Edexcel A Level Geography - Water Cycle Terms Only.
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what is the hydrological cycle known as
a system comprised of
stores - the holding of water
flows - measure the rate of flow between stores
processes - physical factors that drive the water
what drives the hydrological cycle
Solar energy and gravitational potential energy
what is the global water budget
the annual balance of water flows and the size of the water stores
what is residence time
the average time a water molecule will spend in a reservoir or store
how much percent of the earths water is stored in the ocean
97%
what is a drainage basin
an area of land drained by a river and its tributaries
what is a watershed boundary
an area of land that separates water flowing to different rivers
what is the ITCZ
inter tropical convergence zone, it is a low pressure belt encircling the Earth, near the equator, it moves and impacts precipitation
the 3 cells around the earth giving different temperatures at different latitudes
polar - 60-90 degree
ferrel - 30-60 degree
hadley - 0-30 degree
what is convectional rainfall
Due to heating by the sun, warm air rises, condenses at higher altitudes and falls as rain
what is orographic rainfall
caused by uplifting and cooling of moist air over mountains
what is frontal rainfall
when a warm air mass meets a cold air mass, forcing the warmer air to rise and cool over the denser air
The UK's rainfall
the tees- exe line separates the rainfall of the UK, with orographic rainfall mainly happens in the west, and convectional in the south, but over a year, frontal rainfall brings the most to the whole UK
how does deforestation affect the drainage basin
reduces evapotranspiration, less ground water to aid in dry days, rainwater runs quickly, flooding
3 human factors affecting a drainage basin
deforestation, urbanisation reservoirs
how does urbanisation affect a drainage basin
buildings have far more run off than nature at 55% to 10%, and far less infiltration and deep infiltration
how does reservoirs affect a drainage basin
they are man made, that interrupt the flow of water, reduce river flow, e.g Kenya tana river flood plain forest is dying lack of floods upstream
what physical factors affect a drainage basin
vegetation cover
temperature
geology
soil type
what is the only input to a drainage basin
precipitation
what is the water budget
show the annual balance between inputs and outputs
What does the water budget graph show
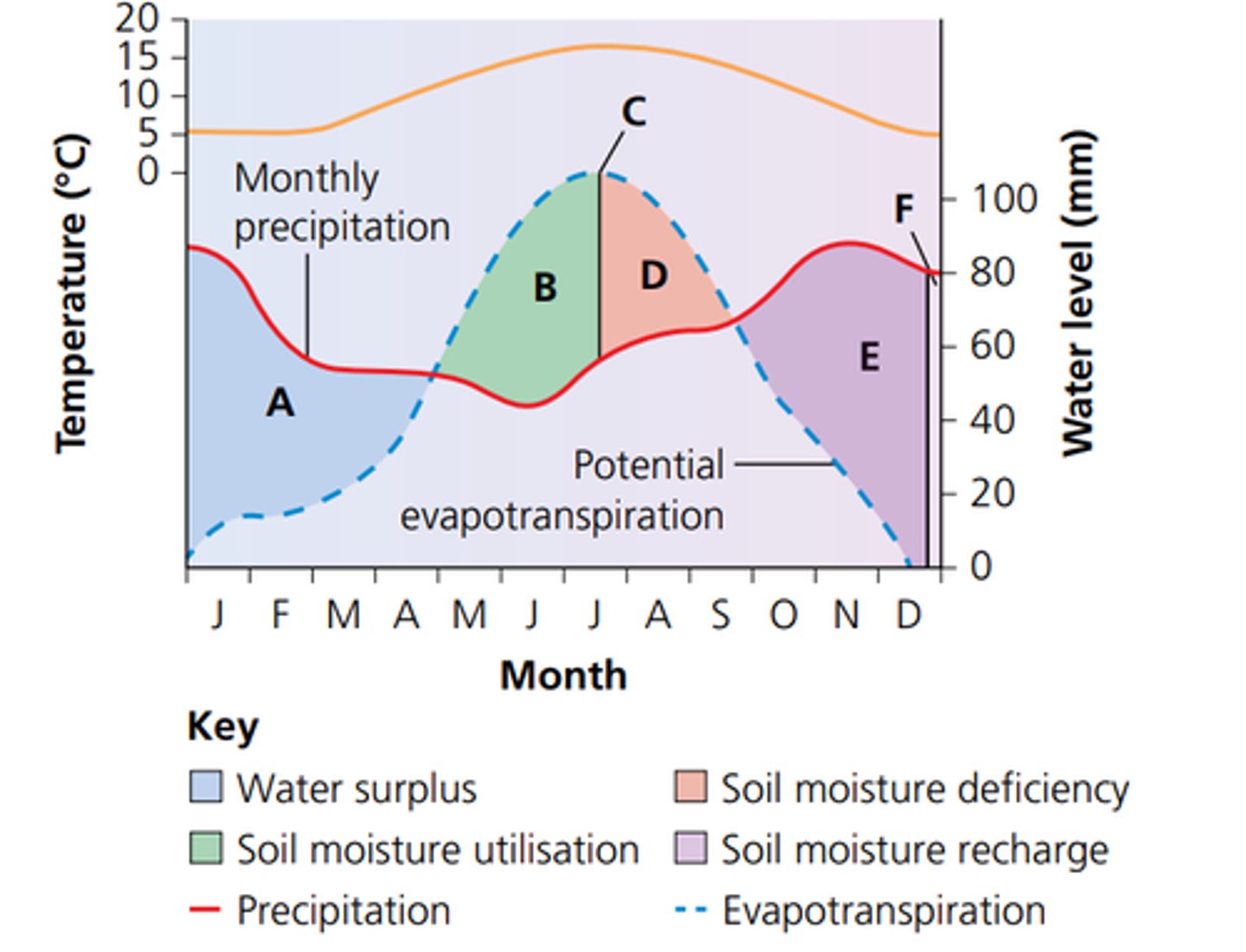
what is precipitation
rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to the ground.
what is interception
A temporary storage whereby water is captured by plants and buildings before reaching the ground.
what is surface storage
water in lakes, ponds, puddles
what is ground water storage
water held within permeable rocks
what is percolation
When water moves vertically down through soil and rock
what is evapotranspiration
the combined effect of evaporation and transpiration
what is river discharge
The volume of water passing a measuring point in a given time.
what is a river regime
the difference in the discharge of the river throughout the year
what is a simple regime
One where a river has a period of seasonally high discharge (glacier melt, monsoons), followed by low discharge.
what is a complex regime
One that is affected by many variables because they are larger and cross several relief and climatic zones. they are affected by human factors
what is a flashy river
a river with a short lag time, fast flow, impermeable surface
what is a flat river
a river with a long lag time
what is a storm hydrograph
a graph that shows changes in discharge of a river over a short period of time
4 types of drought
meteorological - precipitation is below average
agricultural - lack of growth due to no rain
hydrological - lack of water supplies in streams
socioeconomic - the impact on the population
what is a anti cyclone
areas that experience intense high pressure and sinking air, pressure of 1008mb
What does ENSO stand for
El Nino Southern Oscillation
What is the ENSO cycle, where does it happen between
Movement of warm water mass in the equatorial Pacific Ocean
Australia to south America
what is the 'normal condition' in the pacific ocean
Warm water by Australia and east Aisa, causing warm air to rise, lots of rain
Cold water by South America, air sinks, high pressure and no rain
What is La Nina
the process of intensifying normal conditions
What is El Nino
Weather patterns swap, heavy rainfall in S America, Droughts in Australia
What does over abstraction mean
the amount of water used has been too much and not enough has been replenished, leads to water scarcity.
what is a aquifer
body of permeable rock that can hold or transmit ground water.
what is a confined aquifer
covered by permeable rock deep down, hard for water to get to
what is a unconfined aquifer
a groundwater layer with no impermeable barrier above it.
impact of over abstraction
water reduce in layers
water quality falls
water table sinks
how can humans increase drought risk
deforestation
over-abstraction
impact of deforestation on drought risk
deforestation = no evaporation = less rainfall = decrease in discharge
what does ecosystem functioning mean
the biological, physical and chemical processes that take place within an ecosystem.
impact of drought on forest
younger trees die, canopy cover reduces, exposing dry surface litter fire prone.
what does surface water flooding mean
flooding that occurs when intense rainfall has not enough time to infiltrate the soil , flows overland
what does groundwater flooding mean
prolonged heavy rain, cause land to become saturated, as a result floods happen
what does flash flooding mean
high level of rain, short lag time flood
physical causes of flooding
amount and type of rainfall - influence intensity of rain
impermeable material
relief ( land angle )
human causes of flooding
urbanisation
deforestation
land use
infastructure
what does water scarcity mean
lack of water supply
what is water stress
demand for water exceeds supply
how much percent of the worlds population consume how much of the worlds water.
12% of population = 85% of water
what is privatisation
the transfer of a business, industry, or service from public to private control.
impact of water privatisation
more expensive. e.g Bolivia - 2000, water in rural area cost 20% of average income.
causes of water insecurity
increasing population and urbanisation - Africa and Asia urban population by 2030 2x.
industrialisation - OECD report - global water demand for manufacturing will increase by 400% between 2000-2050
agriculture - some developing countries, 90% of water used on farming
what are the 3 hard engineering strategies used to control water supplies.
- mega dams
- transfer projects
- desalination plants
3 soft engineering strategies to manage water
rain water harvesting
smart irrigation
recycling gray ( agriculture use only ) water
what is integrated water resoucre management (IWRM)
managing water in a fair access