MLS final comprehensive
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
methods to measure osmolality
osmometer→ freezing point (urine and serum)
LD measurements
LDH-1
Dangerous in the LDH flip - seen in cardiac necrosis
LDH-2
Major fraction in healthy adults
LDH-3
Elevated in pulmonary damage and carcinomas
LDH-4 and LDH-5
Seen in liver and skeletal muscle
LDH-6
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Sign of arteriosclerosis cardiovascular failure
Sign of impending death
Other than viability and abnormal forms, what else do we analyze semen for
Liquefaction, Volume, Motility, Viability, Count, Morphology, pH, acid phosphatase,
fructose (ACID PHOSPHATASE IN RAPE CASES)
semen collection
Collect in sterile container, without
condom, after 3-day abstinence. Keep at
room temperature and deliver to lab
within 1 hour of collection. Keep
specimen at 37 C
Viability of sperm eosin stain
red is dead
Chemistry tests most affected by hemolysis
Potassium and LDH
Electrophoresis protein flow
Albumin, A1 (A1-antitrypsin, alpha-fetoprotein), A2 (haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin), Beta, Gamma
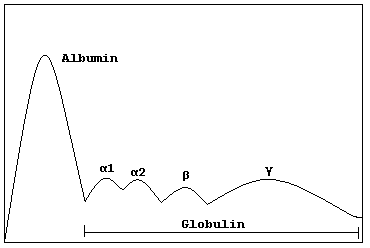
How does electrophoresis flow
cathode to anode
Acid Base reference ranges
pH 7.35-7.45
CO2 45-35
HCO3 22-26
respiratory acidosis
CO2 excess
respiratory alkalosis
CO2 deficient
metabolic acidosis
HCO3 deficit. diabetic ketoacidosis- hyperventilation for compensation
metabolic alkalosis
HCO3 excess. hypoventilation for compensation
how do you screen for cushings disease
cortisol levels, 24 hour urine cortisol, cushings is increased cortisol without normal diurnal variation of cortisol
blood draw times for peak and trough drug levels
peaks drawn 1-2 hours after administration (depends on IV or IM or oral). troughs drawn right before next dose administered.
voided urine
first morning (ideal)
what urine sediments polerize
uric acid and cholesterol
what test can we do to differentiate urine from amniotic fluid
creatinine
transferase enzymes
transaminase, phosphotransferase, hexokinase
lead screening
lead measurement on whole blood, observation of basophilic stippling
method for measuring drugs of abuse
screen by immunoassay, confirm by GCMS or LCMSMS
what is hemoglobin A1C
glycosylated hemoglobin test for diabetes. normal = 5.7-6.4 prediabetes= >6.5
how does lab measure glucose
glucose oxidase→ converts glucose into gluconic acid and H2O2
hexokinase→ reference method
blood gasses hemolyzed
increase potassium and LDH
blood gasses exposed to air
decreased CO2, increased pH, increased O2
what tests are affected if the blood is not spun for hours
glucose, liver function, renal function, serum electrophoresis
prealbumin
transthyretin, appears as faint band on serum electrophoresis used to assess nutritional status
alpha fetoprotein tumor marker
liver, ovaries, and testes
carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
colon, breast, lung
CA 15-1, BR 27-29
breast
CA 125
ovaries
CA 19-9
pancreas
estrogen and progesterone receptors tumor marker
breast
prostate specific antigen (PSA)
prostate
human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) tumor marker
testicular
beta-2-microglobulin tumor marker
multiple myeloma, CLL
what contributes to specific gravity but not osmolality
protein
what protein forms a hyaline cast
tamm horsfall
what antibodies cause intravascular hemolysis
igM
what antibody causes extravascular hemolysis
IgG, Rh, Kell, Duffy, MNS (anti-Ss more than anti-MN)
HDFN ABO
increase spherocytes, weakly positive DAT, delayed jaundice, 1st pregnancy (O mother with A baby typically)
HDFN Rh
increase reticulocytes, strong positive DAT, immediate jaundice, usually not 1st pregnancy (D negative mother D positive baby)
intrauterine transfusions
irradiated, O negative, compatible with mother’s plasma, negative for sickle cell, <7 days old, CMV negative
MUST BE COMPATIBLE WITH MOTHER (antigen negative for corresponding antibody)
Calculation for KB
#cells counted/2000 × 5000 =mL of bleed (/30 to calculate vials)
→ 1 vial even if none seen for procautions
→ round up
Acceptable donors
17 years or older
35.7 or 99.5 temp
systolic 90-180
diastolic 50-100
>12.5 hgb
>38 hct
>110lb
permanent deferrals
Hep B positive, HIV, T. cruzi present or past, drug use, creutzfeldt jakob, babesias
3 year deferral
malaria lived in malaria endemic country
1 year deferral
hep immunoglobulin, tattoo, needle stick exposure, blood exposure, completion of therapy for syphilis or gonorrhea, >72 hours in a correctional facility
tests for a transfusion reaction
DAT, post AB screen, type and screen
acute hemolytic transfusion (intravascular)
immediate- 24 hr, hemolysis, ABO system error, fever, pain at transfusion site and lower back pain
delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction (extravascular)
24 hours- 2 weeks after transfusion, no indication, positive DAT, often due to KIDD
transfusion related acute lung injury
pulmonary edema without cardiac failure, chills, fever, hypotension, caused by antibodies in the plasma to neutrophils or HLA antibodies
GIVE FFP FROM MALE DONOR
febrile reaction
1 degree temperature increase, fever, chills, recipient performed leukocyte antibodies to lymphocyte, granulocytes, and platelets
GIVE LEUKOREDUCED RBC
transfusion associated circulatory overload
pulmonary edema with hypertension
SLOW TRANSFUSION RATE
allergic transfusion reaction
recipient preformed IgE antibodies to donor soluble plasma proteins, mild, rash or hives with itching
GIVE WASH PACKED RBC
anaphylactic transfusion
hypotension, shock, IgA deficient patient with anti-IgA reacting with IgA donor plasma
GIVE IGA DEFICIENT BLOOD PRODUCTS OR DEGLYCERIZED RBC
Antibodies enhanced by enzymes
Kidd, rh, lewis, I, P1
antibodies destroyed by enzymes
Duffy, Kell, MNS
Genotype vs phenotype
genotype→ the observed alleles for an individual at a genetic locus (AA, AO, BB, BO, AB, OO)
phenotype→ observable characteristics (Group A, Group B, Group O, Group AB)
Fisher race
R0 Dce
R1 DCe
R2 DcE
Rz DCE
r dce
r’ dCe
r” dcE
ry dCE
Bombay phenotype (anti-H)
hh, no H antigen
IgM antibodies
pentamer, better at agglutination, cold/body temps, can’t cross placenta
IgG antibodies
monomer, not as good at agglutination as IgM, AHG, can cross placenta
IS AB
anti-… I, M, N, H, Lea, Leb, P1
37 AB
anti-… Rh, D, C, E, c, e
AHG AB
anti-… D, C, E, c, e, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, M, Lea, Leb
HLA system (DR/Bg)
Bg→ class I antibodies, anti-Bgb is an antibody directed against HLA antigens on red cells
Dr→ present peptide antigens, potentially foreign in origin, to the immune system for the purpose of eliciting or suppressing T (helper) cell response that eventually lead to production of antibodies against the same peptide antigen
absorption for patients with WAA
patients own serum and cells, auto absorb the antibody to uncover the alloantibody
IAT vs DAT
DAT→ invivo, what happening on patients red cells
IAT→ in vitro, antibody screen
ABO discrepancies aquired B phenomenon
from bacterial infection
ABO discrepancy subgroups of A
LISS
lowers zeta potential, enhances antibody uptake
PEG
removes water, lowers zeta potential
Lewis neutralization
saliva
P neutralization
hydatid cyst fluid, pigeon egg white
sda neutralization
urine
chido/rodgers neutralization
complement
Anti-I
adult, absent or weak, anti-I is cold reacting, and can mask a clinically significant antibody
anti-i
infant, in cord cells
antibody screening using group O cells
IAT, use group O cells as there are no A or B antigens present
minor crossmatch
patient red cells and donor plasma
major crossmatch
patient plasma and donor red cells
what blood product do we give for chronic granulomatous disease
granulocytes
what blood products do we give for IgA antibodies
IgA deficient blood products
what blood products do you give for anemia
red cells packed
storage conditions blood
1-6 c, frozen >-65 c
FFP conditions
>-18 c
platelet storage
22-24c with constant agitation
expiration date on blood
frozen 10 years, 24 hours after alterations
expiration on FFP
1 year
expiration on platelets
5 days
expiration on cryo
1 year if frozen 24 hr thaw
P antigen associated with
paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
duffy antigen associated with
malaria resistance
A suagr
N-acetylgalactosamine
B sugar
D-galactose
O sugar
fructose
dolichos biflorus
anti-A
ulex europaeus
Anti-D/O
Lab tests to measure platelet function
platelet function assay