Neuro Basics & Examination
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FF Week 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Frontal lobe
Function:
CEO: on top of everything
C: controls planning, programming, movement
E: emotion, behavior, personality
O: olfaction (sense of smell)
Broca’s aphasia when affected
Temporal lobe
Function:
Hearing and language comprehension
Wernicke’s aphasia when affected
Broca’s aphasia
BEN has Broca’s
Broken speech (difficulty speaking, words don’t come out)
Expressive aphasia
Non-fluent aphasia
Frontal lobe
Use yes/no questions during treatment sessions
Wernicke’s aphasia
Unable to understand
Receptive aphasia
Fluent aphasia
Word salad (speak fluently, words don’t make sense)
Temporal lobe
Use gestures/demonstrations during treatment sessions
Aphasia nugget
Left hemisphere is usually called the dominant hemisphere
Broca’s and Wernicke’s aphasia are more often seen with Left hemisphere lesions
Parietal lobe
Gives perceptual information
With lesion:
Perceptual disorders e.g. unilateral neglect
Sensory loss
Occipital lobe
Gives visual information
With lesion:
Visual loss
Cranial nerve pneumonics
I: Olfactory: On: Some
II: Optic: On: Say
III: Oculomotor: On: Money
IV: Trochlear: They: Matters
V: Trigeminal: Traveled: But
VI: Abducens: And: My
VII: Facial: Found: Brother
VIII: Vestibulocochlear: Voldemort: Says
IX: Glossopharyngeal: Guarding: Big
X: Vagus: Very: Brains
XI: Spinal Accessory: Secret: Matter
XII: Hypoglossal: Horcruxes: Most
“S” = sensory; “M” = motor; “B” = both
Cranial nerve location
CE MI PONS MEDU
Cerebrum
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Number of letters = number of cranial nerves in that location
CE: CN I & II
MI: CN III & IV
PONS: CN V, VI, VII, & VIII
MEDU: CN IX, X, XI, & XII
Cranial nerve I (1)
Olfactory (On, Some)
Sensory Function: sense of smell
When affected: anosmia - loss of sense of smell
Test: identify familiar odors with eyes closed
Cranial nerve II (2)
Optic (On, Say)
Sensory Function: vision - color, acuity (clarity), peripheral vision, Pupillary Light Reflex
When affected: blindness, myopia - short sighted (can see close objects), presbyopia - far sighted (can see far objects)
Test: test visual fields
Pupillary light reflex
Protective reflex
Sensory/afferent: sensing light - CN II
Motor/efferent: constriction - CN III

Cranial nerve III (3)
Oculomotor (On, Money)
Motor
Motor Functions:
Movement of eyeball: up, down, in, & up/in (innervates all eye movement muscles besides superior oblique and lateral rectus - SO4 & LR 6)
If affected: lateral strabismus - abnormal resting eye position; eye at rest points out
Opens eyelids
If affected: ptosis - drooping of eyelids
Constricts pupils
If affected: dilation of pupils
Test: upward, downward, and medial gaze
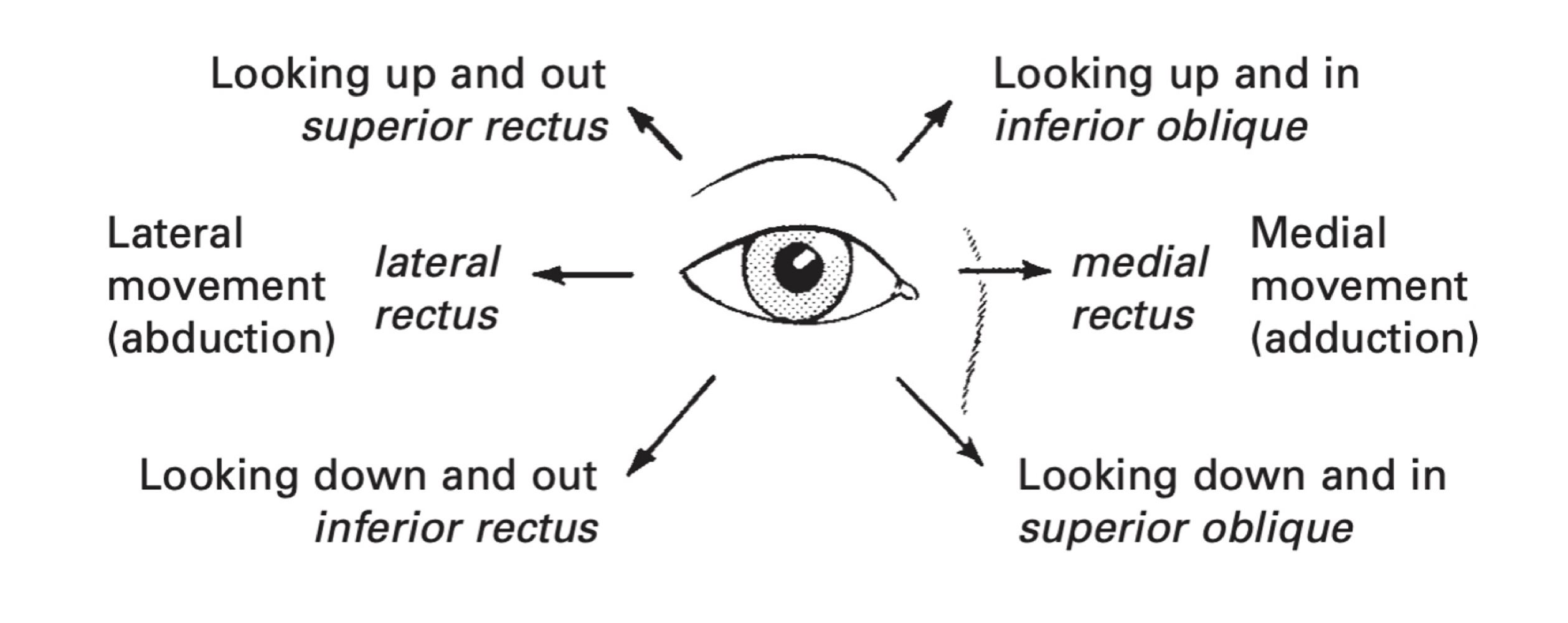
Cranial nerve IV (4)
Trochlear (They, Matters)
Motor Function: eye movement (SO4) - down/in (looks at nose; nose has 4 letters for CN 4)
Test: downward and in gaze
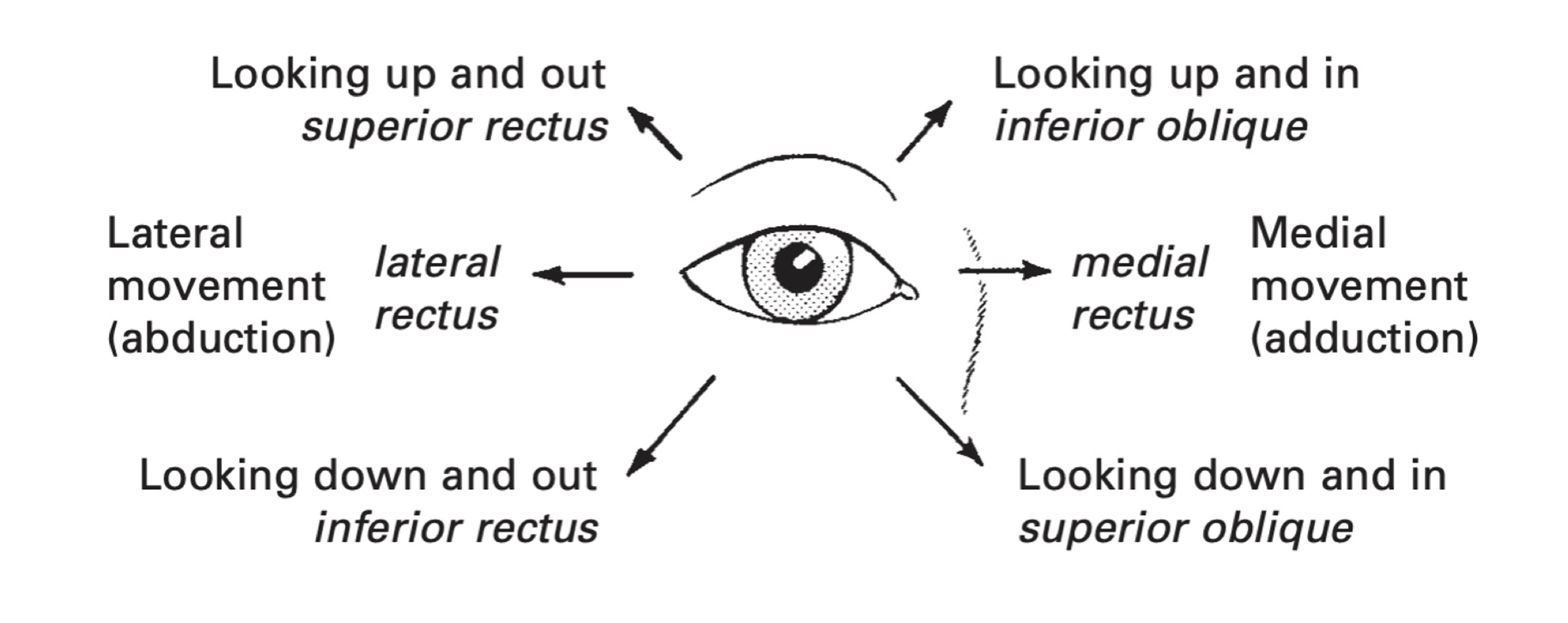
Cranial nerve VI (6)
Abducens (And, My)
Motor Function: eye movement (LR6) - out
Test: lateral gaze
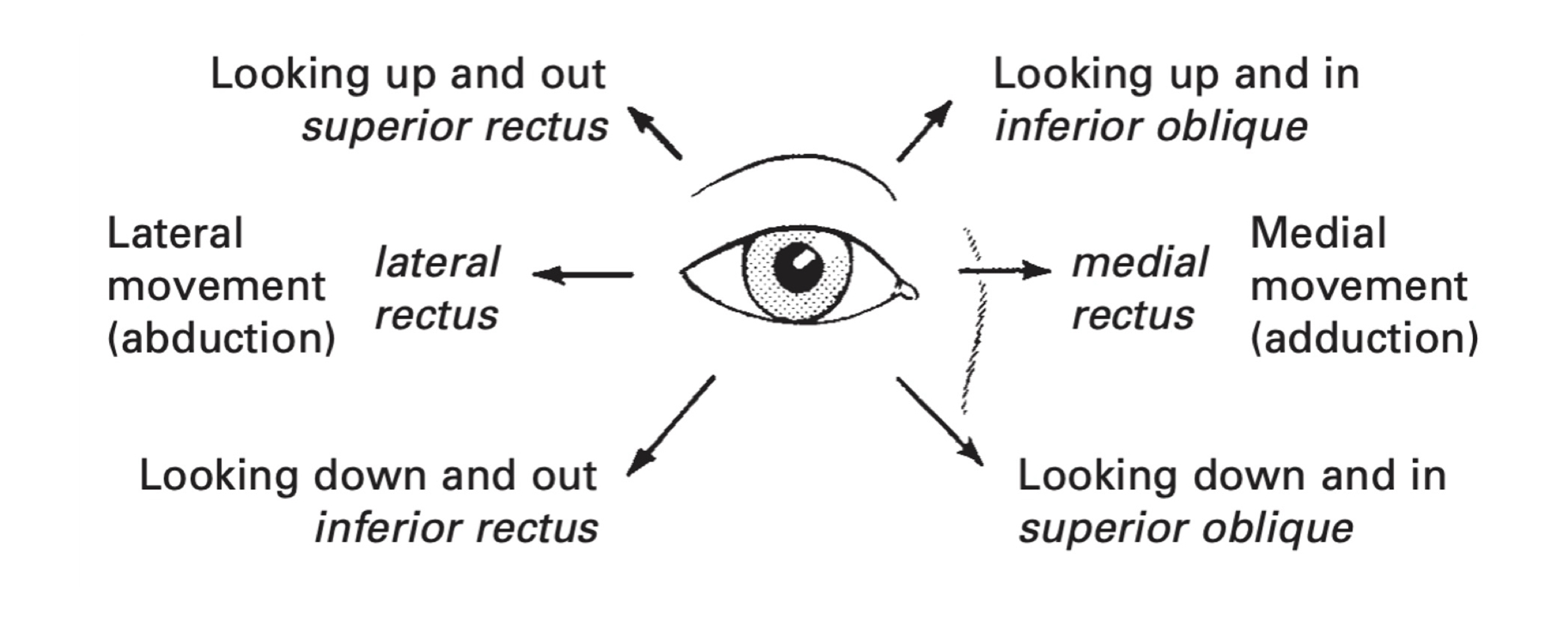
Cranial nerve V (5)
Trigeminal (Traveled, But)
Sensory Functions:
Sensation to face
Afferent/sensory component of Corneal Touch Reflex
Sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue: temperature, texture, etc.
Motor Functions:
Chewing (tri-CHEW-minal)
Dampens sounds (hyperacusis if affected)
Jaw jerk reflex: a quick, involuntary upward closing of the jaw when the chin is tapped
Normal response: absent/slight
Abnormal responses:
Exaggerated/brisk (often with clonus) - indicates UMN lesion
Absent - LMN lesion or CN 5 lesion
Test: sensation of face, muscles of mastication, corneal reflex, and jaw reflex
Cranial nerve VII (7)
Facial (Found, Brother)
Sensory Function:
Taste to anterior 2/3 of the tongue: spicy, sour, bitter, etc.
Motor Functions:
Movement of face (besides opening eyelids and chewing)
Efferent/motor component of Corneal Touch Reflex
Dampens sounds (hyperacusis if affected)
Lacrimation (crying)
Salivation
Test: muscles of facial expression, taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue - identify familiar tastes, close eyes tight, smile with teeth, puff cheeks
Cranial nerve nugget
Happy hour opens at 3 and closes at 7
CN 3 - opens eyelids
CN 7 - closes eyelids
Cranial nerve VIII (8)
Vestibulocochlear (Voldemort, Says)
Sensory Functions:
Balance
Hearing (conductive vs sensorineural hearing loss)
Test: hearing tests, balance and coordination tests: finger to nose
Diagnosing hearing loss
Conductive vs Sensorineural hearing loss
Step 1 - Rinne’s Test: determines type (conductive vs sensorineural)
Start by place tuning fork on bone behind the ear (Rinne behind the pinne; pinna is outer portion of ear) once they can no longer hear, switch to placing it lateral to outer ear
Normal: AC > BC
Sensorineural loss: AC > BC
Conduction loss: BC > AC
AC = air conduction
BC = bone conduction
Testing to see if patient hears air conduction or bone conduction as louder
Step 2 - Weber’s Test: determines side (L vs R)
Place tuning fork in the middle of the top of the patient’s head
Normal: heard equal on both sides
Sensorineural loss: heard louder in normal ear
Conduction loss: heard louder in affected ear
CANS for Weber’s test
(CA): Conductive is louder in Affected ear
(NS): Sensorineural is louder in Normal ear
*May be easier to remember how sensorineural loss will present with Weber’s test, and then just know that conductive loss will be opposite
Cranial nerve IX (9)
Glossopharyngeal (Guarding, Big)
Motor Functions:
Swallowing control
Salivation
Sensory Functions:
Sensation and taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue
“P” kinda looks like “9” (cranial nerve 9 = Posterior tongue)
Gag reflex - afferent pathway
Test: taste and sensation to posterior 1/3 of tongue, ability to swallow, gag reflex (afferent)
Cranial nerve X (10)
Vagus (Very, Brains)
Motor Functions:
Speech and swallowing
Gag reflex - efferent pathway
Deviation of uvula
“Punching bag” like structure, if you punch from the right (lesion) it deviates to the left
Sensory Functions:
Sensation from organs like the heart and lungs
Main nerve for parasympathetic influence - “rest & digest”
Test: gag reflex (efferent), say “ahh”, rise of uvula when stroked
Cranial nerve XII (12)
Hypoglossal (Horcruxes, Most)
Motor Function:
Moves tongue
Lesion moves tongue to same side of lesion
“Lick your lesion”
Test: tongue protrusion - if injured, will deviate towards side of lesion
Cranial nerve XI (11)
Spinal Accessory (Secret/Ancient, Matter)
Motor Function:
Innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Test: resisted shoulder shrug