policy 210 final
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
value disagreements
people working on a policy might not be focusing on the same values
opposite: opinion policy congruence
empiricial evidence
evidence based on scientific research
based on observation or experience, able to be verified
normative
relating to or determining standards; a "should" thing
heuristic
a rule-of-thumb problem-solving strategy
positive externalities
when something by complete accident creates a benefit to society
negative externalities
when something creates a negative impact
coalition government
a combination of political parties that govern the area
implemented mostly when countries have more than 2 political parties
direct democracy
when individuals have a direct link to the democratic institution in charge of them
referendums!
real figures
data and statistics that have been adjusted for inflation
nominal figures
not adjusted for inflation
per capita figures
figures that are specifically addressed for each individual
per capita GDP, per capita growth rate, etc
indicator
tools used to quantify and evaluate outcomes or performance
test scores, life expectancy, GDP
index
a combination of indicators
Human Development Index (Bhutan)
mean
the average
median
the middle value in an ordered list
standard deviation
the measure of the deviation from the mean
perverse incentive
the unintended consequences of an incentive
human capital
the value of a human life and contributions
productivity
getting the most inputs for the smallest amount of outputs
higher productivity means a higher quality of life
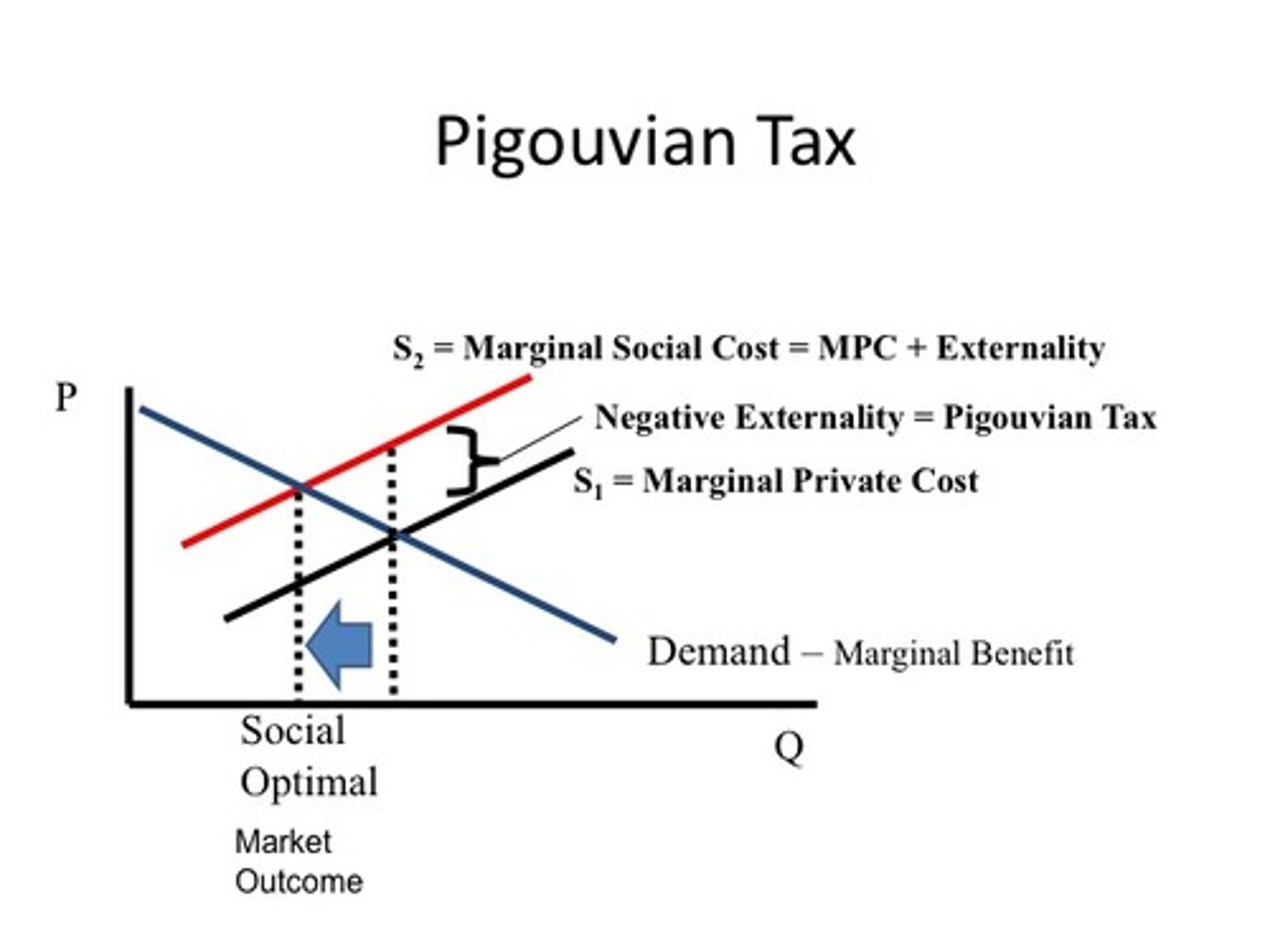
pigouvian tax
a tax that brings the benefit up to the cost
cost benefit analysis
taking into account the cost and then the benefits of a policy option and evaluating it thoroughly
process by which the benefits of a project are tallied up and compared with the costs
cost-effectiveness analysis
a type of evaluation research that compares program costs with actual program outcomes
ranks policies based on costs for achieving some defined objective
value of statistical life
how much money should be assigned to a value of a life
changes depending on industry, stage of life, etc.
institutions
stable, long lasting organizations that help to turn political ideas into policy
laws, organizations, and unwritten rules that make public policy better
public institutions
have the capacity to design/operate/enforce consistent policies
the policy process
identify a social goal
problem diagnosis
identify the institution for action
evaluate options
implement and monitor
redistributive policy
policy that moves wealth that has been distributed unevenly back to where it is even
distributional effects
impact of a policy change on different groups
distributive policy
provide goods and services to the majority with taxpayer money
regulatory policy
encourage some behaviors and discourage others
constituent policy
creation and running of government agencies
institutions!
market failures
when goods and services are not distributed equitably and efficient
reasons for market failures
public goods are non exclusive
externalities
natural monopolies
information asymmetry
goal of public policy
defend people and property while keeping order
support/make effective non-governmental actors
promote thriving
collective-action problems
each individual is acting rationally but the outcome is bad, creating collective irrationality
sheep pasture and open fishing
using up common pool resources
TRAGEDY OF THE COMMONS
pareto-efficient
when changing allocation is not able to make any individual better without making one worse off
deadweight loss
when the loss of welfare to 1 party is greater than the gain by another - i.e. it doesn't make any sense to do this
principal agent problems
1 party, "principle" expects another party with different motivations, the agent, to act in a way consistent with the principal's goals but doesn't monitor their behavior
dominant strategy
what will produce the best outcome for them - the one that people will turn to most often
absolute figure
present in a unit of measure
relative figure
proportion of another quantity - relative to another value
percentage chance
extent to which a value has changed relative to the original
new - old / old
percentage point change
75% to 50% - 25 percentage point decrease
opportunity cost
what you have to give up to get what you want
positive analysis
analysis on data sans opinions
normative analysis
analysis on what should be done - best practices memo
constitutional actors
representatives of unique populations in govt
regional (House), state (Senate), national (President)
bureaucracy
non elected people responsible for carrying out policies
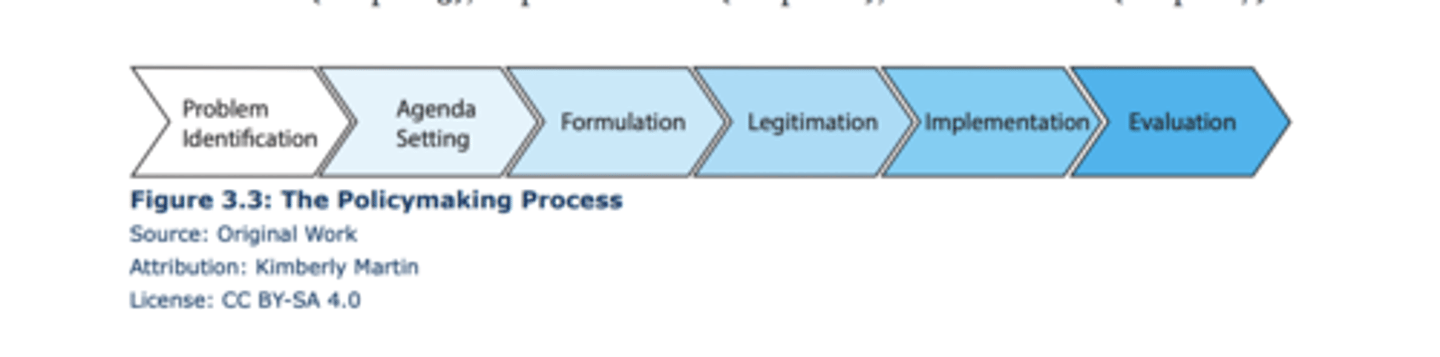
stages model of public policy
problem ID
agenda setting
formulation
legitimation
implementation
evaluation
will not necessarily be linear or in that order
models
simplified explanations of how things work
often can't model complexity
a very common one is supply and demand
utility
the public policy term for units of well-being, units of utility
moral hazard
individuals/firms are protected so they act with less caution and make a bad outcome more likely
adverse selection
individuals use private information to put themselves in or out of a market transaction
coase theorem
externalities will be corrected by the market if:
1) property rights are clearly defined
2) transaction costs are low
earmarks
mechanism by which members of congress insert money into projects
Alaska's bridges to nowhere
logrolling
get their buddies to support a bill so that they can get it earmarked
plurality
person with the most votes wins (regardless of a majority)
arrow's theorem
3+ options being considered, a collective decision cannot be made without violating:
1) unrestricted domain
2) completeness
3) transisvity
4) pareto optimality
5) nondictatorship
6) independence of irrelevant alternatives
gatekeepers
usually committee chairs - can make or break bills
rent-seeking
when political interests use govt power to get an economic advantage
economic rent
benefit can get erased by competition
marginal cost
cost of producing one additional unit of a good or service
marginal sale
the market price = benefit to the consumer
market equilibrium
where marginal costs = marginal benefits
optimal product prices
social marginal cost = social marginal benefit
public goods
nonrival and nonexclusive
variance
how far data points lie from the mean
standard deviation is the square root of the variance
68-95-99.7 rule (central limit theorem)
confidence interval
likelihood that the population mean lies within a certain distance of the sample mean
95%, 99%: common levels of confidence
future value
a value that a sum will grow to with interest
present discounted value
using the discount rate to bring a future projected value down to current times' values
market system
when sellers and buyers agree on transaction terms
central planning
when the govt is in charge of handling everything - hard to udo and goes sour fast
elasticity
how much supply and demand will change in response to a change in price
inelastic: if it doesn't change
sensitivity analysis is very similar
marginal product of labor
incremental output produced by 1 additional 'unit' of labor
absolute advantage
they are better at doing something than others
comparative advantage
when an entity has the lowest opportunity cost of producing that good or service
stratified sampling
a variation of random sampling; the population is divided into subgroups and weighted, taking SRS of each strata
cluster sampling
divide into clusters and take all of the people from that cluster
type 1 error
null hypothesis is rejected when true
type 2 error
null hypothesis is accepted when it is false
agenda universe
all of the possible topics for discussion
systemic agenda
topics currently on the minds and discussion of policymakers
institutional agenda
issues actually up for consideration
a bill and committee have been created
decision agenda
actively making a plan to vote on it
problem stream
tells us something is wrong
relies on indicators (extreme fluctuation indicates a problem)
policy stream
proposals developed to solve an issue
political stream
change in electoral/public opinion leads to reform
focusing events
sudden and rare events that draw media and public attention to harm
economic cost/benefit
direct tangible gain or loss (pecuniary)
noneconomic cost/benefit
intangible gain or loss
use value
the way that a product/commodity can be used directly - recreation, commercial purposes
nonuse value
intangible - attach value to a resource
willingness to pay
the price of something should be around the price that consumers are willing to pay for it
hedonic market analysis
uses regression analysis to isolate the value of a cost/benefit
policy design
process by which policies are designed through technical analysis and the political process
equity
redistributive policies that move resources equitably
efficiency
get the biggest bang for your buck
rational comprehensive model
considers all options, does a CBA, chooses wisely
incrementalism
policies are formulated to continue previous or make only gradual changes over time
garbage-can model
decision making is irrational + uncertain - conflict over goals and ambitions
throw a bunch of stuff at the wall and see what sticks