Human Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
anatomy
the study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another
physiology
the study of the function of a body part
chemical, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
List structural levels from simplest to most complex
proton
in nucleus, positive charge
electron
in orbitals, negative charge
neutron
in nucleus, neutral charge
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
four most abundant elements in our bodies
contains carbon
what is the characteristic of all organic molecules?
carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acid
what are the most important organic molecules?
homeostasis
maintaining a stable internal environment
negative feedback
acts the opposite way to stimuli
EX/ blood pressure, temperature, heart rate
positive feedback
exaggerates stimuli
EX/ child labor, blood clotting
receptor
cells that detect stimuli
afferent pathway
first pathway information is sent along
control center
determines the set point, which is the level/range at which the variable is to be maintained (CNS)
efferent pathway
second pathway information is sent along
effector organ
organs carrying out response to stimuli (muscles and glands)
urinary system
Regulates water levels in the body
endocrine system
Thyroid and adrenal glands
immune system
returns leaked fluid back to blood
cardiovascular system
Transports gases, wastes, and nutrients
nervous system
Fast and immediate communication and control
skeletal system
blood cell production
muscular system
facial expression and heat production
digestive system
Breaks large molecules down so they can be absorbed into the blood
respiratory system
Brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide
energy for cell to do work
What is the function of ATP?
(made of phosphate ribose, and adenine)
transcription
transfer of information, a segment of DNA called a gene is copied as RNA
translation
the language of nucleic acids is translated into the language of proteins
mRNA
carries protein information from the DNA in a cell's nucleus to the cell's cytoplasm
tRNA
serves as a link (or adaptor) between the mRNA molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein
rRNA
serves as a location for protein synthesis. rRNA is the location in which mRNA and tRNA are able to come together to synthesize proteins
(interphase) G1, S, G2 (mitotic phase) mitosis, cytokinesis
Major phases of the cell cycle
telophase
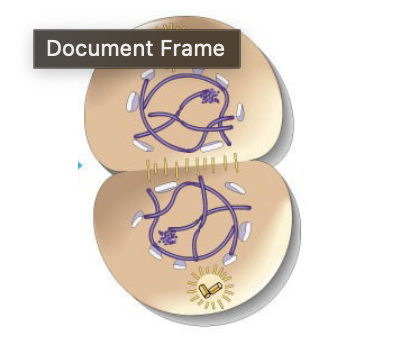
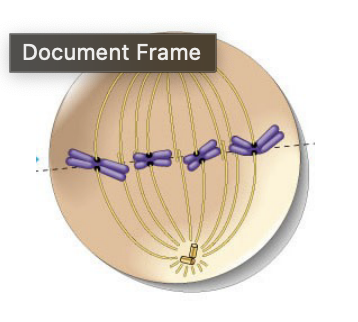
metaphase
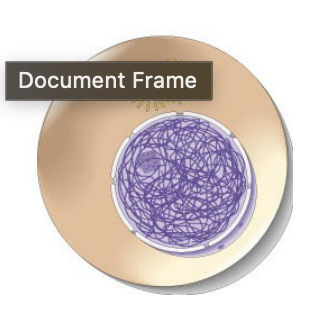
interphase
early prophase
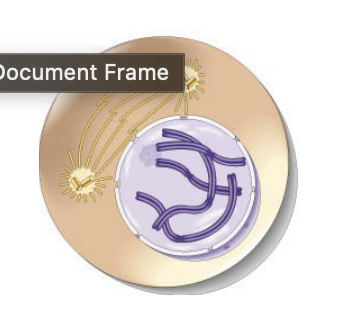
anaphase
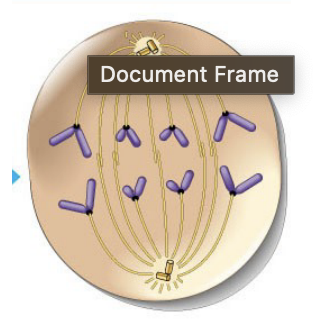
late prophase/prometaphase
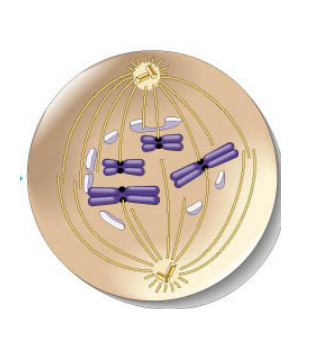
plasma membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
three main components of cells
nucleus
stores genetic information (DNA)
ribosome
makes protein
mitochondria
makes energy (ATP)
golgi
sorts, modifies, and ships proteins
lysosome
removes unwanted material and waste (digesting)
rough ER
makes proteins for endomembrane system
smooth ER
Detoxifies the cell and makes lipids
active transport
the cell provides the metabolic energy needed to move substances across the cell membrane
low to high
requires ATP
passive transport
substances cross the membrane without any energy input from the cell
high to low
does not require ATP
simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
three examples of passive transport
phagocytosis
the cell engulfs some relatively large or solid material
eating
white blood cells
pinocytosis
a bit of infolding plasma membrane surrounds a very small volume of extracellular fluid containing dissolved particles
drinking
exocytosis
materials move OUT of the cell by fusion of vesicles formed inside the cell with the plasma membrane
epithelial tissue
polarity
specialized contacts: tight junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes
connective tissue support: basement membrane
avascular
innervated
mitotically active
connective tissue proper, bone, cartilage, blood
4 main classes of connective tissue
collagen fiber
strength, prevents tears or separation from surrounding tissues (fiber)
elastic fiber
elasticity for lungs, blood vessels, and skin (fiber)
reticular fiber
support (fiber)
ground substance, fibers
What is matrix made up of?
skeletal muscle
Long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells
obvious striations
Voluntary control
smooth muscle
Spindle shaped elongated, uni-nucleated cells
no striations
involuntary control
cardiac muscle
highly branched, uni-nucleated cells
striated
involuntary control
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage, but more elastic fibers in matrix
Location: external ear and epiglottis (blocks digestive/respiratory tract)
hyaline cartilage
gristle/smooth, is the most abundant cartilage in the body
Glassy and smooth
Supportive but pliable
Lots of fibers
Location: covers ends of long bones in joint cavities, ribs, nose, trachea, larynx, and bronchi
fibrocartilage
thickest collagen fibers
Absorbs shock
Location: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joints
epidermis (epithelial cells), dermis (dense connective), hypodermic (adipose)
three major layers of skin
stratum basale
new cells being produces
melanin is deposited into cells
layer containing keratinocyte stem cells and melanocytes
stratum lucidum
only present in thick skin
cells are dead
stratum corneum
thickest layer
cells are dead
stratum granulouum
cells start the process of keratinization
protects from sun damage
What is the function of melanin?
compact bone
hard/solid, outside of bones
structural unit is osteon
spongy bone
honeycomb, inside of bones
structural unit is trabeculae
osteoblast
forms bone
osteoclast
breaks down bone
lamellae
tubes of osteons
osteoid
the non-mineral, organic part of the bone matrix made of collagen and non-collagenous proteins
osteon
structural unit of compact bone
axial skeleton
made up of skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
Forms the longitudinal axis of the body
Supports head, neck, and trunk
Protects the brain, spinal cord, and the organs in the thorax
appendicular skeleton
made up of bones that form the limbs and girdles
Function: Movement
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx
Types of bones of vertebral column in order
brain, spinal cord
Components of the central nervous system
cranial/spinal nerve, ganglia
Divisions of the peripheral nervous system
sensory neuron
carries information from body to CNS
unipolar
motor neuron
carries information from CNS to body
multipolar
association neuron
carries information between sensory and motor pathways
multipolar
-70mV
what is the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
depolarization
whenever the charge inside the cell becomes less negative compared to the outside
Charge inside the cell is moving closer to, and may exceed zero
Na+ moving into the cell (making it more positive)
repolarization
after being depolarized, the cell returns to its polarized state of -70mV
Charge decreases back to -70mV
K+ leaves the cell, taking a positive charge with it (making it more negative)
hyperpolarization
whenever the charge inside the cell becomes more negative than it is at rest
Cause: K pumps are sluggish, allowing too many positive ions to escape
Correction: Na/K pump
sarcolemma, ACH
Membrane of a muscle cell and the neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle cells
AChE
What enzyme is responsible for inactivating the neurotransmitter that activates muscle cells?
actin and myosin proteins slide
Know the protein interactions during the shortening of a sarcomere
ATP creatine phosphate, anaerobic glycolysis, aerobic glycolysis
The order energy pathways kick in during muscle contraction
agonist
(prime mover) muscle responsible for producing a given movement
EX/ bicep in barbell curl
antagonist
opposes or reverses specific muscle movement
EX/ tricep in barbell curl
synergist
helps prime movers by adding extra force to the same movement
Reduces undesirable or unnecessary movement
dura mater, subdural space, arachnoid mater, subarachnoid space, pia mater, epidural space
meninges and spaces from outermost to innermost
choroid plexus, protection
What structure makes CSF? What are the functions of CSF?
contralateral
reflex on different side