lect8 amines part 3
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What causes Parkinson’s disease in terms of dopamine pathways?
Degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway, leading to motor dysfunction.
Which dopamine pathway degenerates in Parkinson’s disease?
The nigrostriatal pathway.
How is Parkinson’s disease treated pharmacologically?
With L-DOPA, MAO inhibitors, and COMT inhibitors, which increase brain dopamine levels.
Name three drug types used to enhance dopamine in Parkinson’s treatment.
L-DOPA, MAO-Is, COMT-Is.
What dopamine dysfunction is linked to schizophrenia?
overactivity/underactivity in which pathways?
Overactivity in mesolimbic/
underactivity in mesocortical dopamine pathways.
Which dopamine pathways are overactive in schizophrenia?
mesolimbic
How do antipsychotic drugs act on dopamine systems?
They block dopamine receptors, especially D2 receptors, reducing psychotic symptoms.
What is the main target of psychotropic drugs in schizophrenia?
Dopamine D2 receptors
Why can antipsychotics cause Parkinson-like side effects?
They block dopamine in the nigrostriatal pathway, leading to extrapyramidal symptoms.
Which side effect of antipsychotics mimics Parkinson’s disease and why?
Motor symptoms due to nigrostriatal D2 blockade.
How can antipsychotics affect hormone levels?
By blocking dopamine in the tuberoinfundibular pathway, they cause increased prolactin secretion.
What hormonal imbalance may occur due to TI pathway dopamine blockade?
Hyperprolactinaemia (due to loss of dopamine inhibition).
Where do serotonin (5-HT) pathways in the CNS originate?
They originate in the raphe nuclei of the brainstem.
What is the main source of serotonin neurons in the brain?
The raphe nuclei.
What are the projection targets of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei?
They project to the forebrain and cerebellum.
Which brain areas receive serotonin from the dorsal and median raphe?
The forebrain and cerebellum.
Which areas are innervated by the caudal raphe nuclei?
The spinal cord and cerebellum.
What is the target of serotonin projections from the caudal raphe?
The spinal cord and cerebellum.
Why is serotonin sometimes called the “appetite’s chemical”?
Because it helps regulate eating behavior, satiety, and food-related impulses.
How is serotonin involved in appetite regulation?
It promotes satiety and reduces food intake, earning the nickname “appetite’s chemical”.
What types of receptors does serotonin act on?
Mostly GPCRs (5HT1–7), except 5-HT3, which is ionotropic.
Which 5-HT receptor is ionotropic, and what are the rest?
: 5-HT3 is ionotropic, the rest (5HT1–2, 4–7) are GPCRs.
How does serotonin affect mood?
Through cortical and limbic system projections, 5-HT controls emotion and mood; dysfunction is linked to depression.
What mental health condition is associated with low serotonin?
Depression.
How does serotonin affect sleep and wakefulness?
Activation promotes wakefulness and insomnia.
Low activity promotes sleep and sedation.
: What happens to sleep with high vs. low serotonin activity?
High 5-HT → insomnia; Low 5-HT → sleep/sedation.
: How does serotonin regulate appetite?
Increased 5-HT → reduced appetite, weight loss.
Decreased 5-HT → increased eating, weight gain.
What is the effect of increased serotonin on feeding?
It suppresses appetite.
What is serotonin’s role in sensory transmission?
It gates pain signals in the spinal cord and dampens sensory overload in the cortex.
How does 5-HT help control sensory input?
It modulates pain transmission and prevents overstimulation from sensory input.
What is the dietary precursor of serotonin (5-HT)?
Tryptophan, an essential amino acid from the diet.
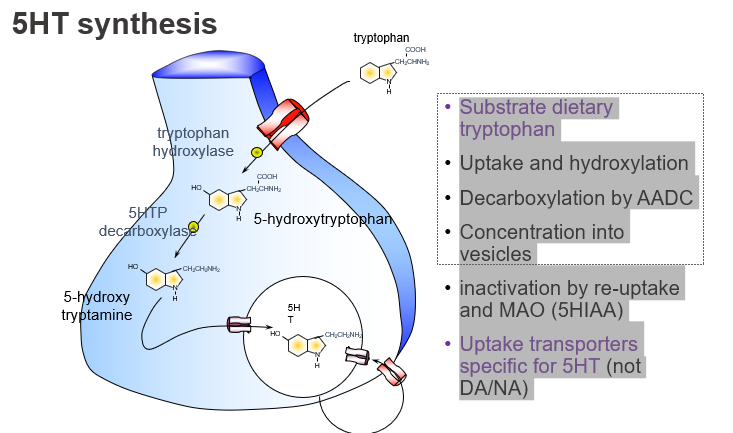
Which amino acid is the starting point for serotonin synthesis?
Tryptophan.
What enzyme converts tryptophan to 5-HTP, and what kind of step is this?
Tryptophan hydroxylase, and it’s the rate-limiting step.
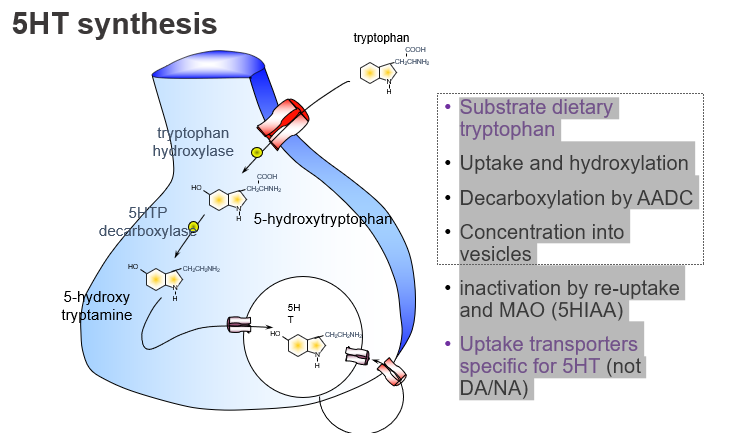
What is the first step in serotonin synthesis?
Hydroxylation of tryptophan to form 5-HTP.
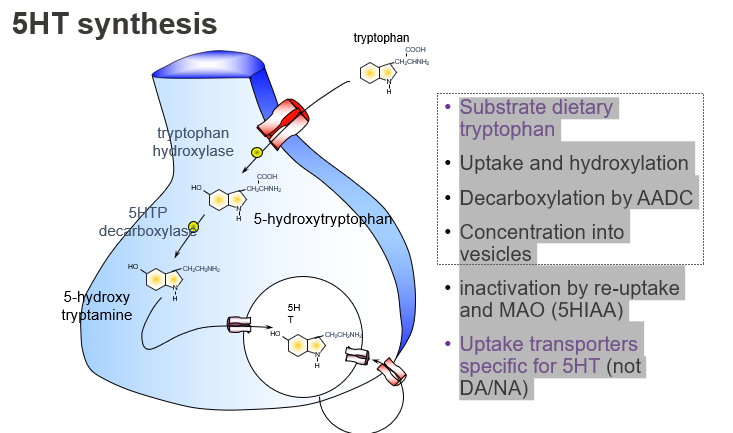
Which enzyme converts 5-HTP to serotonin?
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC).
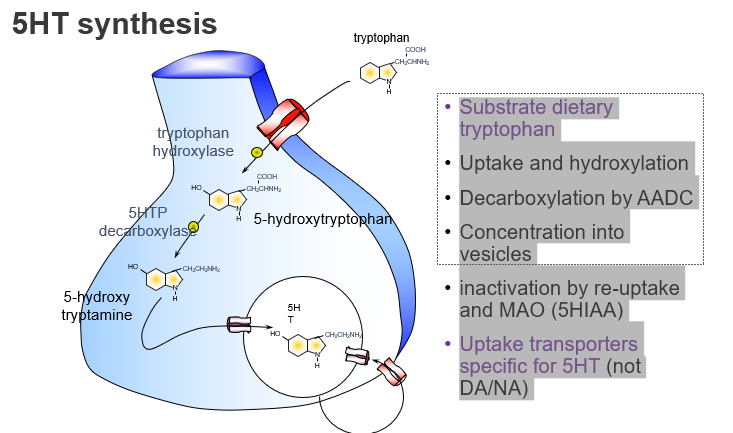
What enzyme is responsible for the final step of 5-HT synthesis?
AADC, which decarboxylates 5-HTP to form serotonin.
How is serotonin stored before release?
: It is packaged into vesicles via VMAT.
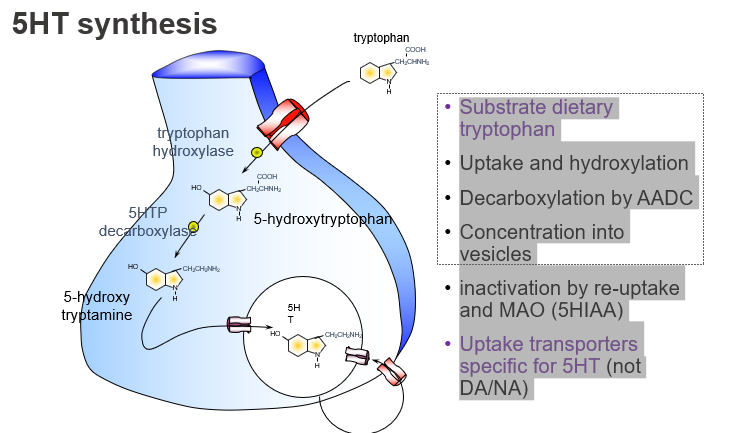
What transports serotonin into storage vesicles?
The vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT).
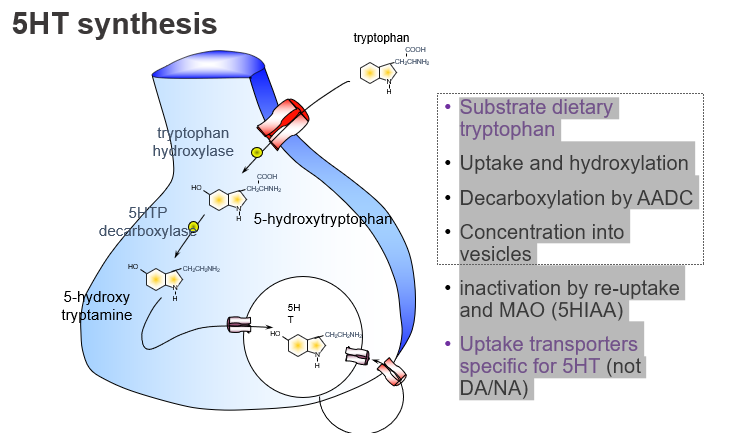
How is serotonin inactivated after release?
By reuptake into the presynaptic neuron and degradation by MAO into 5-HIAA.
What are the main ways serotonin is cleared from the synapse?
Reuptake and breakdown by MAO into 5-HIAA.
What is the name of the transporter specific for serotonin reuptake?
SERT (serotonin transporter).
Which transporter clears serotonin but not dopamine or noradrenaline?
SERT, which is specific for 5-HT.
is tryptophan hydroxylase saturated in the brain?
No — it’s not saturated, so more tryptophan can increase its activity.
Can increasing tryptophan boost serotonin synthesis?
Yes, because tryptophan hydroxylase is not saturated.
What is the rate-limiting step in serotonin synthesis?
Tryptophan availability limits how much serotonin can be made
What limits the amount of serotonin produced?
How much tryptophan is available.
How might tryptophan or 5-HTP be used therapeutically?
They can increase serotonin synthesis and are explored as antidepressants.
Why is 5-HTP considered a potential antidepressant?
It’s a precursor that boosts 5-HT levels.
What does reserpine do to serotonin storage?
it blocks vesicular uptake via VMAT, depleting serotonin.
Why can reserpine cause depression?
It prevents serotonin storage, leading to 5-HT depletion.
How is serotonin inactivated in the synapse?
Mainly through reuptake by the SERT transporter.
What clears serotonin from the synaptic cleft?
Reuptake into presynaptic neurons.
How do SSRIs treat depression?
they block serotonin reuptake, increasing 5-HT in the synapse.
What’s the mechanism of SSRIs like fluoxetine?
they inhibit reuptake of 5-HT, raising its synaptic levels.
Where do magnocellular ACh neurons project in the brain?
: To the cortex and limbic system, including the amygdala
Magnocellular ACh neurons = large nerve cells that make acetylcholine (ACh) — a neurotransmitter important for memory, attention, and learning.
What is the role of magnocellular cholinergic neurons?
They send projections to the cortex and limbic areas, supporting motivation and emotion.
Which brain structure receives ACh input for memory formation?
The hippocampus.
Which ACh projection is key for learning and memory?
From the basal forebrain to hippocampus.
What do brainstem cholinergic neurons project to in the CNS? where?
To the thalamus and other regions, regulating arousal and sleep.
Which cholinergic pathway affects alertness and wakefulness?
Brainstem to thalamus cholinergic projections.
What role does ACh play in the basal ganglia?
ACh is used by local interneurons to modulate motor function.
How does ACh affect movement in the striatum?
Through local cholinergic interneurons, influencing motor control.
Why is ACh called the “memory/motivation chemical”?
Because it is crucial for attention, learning, and motivation, especially in the hippocampus and cortex.
What functions make ACh important for cognition?
Its role in memory formation, focus, and motivated behaviour.
What are the two main types of ACh receptors in the CNS?
Nicotinic (ionotropic) and muscarinic (GPCR) receptors.
Which ACh receptor types are fast vs. slow acting?
Nicotinic → fast; Muscarinic → slow/modulatory.
Which brain system uses ACh to regulate arousal and sleep?
The reticular activating system (RAS) from the brainstem.
What role does brainstem ACh play in consciousness?
It activates the RAS, supporting waking and alertness.
What happens when ACh levels increase in the cortex?
Arousal increases; the brain becomes more alert and awake.
How does ACh influence sleep-wake cycles?
High ACh = wakefulness, low ACh = sedation.
What is the function of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons?
they project to the cortex, supporting cognition and attention.
Which part of the brain supplies ACh for cognitive function?
The basal forebrain, especially the nucleus basalis.
Which disease is linked to degeneration of ACh neurons in the basal forebrain?
: Alzheimer’s disease.
What neurotransmitter system is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease?
The cholinergic system (ACh neurons).
What ACh pathway is important for learning and memory?
The septo-hippocampal pathway.
Which ACh projection supports memory and spatial learning?
From the medial septum to the hippocampus.
How does ACh influence motor control in the basal ganglia?
Via local interneurons that regulate striatal activity.
What motor-related diseases involve ACh dysfunction in the basal ganglia?
Parkinson’s and Huntington’s chorea.
Is ACh synthesis in the brain different from at the neuromuscular junction?
No — it's the same process in both the CNS and NMJ.
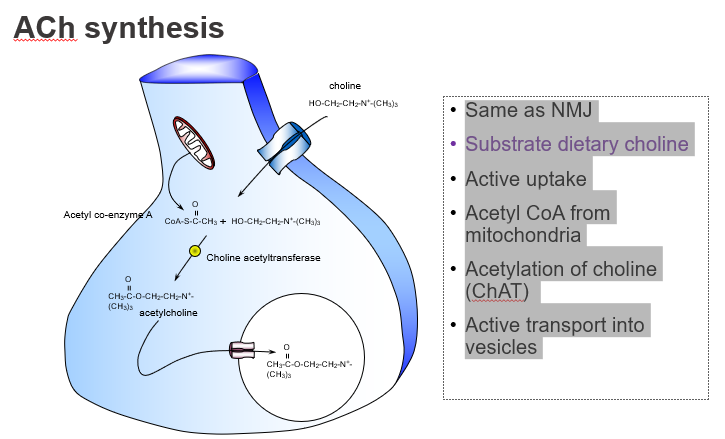
What’s similar between ACh synthesis in muscles and the brain?
Both use the same synthesis pathway involving choline and acetyl-CoA.
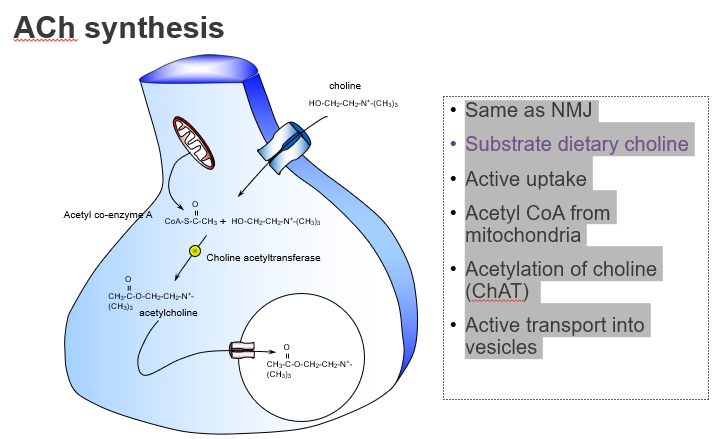
What dietary nutrient is required to make ACh?
Choline, obtained from the diet
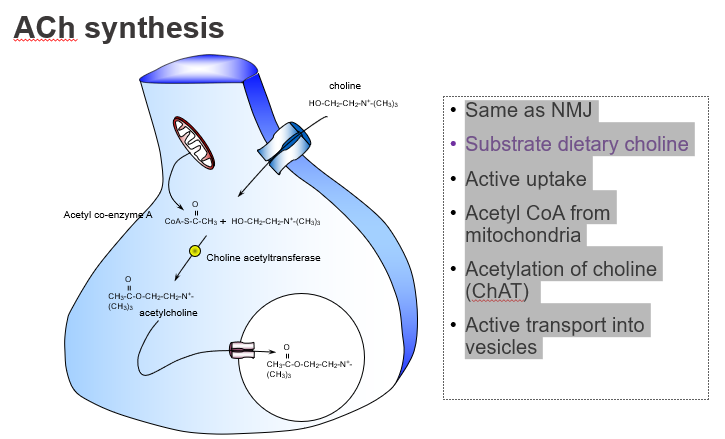
Which dietary precursor is essential for ACh production?
Choline.
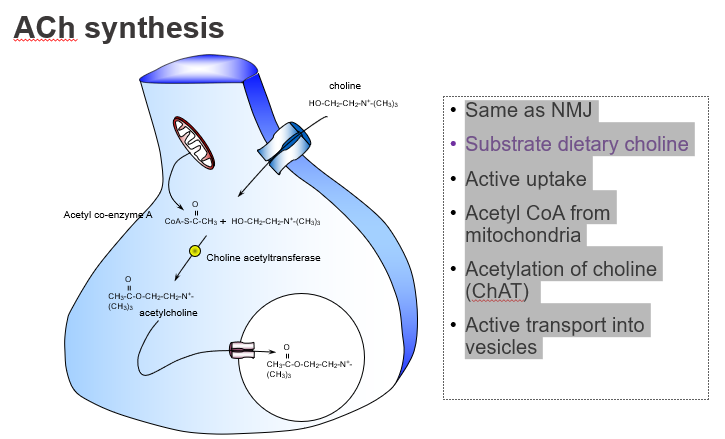
How is choline taken into neurons?
Through active transport by high-affinity choline transporters.
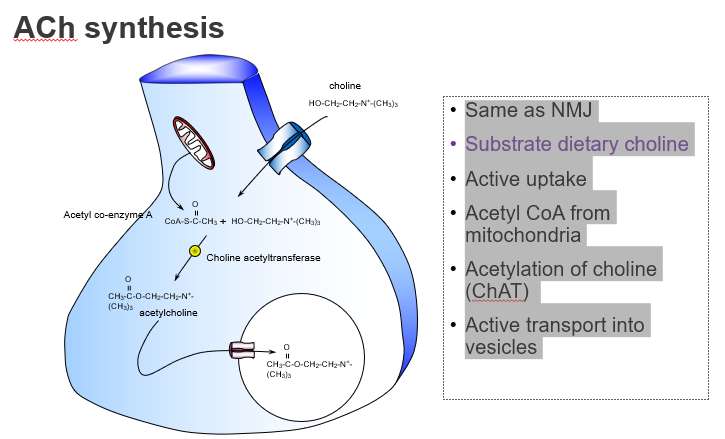
Is choline uptake into neurons passive or active?
Active uptake.
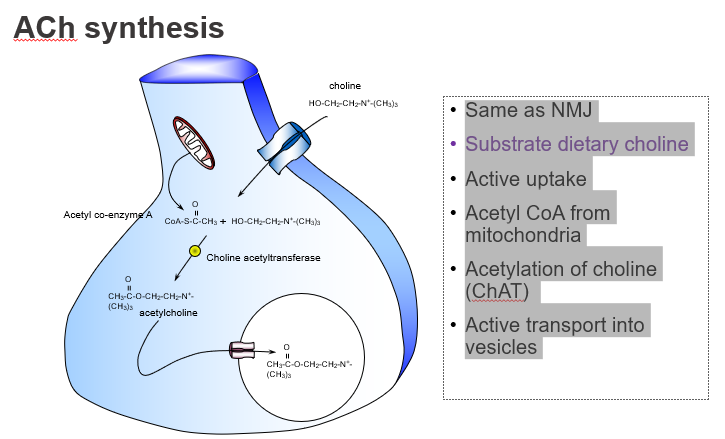
What molecule donates the acetyl group in ACh synthesis?
Acetyl CoA, produced by mitochondria.
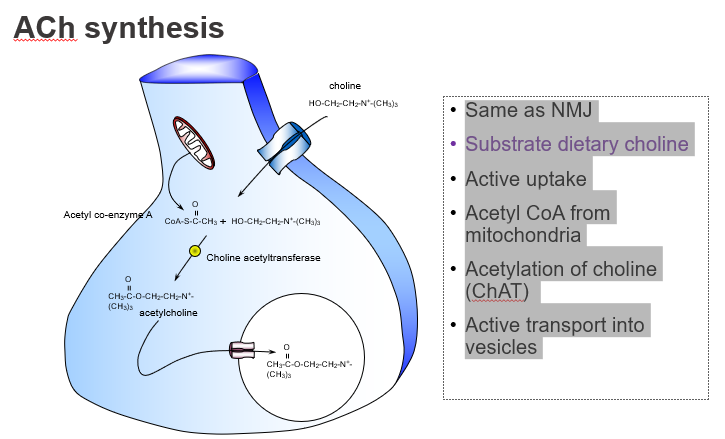
Where does the acetyl group in ACh come from?
From acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA).
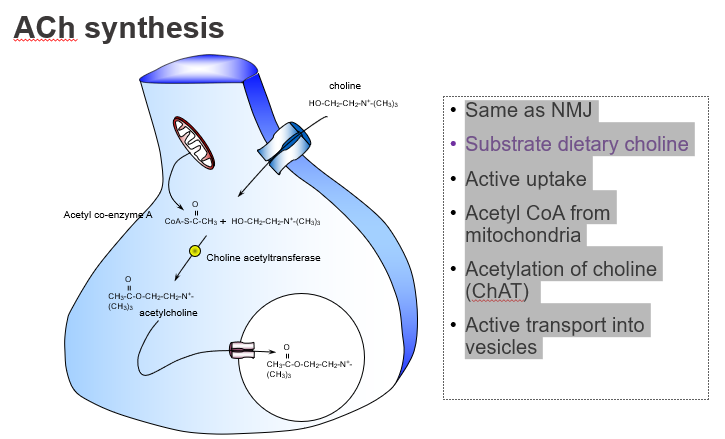
What enzyme synthesises acetylcholine?
Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT).
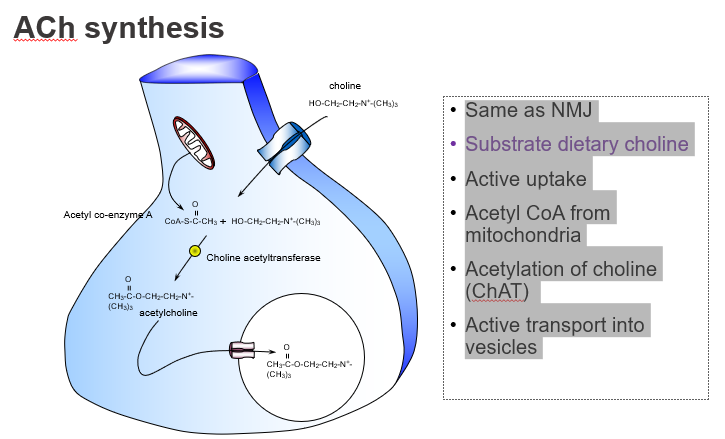
Which enzyme catalyses the reaction: choline + acetyl-CoA → ACh?
ChAT.
How is ACh stored before release?
It’s actively transported into vesicles by VAChT.
Where is ACh stored in the neuron?
In synaptic vesicles, via vesicular transporters.
Is choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) saturated under normal conditions?
No — it’s not saturated, so choline availability is rate-limiting.
What limits the rate of ACh synthesis?
Choline, because ChAT is not saturated.
hat happens when choline levels are increased in neurons?
ACh synthesis increases due to more substrate for ChAT.
How can ACh levels be boosted in the brain?
By increasing choline supply.
What enzyme breaks down ACh in the synaptic cleft?
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
How is ACh inactivated after it’s released?
By rapid degradation via AChE.
What are the breakdown products of acetylcholine?
Choline and acetic acid.
What does AChE produce when it breaks down ACh?
Free choline and acetic acid.
How is choline recovered after ACh breakdown?
It is actively taken up by high-affinity choline transporters.
What happens to choline after ACh is broken down?
It’s recycled into the neuron for new ACh synthesis.