nurs 337: Inflammation (part one)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is inflammation?
body's protective immune response to injury, infection, or irritants
In what two ways does inflammation protect the immune system?
1.) Eliminate foreign substances and damaged tissues
2.) Protect by eliminating CAUSE of cell injury and necrotic cells
On a cellular level, what occurs during inflammation?
leukocytes are induced by chemical mediators to the site of infection in response to injurious stimuli
What are the 5 cardinal signs of inflammation?
1.) Calor; heat
2.) Dolor; pain
3.) Rubor; redness
4.) Tumor; swelling
5.) Functio Laesa; loss of function
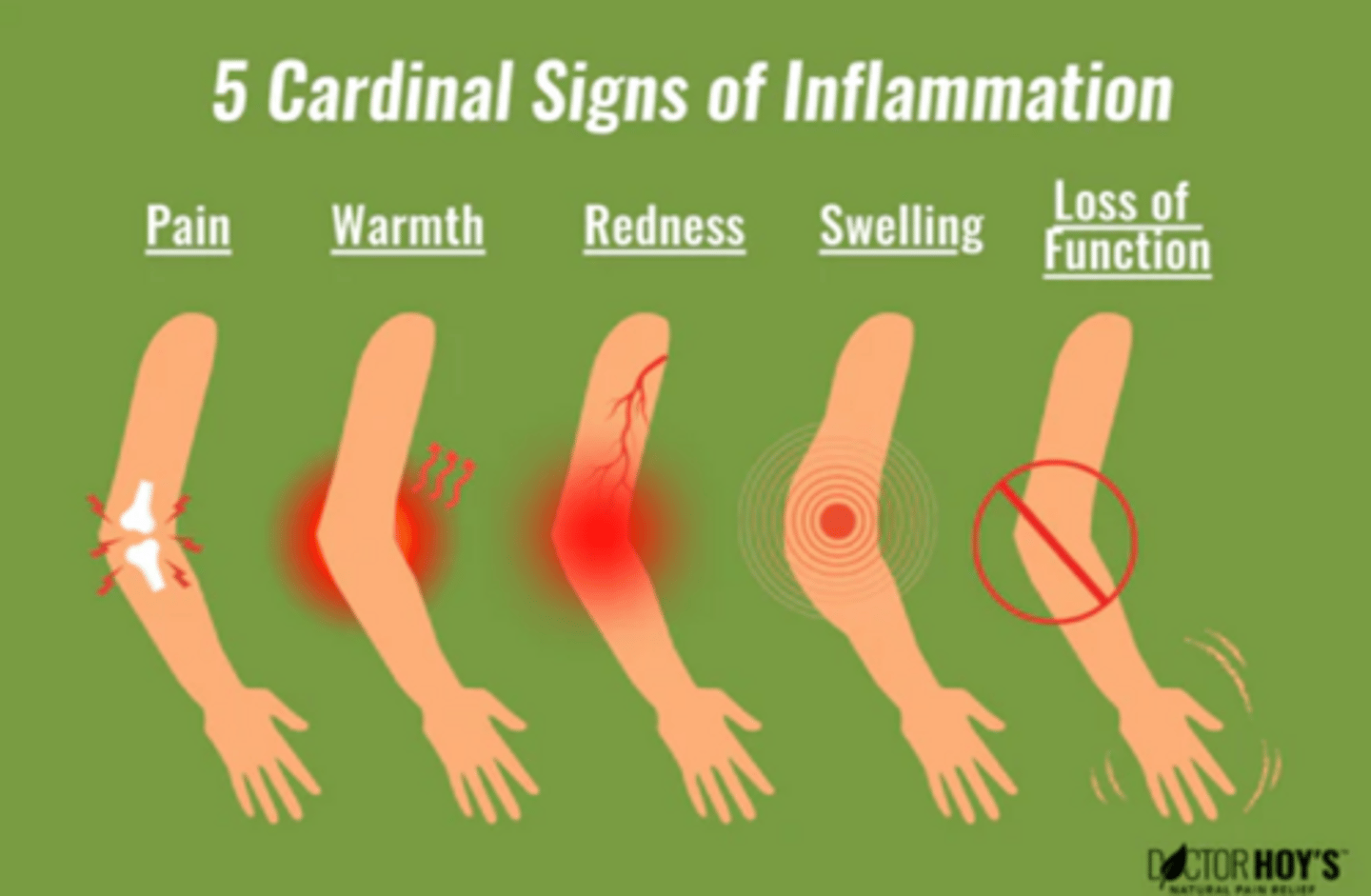
Inflammation is normally ____ and _____.
controlled, self-limited
What is the first line of defense?
"innate immunity"; physical and chemical nonspecific barrier that prevents pathogen entrance w/ mechanical actions
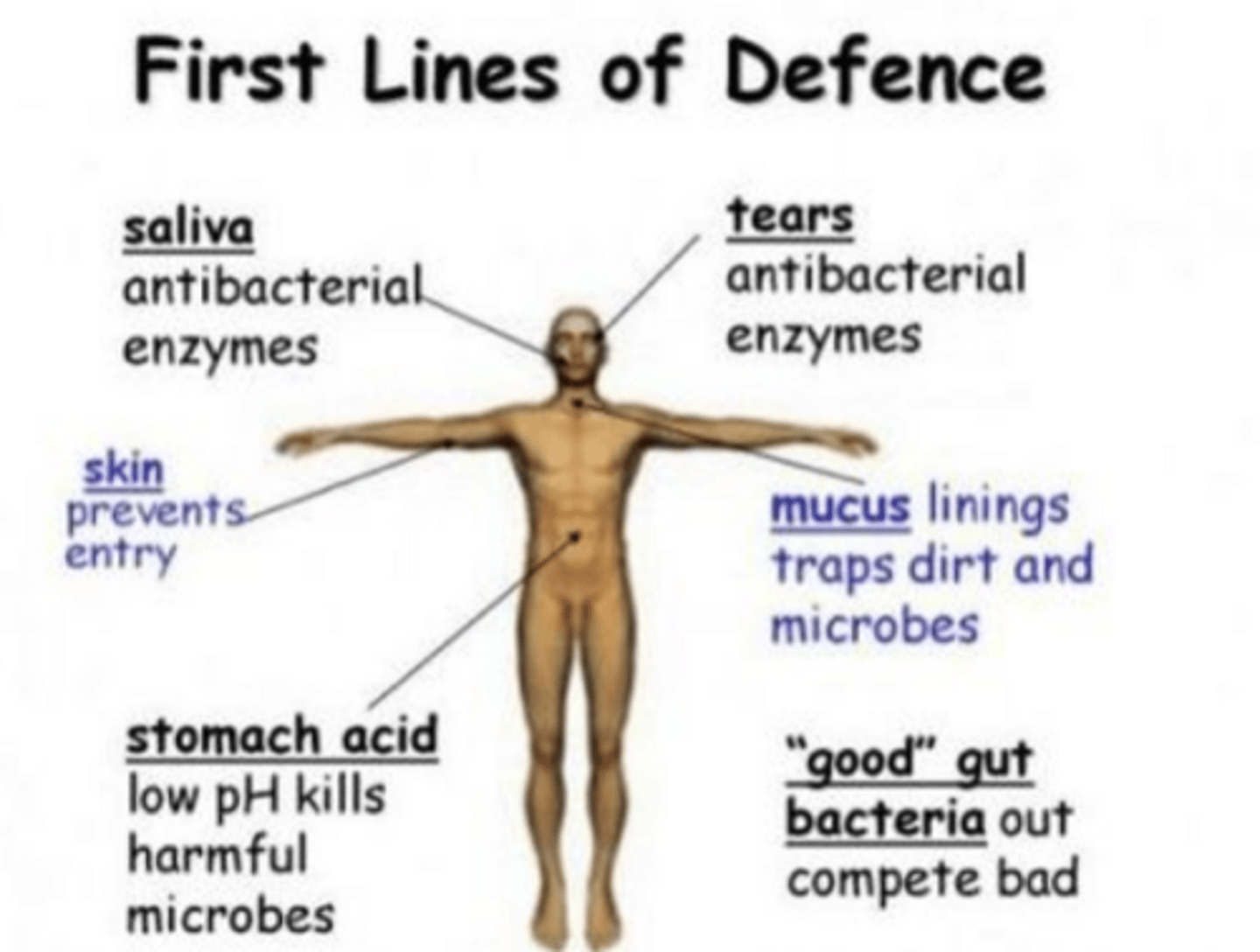
What are examples of the first line of defense?
skin, mucous, tears
What are mechanical actions used for the first line of defense?
sneezing, coughing
What is the second line of defense?
"innate immune response"; nonspecific internal defense that work to contain and eliminate invaders like bacteria and viruses
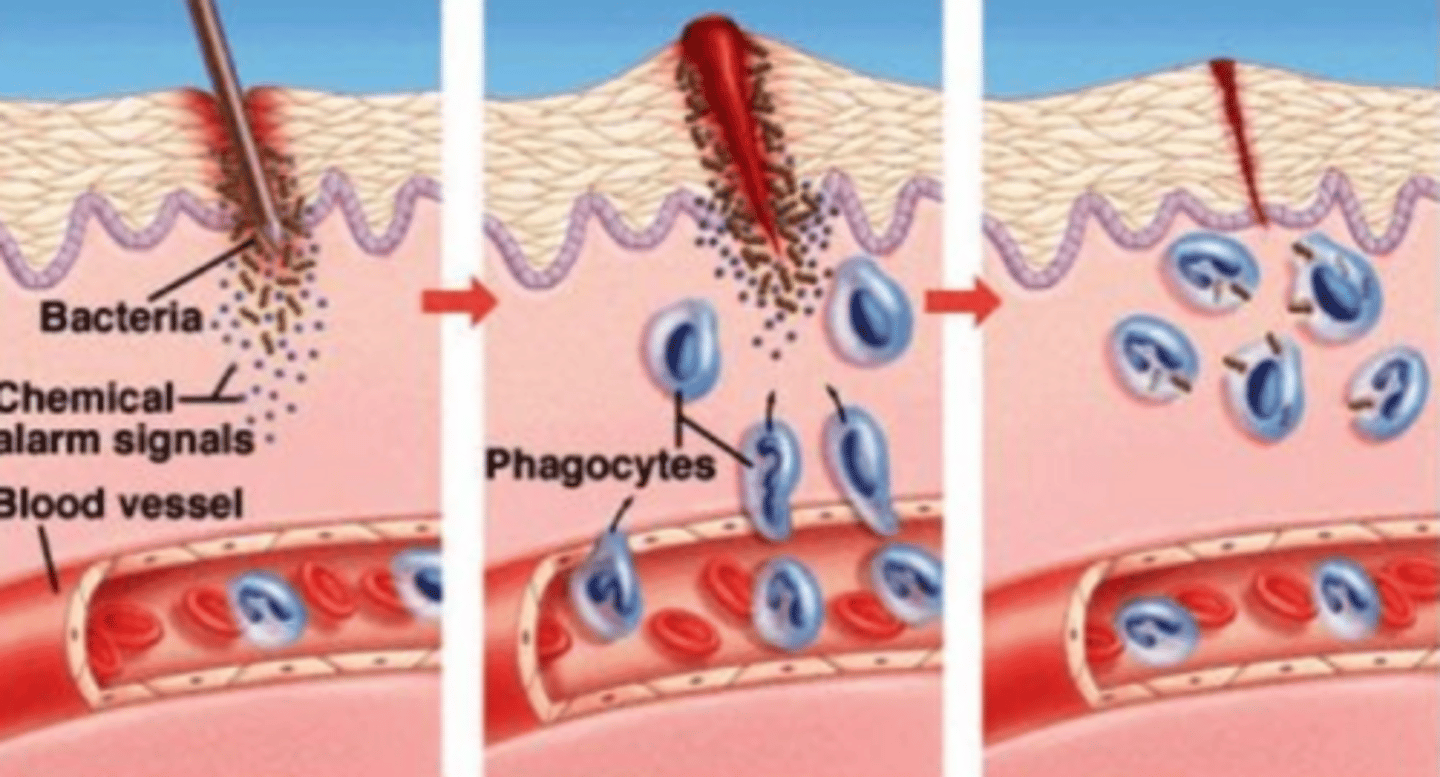
What are examples and components of the second line of defense?
phagocytes, inflammation, natural killer cells, compliment system
What is the third line of defense?
"adaptive/aquired immunity"; specific memory based response targeting particular pathogens and remember for the future for long lasting immunity
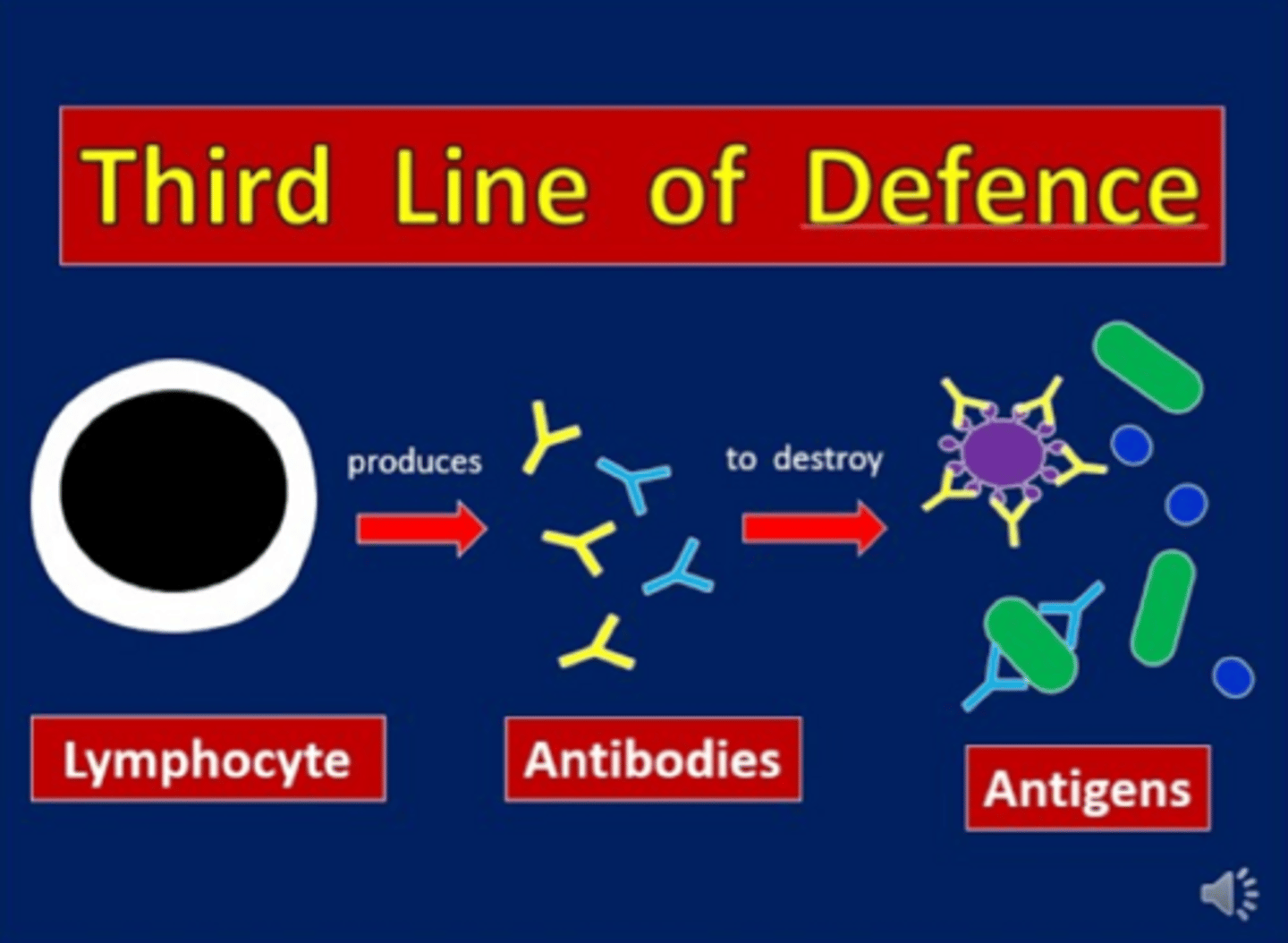
What are examples/components of the third line of defense?
antibodies/B cells, cell mediated immunity, T-cells
What are causes of inflammation?
Direct physical damage
Caustic chemicals
Ischemia or infarction
Allergic reactions
Extremes of heat or cold
Foreign bodies
Infection
What are the two types of inflammation?
acute and chronic
What is acute inflammation?
self-limiting, nonspecific protective response w/ fast delivering of leukocytes and plasma proteins; last 8-10 days
What is chronic inflammation?
initiated if acute is inadequate; lasts weeks to months
What does "self limiting" mean?
body's natural healing response resolves inflammation on its own after infection and initial injury is gone
What are the two components of acute inflammation?
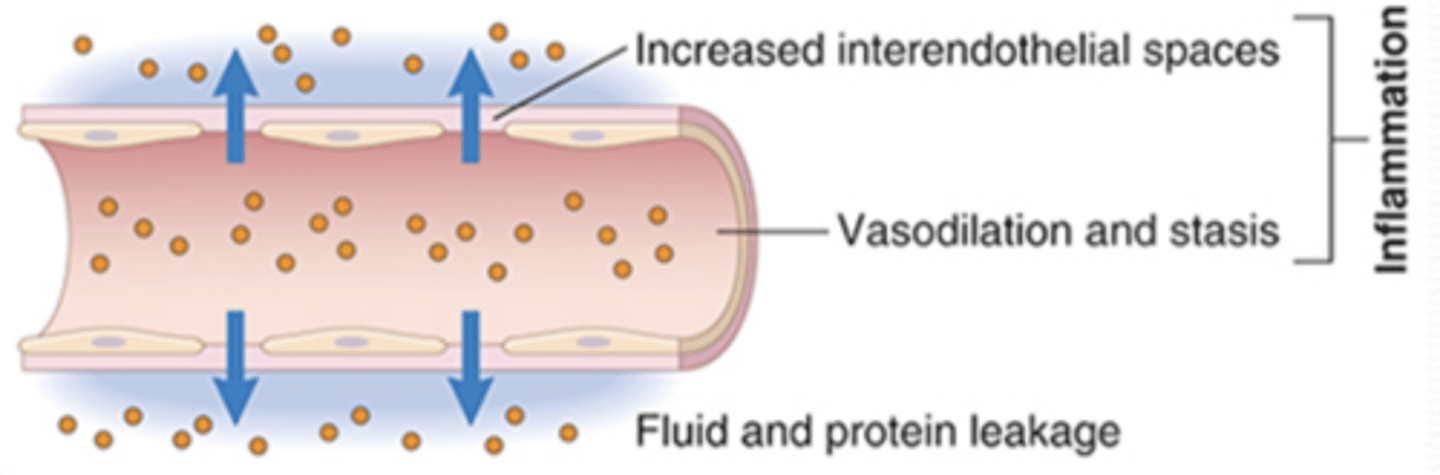
1.) Vascular; vasodilation and vascular permeability
2.) Cellular; recruitment, activation, and elimination
What is the effect of vasodilation and vascular permeability in inflammation?
to deliver immune cells and plasma proteins to site of injury and have it enter tissues
What is the effect of cellular recruitment, activation, and elimination in inflammation?
DELIVER immune cells to site of injury to be ACTIVATED which enhances pathogen killing to ELIMINATE pathogens, dead cells and damaged cells
Why does rubor and calor occur?
redness/heat; increased blood flow to damaged area
What occurs during tumor?
swelling/edema; shift of protein and fluid into intersitial space
What occurs during dolor?
pain; increased pressure of nerves release chemical mediators
What occurs during functio laesa?
loss of function; develops when cells lack nutrients
How can edema cause loss of function?
interfere with movement
What is exudate?
any fluid from circulatory system into lesions or area of inflammation
What are the four types of exudate?
serous, fibrinous, purulent, hemorrhagic
What is serous exudate?
watery; fluids, proteins, WBCs
What is fibrinous exudate?
thick, sticky, high cell and fibrin
What is purulent exudate?
thick, yellow-green; leukocytes, cell debris, microorganisms
What is an abcess?
localized pocket of purulent exudate in solid tissue
What is hemorrhagic exudate?
when blood vessles damaged
How long does retraction of endothelial cells occur?
rapid and short lived; minutes
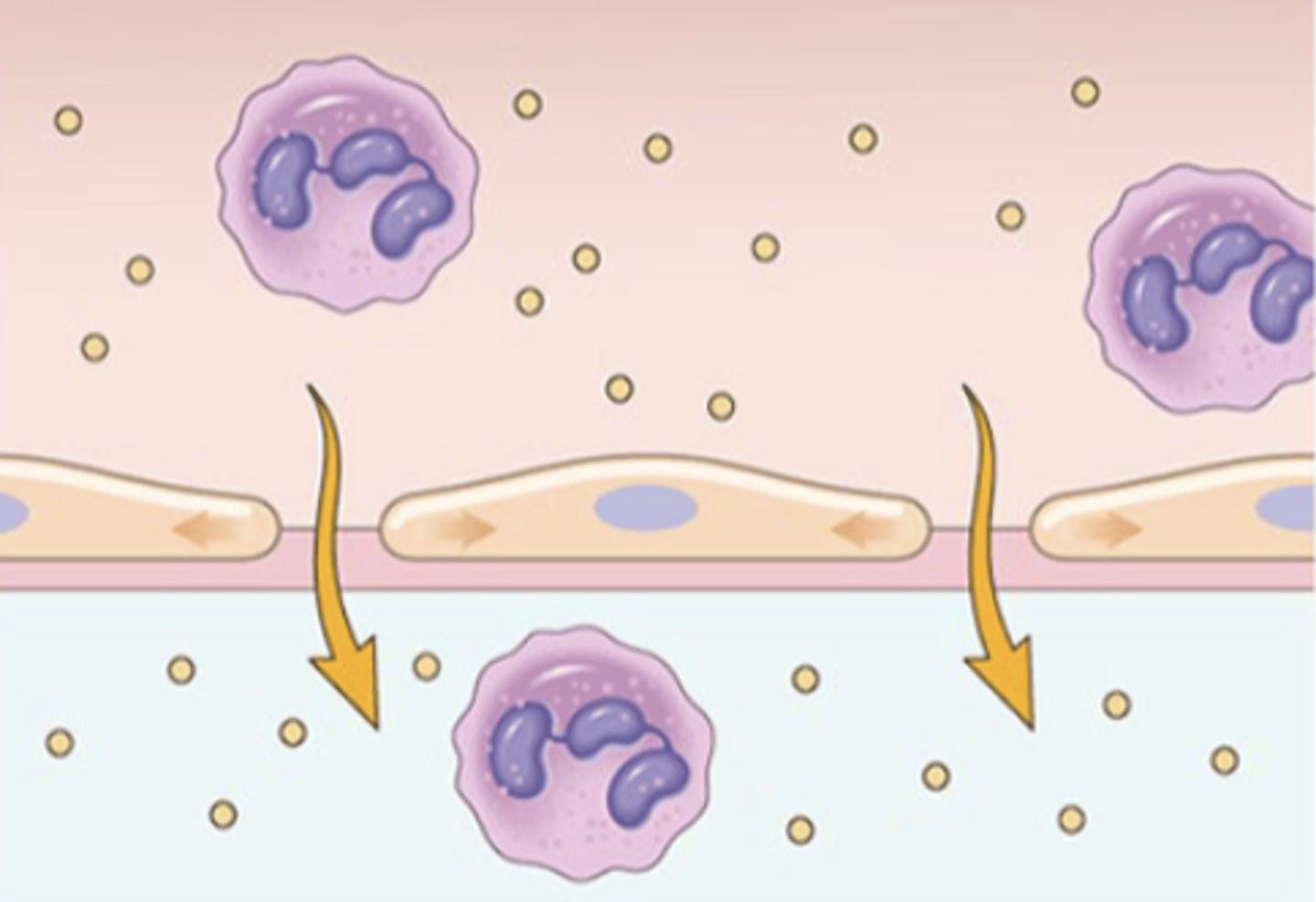
What is the retraction of endothelial cells induced by?
histamine and other chemical mediators
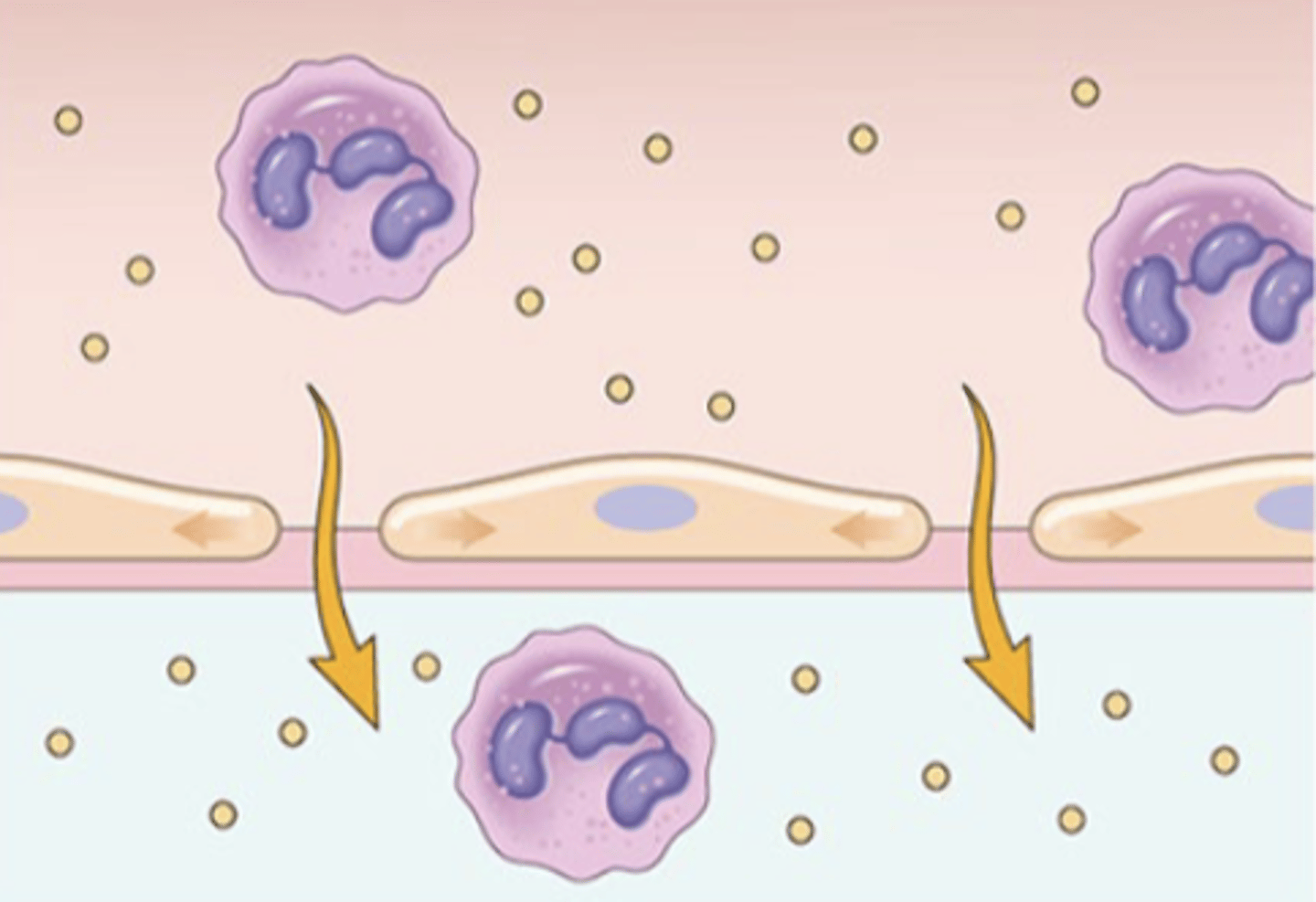
How long does endothelial injury occur?
rapid, may be long lived; hours to days
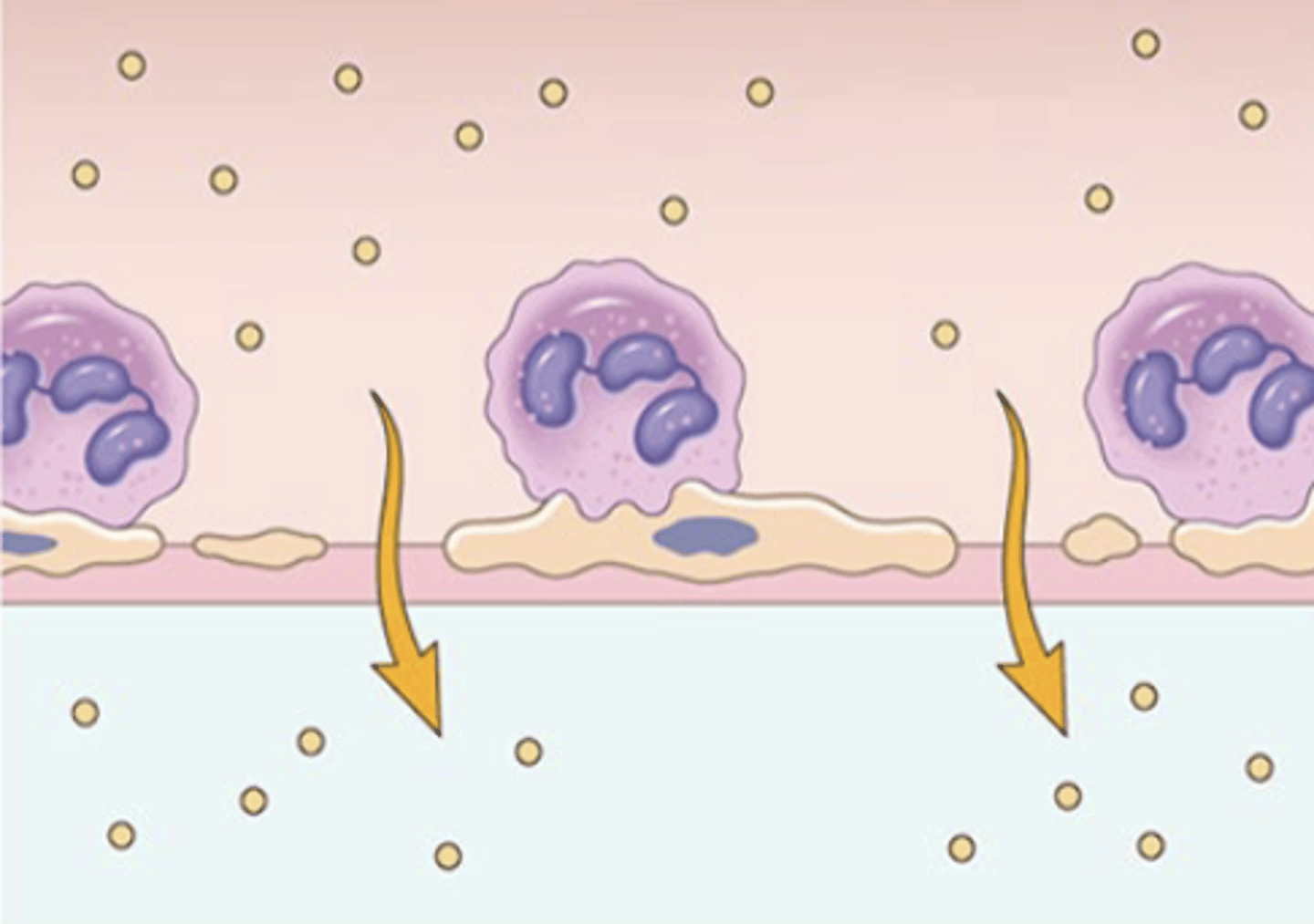
What is endothelial injury induced by?
burns, some microbial toxins
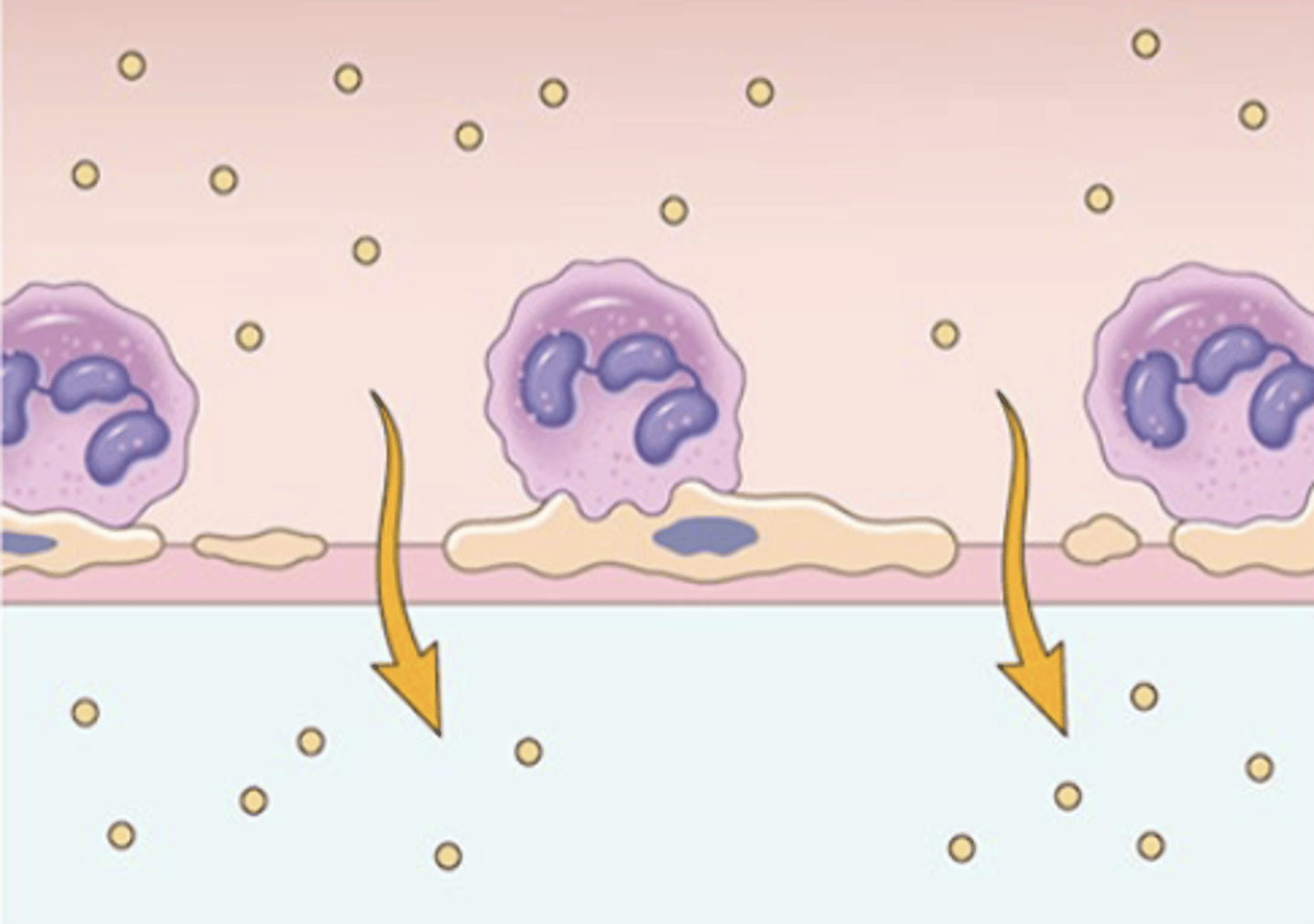
What are transudates caused by?
disturbances of hydrostatic or colloid osmotic pressure
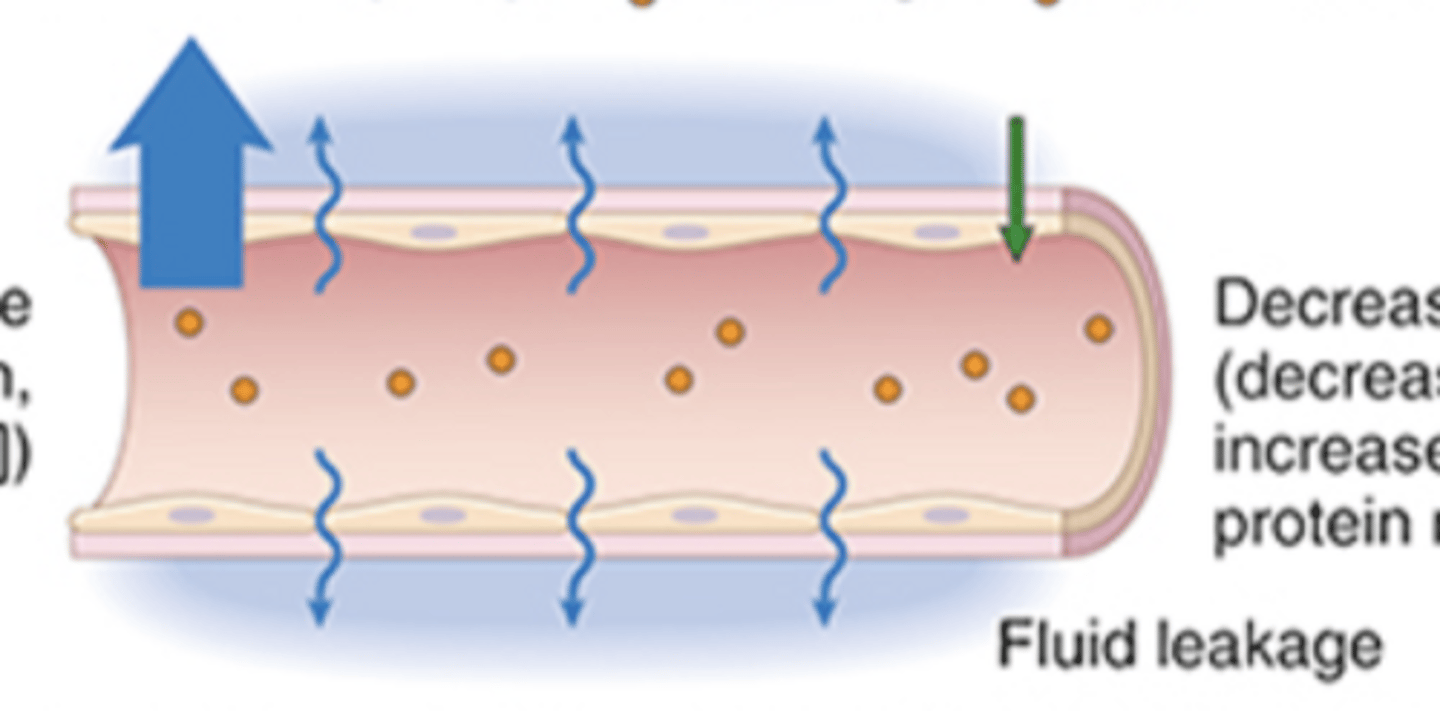
What are exudates caused by?
inflammation
What are chemical mediators?
initiate, regulate, and resolve inflammation by coordinating vascular and cellular responses at the site of injury
How do chemical mediators act?
bind to specific receptors on different cells
How long do chemical mediators last?
tightly regulated and short lived, but can cascade
What is a cascade?
mediator activates others and causes AMPLIFIED inflammatory responses
What are some examples of chemical mediators?
histamine, kinins, prostaglandins
What are five systemic effects of inflammation?
pyrexia, malaise, fatigue, headache, anorexia
What is pyrexia?
mild fever that is enduced if inflammation is extensive resulting in the release of pyrogens
What is malaise?
feeling unwell