biology alevel core concepts
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
Atom
Smallest unit of an element that retains all chemical properties ,has a nucleus containing protons and neutrons with electrons orbiting
Water formation
It has a negative oxygen and a positive hydrogens therefore it is polar and can form hydrogen bonds
High specific heat capacity in water
Large amount of energy is needed to raise the water temperature which prevents large fluctuations in water to keep aquatic habitats stable
High latent heat of vaporisation in water
Lots of energy needed for it it turn to gas needed for temperature control for body cooling
molecule
2 or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
element
pure substance made of one type of atom
compound
substance formed from two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
organic
molecules containing carbon and other elements, typically associated with living organisms.
inorganic
a charged atom or group of atoms that does not contain carbon
magnesium
component of chloropyll needed for photosynthesis
iron
component of haemoglobin and myoglobin enabling oxygen transport and storage
phosphate
components of DNA ,RNA, ATP, phospholipids needed for genetic information, energy transfer and cellular membranes.
calcium
important for bone structure and teet
Cohesion in water
The attraction of water molecules for each other because of the dipole structure of water producing hydrogen bonds between them
High surface tension in water
Cohesion between water molecules produces surface tension
High density in water
Ice is less dense than water as the hydrogen bonds holds then further apart than in liquid therefore ice can float and acts as an insulator
Water is transparent
Allows light to pass through for plants to synthesise
Monosaccharide
An individual sugar molecule
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides combined via a glycosidic bond
Isomers
Molecules that have the same chemical formula but a different arrangement
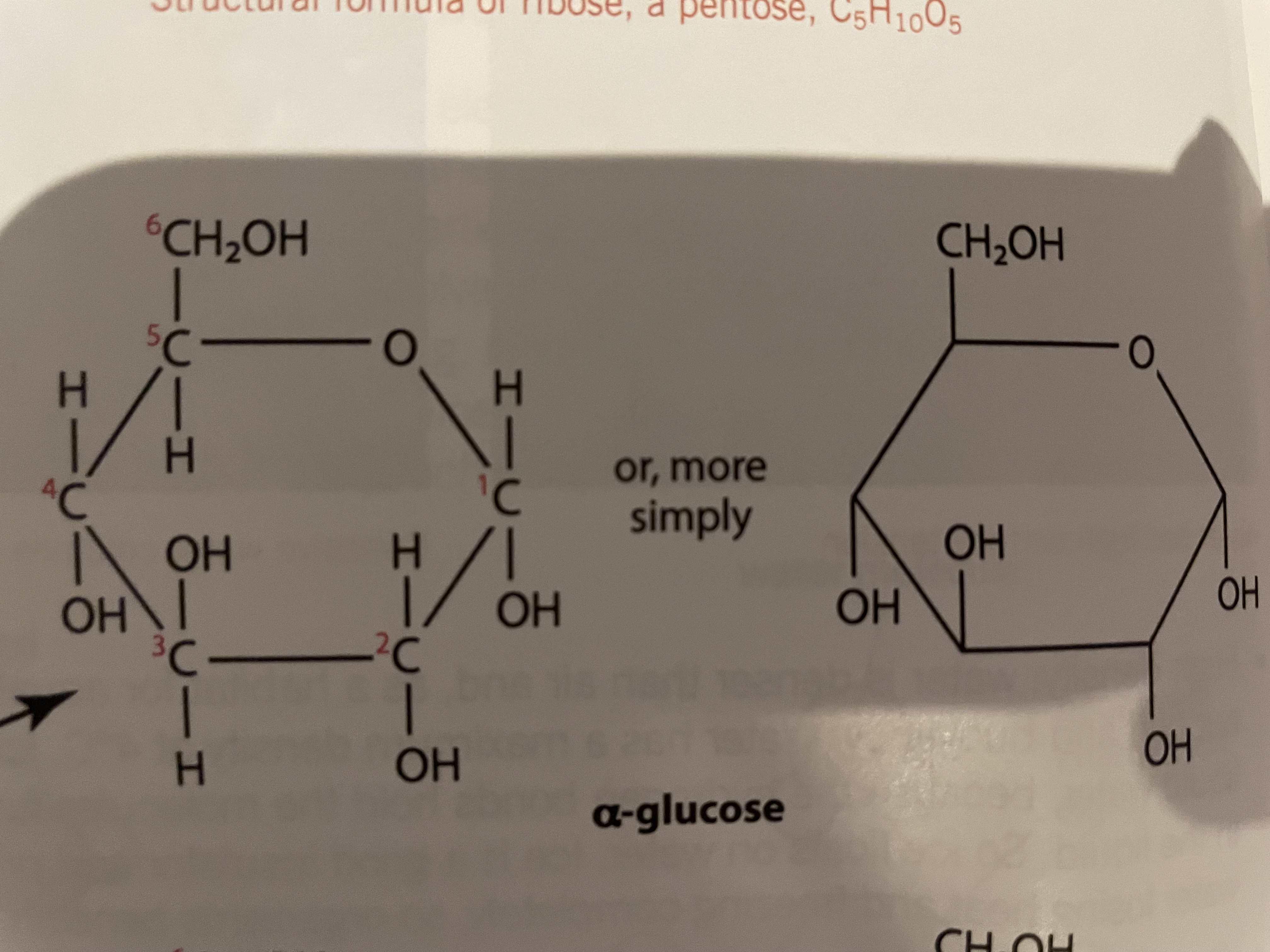
Alpha glucose
OH group is on the bottom of carbon 1
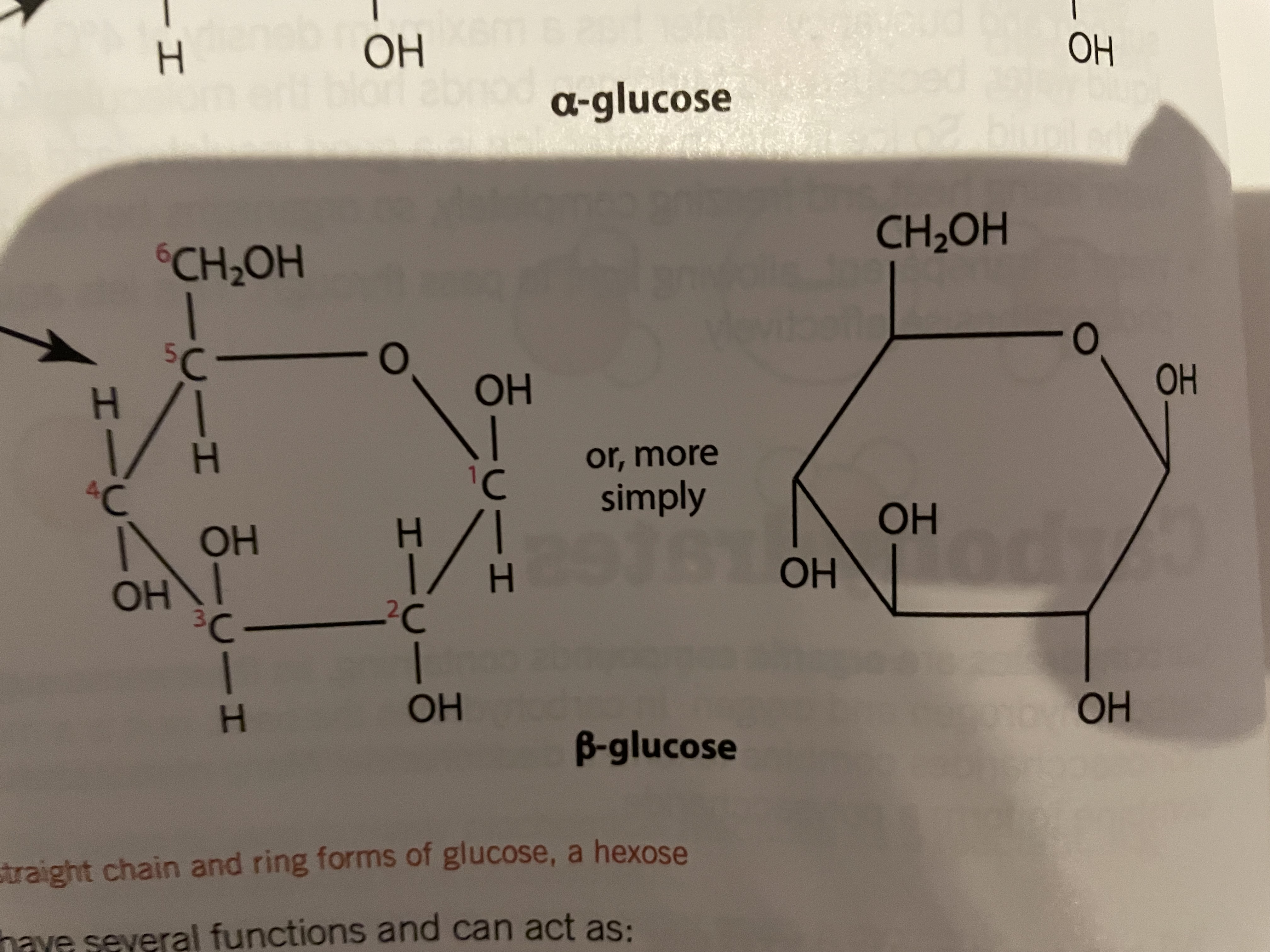
Beta glucose
OH group is on the top of carbon 1
Monosaccharides functions
-source of energy in respiration
-building blocks for larger molecules
-intermediate in reactions
-constituents of nucleotides
Disaccharide components
Glucose+glucose= maltose (germinating seeds)
Glucose + fructose =sucrose(transport in phloem of flowering plants)
Glucose + galactose = lactose(mammalian milk)
Reducing sugars (glucose)
Add Benedict’s solution and heat if positive = blue to green to yellow to orange to brick red precipitate negative = blue
Starch
Add iodine positive= blue/black negative = yellow
Non reducing sugar(sucrose)
Add HCl to hydrolyse glycosidic bond and then neutralise with sodium hydrogen carbonate then add Benedict’s solution and then heat positive= brick red precipitate negative = blue
Protein
Add biuret solution and shake gently positive = purple negative = blue
Lipid
Add ethanol then 1:1 with water and shake vigorously positive = cloudy white emulsion negative = colourless
Starch(amylose)
1-4 alpha glucose, helical, stored in plants for respiration, Insoluble and no osmotic effect on cells
Starch(amylopectin)
1-6 and 1-4 alpha glucose,branched, stored in plants for respiration, in soluble and no osmotic effect on cells
Glycogen
1-4 alpha glucose ,branched ,long chains of C6H12O6 ,insoluble can be broken at the end for respiration
Cellulose
Beta glucose, fibrous chains, parallel chains, hydrogen bonds , C6H12O6 rotates 180° ,strong support for cell wall prevents from bursting when it is turgid
Chitin
Beta glucose , acetyleamin , unbranch polymer waterproof lightweight
Elements of lipids
Carbon,hydrogen,oxygen
Lipid solubility
Leopards are non polar therefore they have no charge to bond with water but they combine with proteins as a Lipoprotein in the blood plasma
Functions of lipids
-Energy source and storage
-protection
-oxidation
-membranes
-waterproofing
-insulation
-hormones

Bonded via 3 ester bonds
Factors contributing to heart disease
Diet high in saturated fats, smoking ,lack of exercise, aging
Low density lipoprotein
Diet high in saturated fats which builds up causing an atheroma that can form in the coronary arteries which restricts blood flow to the heart muscle therefore less oxygen and glucose is delivered to cardiac muscles which can result in the vessels getting blocked therefore causes a heart attack
High density lipoprotein
Diet high in unsaturated fats that carry unsaturated fats so liver for breakdown therefore a lower risk of cardiovascular and coronary heart disease a.k.a. high cholesterol
structures of a protein
Primary ,Secondary ,tertiary,quaternary
Primary structure of a protein
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain (peptide bond)
Secondary structure of a protein
The folding of the potty peptide chain into a alpha helix or a beta pleated sheet(hydrogen bonds)
Tertiary structure of a protein
The folding of a polypeptide chain into a 3-D globular shape
Quaternary structure of a protein
Two or more polypeptide chains bonded together(disulphide,ionic, Hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions)
Dispirited is bonded via a peptide bond
Globular proteins
Water soluble, transports proteins, haemoglobin
Fibrous proteins
Water insoluble ,structural proteins, collagen
Hydrolysis
Water is added to break the glycosidic bond
Condensation
Water is removed to create a glycosidic bond
Induced fit
Substrate collide with the active site, active site changes shape to fit the substrate and enzyme substrate complex is formed change in the enzyme shaped places a strain on the substrate lowering the activation ,energy active site returns to original shape after reaction ,product is released
Lock and key
Enzyme have a specific shape active site which is complimentary to the shape of the substrate and enzyme substrate complex is formed. Product is released active site does not change shape.
Activation energy
Energy required to enable a reaction to occur
Denature
When the enzymes active site has changed, therefore it would be unable to catalyse the reaction
Catalyst
They speed up chemical reactions without being used up during the reactions
Factors that effect the rate of enzymes
Temperature,pH,concentration
Competitive inhibitors
Binds to the active site similar shape complementary to the active site therefore prevents binding ,reversible
Non competitive inhibitors
Binds to the allosteric site site away from active site changes the active site active site is no longer complementary to substrate ,irreversible
Immobilised enzyme
When an enzyme is fixed, bound or trapped in an inert matrix
3 ways Enzymes can be immobilised
Alignant , gel membrane,polythene
Why immobilise the enzyme?
Stabilise the enzyme molecules and they have a wider range of optimum pH and temperature. It is less affected by temperature and pH changes.
Advantages of using immobilised enzymes
They can be recovered and reused ,can control the rate ,cheaper
Nucleus
Contains DNA which codes for protein synthesis
Nucleolus
Synthesis of RNA and ribosomes
Nuclear pore
Allows the transport of mRNA out of nucleus
Nuclear envelope
Separates DNA from cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Allows what enters and exits the cells through a selectively permeable membrane
Cytoplasm
Site of cellular reactions
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration which synthesises for ATP
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Transport proteins
Soft endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesises and transports lipids
Golgi body
Chemically modifies proteins produces lysosomes and glycoproteins packages proteins for secretion out of the cell
centrioles
Spindle formation in cell division
ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Lysosome
Contains an isolates hydrolyte enzymes release these enzymes and destroy organelles
Vesicles
Maintained osmotic pressure
Permanent vacuole
Storage of ions In plants
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Cell wall
Provides strength and support
Plasmodesmata
Exchange of large organic materials via cytoplasmic streaming allows communication between adjacent cells
Calculating magnification
Image size=actual image size*magnification
mm→um
x1000
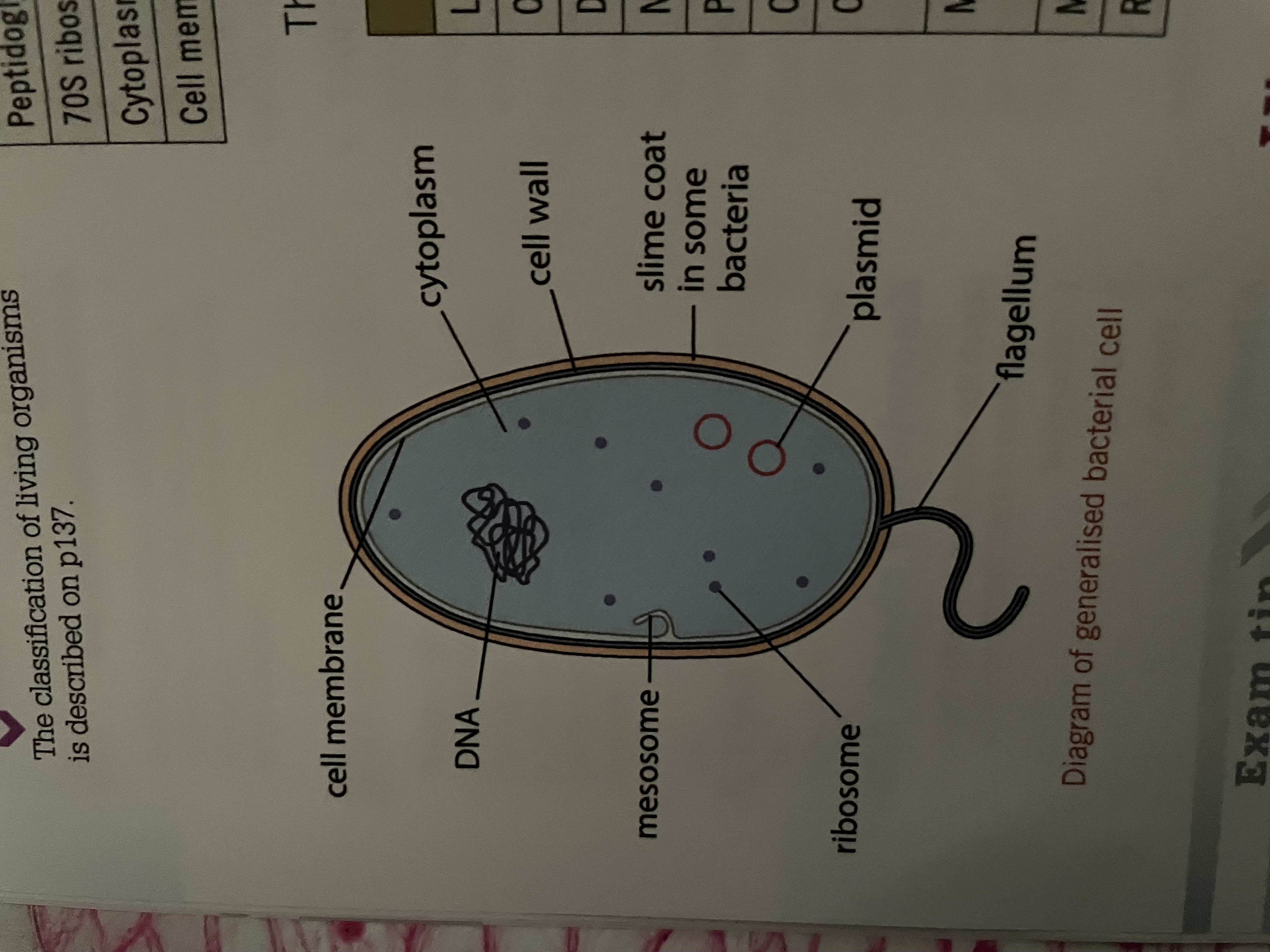
Prokaryotic
They are small no organelles their DNA is free in the cytoplasm ,no nuclear envelope ,plasmid may be present. They have a cell wall ,chloroplast ,no mitochondria but may use mesa home for aerobic respiration are only present in some ,70s ribosome free in cytoplasm
Eukaryotic
Large organelles are membrane bound ,DNA combined with protein in chromosomes. The nuclear envelope is double membrane ,no plasmids ,cell wall in cellulose plants and chitin ,chloroplasts in plants ,has mitochondria ,no mesosome, 80s ribosomes free in cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic Reticulum.
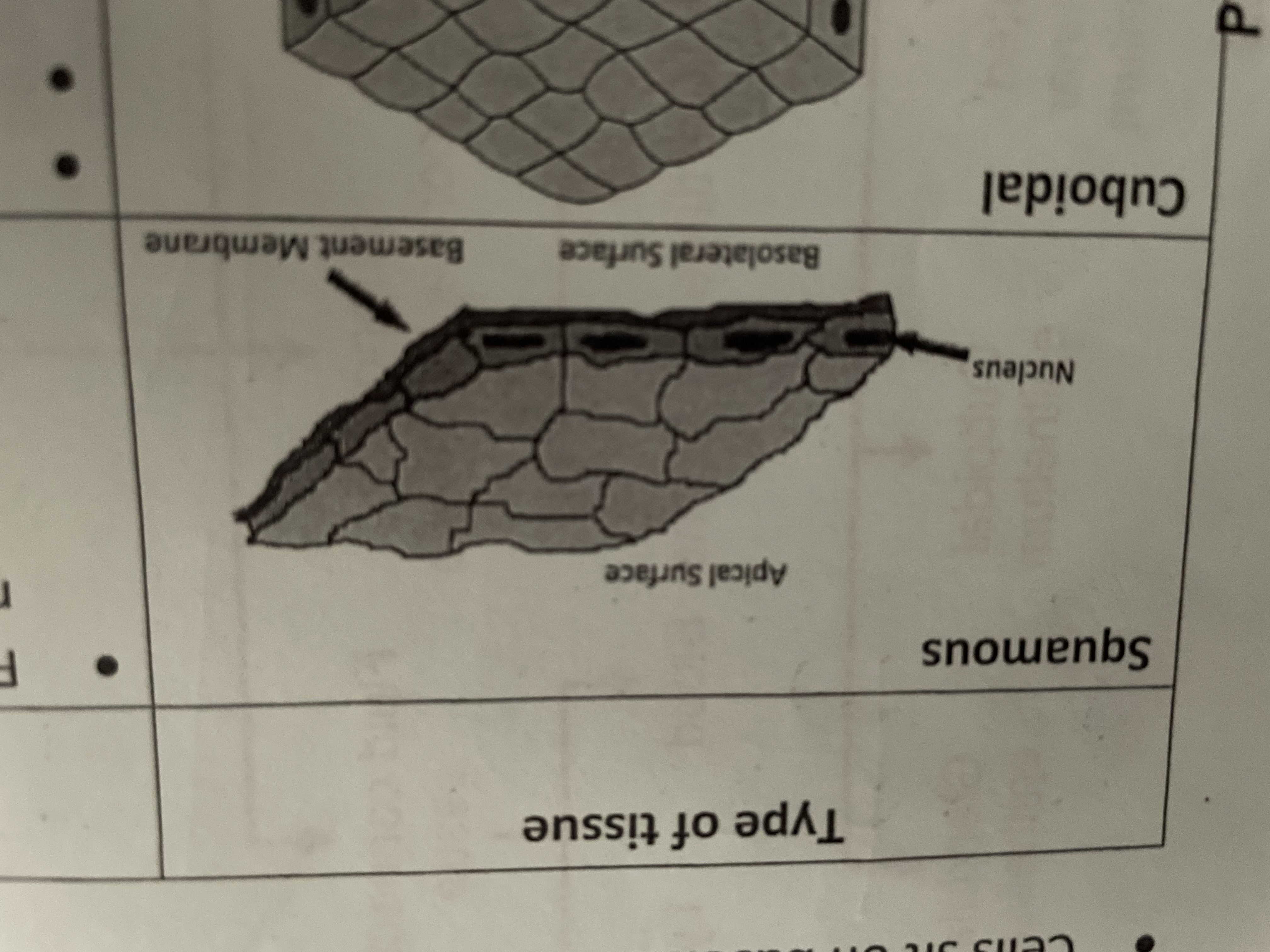
Squares
Lining tissue covers surface of organs, thin layer of cells for exchange walls of alveoli, blood vessels lining of renal capsule of the nephron
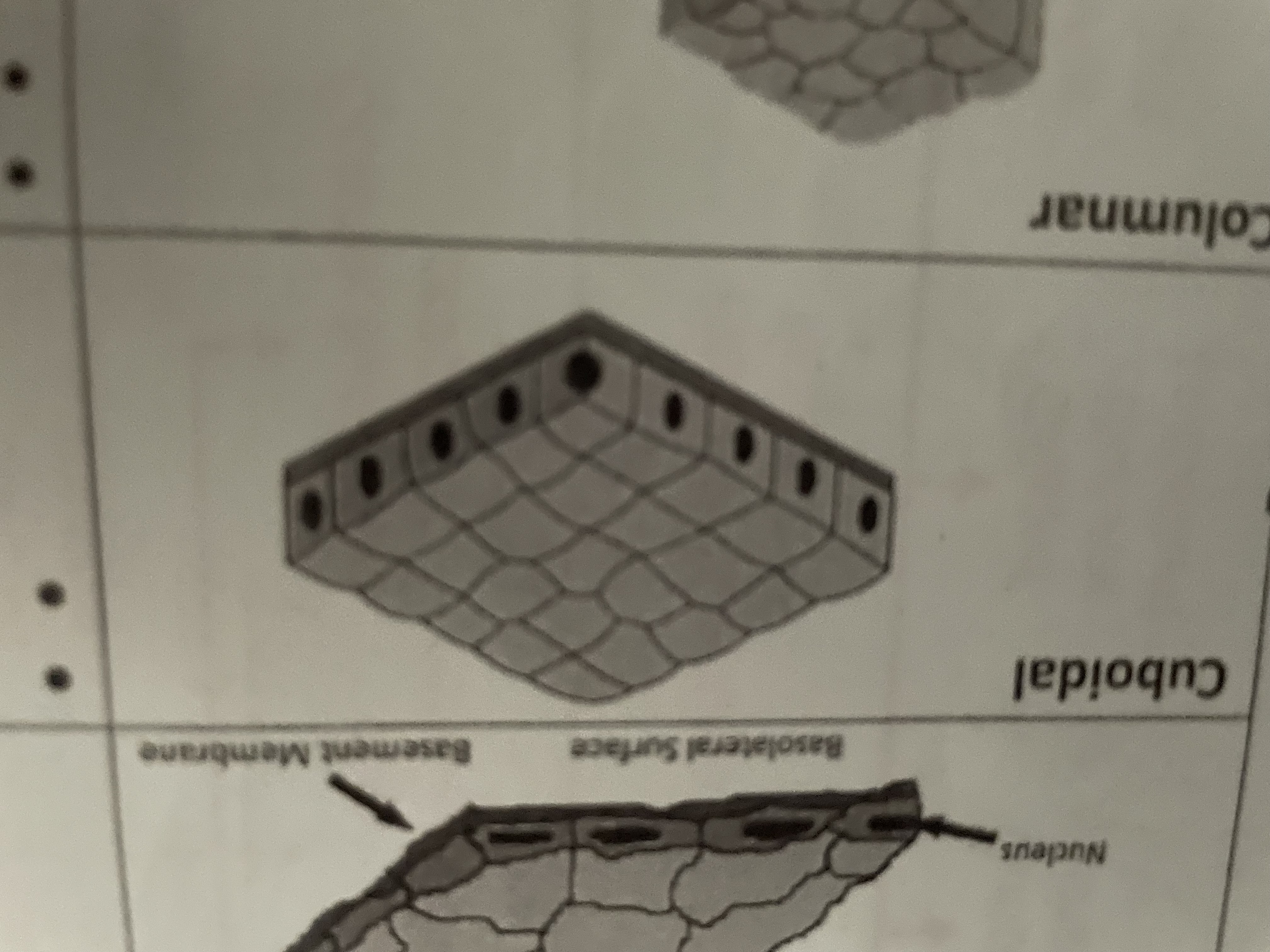
Cuboidal
Secretion and reabsorption ,kidney tubules Glandular ducts
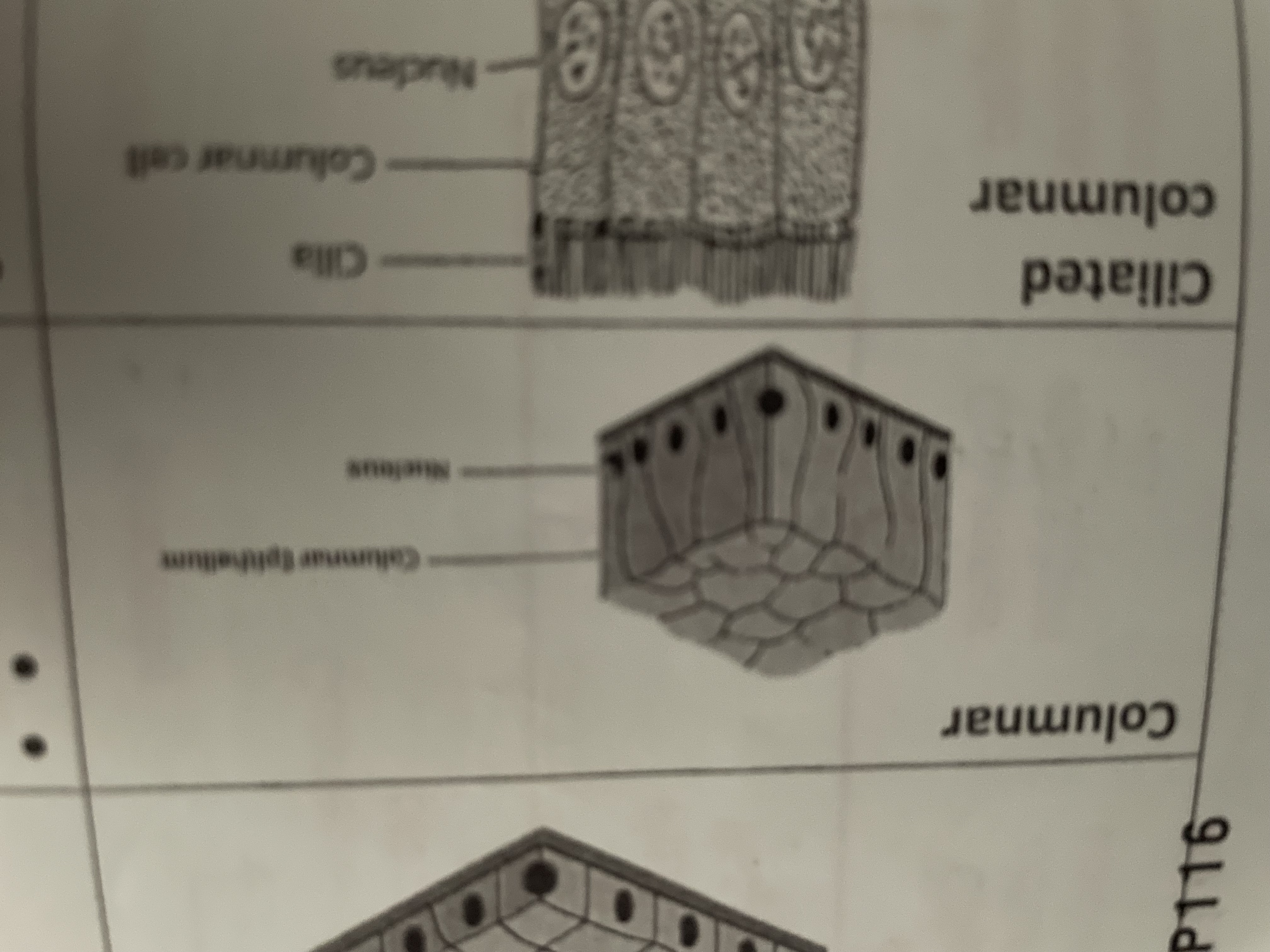
Columnar
Microvilli to increase surface area for absorption found in small intestine
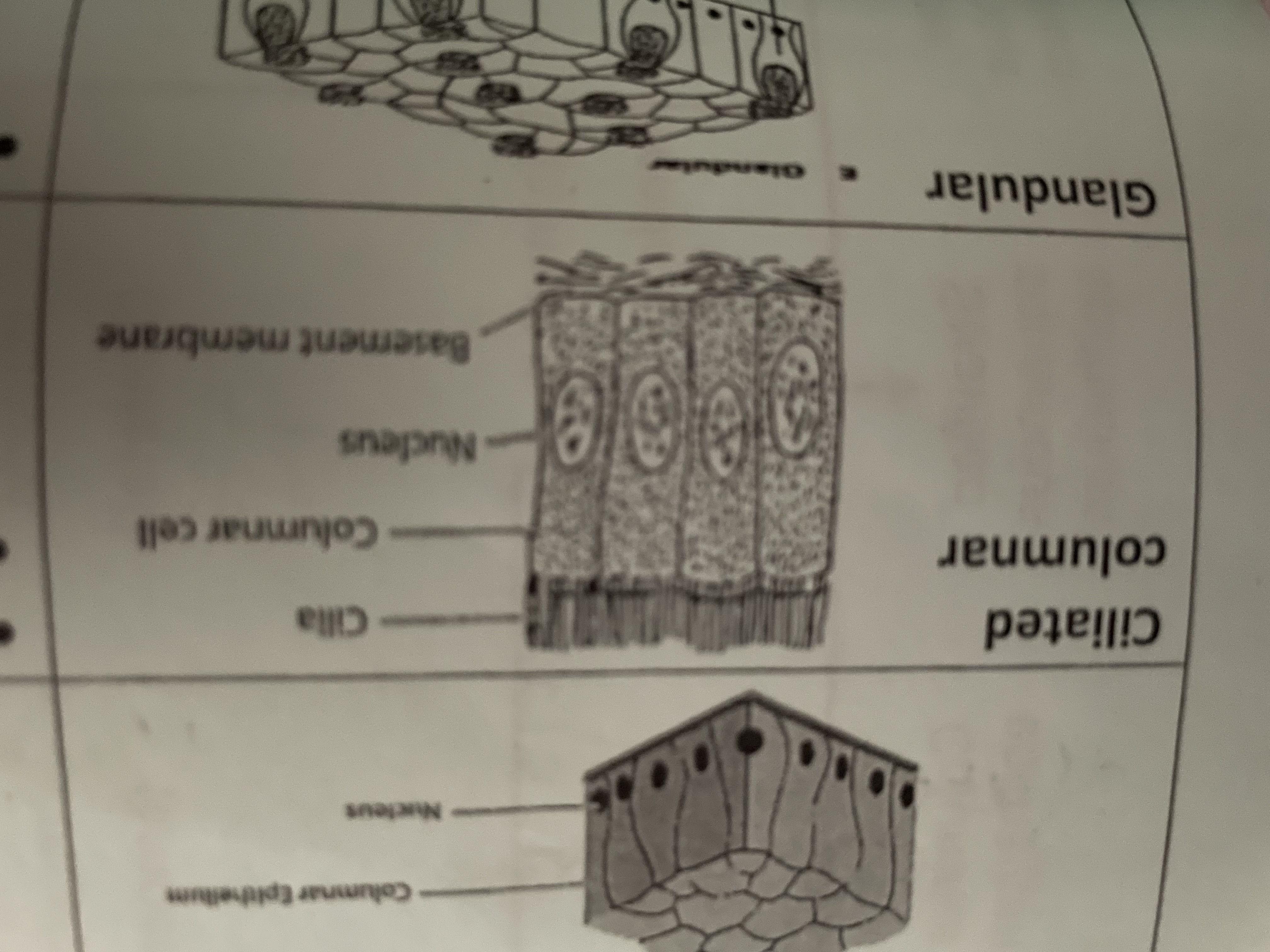
Ciliated columnar
Syria waft to remove dust and dirt out of air passage found in trachea bronchi fallopian tubes
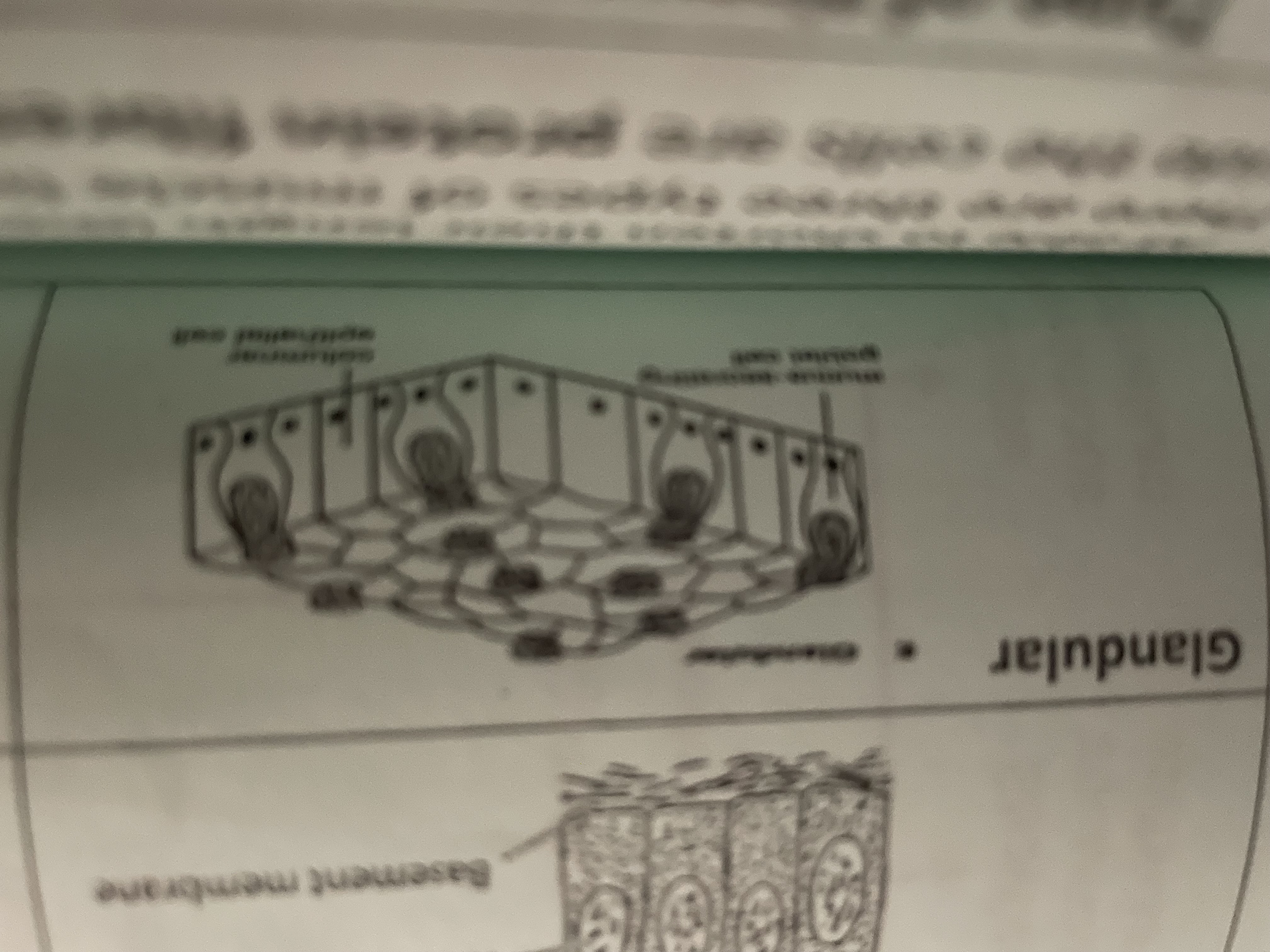
Glandular
Secrete enzymes, hormones, saliva, mucus found in saliva gland pancreas gastric glands in stomach mucosa
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal movements maintains posture and body position support soft tissue found in attached to bone by tendons generates locomotion in mammals

Smooth muscle
Rhythmical involuntary contraction but less powerful than skeletal muscle ,walls of hollow organs ,walls of digestive track ,wall of respiratory tract ,walls of blood vessels ,bladder ,skin

Cardiac muscle
Rhythmic contraction to pump blood to the heart found in the heart
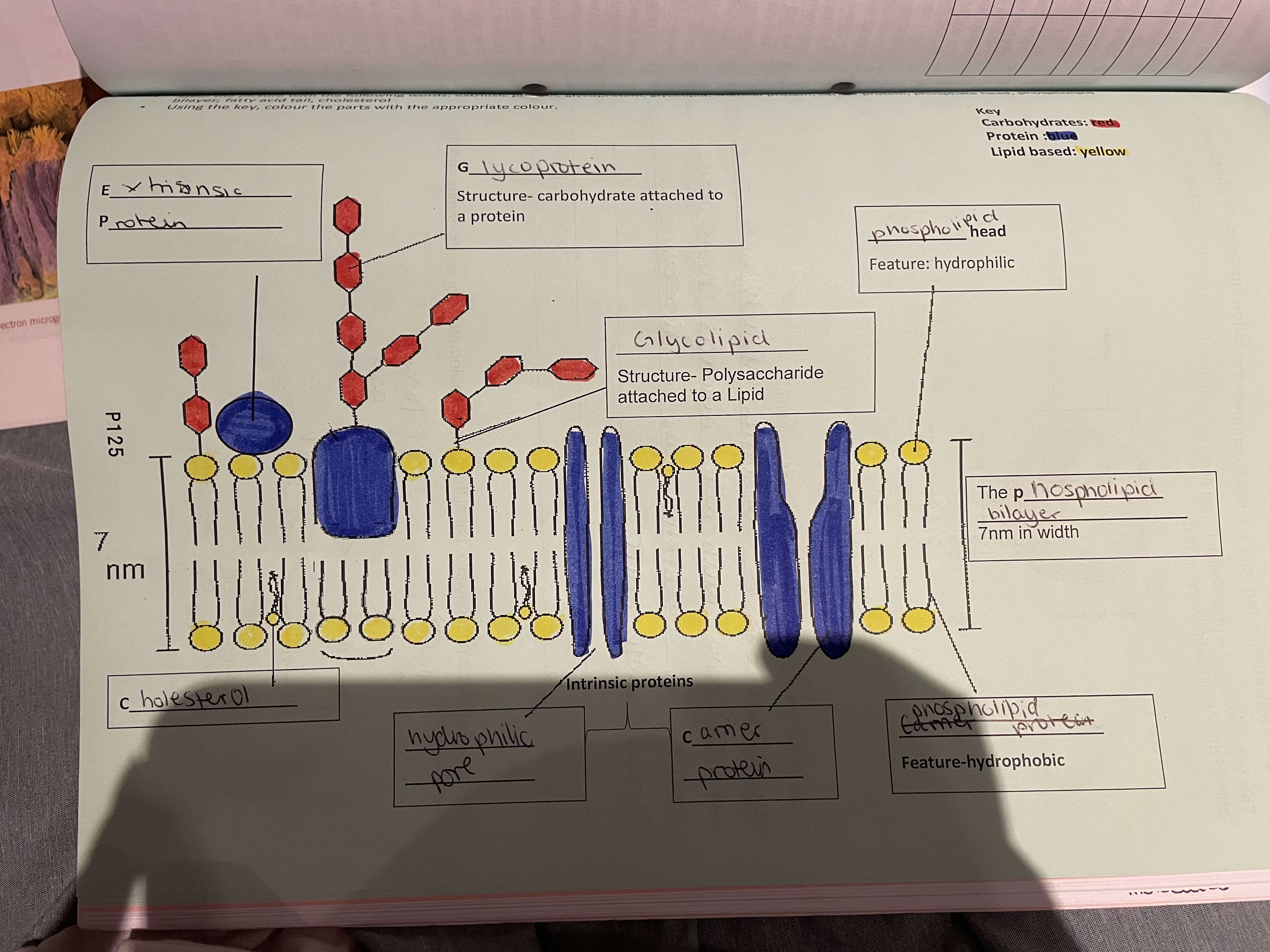
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophilic head (Nonpolar )and hydrophobic tail (polar)
Function of the phospholipid bilayer
Diffusion lipid soluble substances can dissolve in the lipids, nonpolar molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer ,however polar molecules cannot easily pass through unless they are very smaller water through the aquaporens
Plasma membrane-Rolls within the cells
they separate cell components from cytoplasm (compartmentalisation) ,holding the components of metabolic pathway in place
plasma membrane -roles at surface of cells
Separate cell contents from the outside environment ,cell recognition and signalling ,regulating transport of materials into or out of cells
Fluid mosaic model
Phospholipid and proteins move around each other proteins are scattered within the phospholipid and do not form a continuous layer.
Osmosis
The net movement of water from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential through a partially permeable membrane
Water potential of cells
Water potential = solid potential of the cytoplasm+ Pressure potential( water moves to the more negative side)