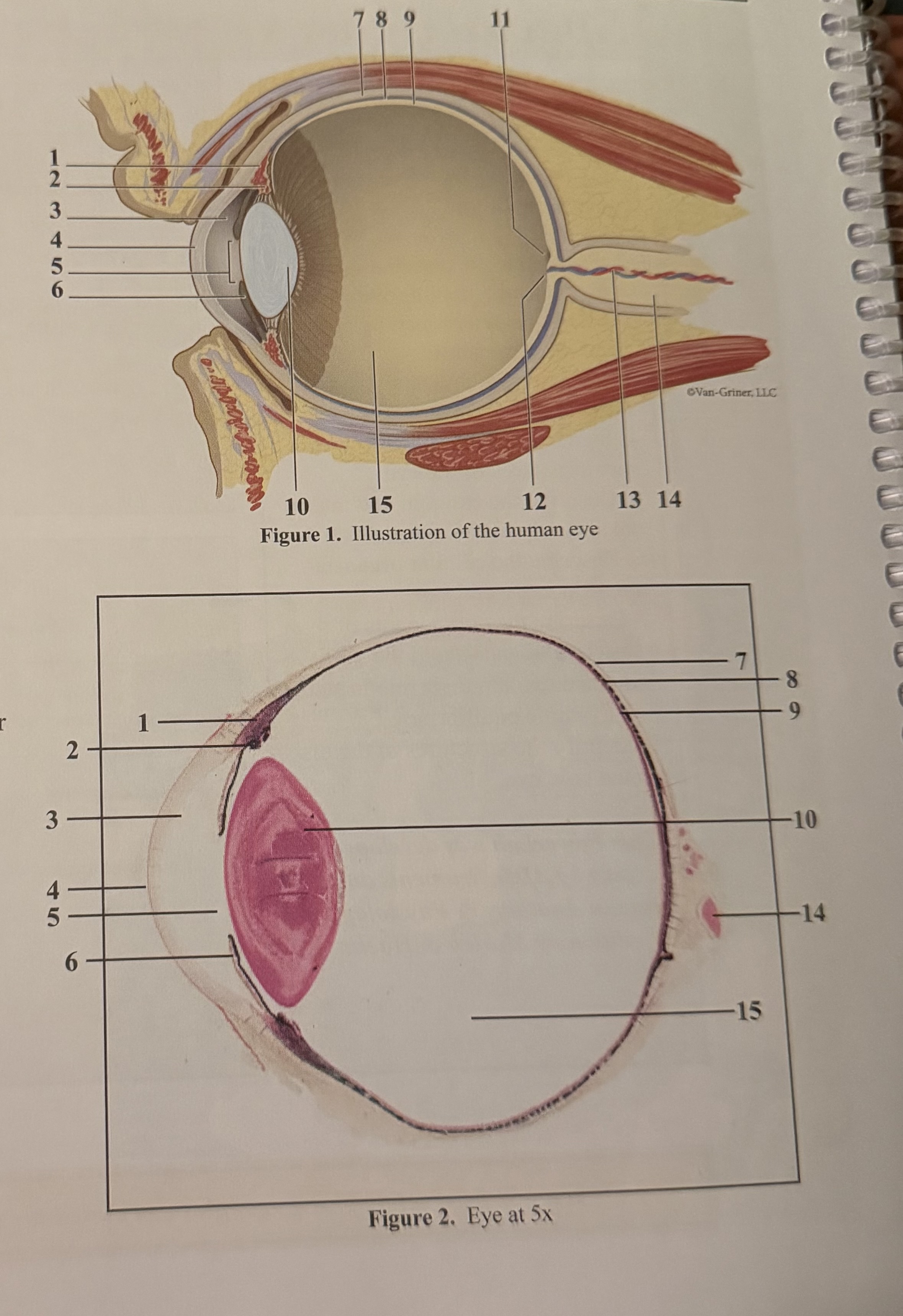
What is 6
Iris
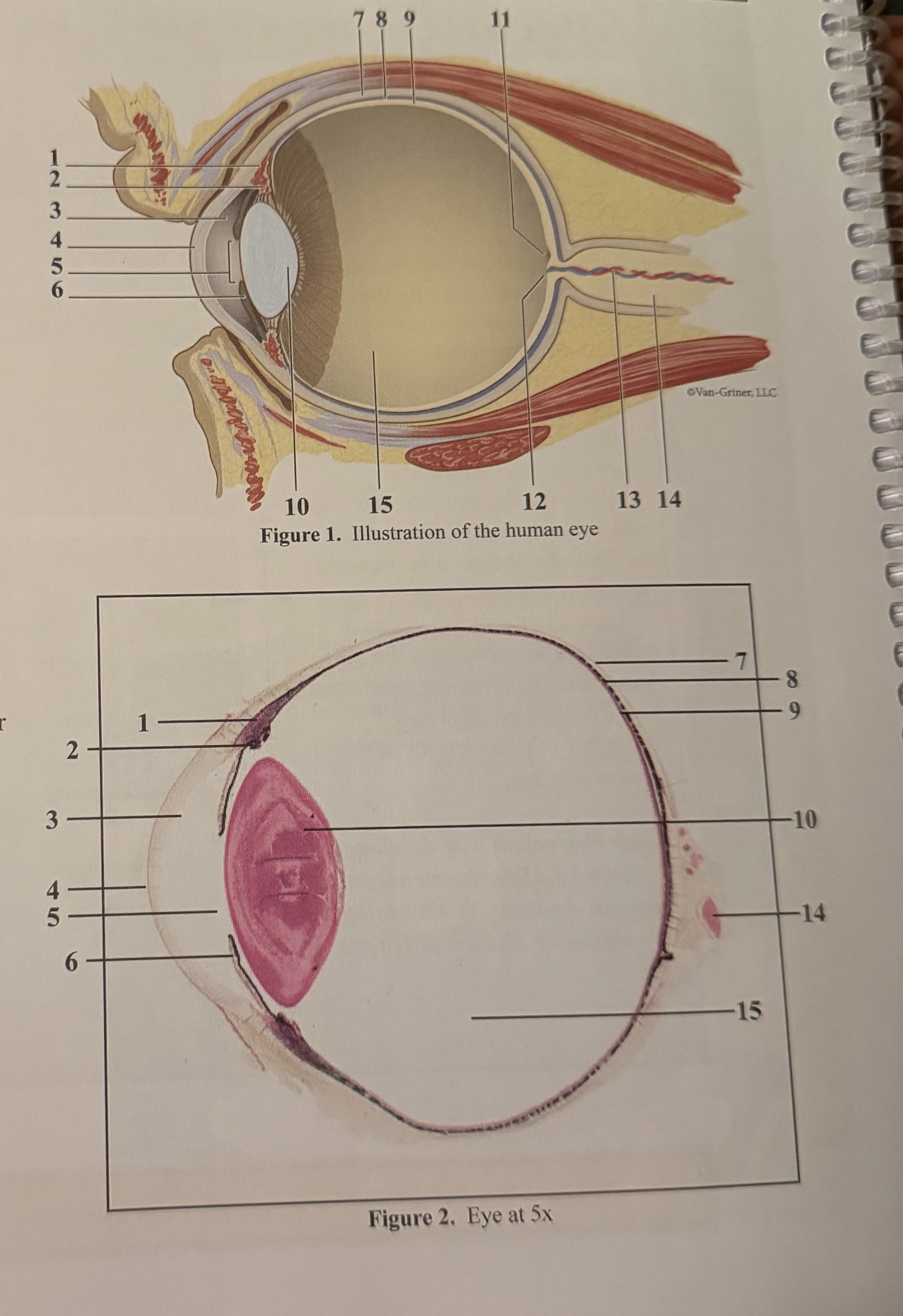
What is 7
Sclera
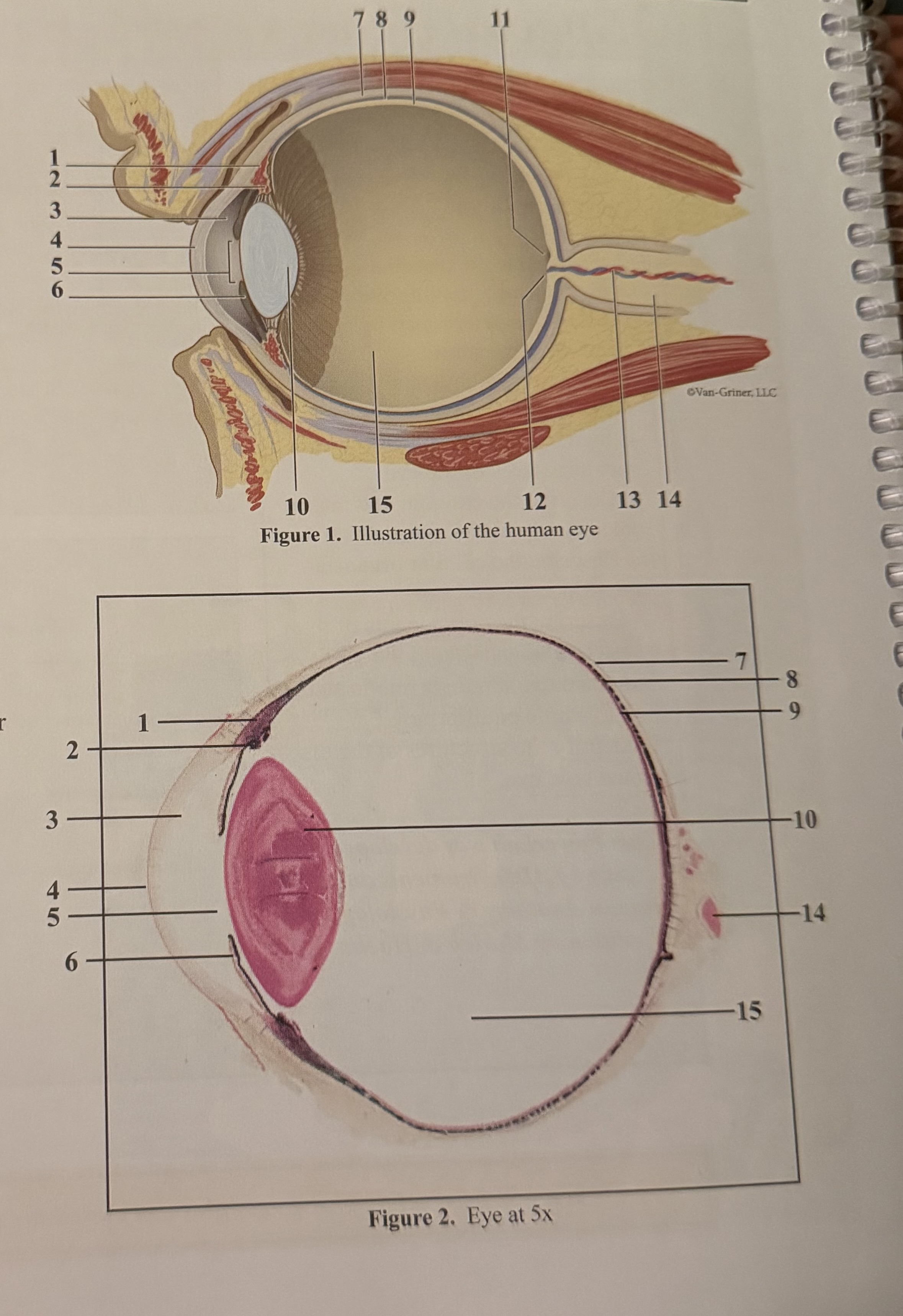
What is 8
Choroid
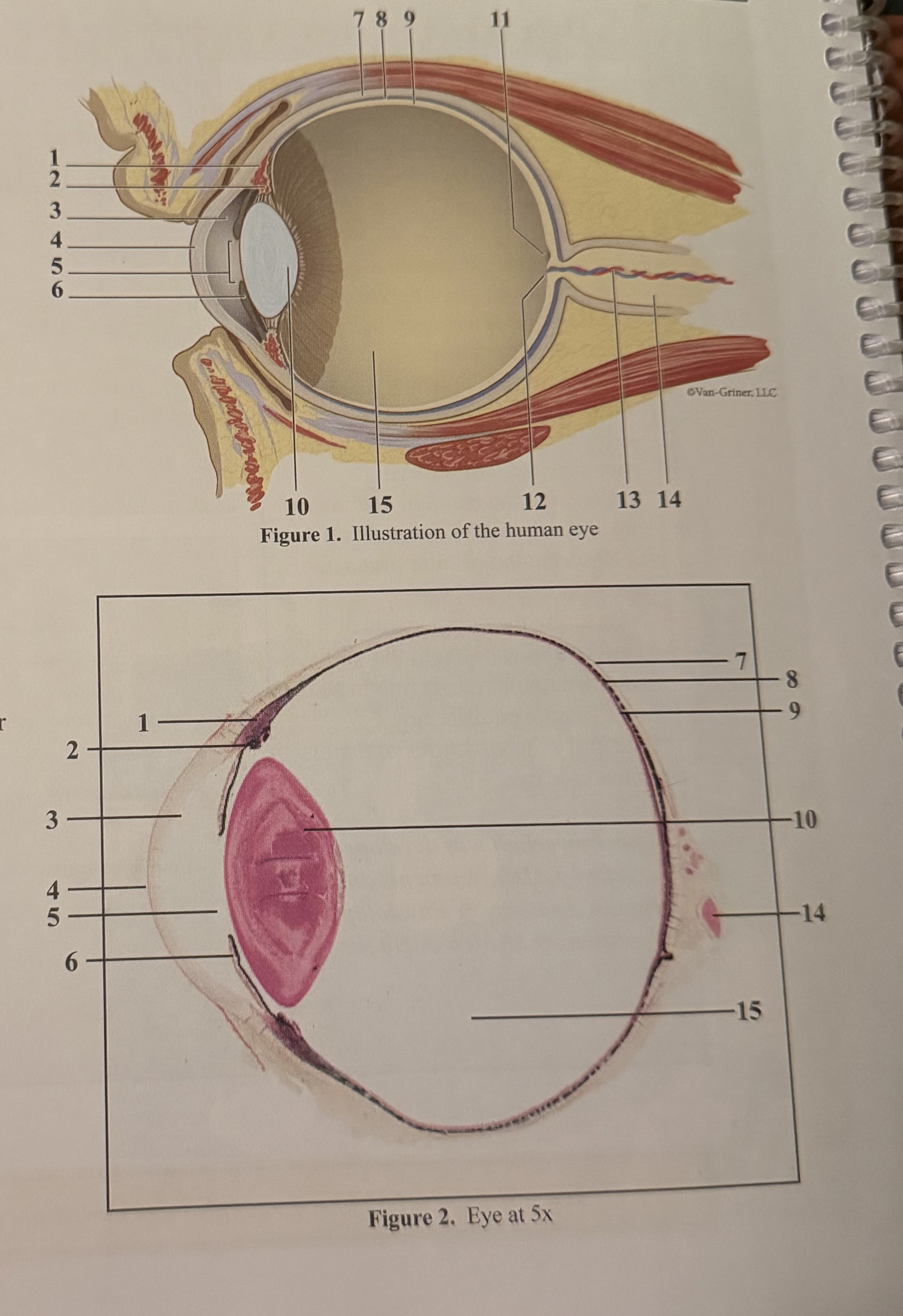
What is 9
Retina
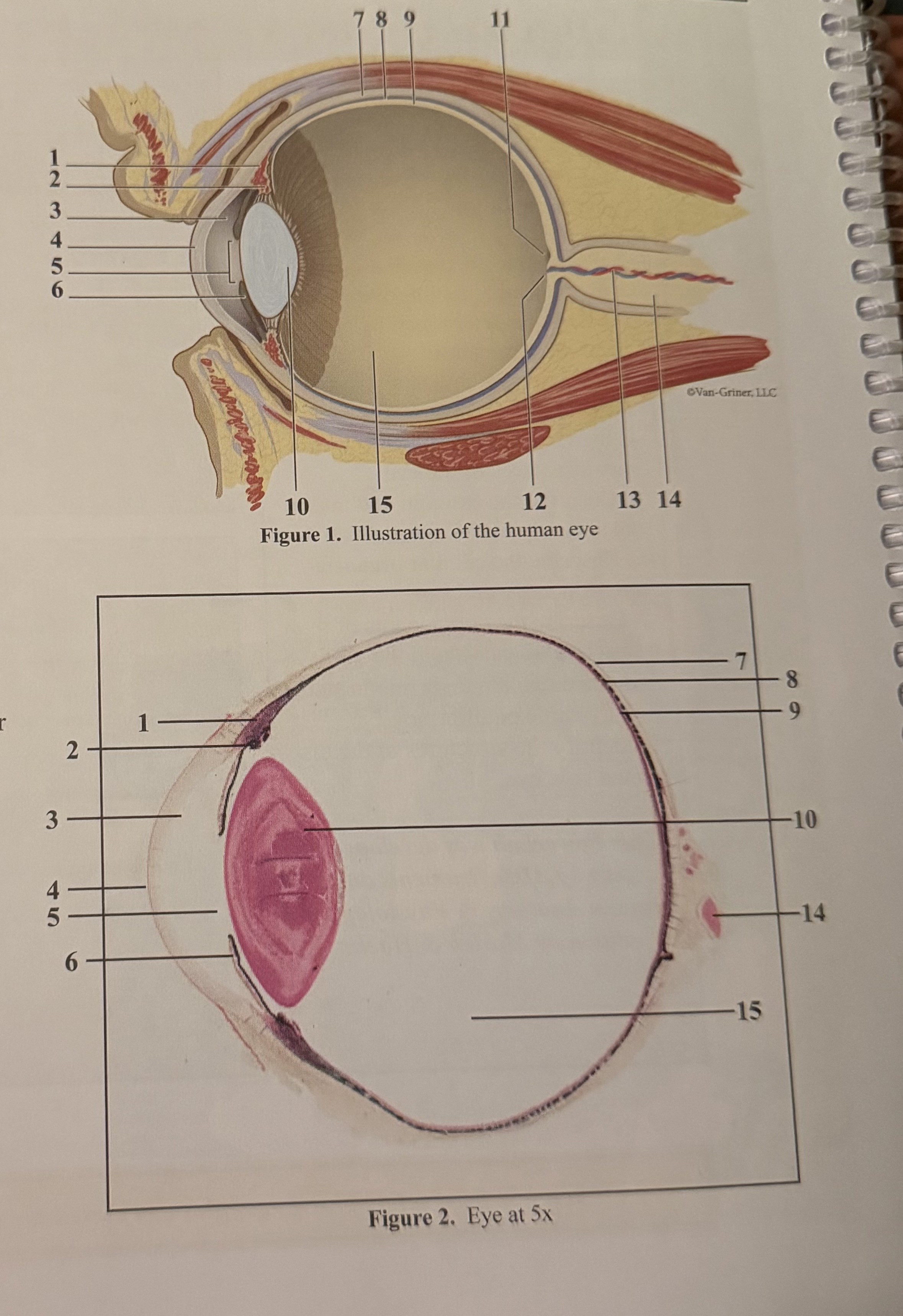
What is 10
Lens
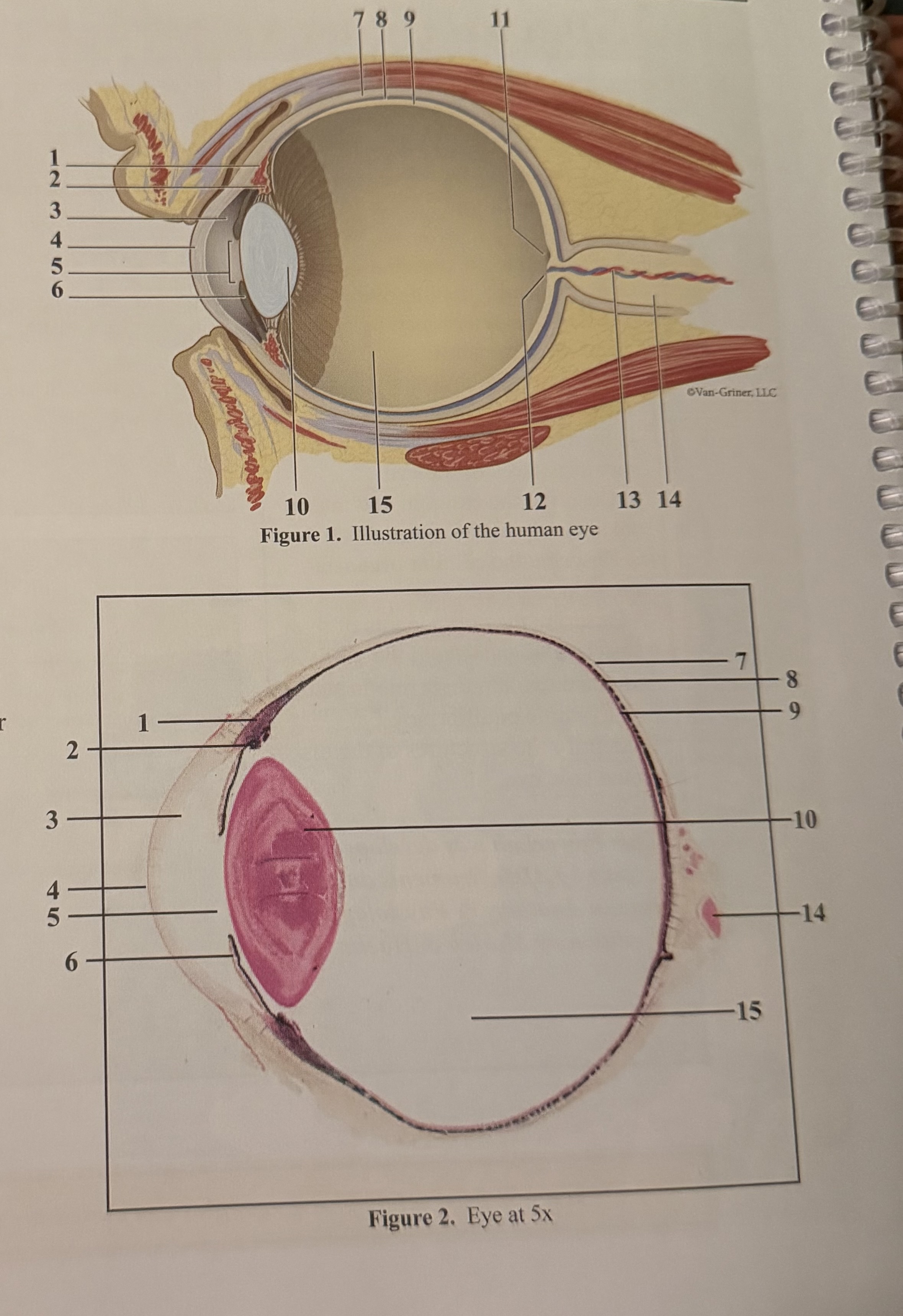
What is 11
Fovea
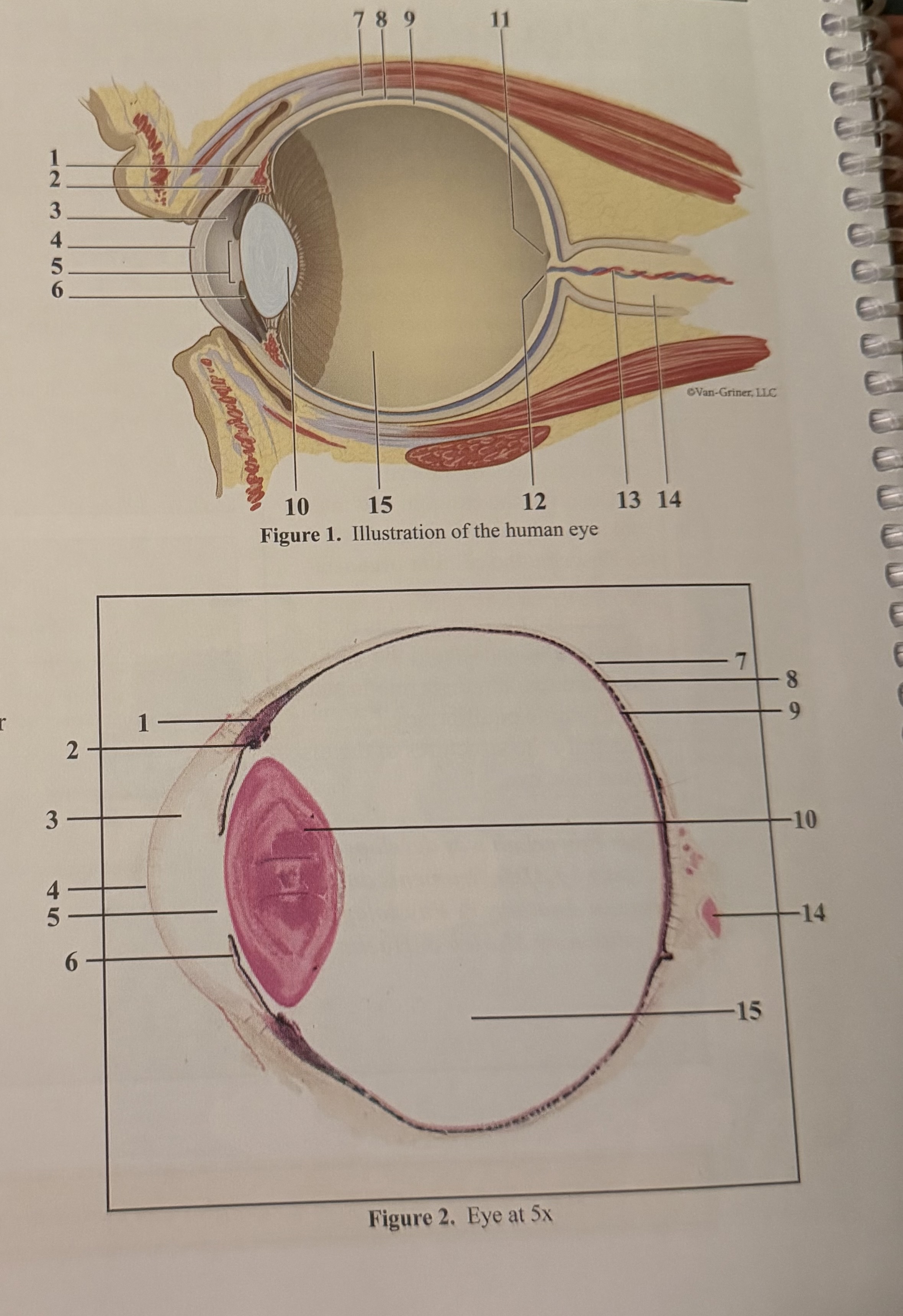
What is 12
Optic disc(blind spot)
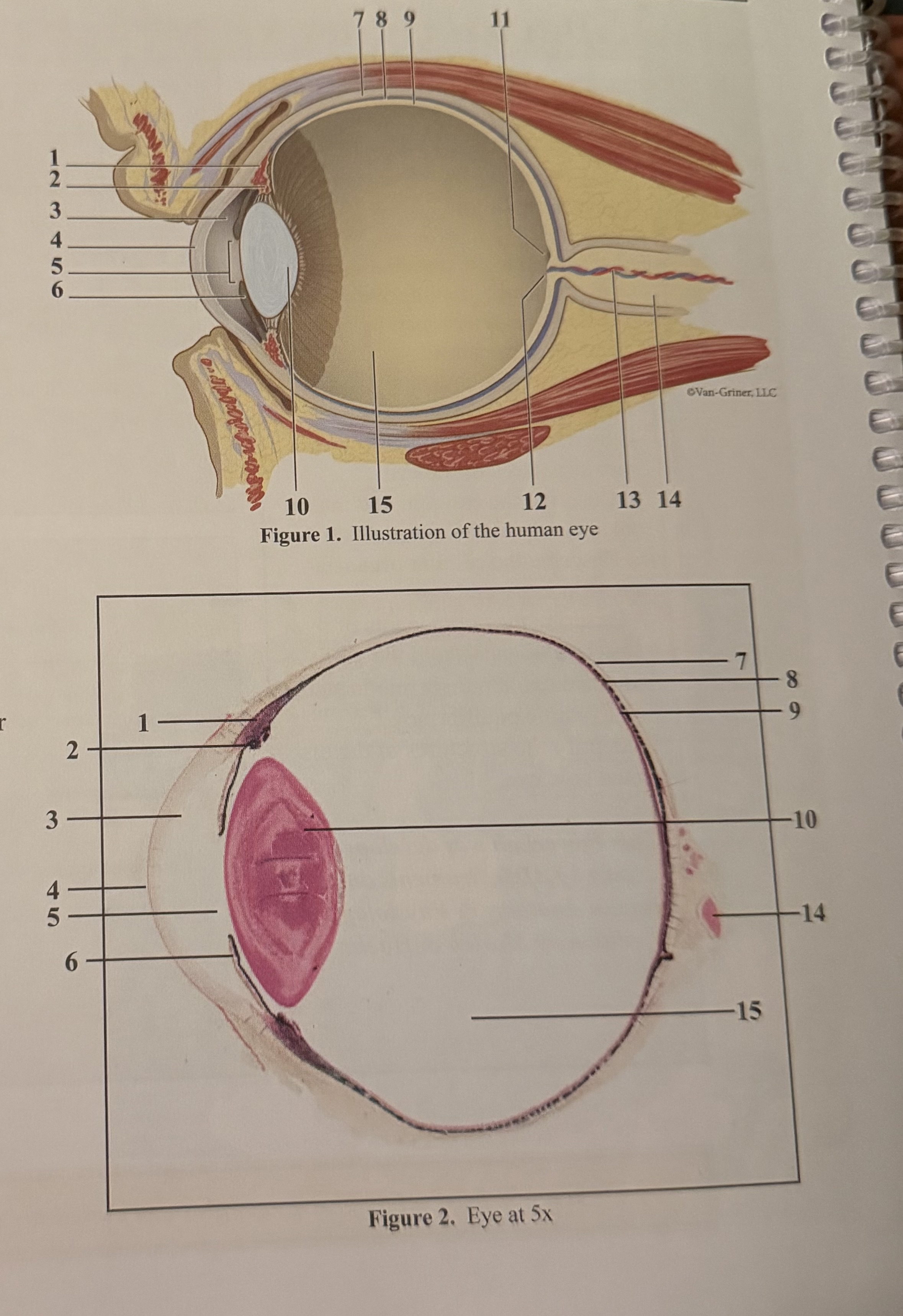
What is 13
Retinal blood vessels
What is 14
Optic nerve II
What is 15
Posterior vitreous chamber
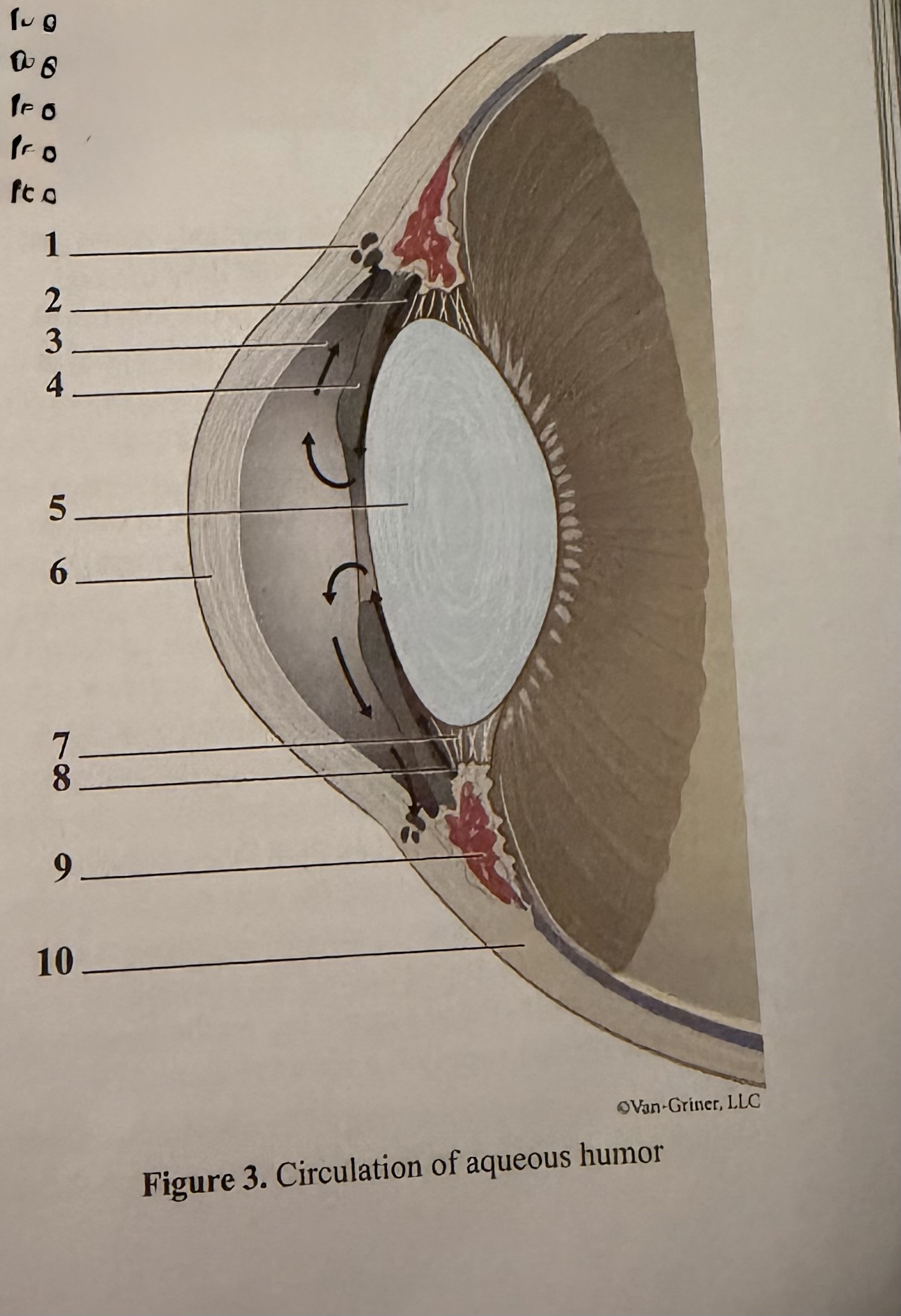
What is 1
Scleral venous sinus
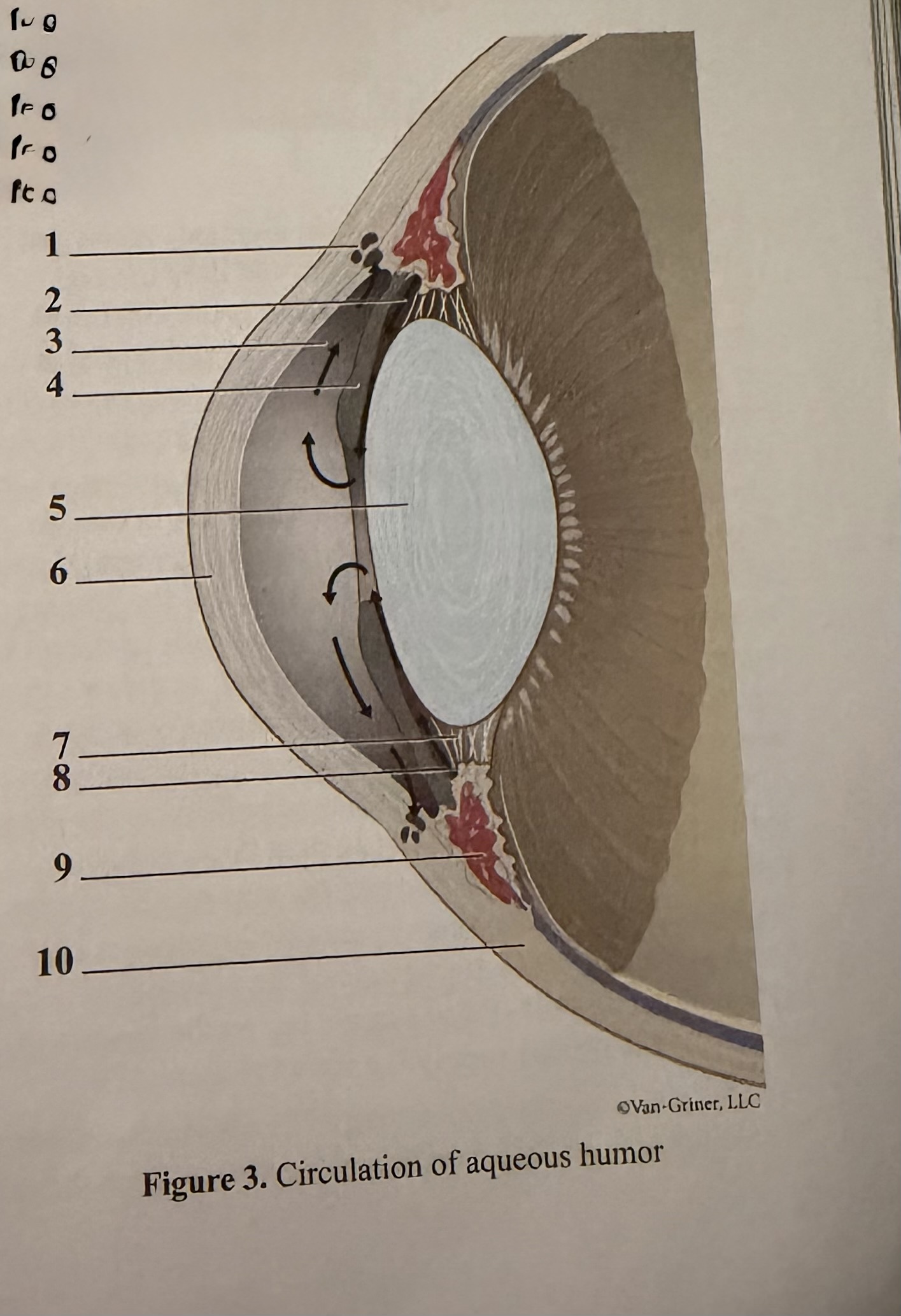
What is 2
Flow of aqueous humor
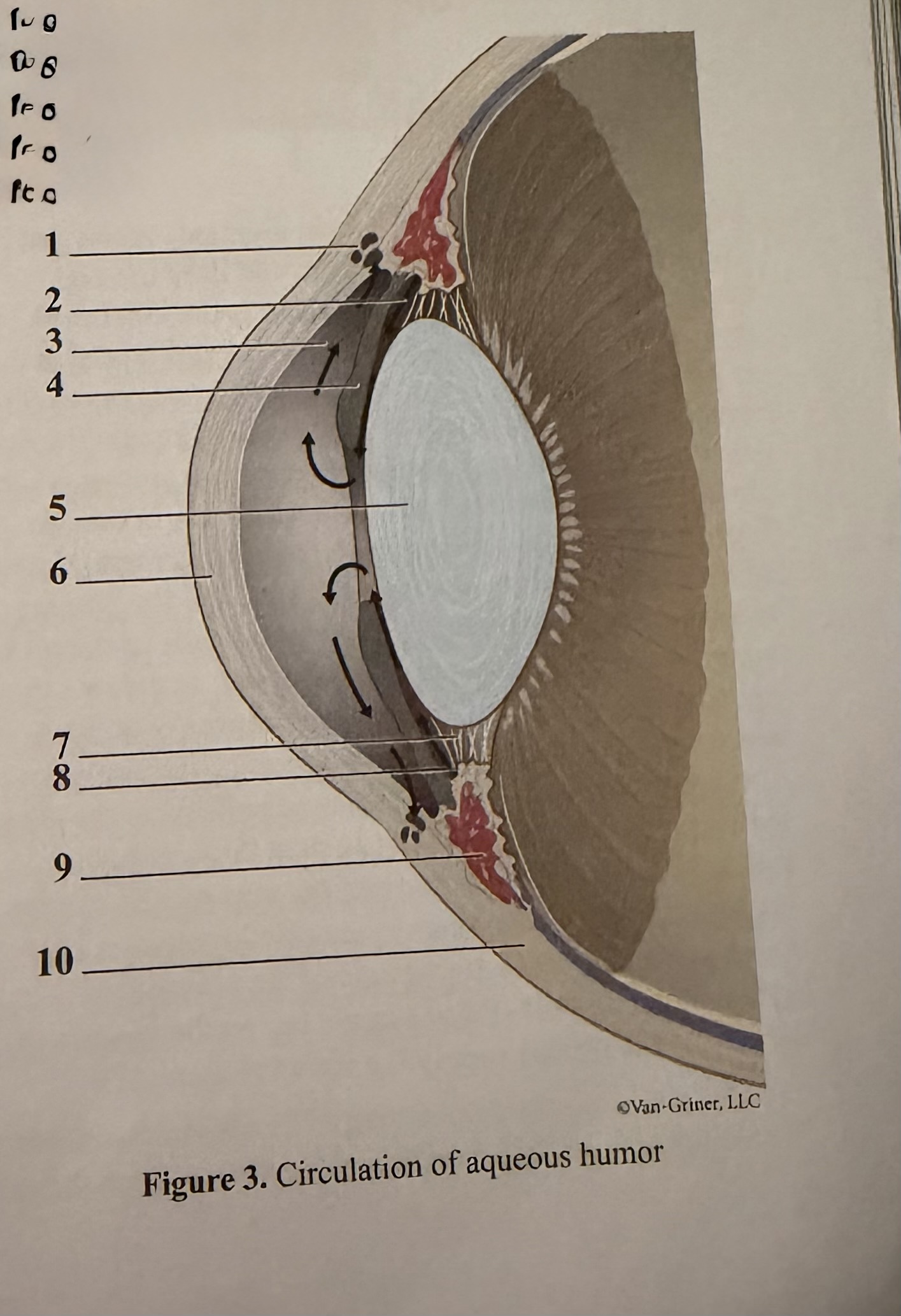
What is 3
Anterior chamber
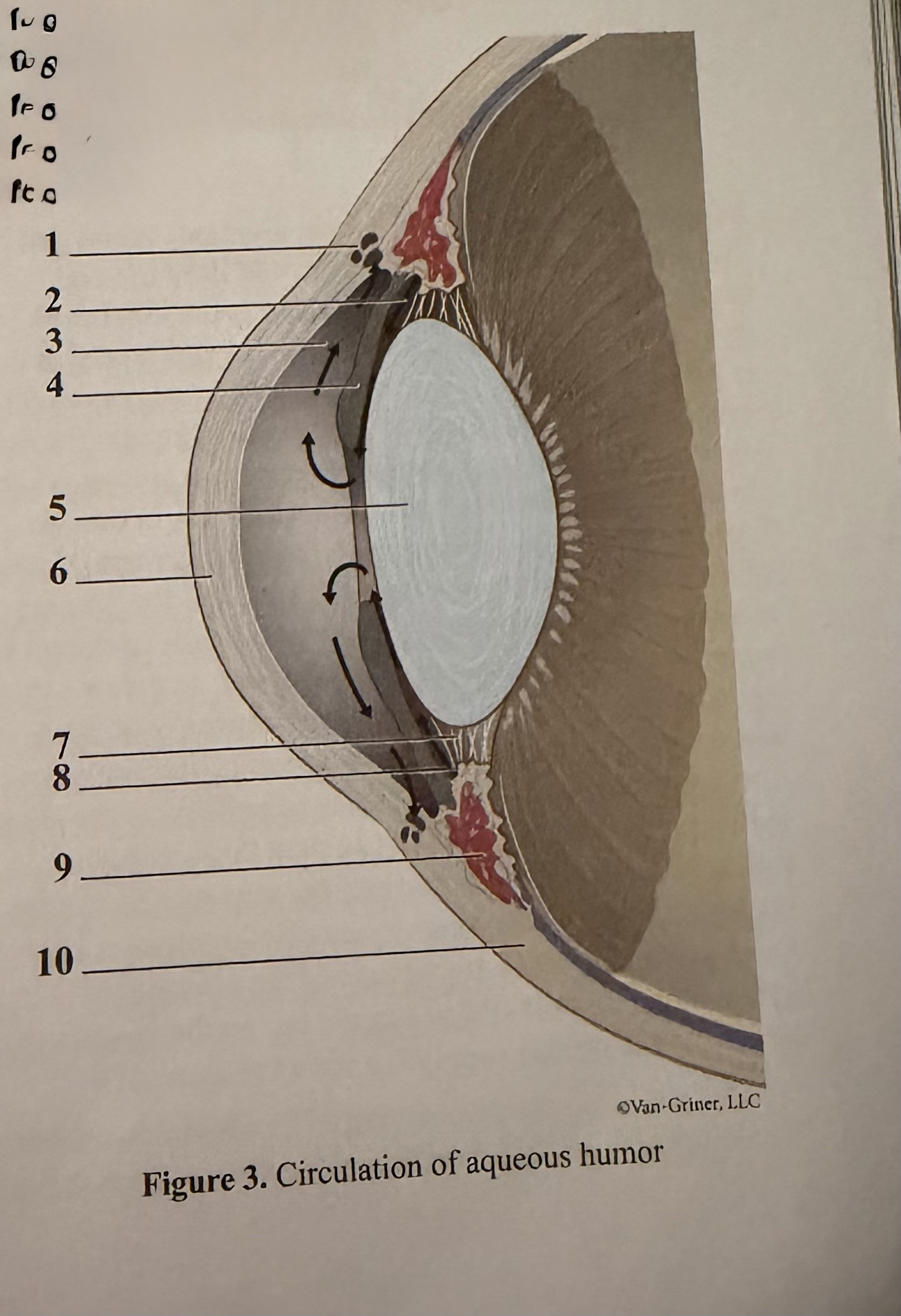
What is 4
Iris
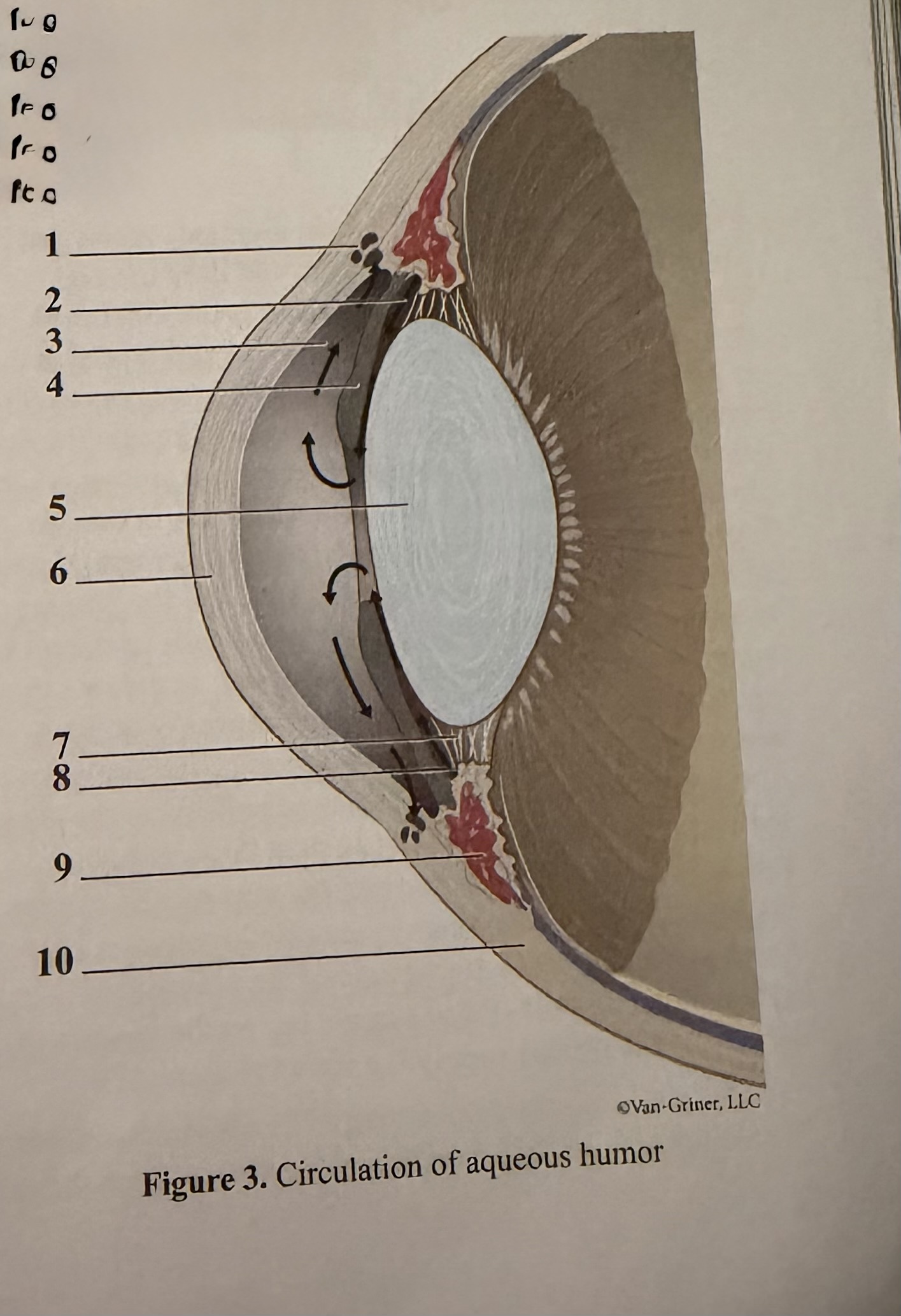
What is 5
Lens
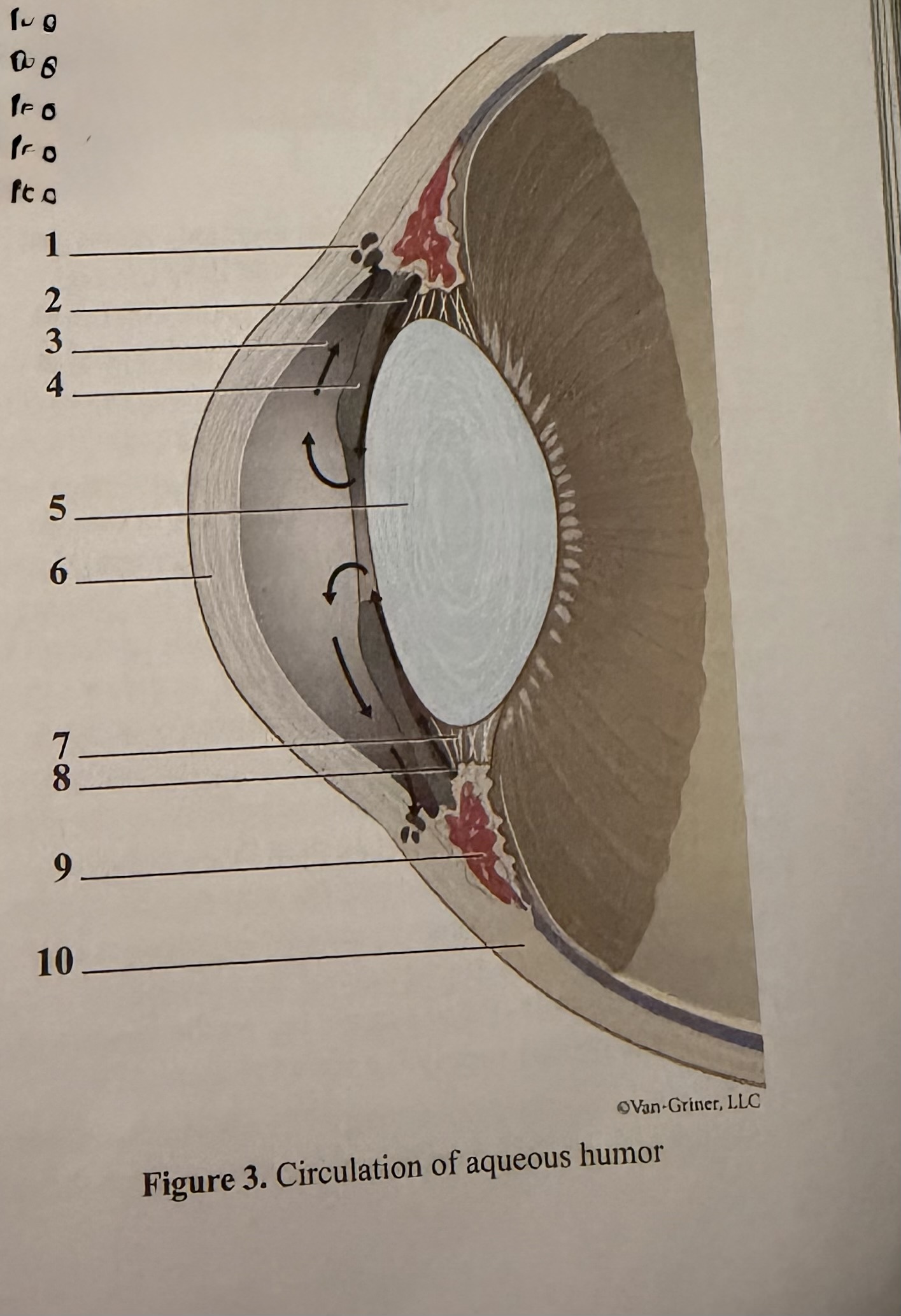
What is 6
Cornea
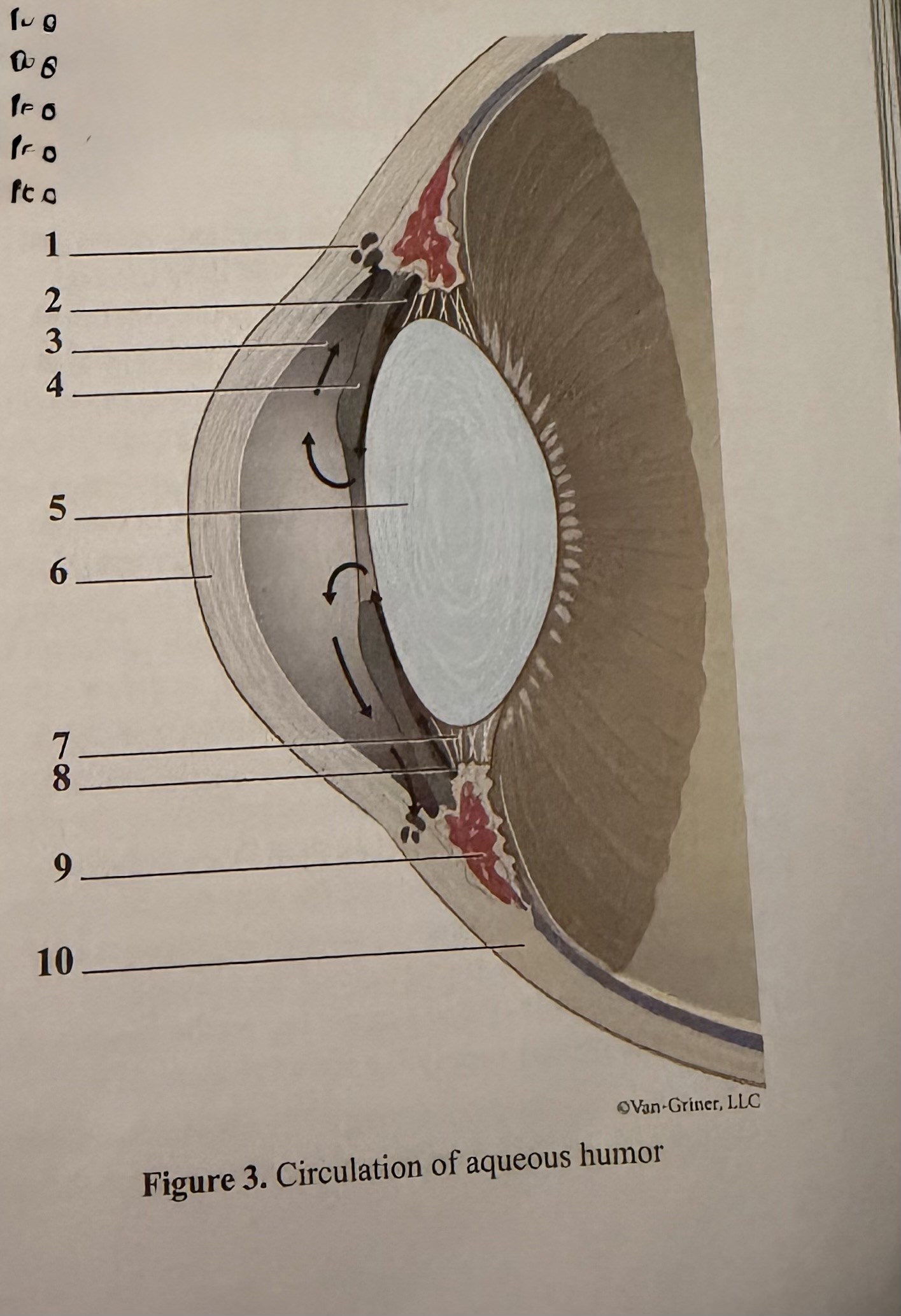
What is 7
Zonular fibers of lens
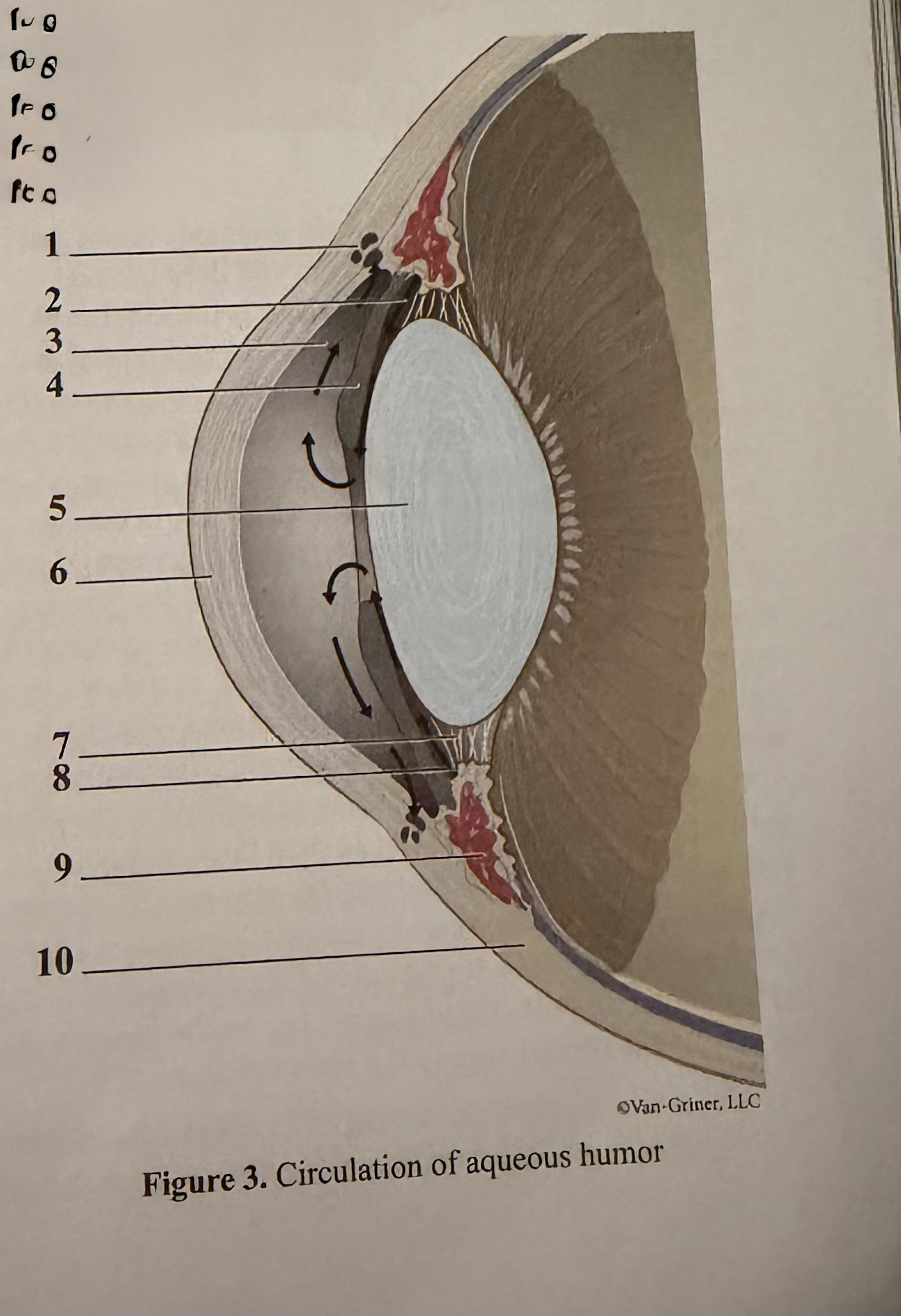
What is 8
Ciliary process
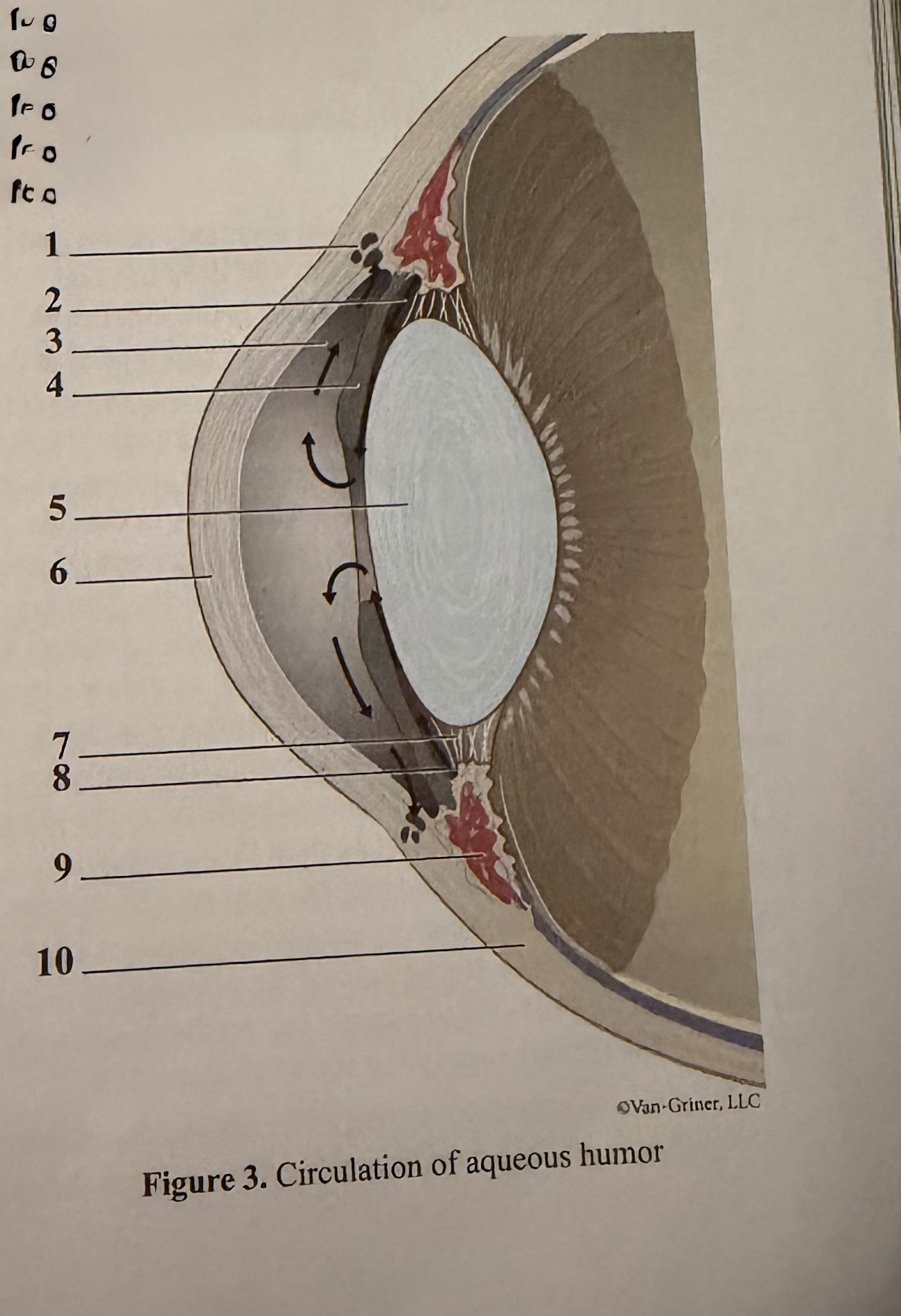
What is 9
Ciliary muscle
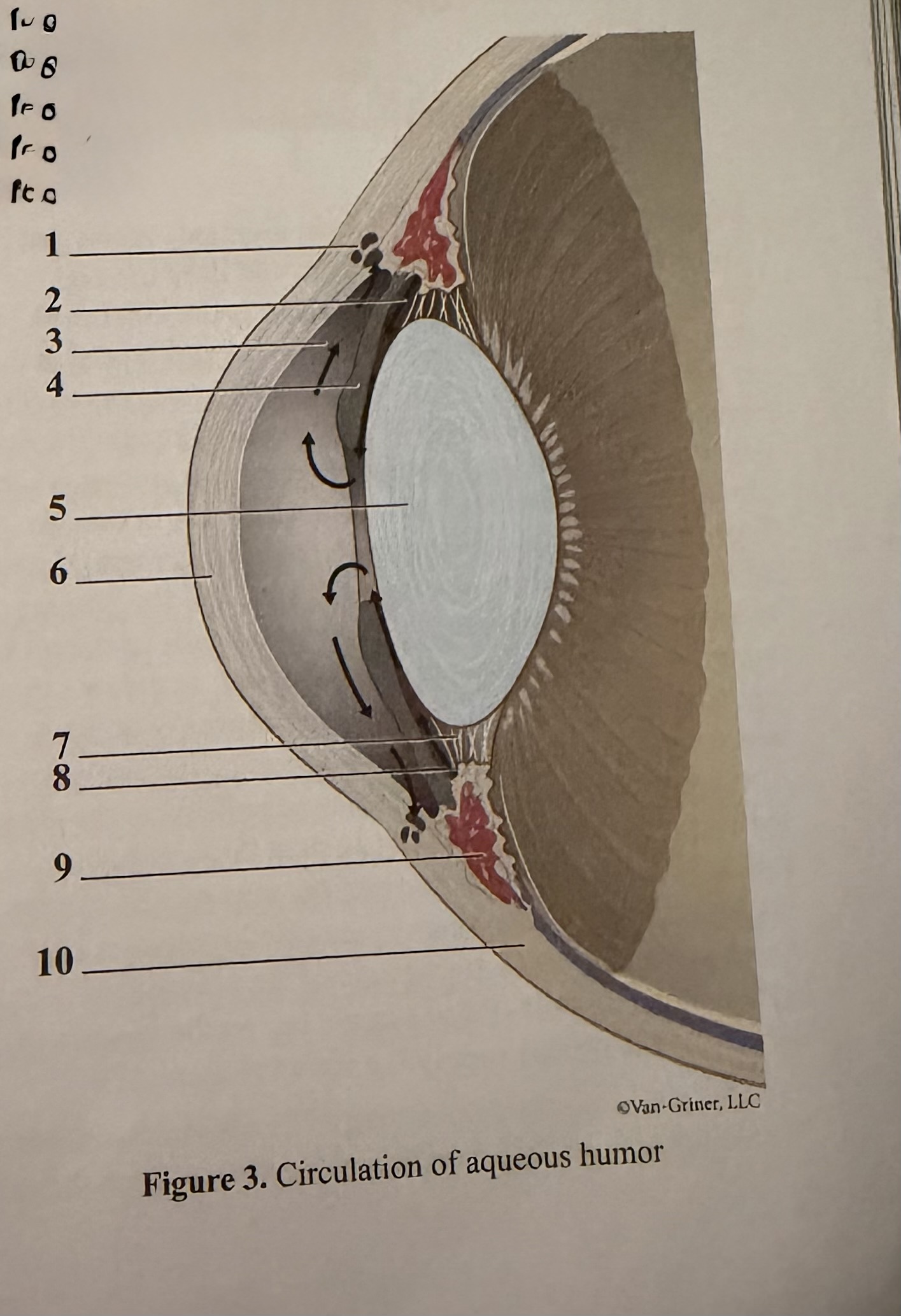
What is 10
Sclera
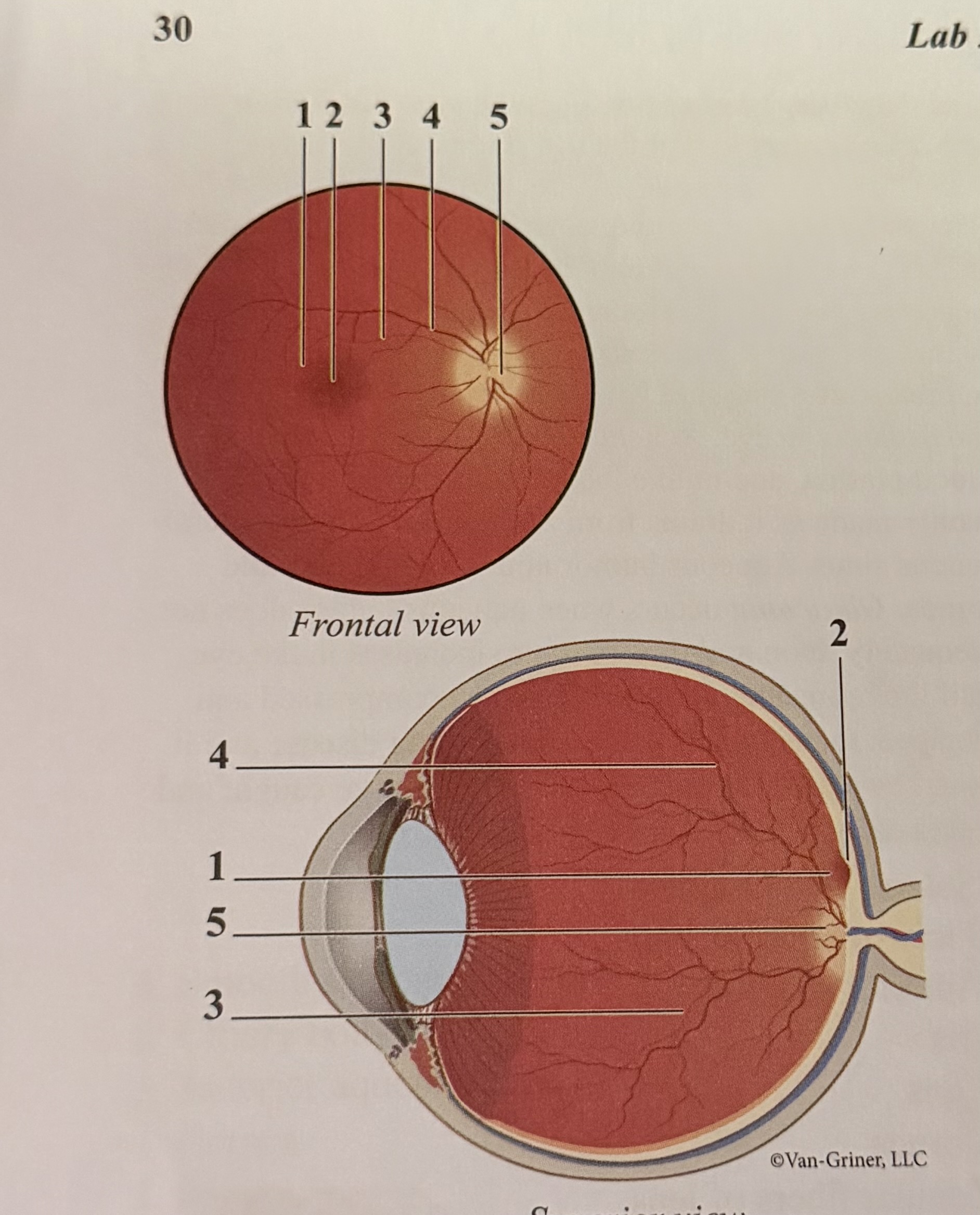
What is 1
Macula
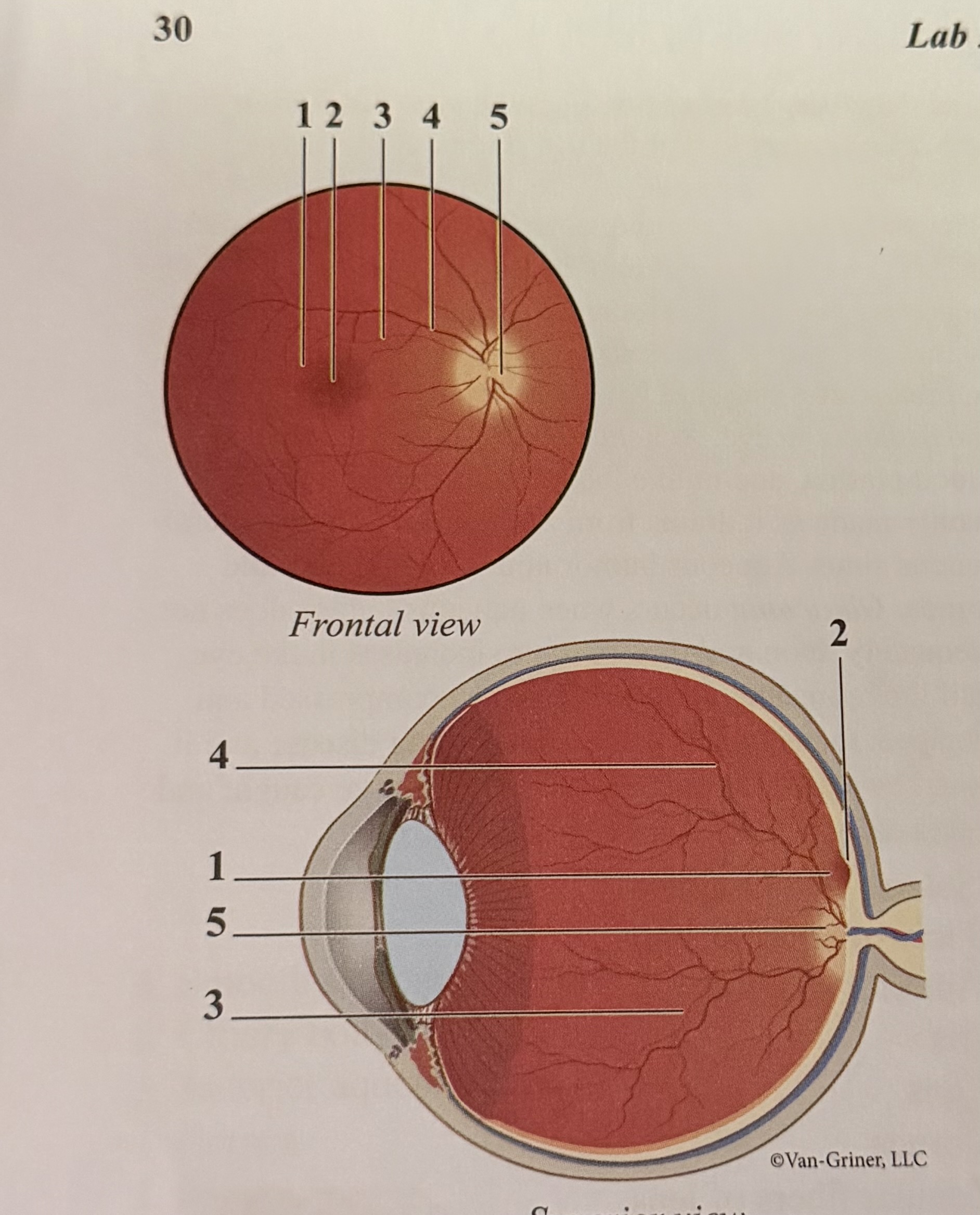
What is 2
Fovea
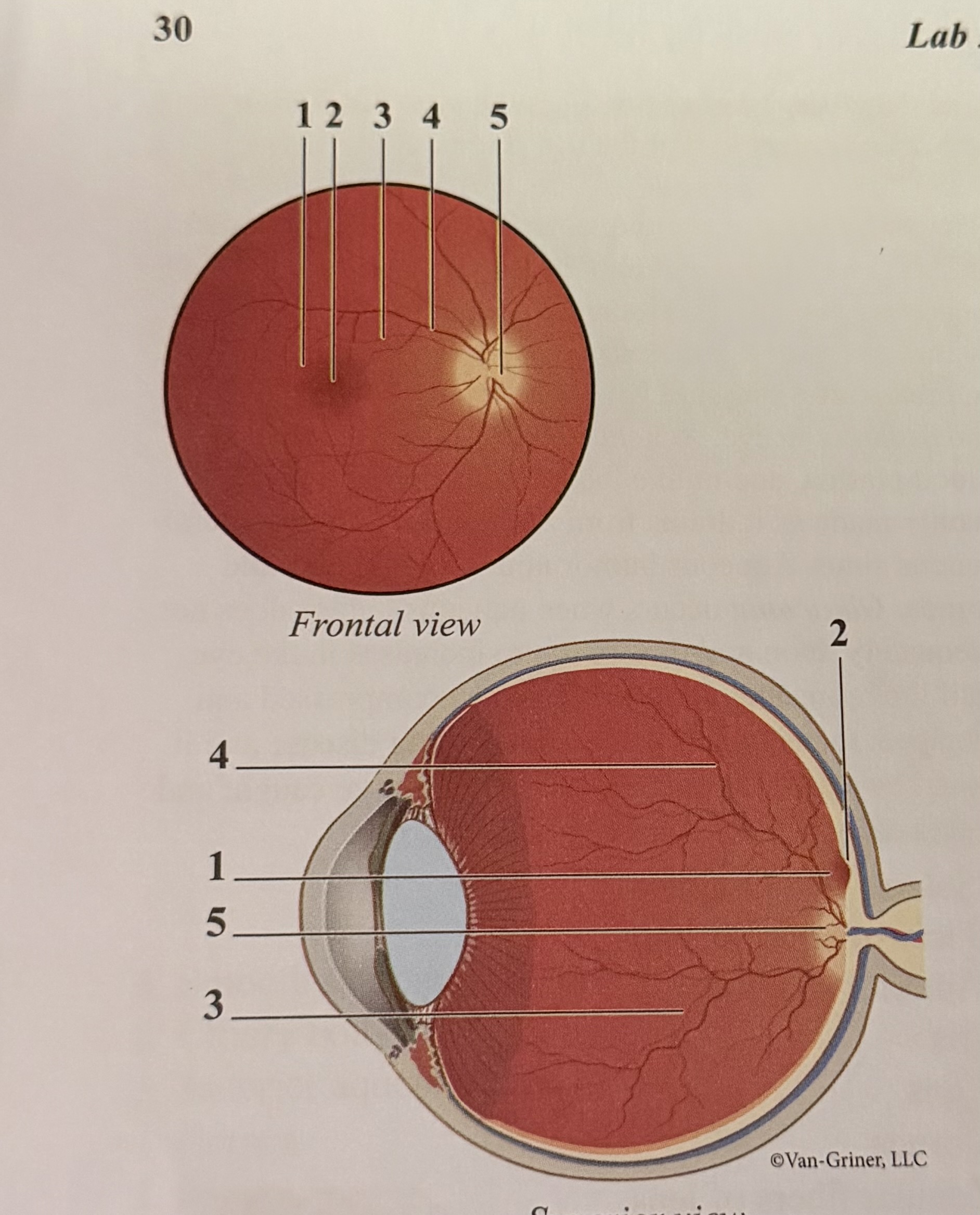
What is 3
Arteriole
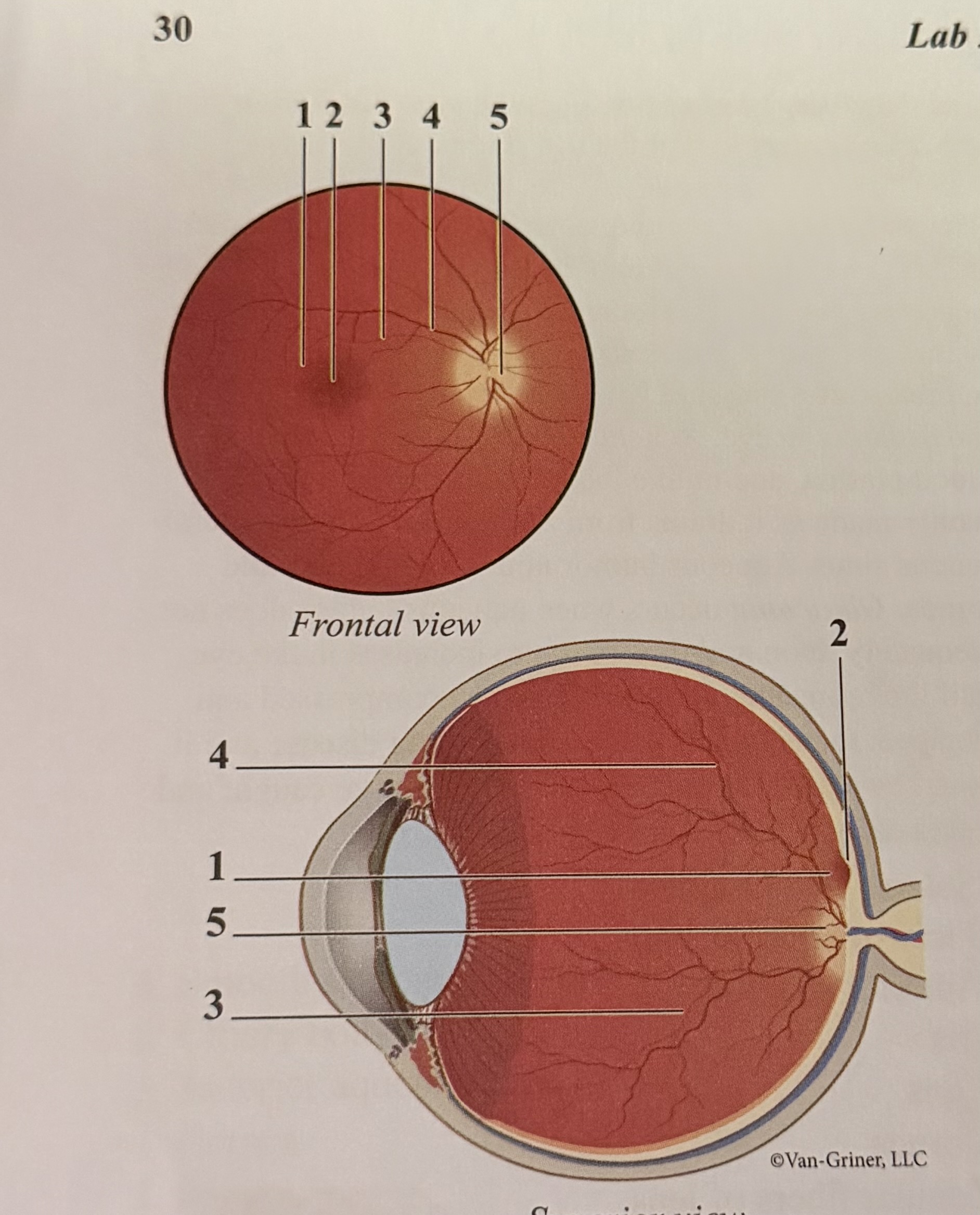
What is 4
Vein
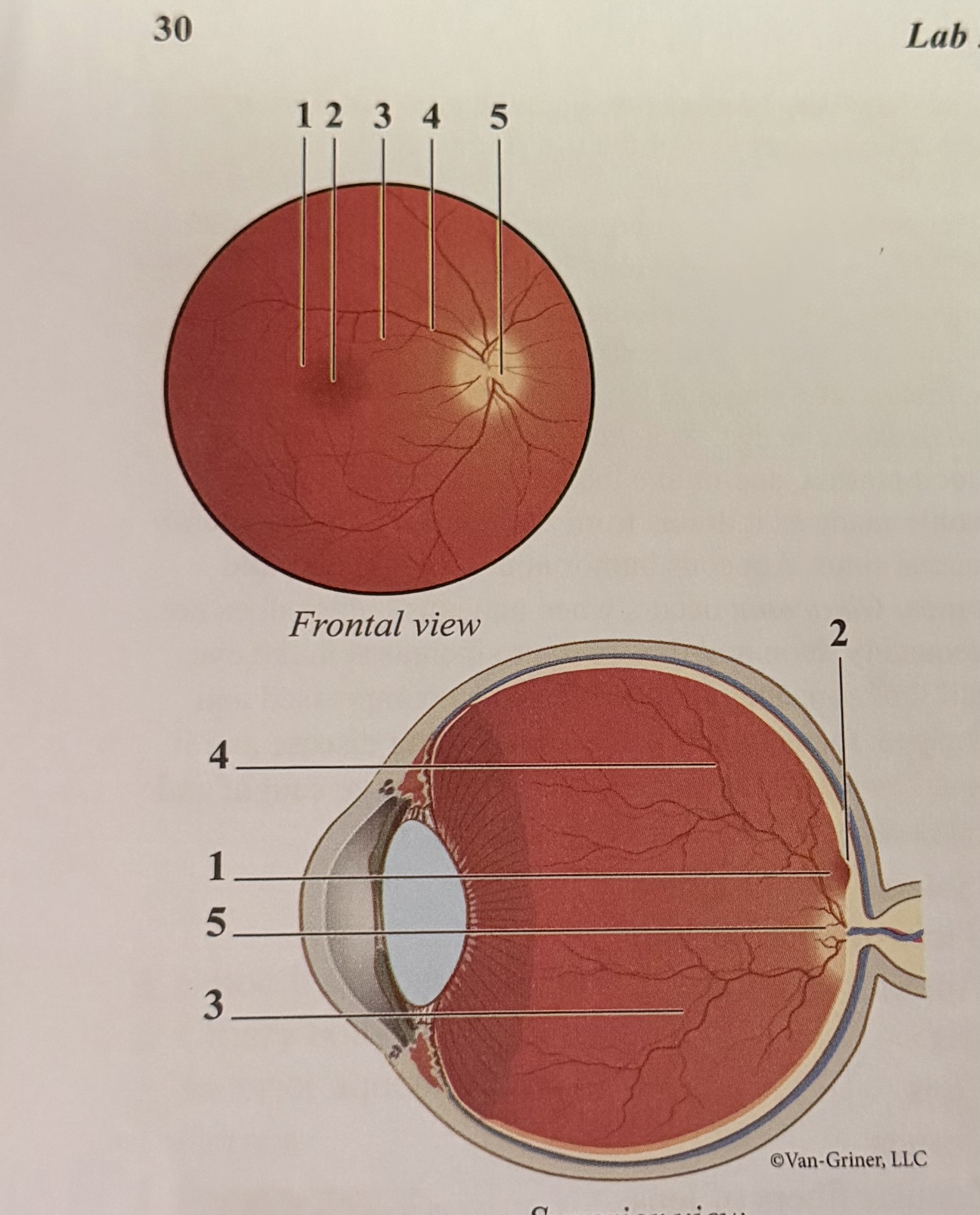
What is 5
Optic disk
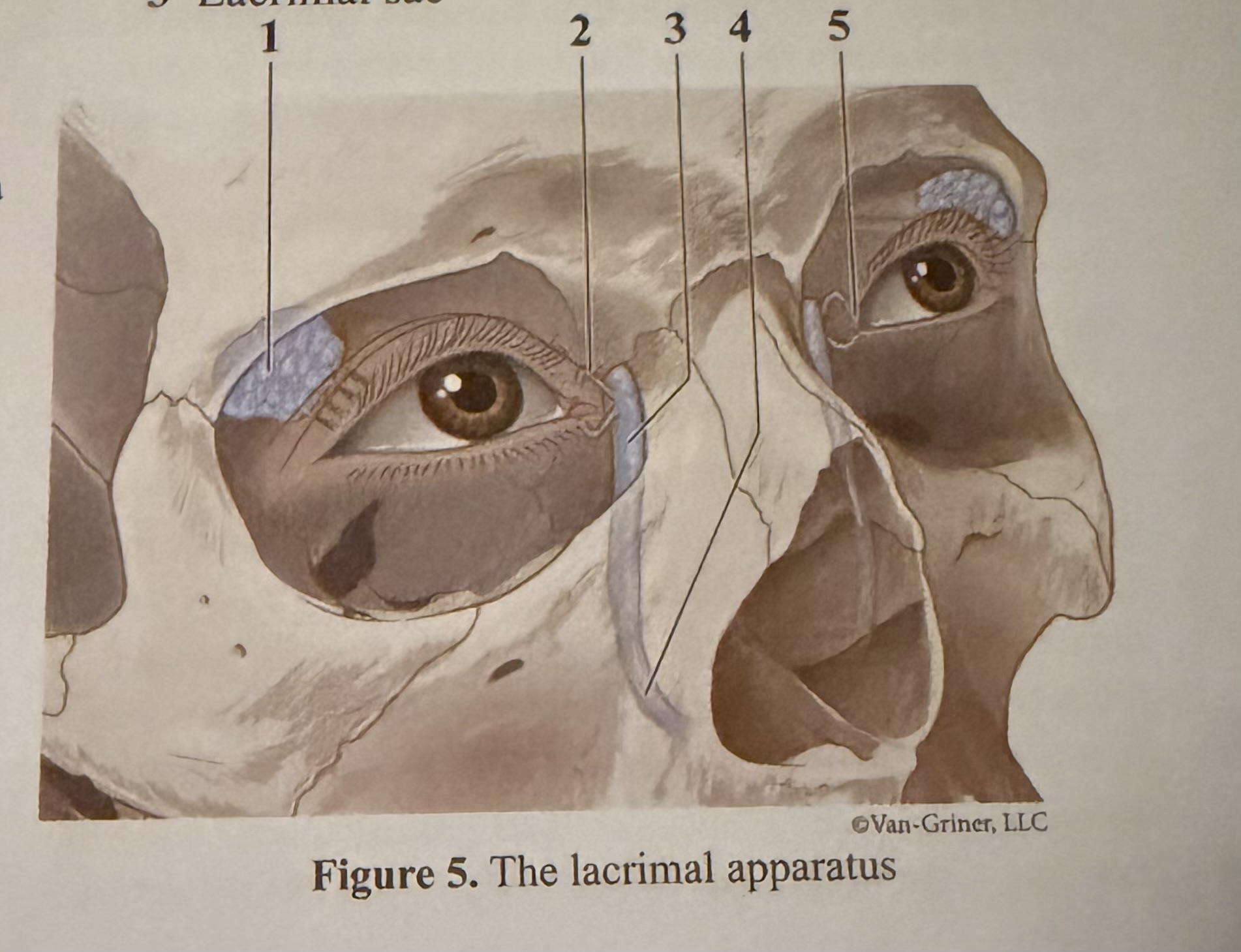
What is 1
Lacrimal gland
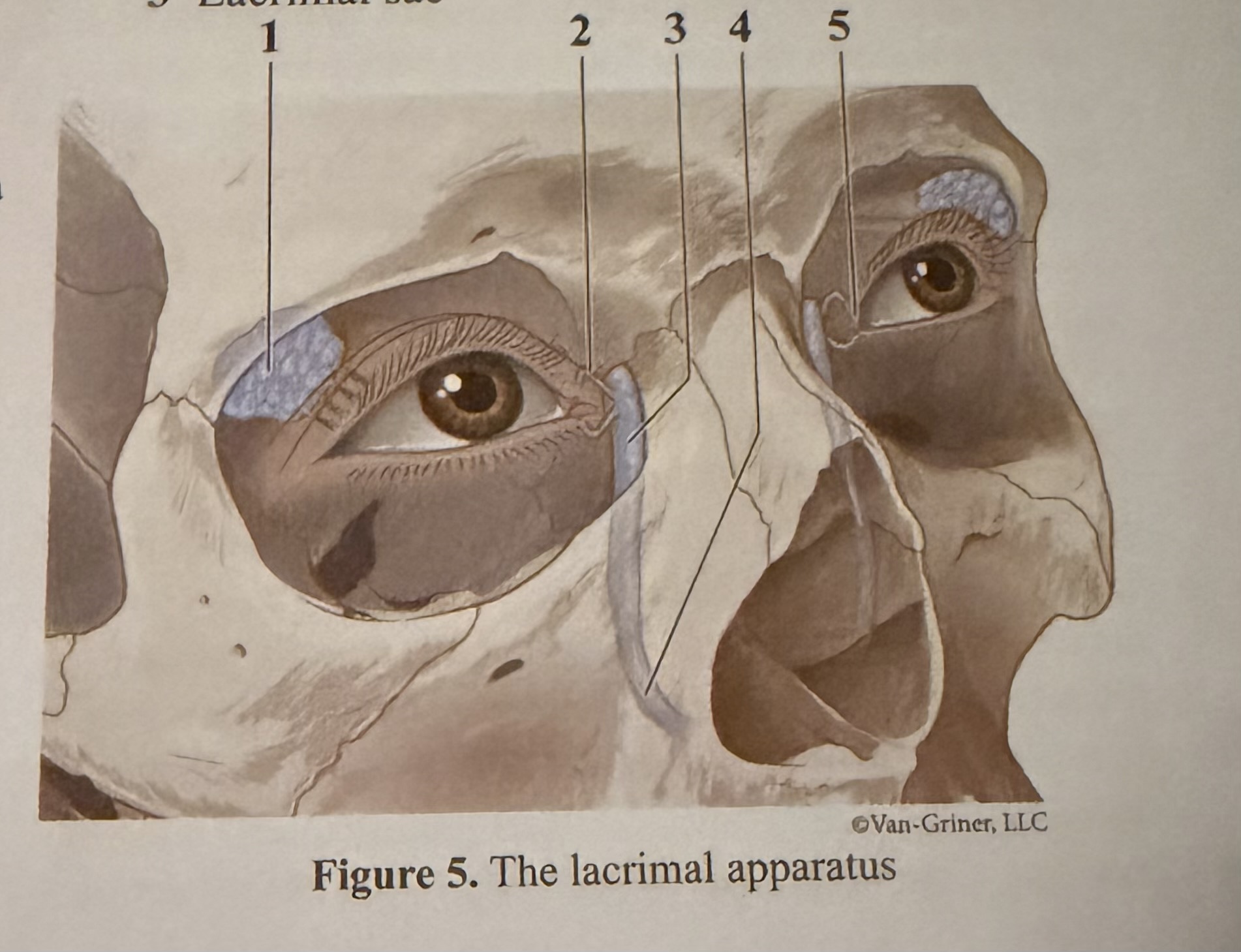
What is 2
Canaliculi
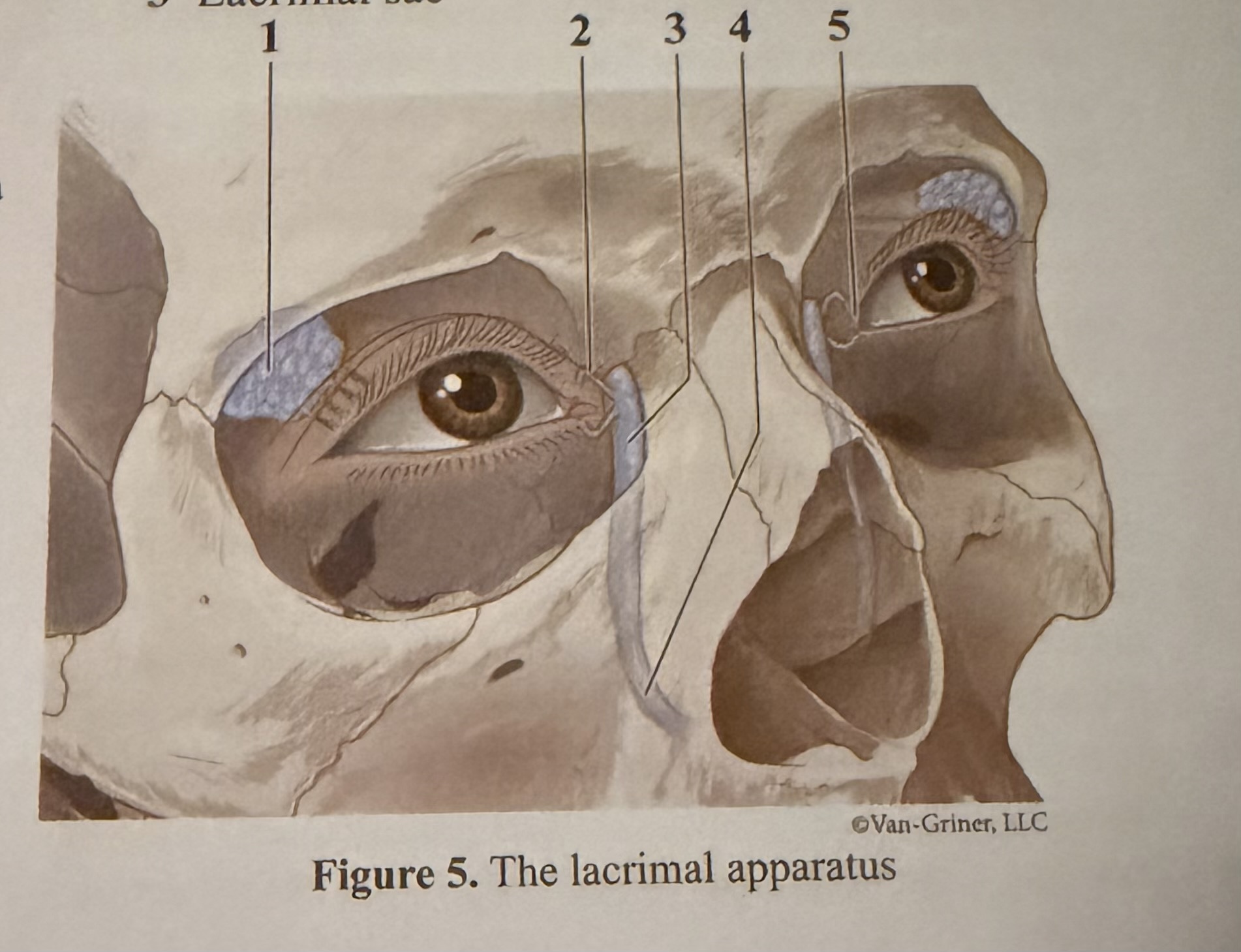
What is 3
Lacrimal sac
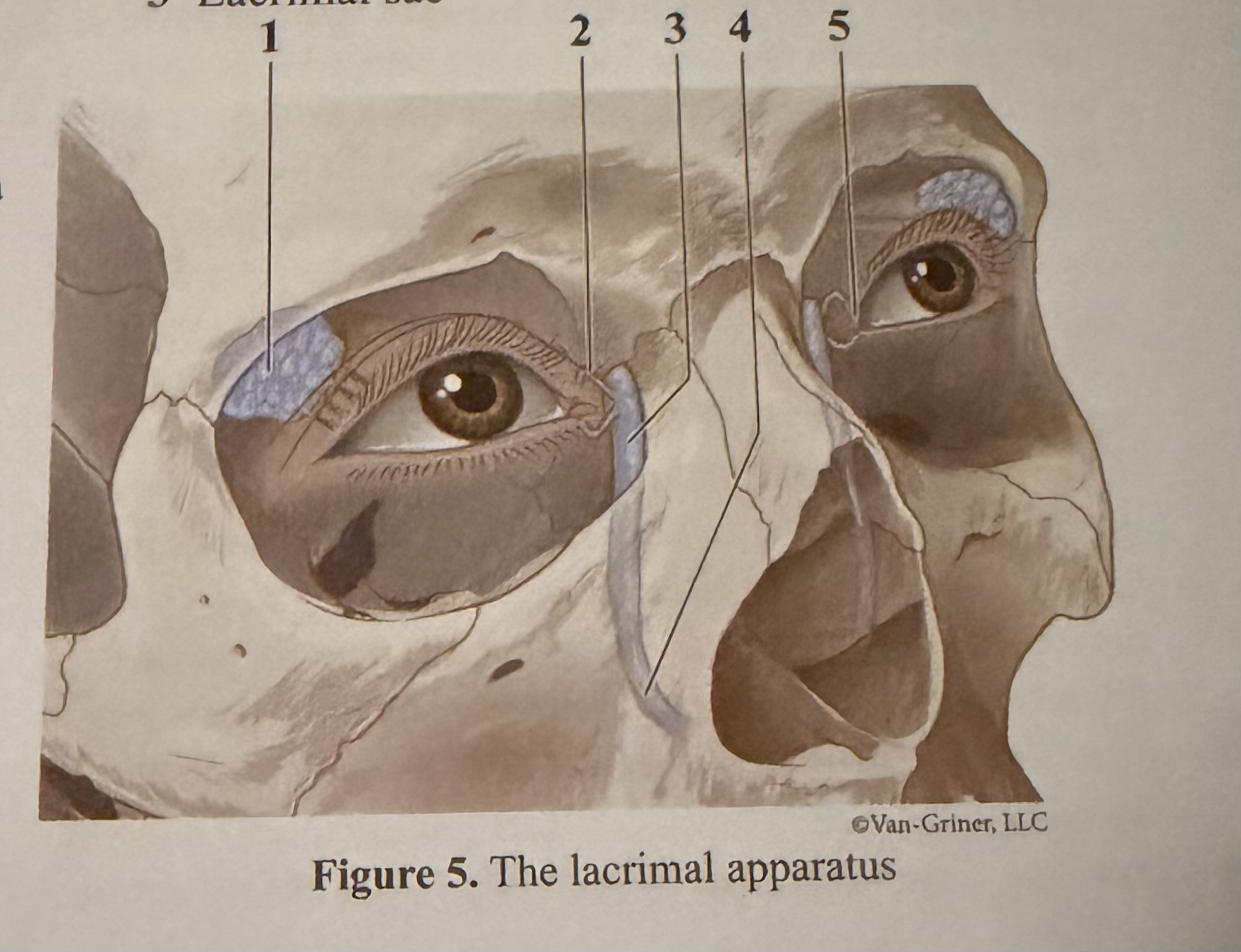
What is 4
Lacrimal duct
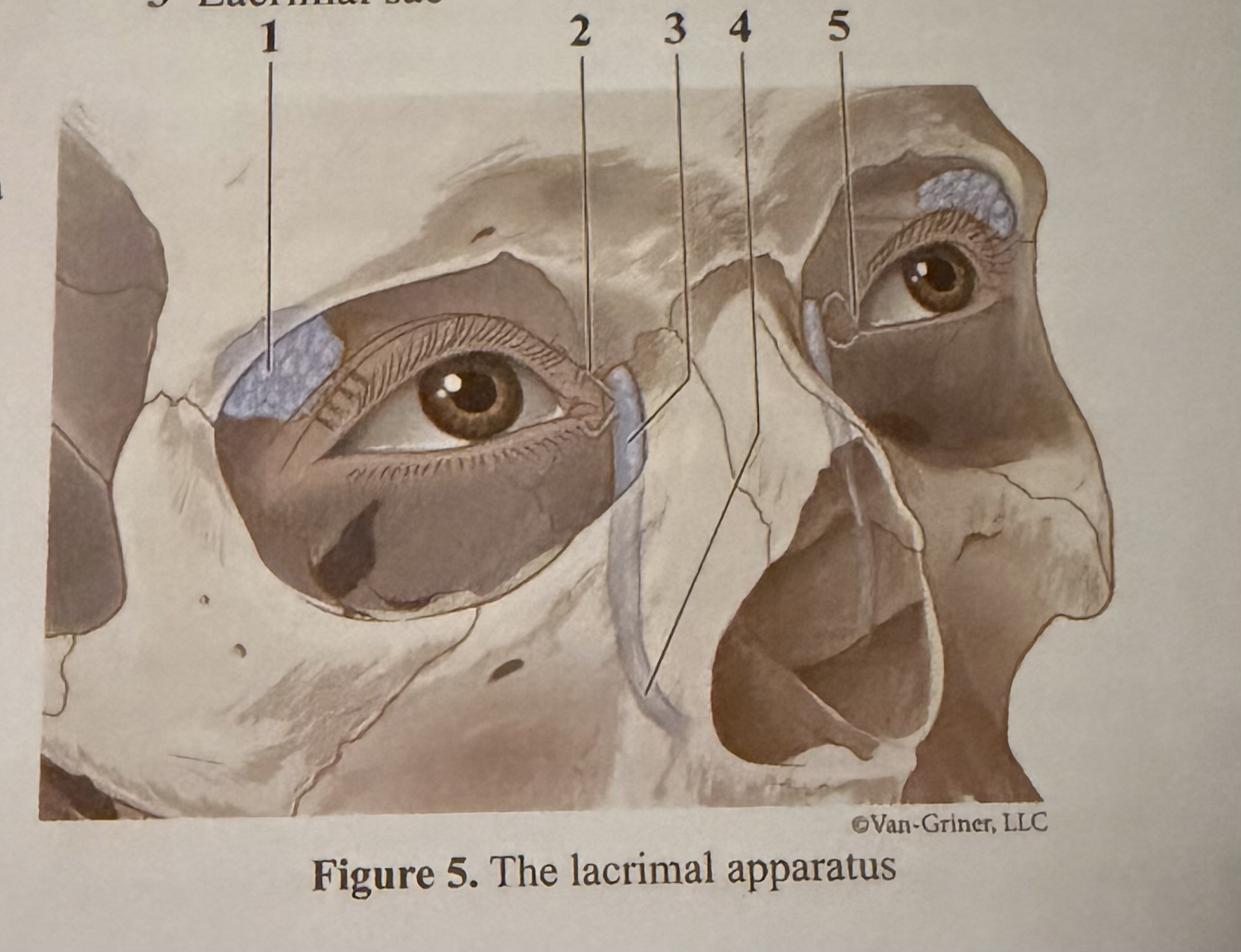
What is 5
Caruncle
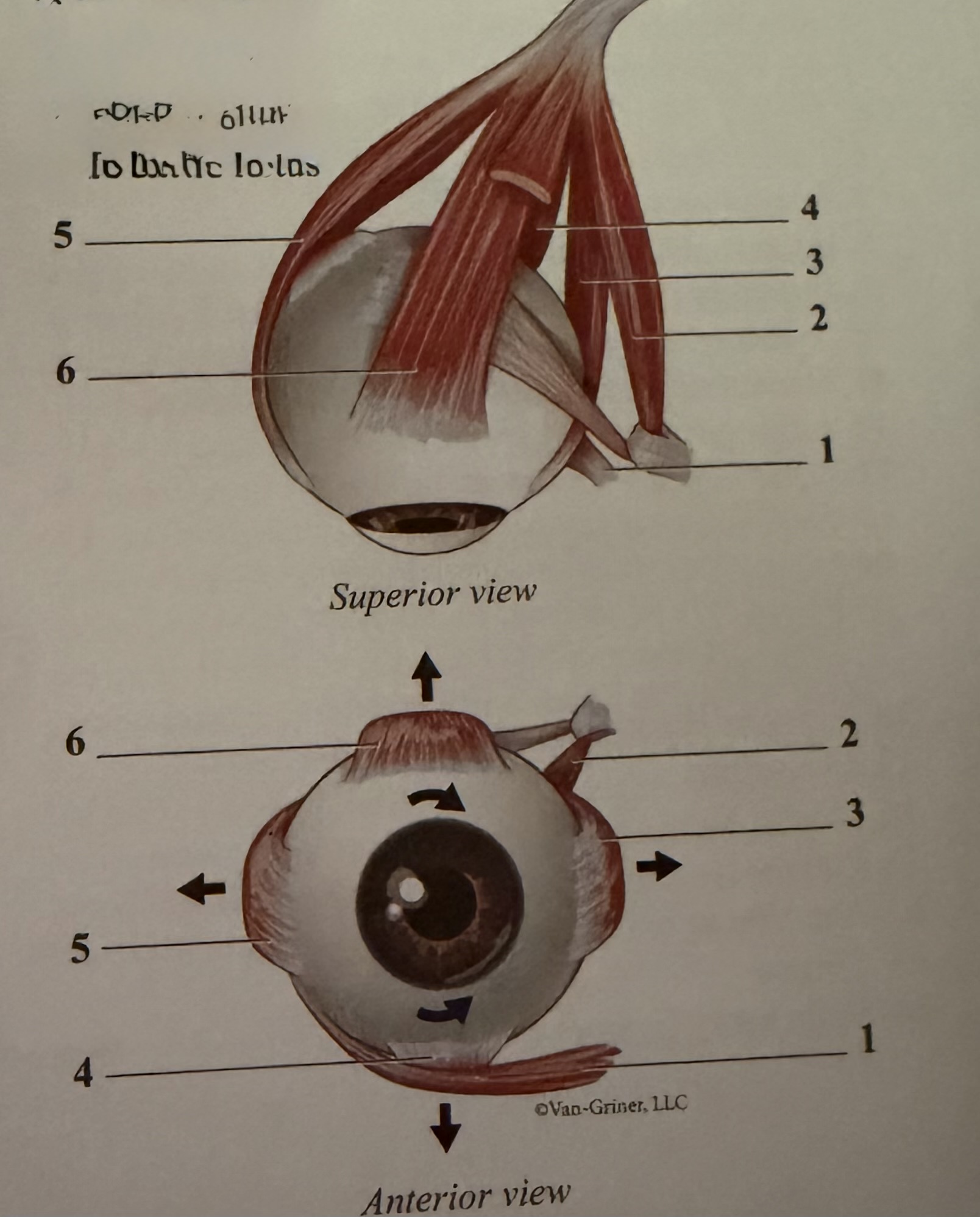
What is 1
Inferior oblique
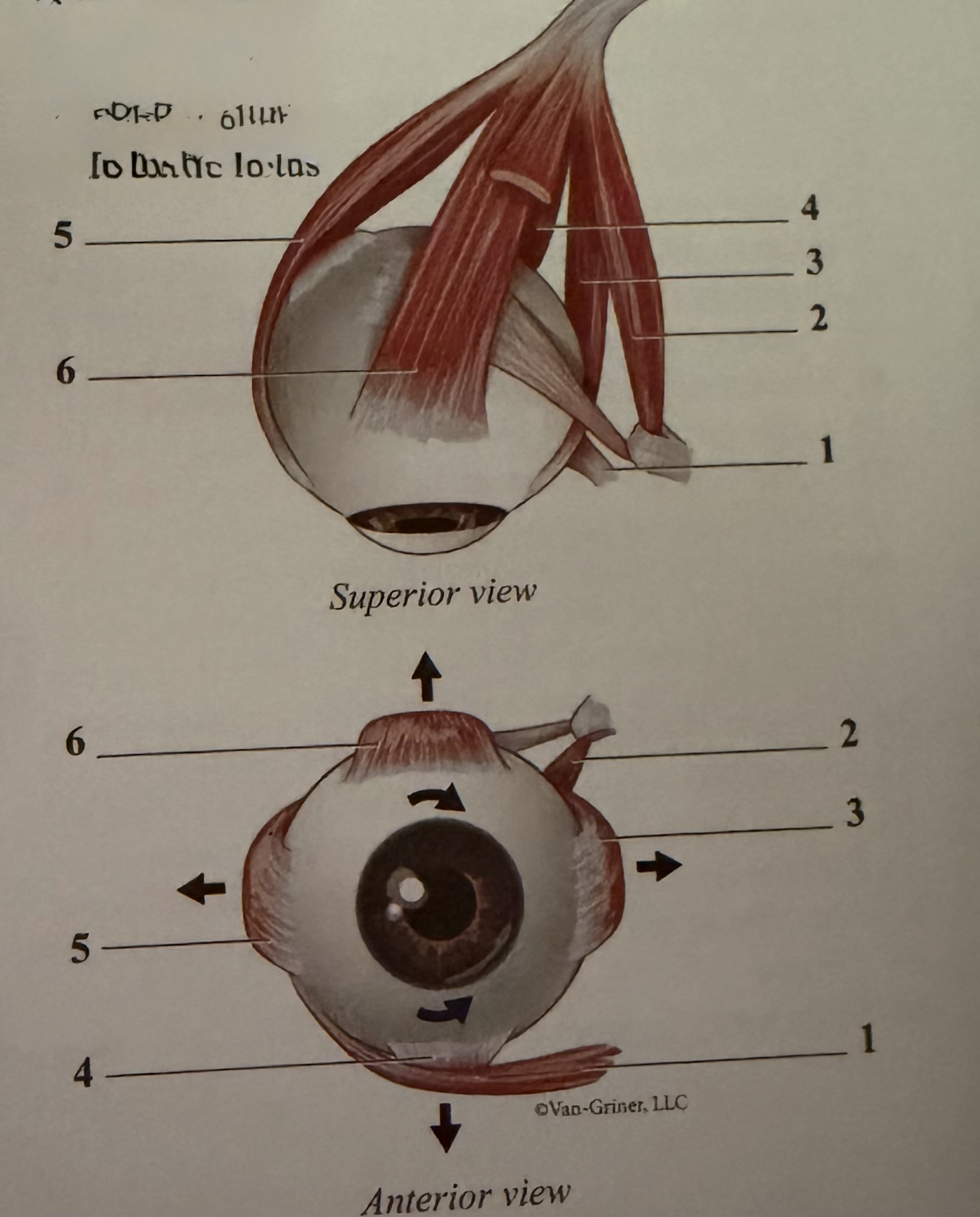
What is 2
Superior oblique
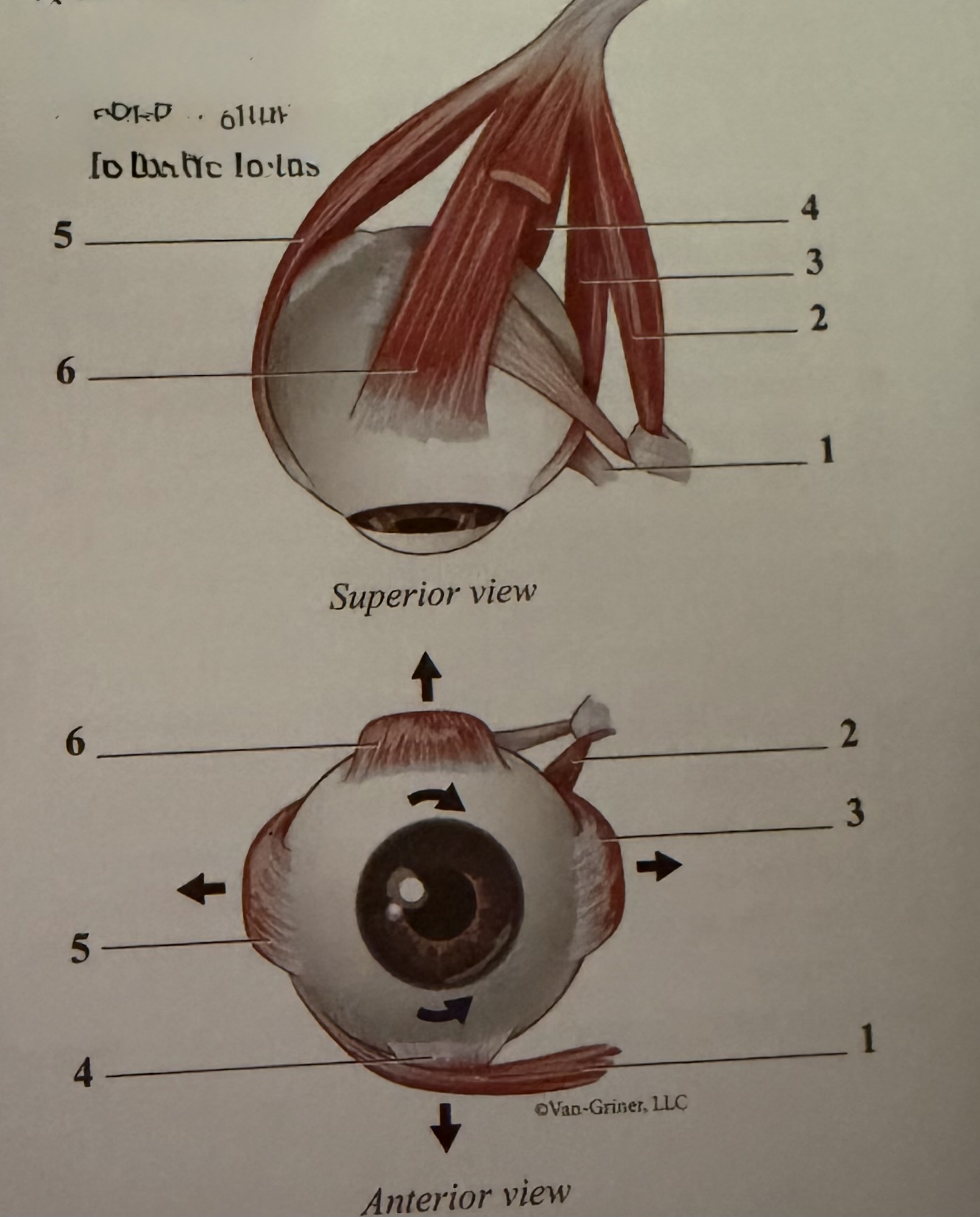
What is 3
Medial rectus
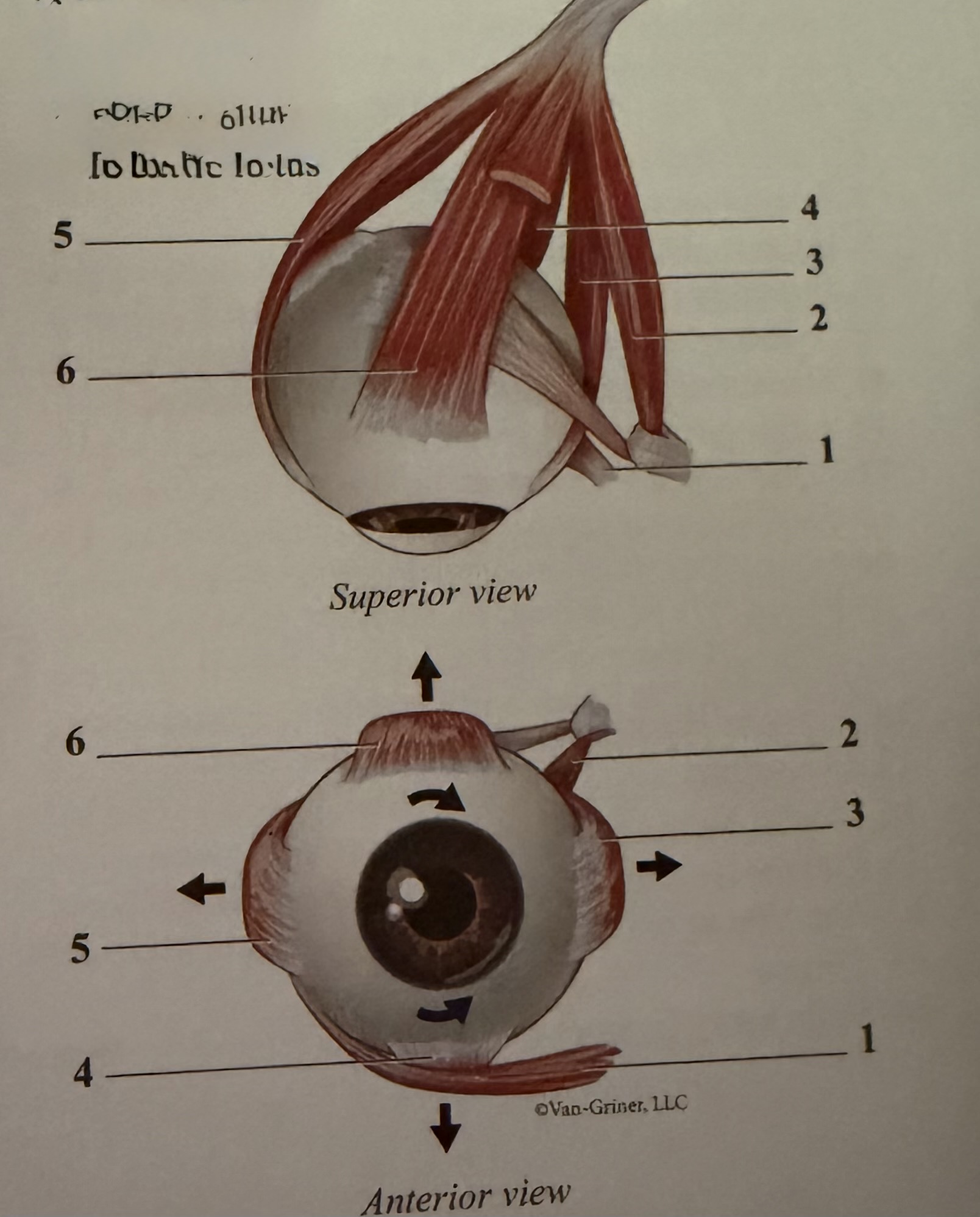
What is 4
Inferior rectus
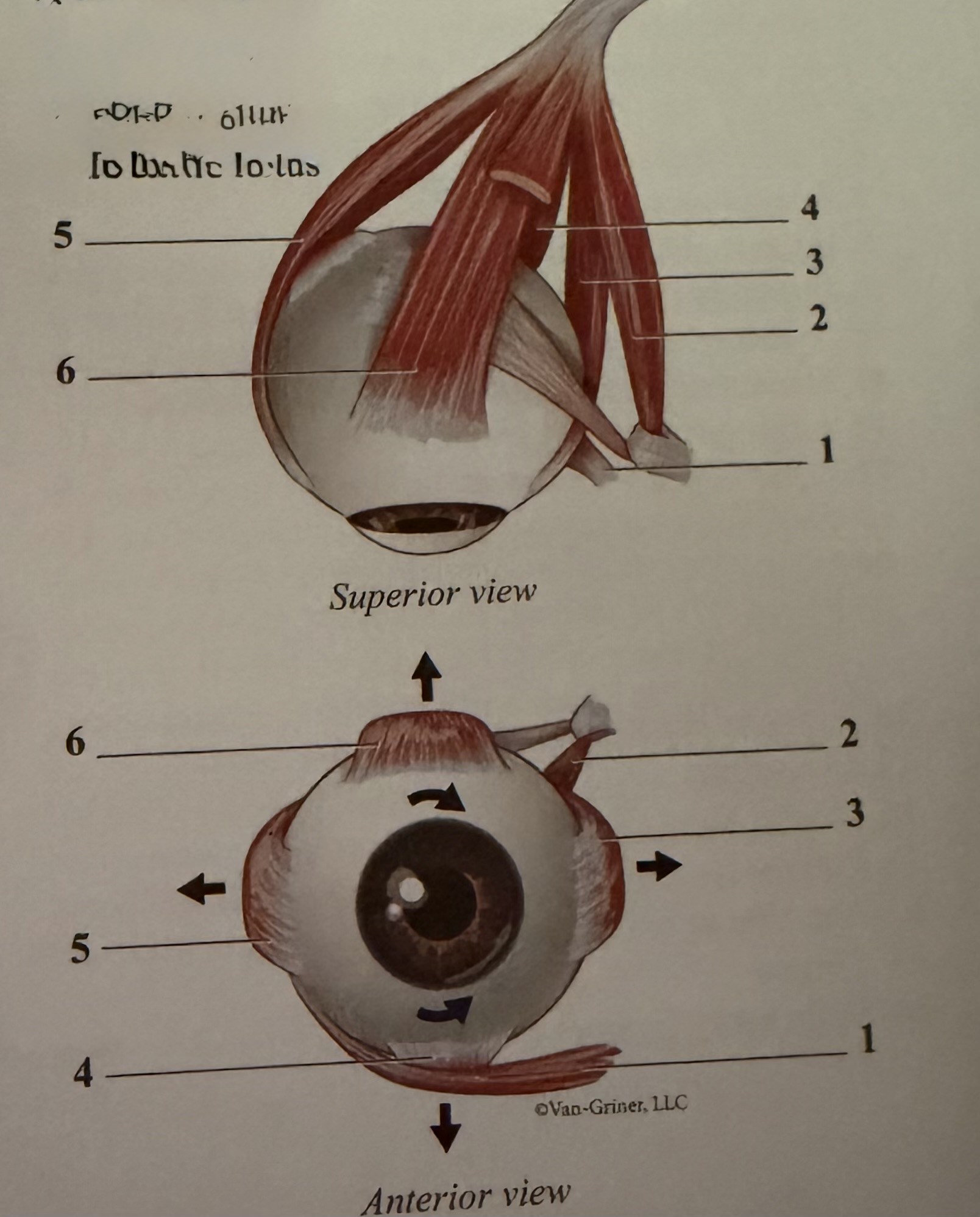
What is 5
Lateral rectus