Condensation polymerisation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is condensation polymerisation?
A reaction where monomers with two different functional groups join together to form a polymer and a small molecule (often water) as a by-product.
How is condensation polymerisation different from addition polymerisation?
Condensation: two types of functional groups, small molecule produced
Addition: one monomer type (alkene), no small molecule produced
What small molecule is often produced in condensation polymerisation?
Water (H₂O).
What types of monomers are needed for condensation polymerisation?
Monomers with two functional groups, e.g., dicarboxylic acids and diols.
What is a polyester?
A polymer made by condensation polymerisation of a dicarboxylic acid and a diol (an alcohol with two –OH groups).
What is the functional group in polyesters?
–COO– (ester link).
What are the products of a polyester condensation reaction?
A polyester and water.
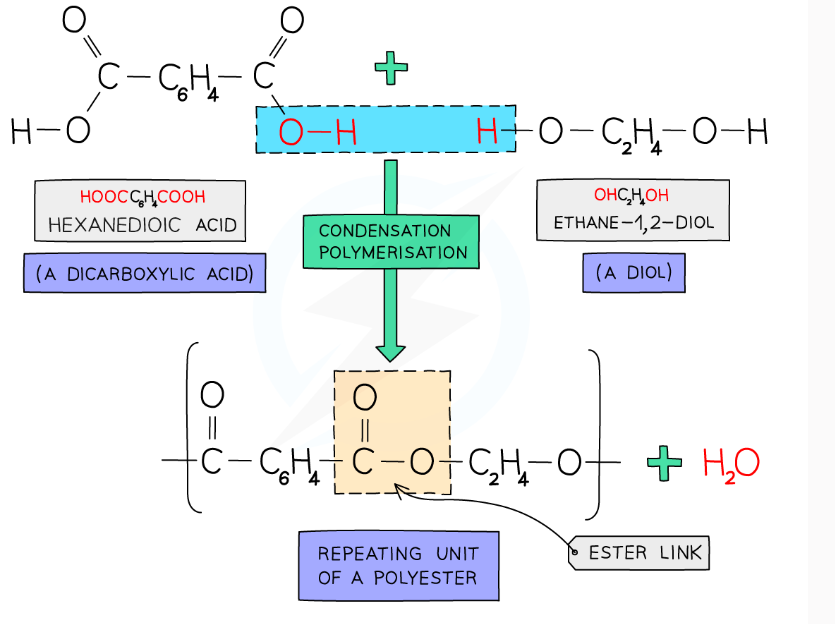
explain how a polyester is formed from condensation polymerisation and how to draw the repeat unit of the polymer
the OH from the COOH joins with the H from the diol OH to form water. This happens with each COOH and OH group from the monomer. From what is left we can deduce the repeat unit of the polymer
start by rewriting what we have left over and straightening the double bonds
we then draw a bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms, and the ester linkage is the COO functional group within the repeating unit that forms an L shape
- there’ll be ester linkage formed from either end of this structure with another monomer
to draw the repeat unit add brakcets to the end with continuation bonds and add aqn ‘n’ to the outside of the brackets
for every ester link formed one molecule of ______ is released
water
why are polyesters biodegradable
- because other microorganisms can break down the ester linkage
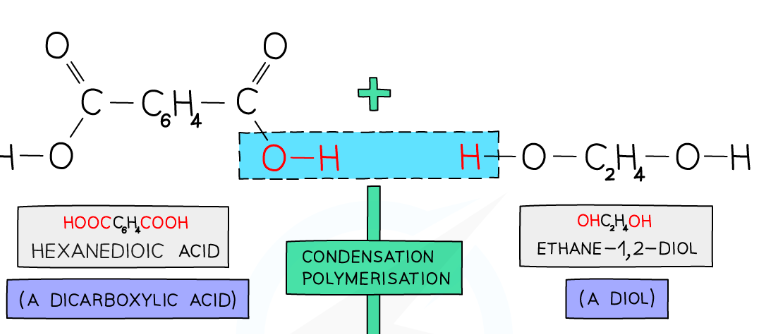
draw the repeat unit of the product if this condensation reaction
.