GPS
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is GPS
A system to calculate a position on the earths surface
What three factors are needed for GPS (segments)
User segments, Control segments, and Satellite segments
How many orbits
6
What are the 4 GPS control segments
Monitor Stations
Master Control
Ground Antennas
Satellites
Monitor Stations
continually monitor satellite position information
Master Control
calculates orbit and clock information every 15 minutes
Ground Antennas
Broadcast updated navigation information to satellites one or two times a day
Satellites
uses updates in their broadcast
GPS User Segments (4 needs)
Continually listening for broadcasts from satellites
Almanac of satellite positions (calendar of days)
Calculate distance
trilateration to determine position of Earths Surface
Satellite Ranging (equation)
Distance = Speed of light x time distance
Satellite ranging
Measures the distance it takes for a signal to go from satellite to ground
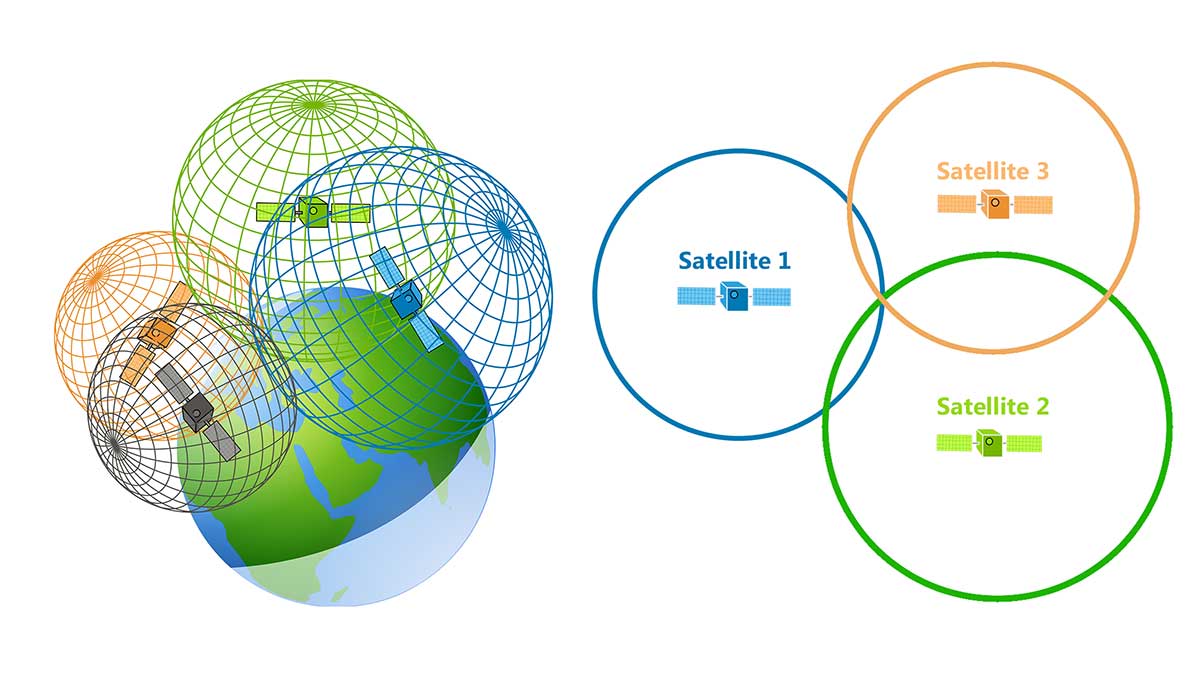
How many satellites are needed?
3, but 4+ are ideal
What accounts for inaccuracies (8)
Atmosphere
Orbit Error
Electronic “noise”
Clock Error
Multi-path error
Receiver Error
Geometric Effects
Operator Error
Atmospheric Delay
The GPS satellite signal bounced around when traveling through the ionosphere and the troposphere
increase time it takes to reach the Earth = altered calculation
Multi-path
The GPS signal is reflected off of an object before it reaches the receiver
Obstruction
Some features of the landscape may block the GPS signals altogether
ex) forests, cities, steep mountains
Positional Dilution of Precision (high vs low)
High PDOP: satellites are close together
Large area of uncertainty
Low PDOP: Satellites widely spaced
Small area of uncertainty
Two methods of improving Accuracy
Differential GPS
Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
Differential GPS
Addition of a base Station into the standard GPS
Base Station
GPS receiver (Base) set up on a precisely known location
Calculates the difference between its true position and the position calculated from satellite signals
Mobile Receivers
The position calculated by the mobile GPS are adjusted according to the differential
WAAS
Continually broadcasting correction information to mobile GPS receivers using standard GPS frequency
3 meters
GPS Data
coordinates position on earths surface
lat/long
Coordinate systems + LONG/LAT (+/-, line names)
Specific points in the system
Lat
East and West
parallels
negative = West
Positive = East
Equator
Prime Meridian
Tropics
Artic Circles
Long
north and south
meridians
Negative = South
Positive = North
Earth degree/tilt
23..5