Astro 7n ALL COMPREHENSIVE exam 2 study guide
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes all copper quizzes from units 3 & 4 Art projects 3 and 4 quizzes And basically everything in between
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
What is the general result of a proton-proton chain?
4 H->He + energy + other products
The corona of the sun is visible when?
solar eclipse
In the convective zone of the Sun:
columns of hot gas rise, cool, and descend
What part of the Sun do we typically see?
photosphere
In nuclear fusion, energy is produced because...
the mass of the reacting chemicals is larger than that of the products
When using different points in the Earth's orbit as a baseline for a parallax experiment it is best to do the observations:
6 months apart
One star is four time farther away than another. The parallax angle of the more distant star is:
four times smaller than that of the nearer star
the parallax angle for the star Hadar is 0.010 arcseconds (0.010"). How far away is Hadar?
100 pc
Put one of your thumbs at arm's length in front of your face. Now focus on something in the background and look through one eye at a time. What do you notice about your thumb?
It appears to move more when it's closer
Star A is 4 times as luminous as Star B. Star A is 2 times as far away as Star B. Which star appears brighter and by how much?
The stars appear the same brightness.
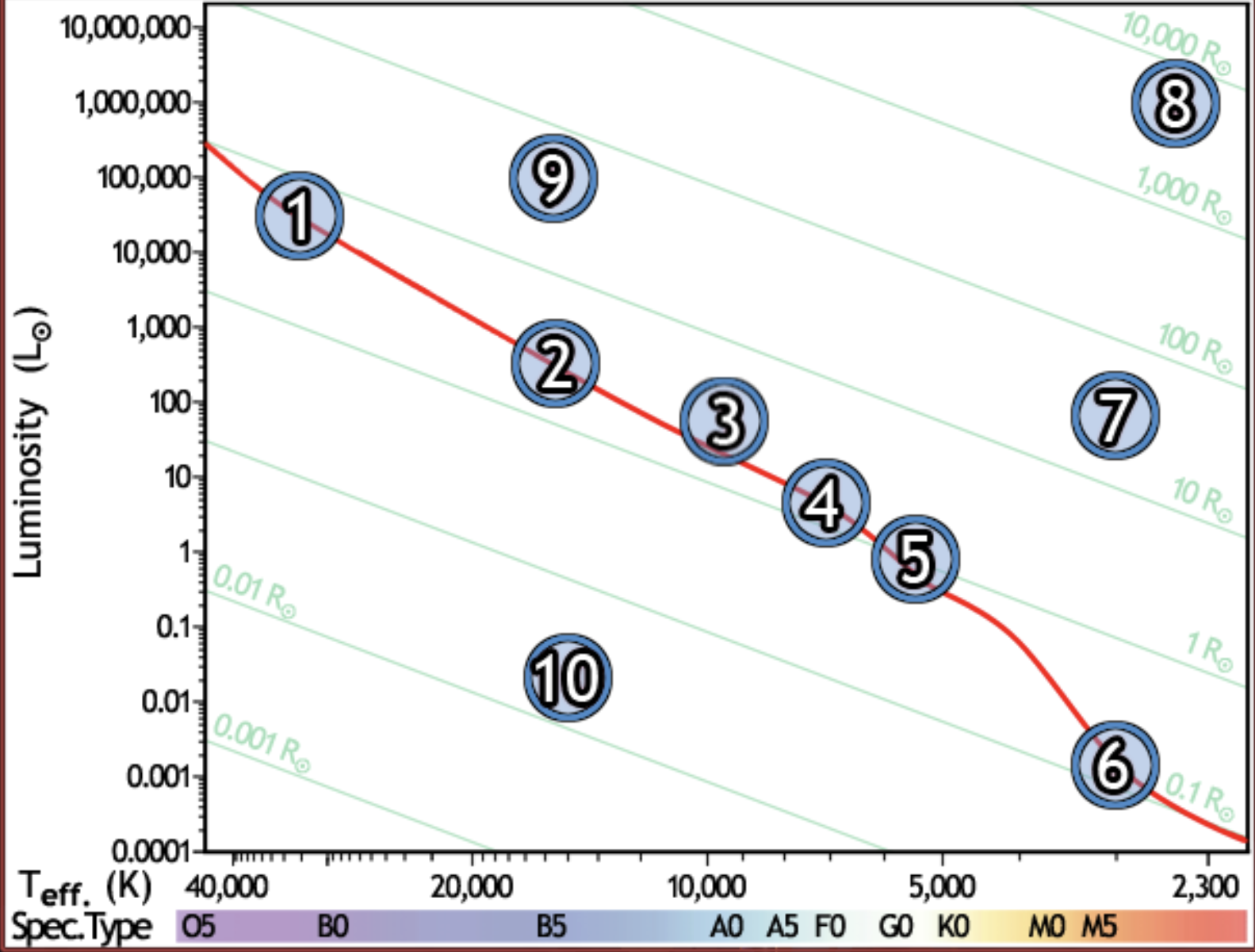
find the hottest star
1
find the star with spectral type F0 on the main sequence
4
find the star with the lowest luminosity
6
Find the main sequence star with the temperature 16,000k
2
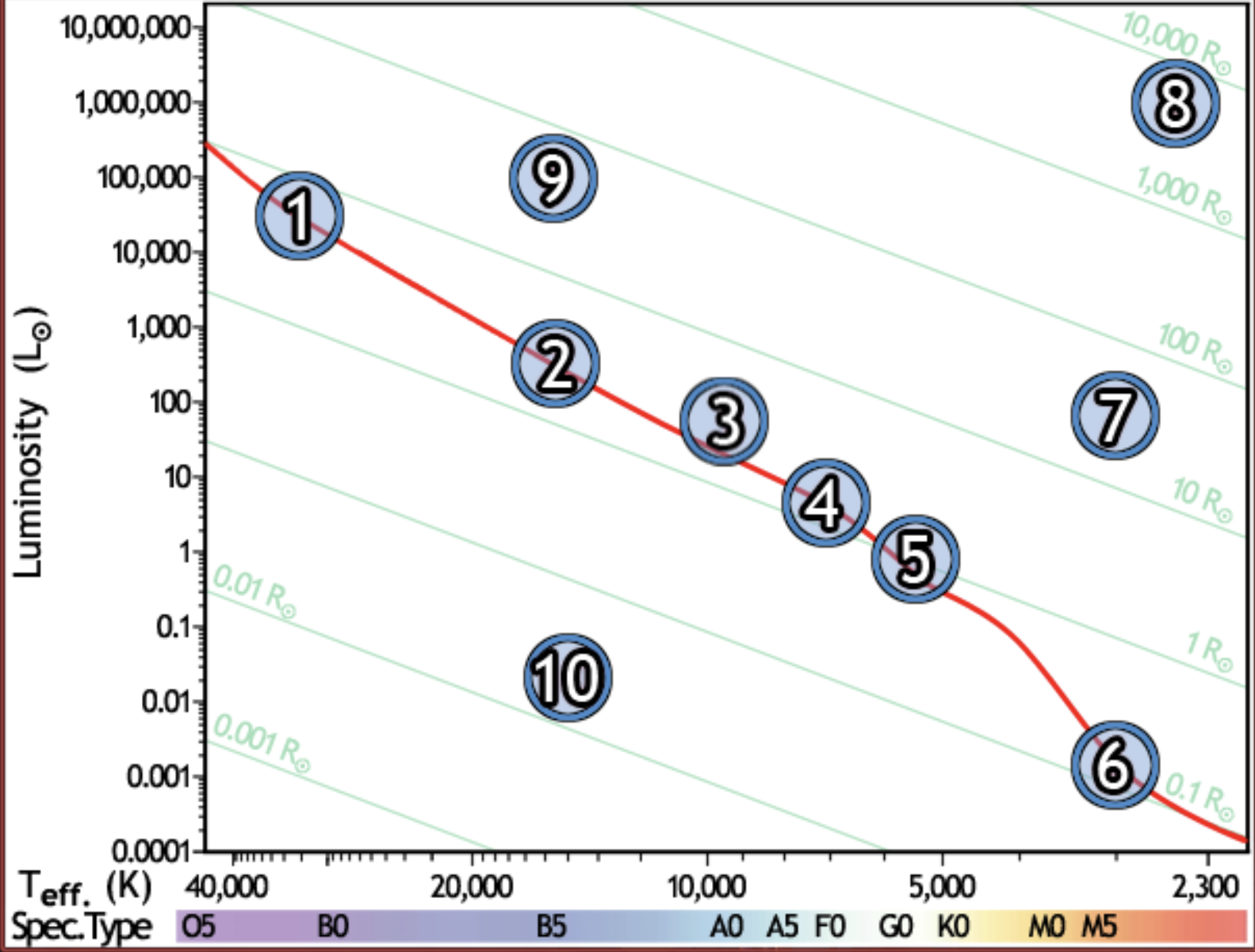
find the star with a temperature of 3000k and a luminosity of 50 solar luminosities
7
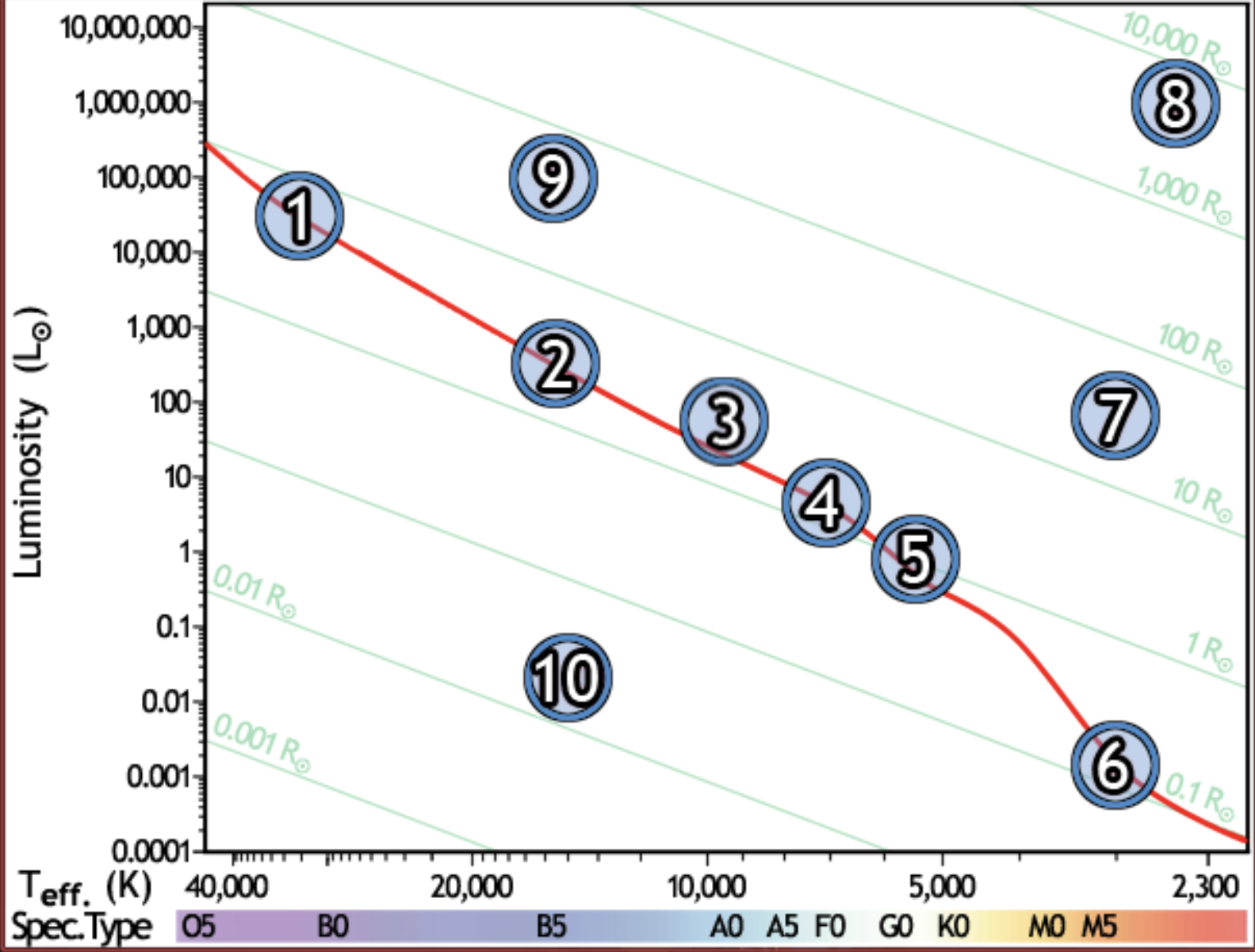
find the star with the lowest mass
6
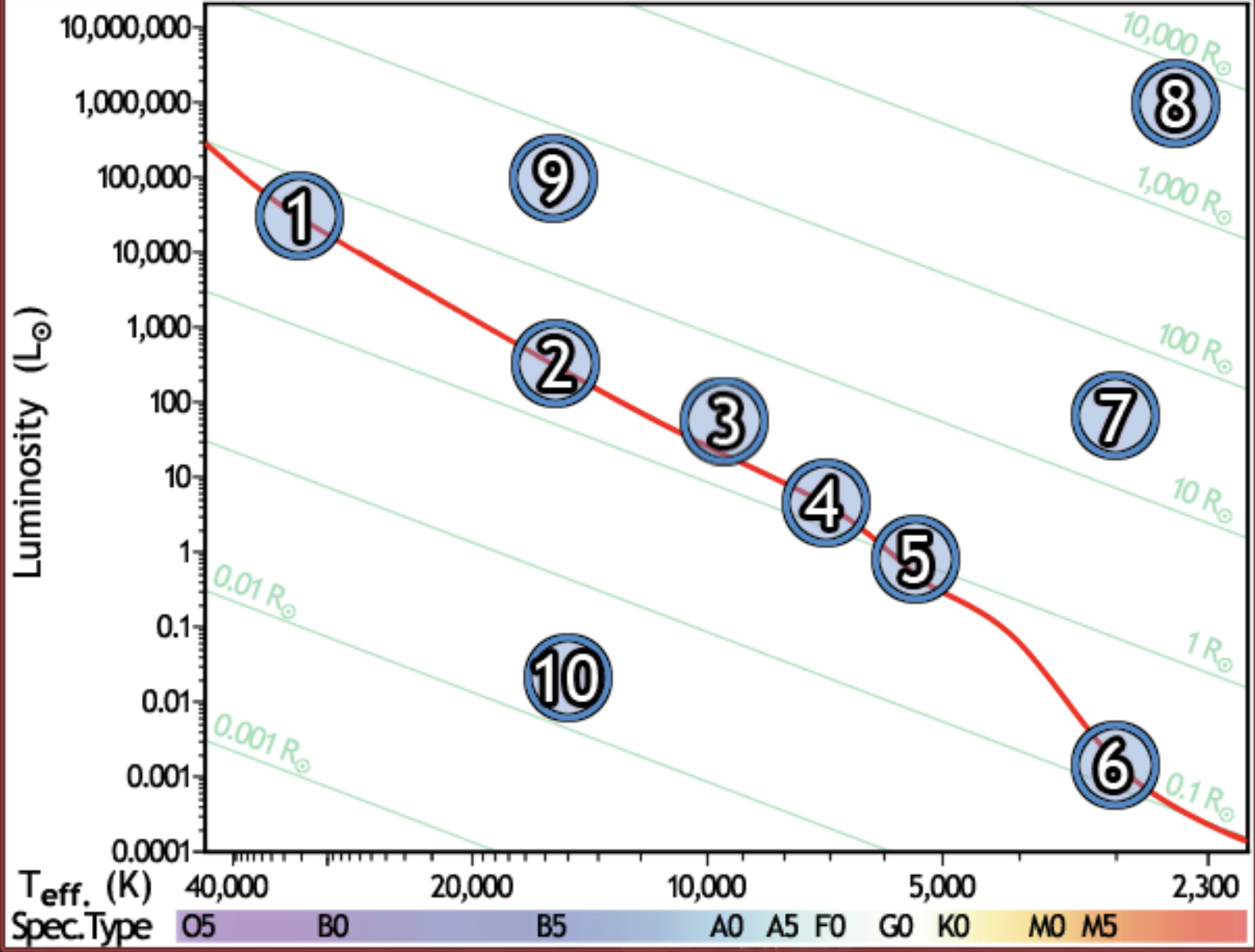
find the red giant star with the largest radius
8
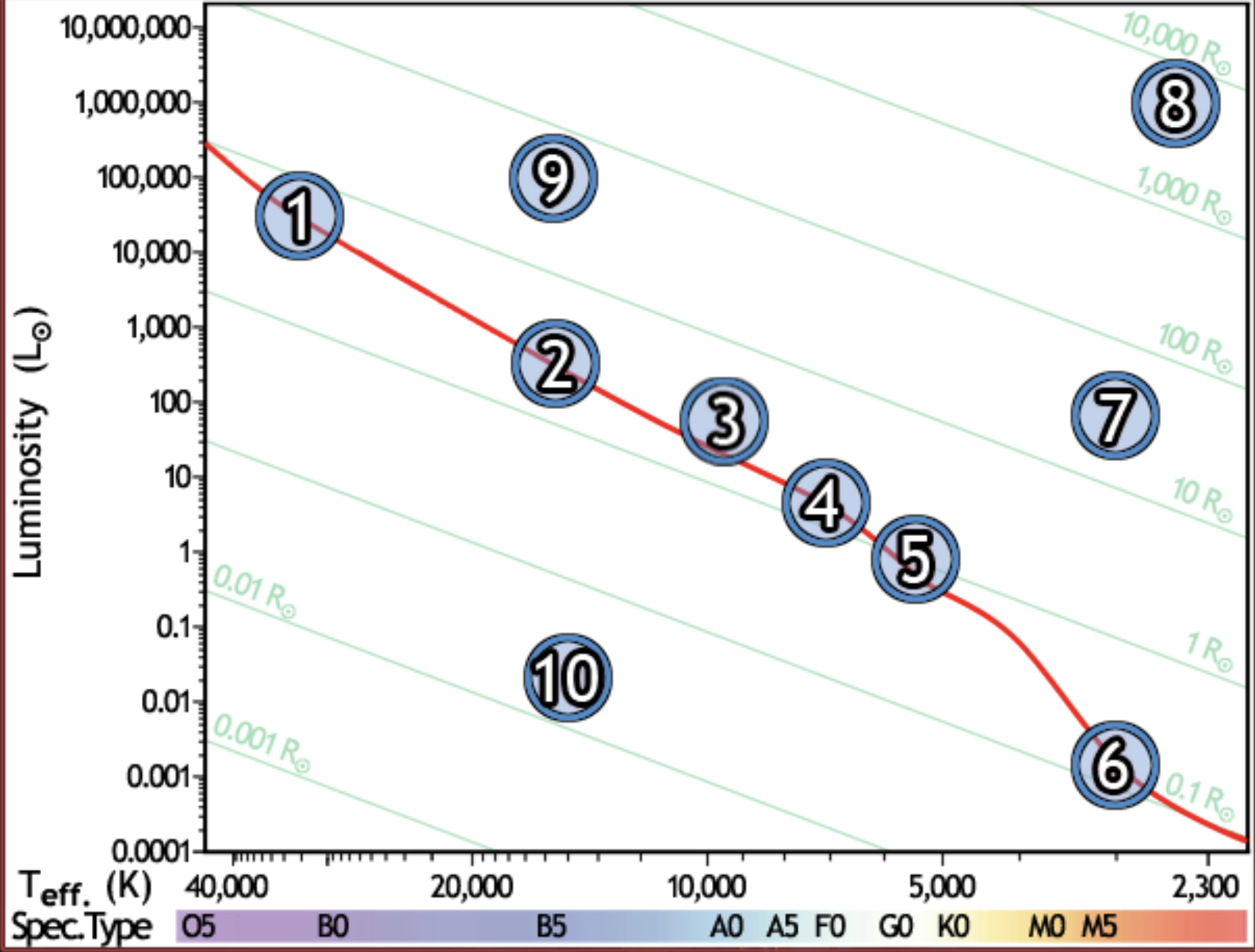
find the bluest star
1
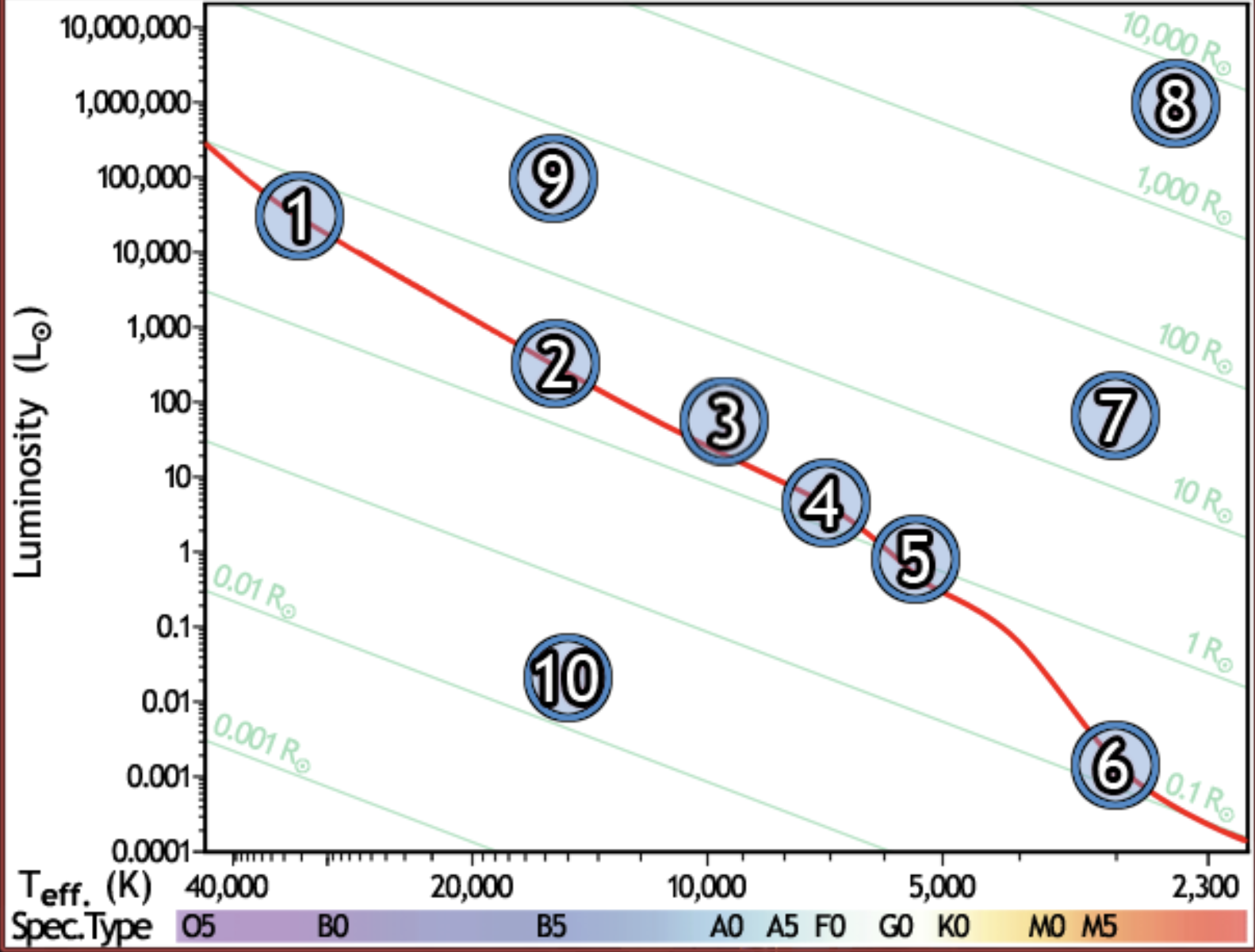
find the star with largest radius
8
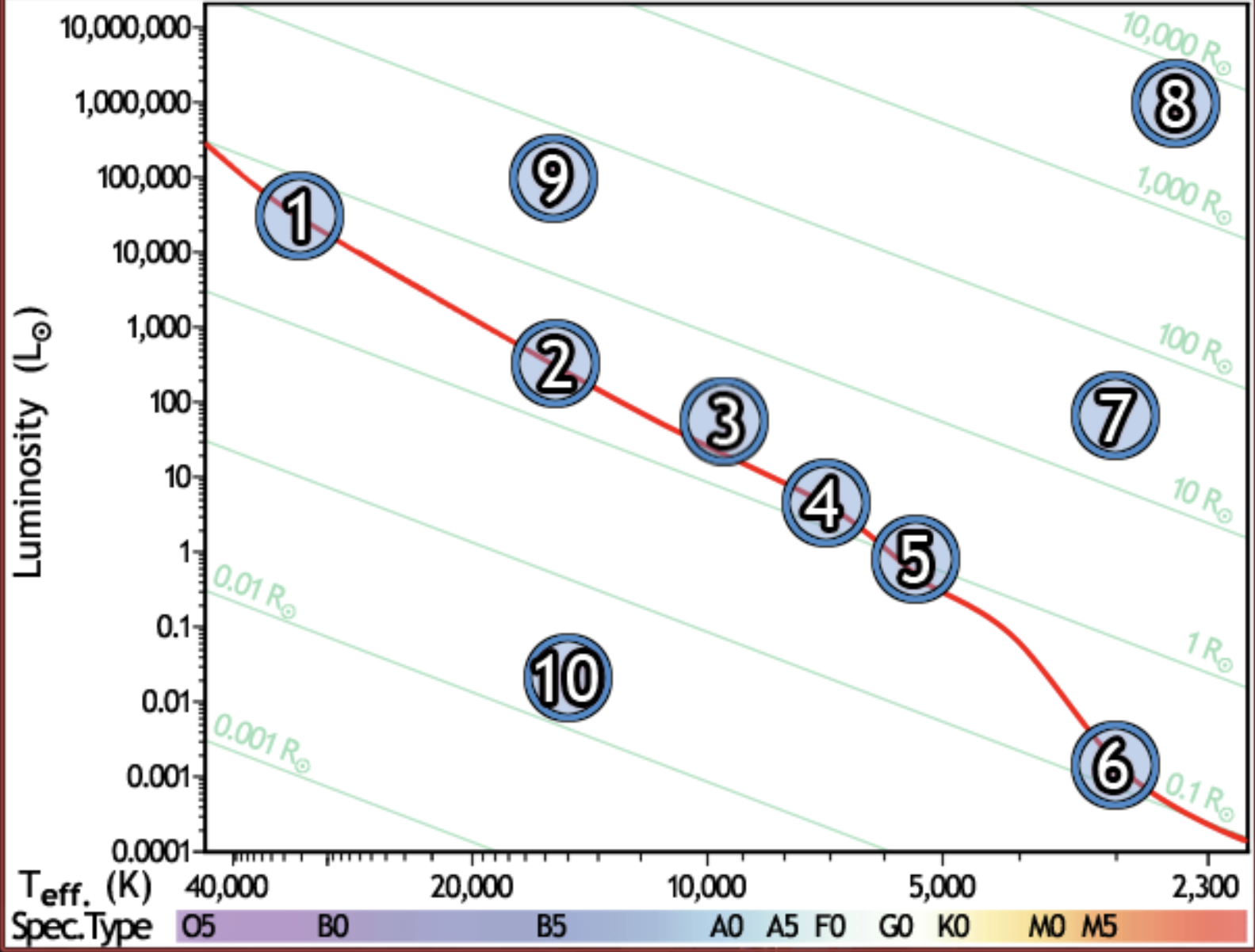
find the star with the longest lifetime
6
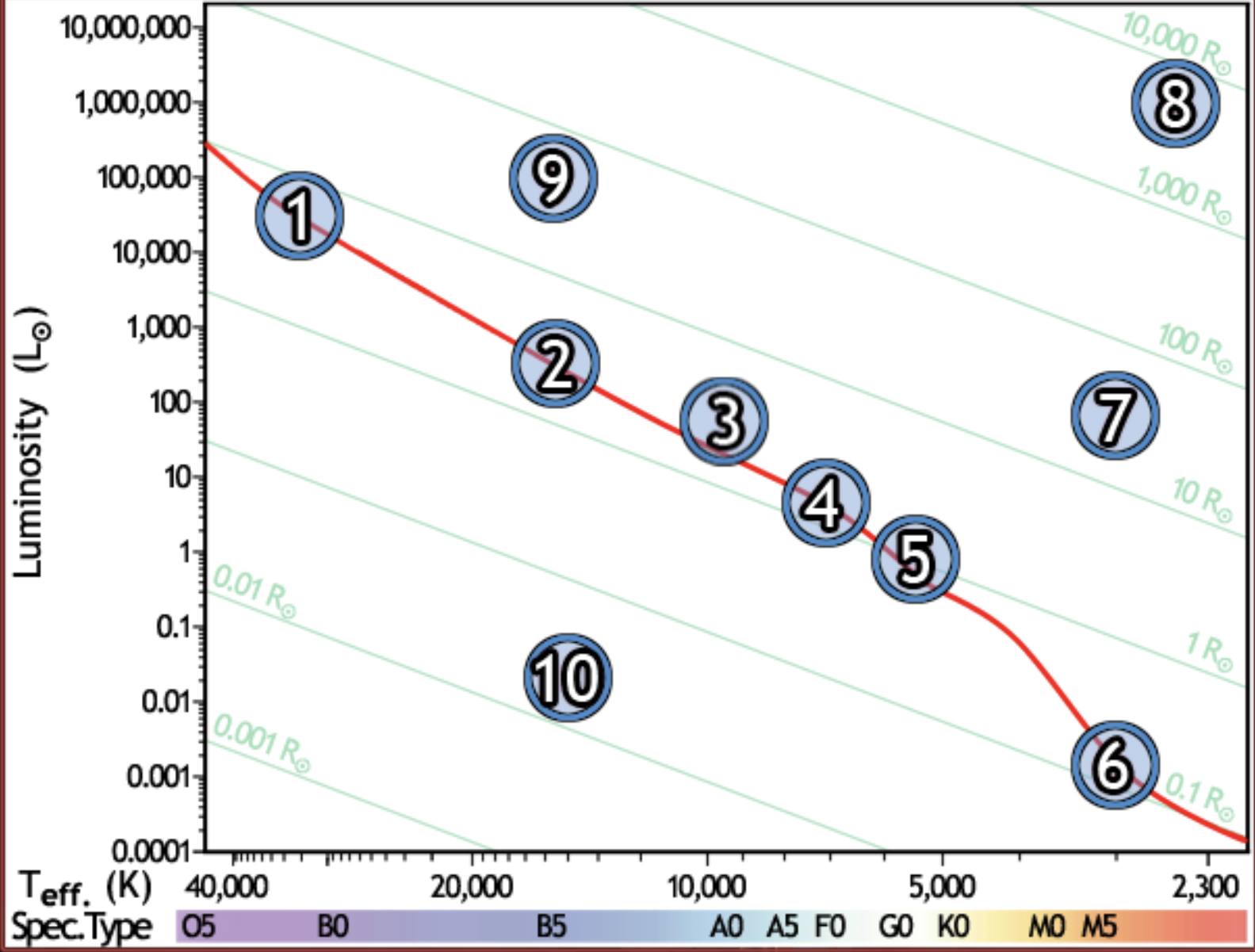
find the sun
5
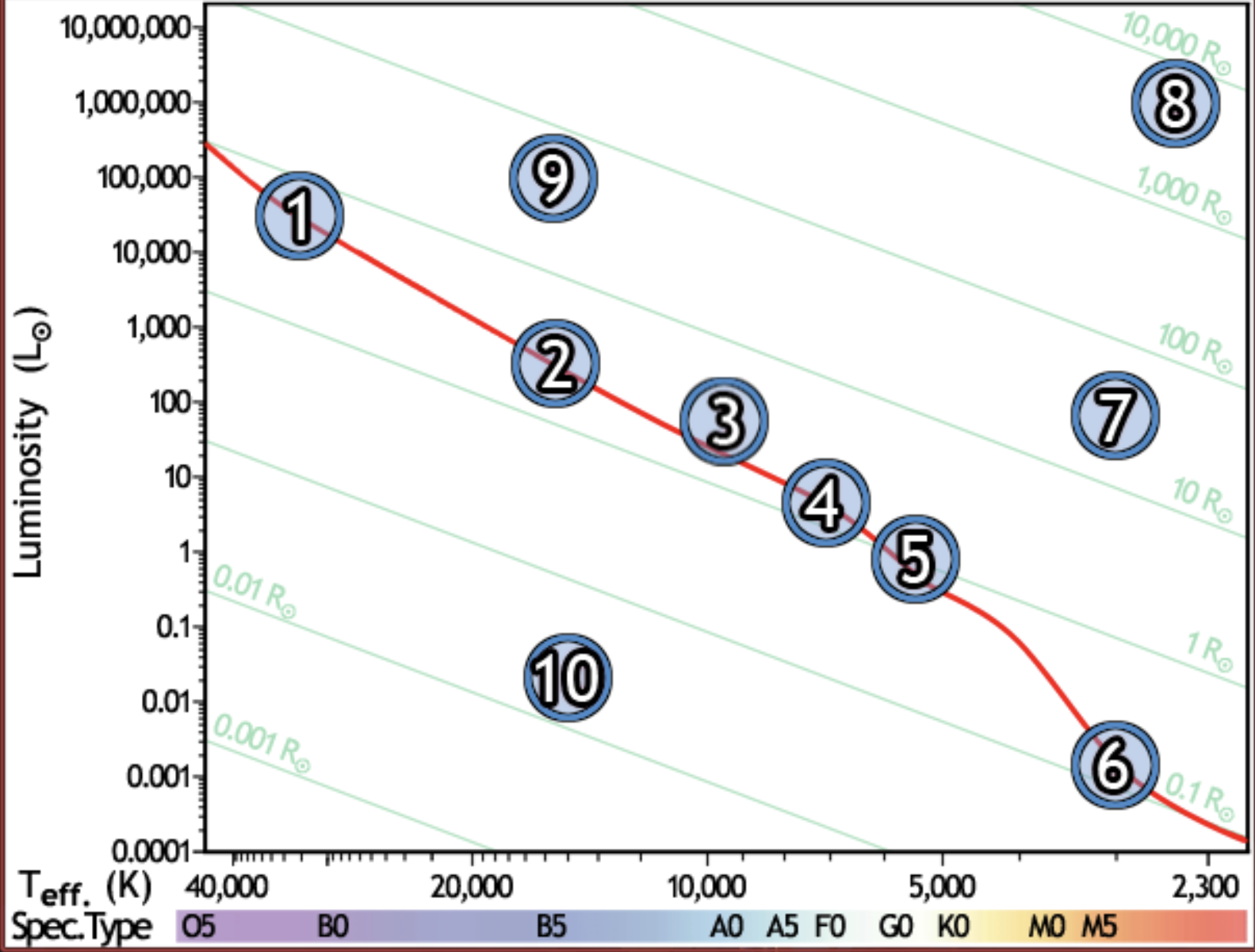
find the star which would appear brightest if all were at the same distance
8
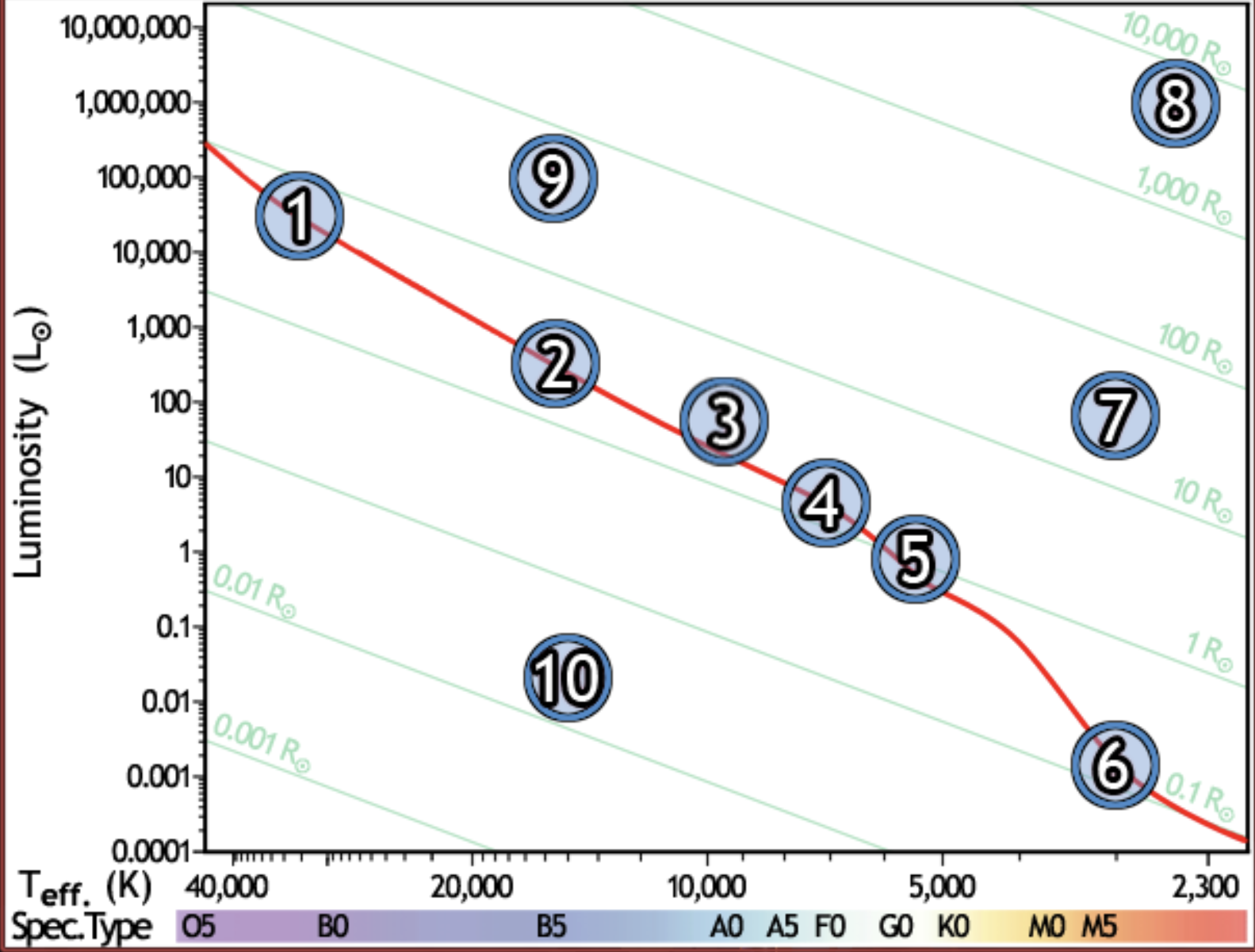
find the white dwarf
10
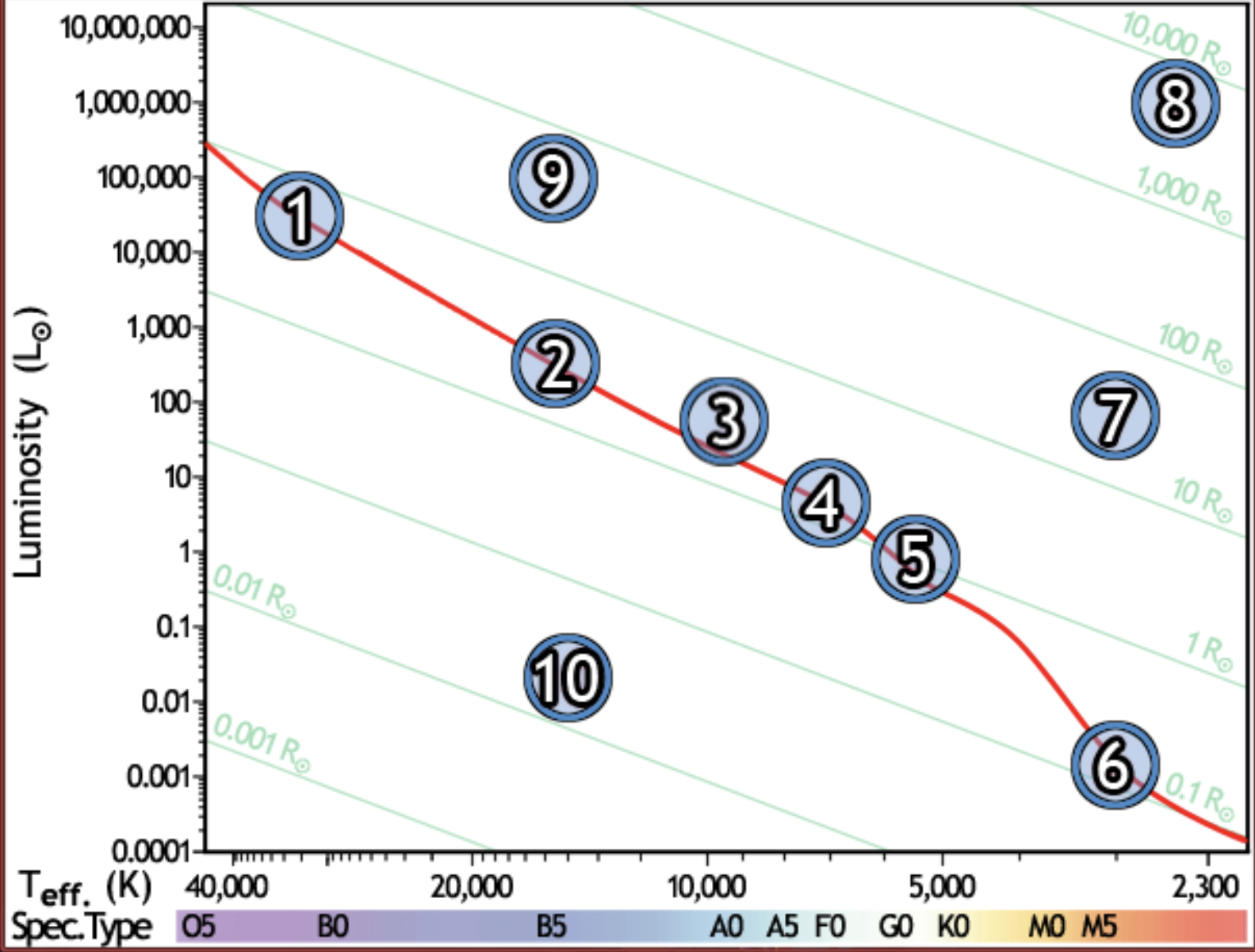
find the B5 type star with a radius of 80 solar radii
9
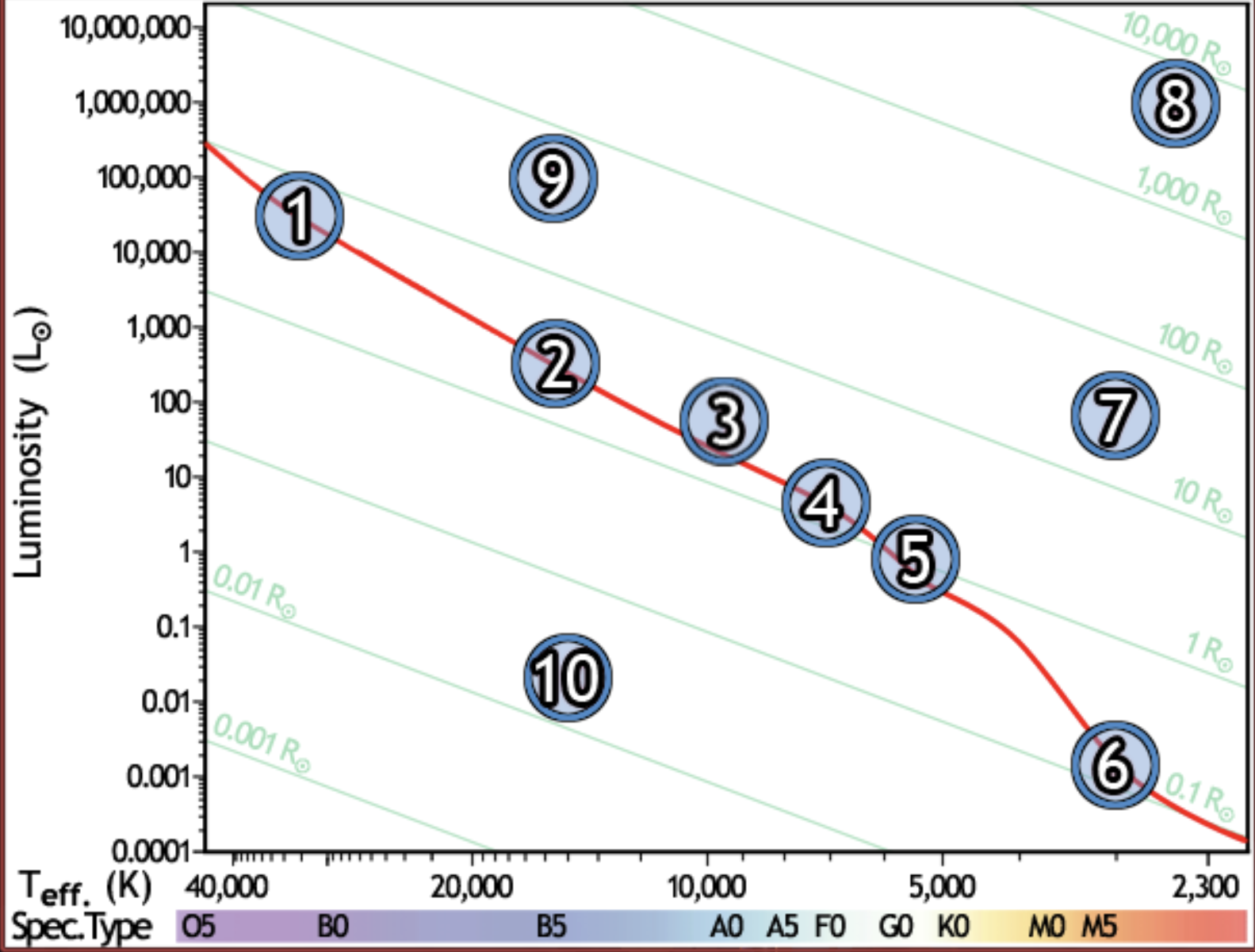
find the main sequence star with 500x the luminosity of the sun
2
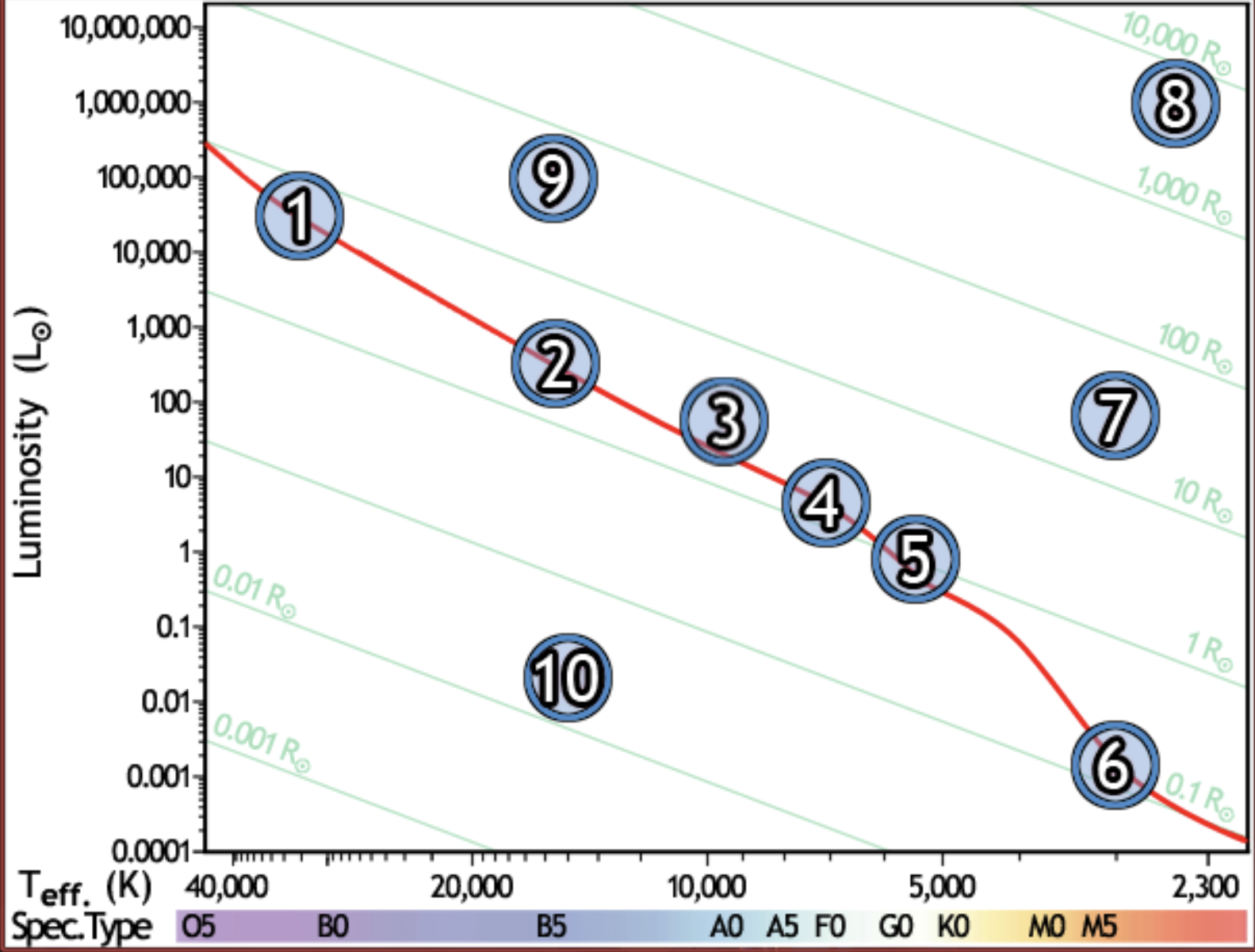
find the closest main sequence star, if all of them have the same apparent brightness
6
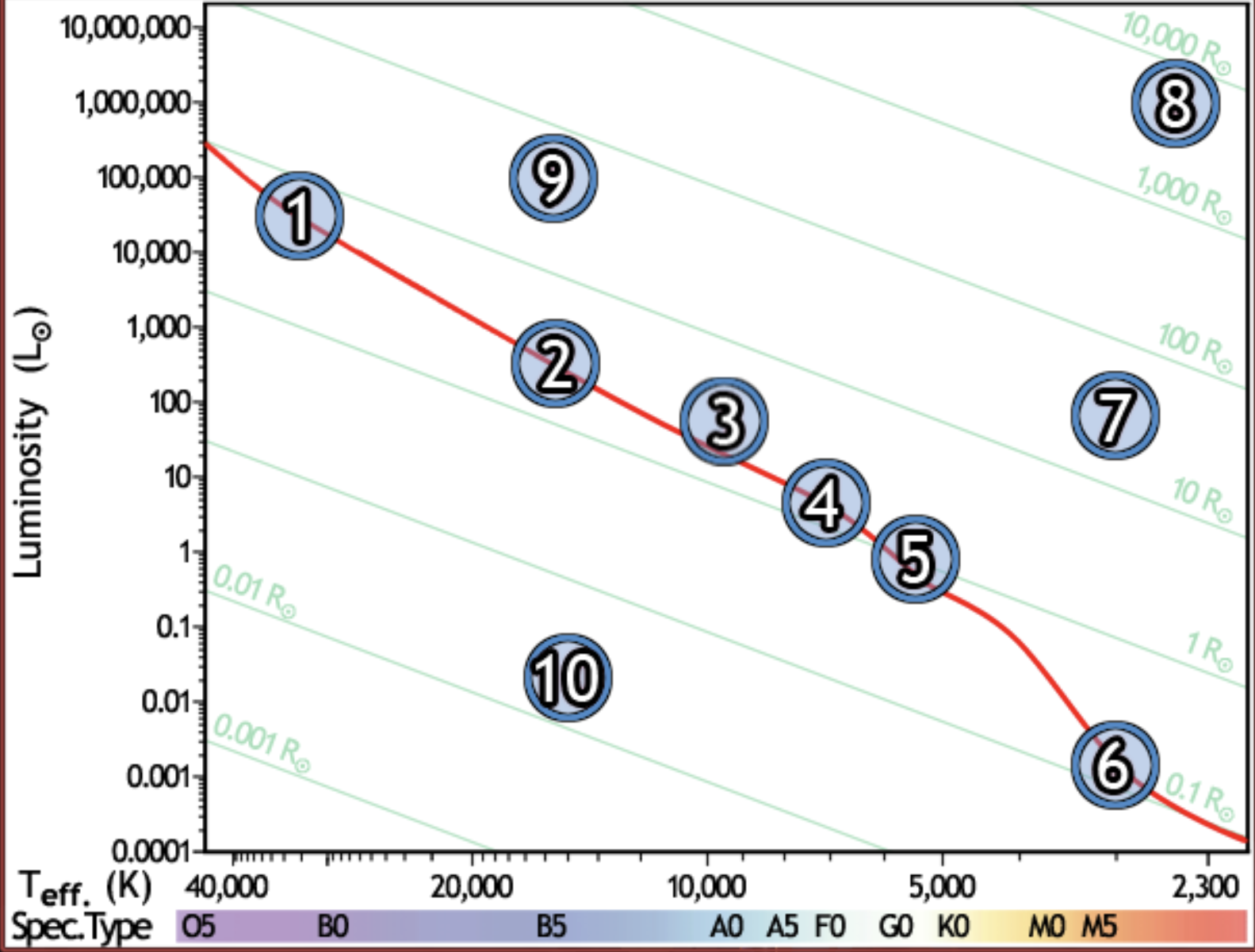
find the main sequence star with a radius of 2 solar radii
4
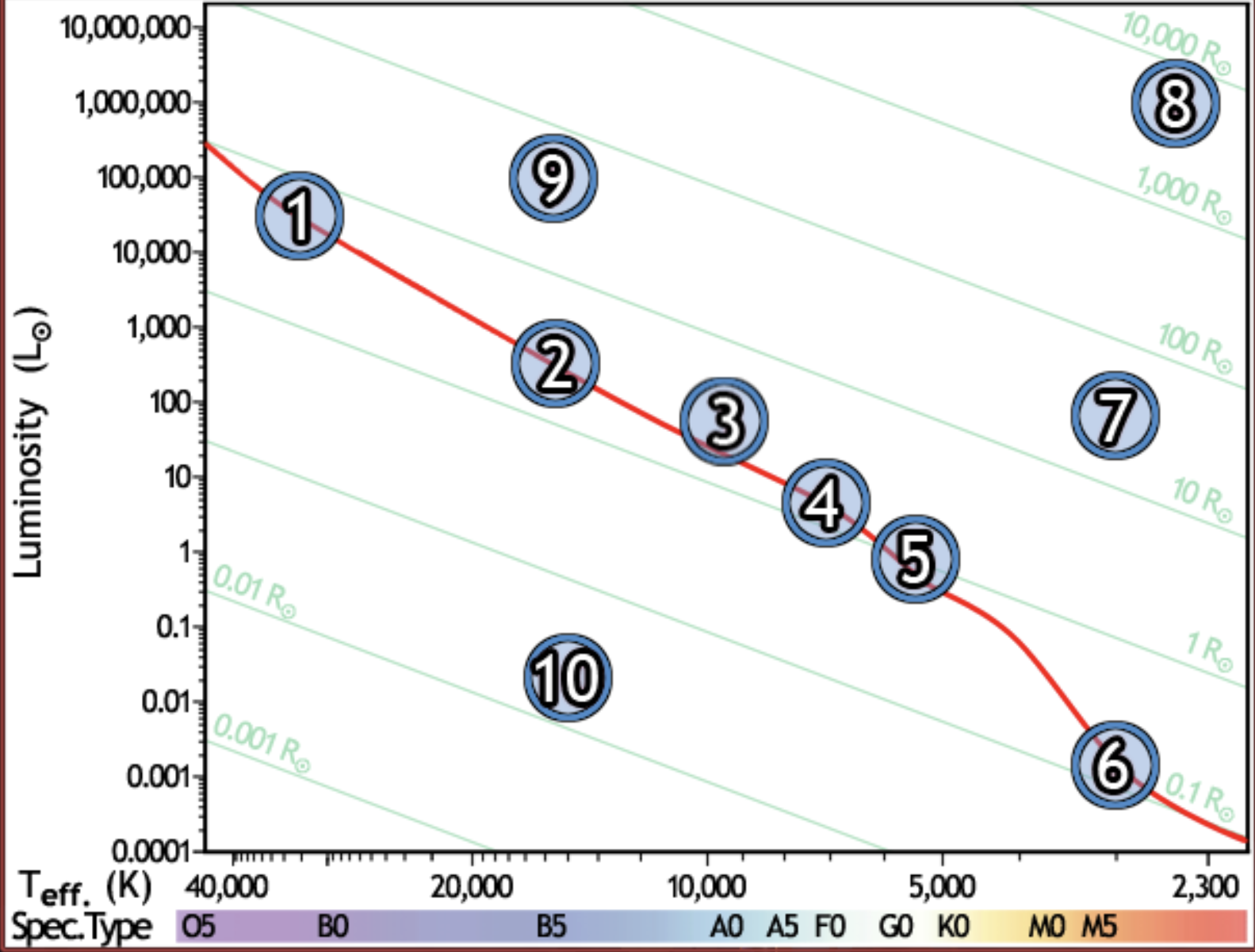
find the star whose temperature is closest to 10,000k
3
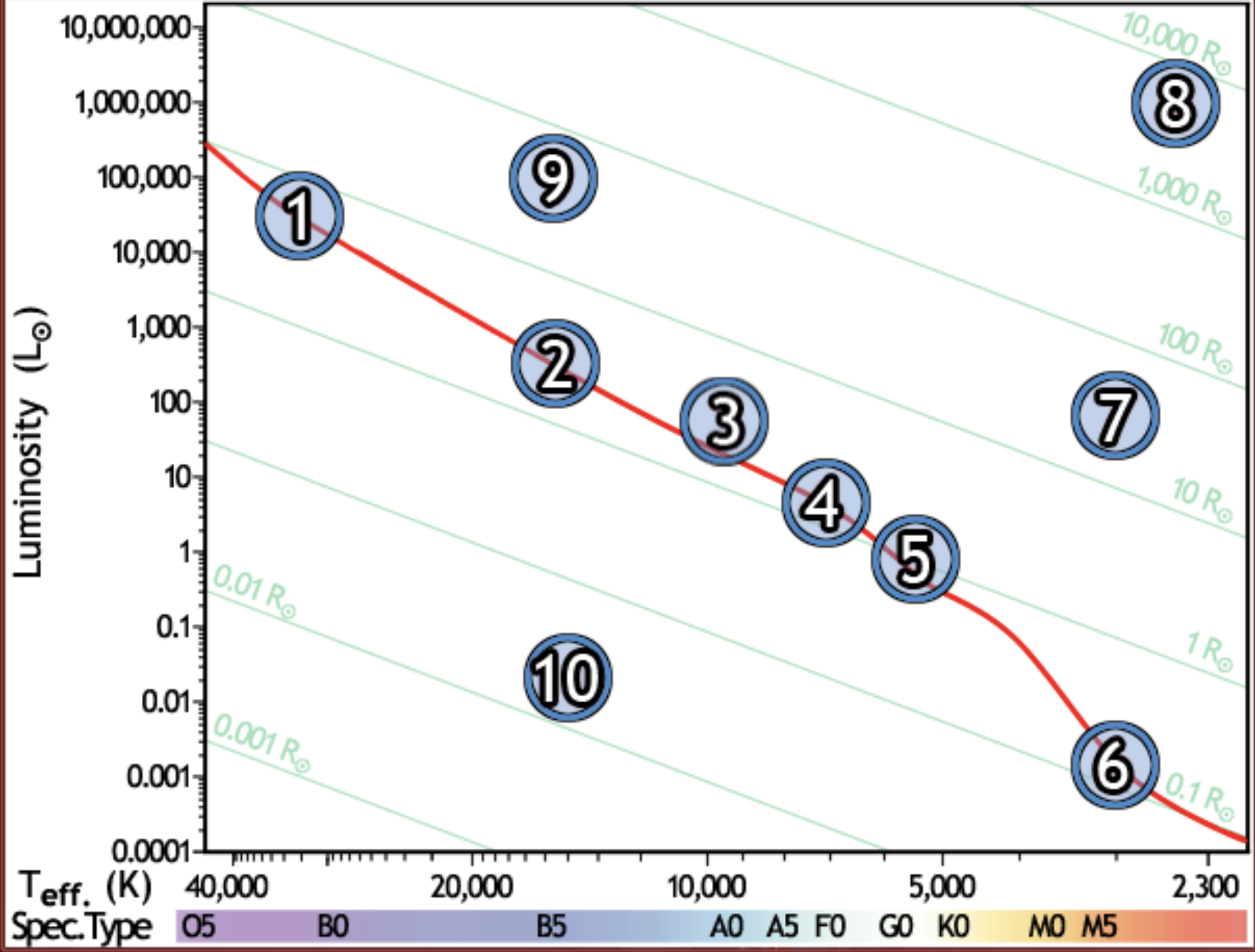
find the coolest star
8
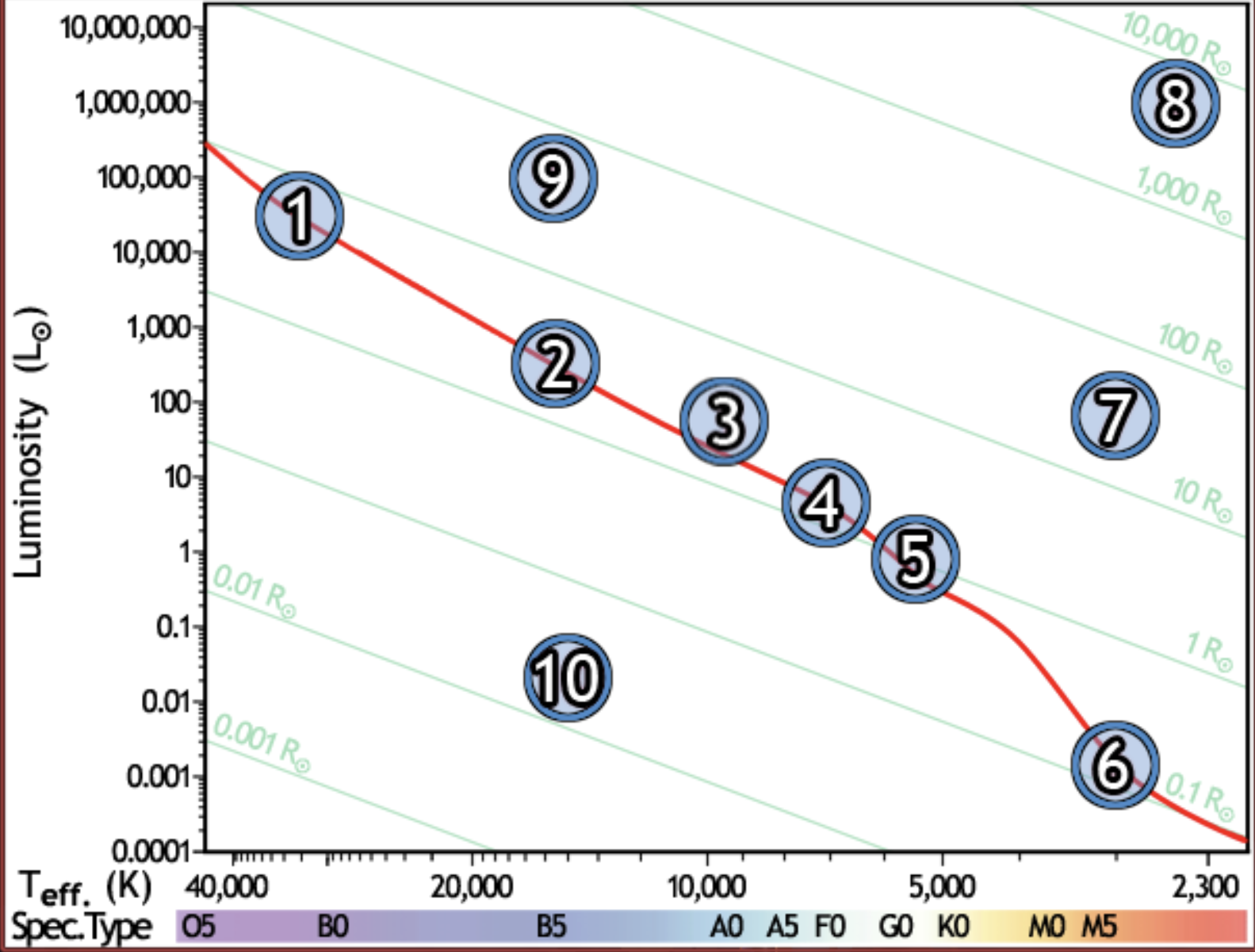
find the main sequence star that is the farthest away, if all appear the same brightness
1
An "onion skin" shell burning structure, with elements up to iron being produced, develops in:
a star much more massive than the sun
What is at the center of a planetary nebula?
the core of the dying star and something that will eventually become a white dwarf
How do solar-sized and smaller stars die? About how large are their remnants?
They become white dwarfs, about the size of the earth
what does not happen when an object approaches a black hole?
it becomes redder because photons lose energy
B: time runs more slowly as it gets closer to the black hole
C: it quickly gets sucked in even from a large distance
D: it gets stretched out because of tidal forces
E: none of the above
it quickly gets sucked in even from a large distance
how can we measure the mass of a black hole?
measure the speed of the orbit of a star in a binary system with the black hole
What is the main requirement for a habitable zone?
liquid water
a star that is twice the mass of our sun would have a habitable zone that includes
includes mars but not earth
a star that is 75 percent the mass of our sun would have a habitable zone that
includes venus only
what factor is not in the Drake equation?
communication lag due to large distances between stars
what does the drake equation estimate
The number of technological civilizations in the Milky Way
what are the differences between open star clusters and globular star clusters?
open clusters are less concentrated, younger, and have fewer stars
which of the following is FALSE?
a supernova is an explosion of a high mass star at the end of its life
b) a nova can be caused by a white dwarf gaining material from a nearby companion star
c) a type la supernova is caused by addition of hydrogen-rich material on a white dwarf
d) a light echo is caused by light from an exploding star that gradually reaches different layers of gas around the star
e) a nova is more luminous than a supernova
a nova is more luminous than a supernova
what kind of a gas cloud can collapse and form stars
the gas cloud must have a mass that exceeds the Jeans mass so that gravity overcomes the internal pressure in the cloud
what is the mass of the black hole at the center of the milky way
4 million solar masses
how do you measure the mass of the supermassive black hole at the center of the milky way
look at the orbits of nearby stars and apply Kepler's third law
about how long does light take to cross the milky way galaxy
about 100,000 years
what does our galaxy look like?
A. It has a large disk with spiral arms, and is relatively flat and thin
B. It has clouds of gas and dust in the spiral arms
C. Older yellow stars are found mostly in the center bulge
D. Old stars and globular clusters are located in a spherical halo above and below the disk.
E. All of the above
all of the above
why do stars in the halo of the galaxy have almost no heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen?
halo stars formed before those elements were made
where do stars form in the galaxy today
in the disk
where are open clusters found
in the disk
in the symbol for the hubble type of a galaxy, SBc, the B denotes
the presence of a bar
what happens to the planets in a galaxy when that galaxy collides with another galaxy
nothing, because the spaces between stellar systems in a galaxy is much larger than their size
white properties of spiral galaxies allow us to sub classify them as Sa, Sb, or Sc
size of buldge and extent of spiral arms
compared to spiral galaxies, elliptical galaxies have:
_ gas, __ colors, _ new star formation
less gas, redder colors, and less new star formation
what is the difference between an E0 and an E7 galaxy
the E7 has an oval shape and the E0 is circular
according to models of galaxy formation, which population of stars formed first
the spheroidal population
what type of galaxy can result from collisions between galaxies
elliptical/irregular
what is a starburst galaxy
a galaxy with a very high rate of star formation
In what part of the spectrum are starburst galaxies brightest?
infrared
what parameters do hubble's law relate to each other
galaxy recession velocity and distance
what technique for measuring distance can you use to discover Hubble's law?
cepheid variables in galaxies and white dwarf supernovae in galaxies
how do you measure the speed of a galaxy relative to you
doppler shifts
what is Hubble's Law?
The faster a galaxy is moving, the farther away it is.
where is the center of the universe
There is no center to the Universe. Expansion is happening everywhere.
How have astronomers interpreted the unexpectedly fast rotation of galaxies?
there must be a lot of dark matter whose gravity can be felt but not seen
which of the following is not true about dark matter
dark matter is the dominant source of gravity in the universe.
dark matter and dark energy are two aspects of the same phenomenon.
evidence for dark matter has been building for many decades
all the above
dark matter and dark energy are two aspects of the same phenomenon
why do we think there is a lot of dark matter in clusters of galaxies?
A. individual galaxies are moving so fast that they could not be held together by the gravity of visible matter
B. we’ve detected some of it with dark matter telescopes
C.and gravitational lensing lets us measure mass even when we can't see it
D. squidward
A and C
how do we know that the universe is speeding up
we look at objects from different times in the past to see how expansion changes with time
how could the universe be accelerating, despite the gravitational pull of all the matter in it
there could be a new force or property of space that affects the universe on its largest scales
what fundamental particles make up a Hydrogen-1 atom
one proton, one electron
which force is responsible for holding the nucleus together via gluons
strong
what three fundamental particles are you made of
up quarks, down quarks, and electrons
how many types of fundamental particles exist
300
how many up quarks are there in helium-3
5
which has the events in the right order from early to late
star formation
quark soup
nucleosynthesis
protons form,
recombination
quark soup, protons form, nucleosynthesis, recombination, star formation
what happens because of recombination
the cosmic microwave background is produced
what forms in nucleosynthesis
most of the Helium-4 in the Universe
what is a quasar
a very luminous source due to a black hole at the center of a galaxy that is quickly growing
how did conditions differ from the present era when the universe was young
the universe was hotter, more dense, and smoother
What occurs when electromagnetic activity in outer layers cause cooling in regions?
sunspots
What percent of solar system mass is the sun?
99.9%
The region of the sun where most visible light is emitted. 6,000 K
photosphere
outside the photosphere with cooler and thinner gas
chromosphere
grainy “bubbly” texture of the sun
granules
a large region below the phtosphere
convective zone
powerful burst of energy on the sun influenced by local magnetic activity
solar flare or prominence
where in the sun does energy travel outward through absorption and re-emission of photons
radioactive zone
place in the sun with high density and temperature; where nuclear reactions occur
and gamma rays are produced
core
first step of pp chain
a proton combines w another to make hydrogen 2, 1 proton is now a neutron
second step of pp chain
_h + _h = _h?
hydrogen two combines with hydrogen to make hydrogen 3
final step of pp chain
_he + _he = _he?
3 he combines with 3 he to make 4 he
absolute power output to a source
luminosity
apparent output observed by distance
brightness
formula for brightness=
luminosity / 4pi(distance)²
formula for distance
1/parallax angle
formula for distance in parsecs
1 / parsec
what does it mean to be a main sequence star?
where stars can covert hydrogen to helium in their cores
what is the sequence of events for a sun-like star?
arrange these in the right order:
white dwarf
protostar
planetary nebula
red giant
sun-like star
protostar, sun-like star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf
What do low mass stars become?
Planetary nebulas and white dwarves
what do medium mass stars become?
super novas and neuron stars