Carboxylic acids
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What do carboxylic acids contain?
A carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (O-H)
The carboxyl group will always be at the end of the molecule
How do you name carboxylic acids?
Find the longest carbon chain and end in -oic acid
The carbon on the carboxyl group is always carbon 1
How do you name a carboxylic acid that has COOH groups on both ends of the chain?
Ends in -dioic acid
Are carboxylic acids strong or weak acids?
Weak acids
How do carboxylic acids dissociate?
They dissociate partially, as they are weak acids, to form a H+ ion and a carboxylate ion
What do carboxylic acids form when they react with carbonates?
A salt, CO2 gas and water
What is the solubility of carboxylic acids in water like?
The smaller carboxylic acids (up to C4) dissolve in water, but after this the solubility rapidly reduces.
How do you form esters?
Esterification-by reacting alcohols with either carboxylic acids (and a sulphuric acid catalyst) or acid anhydrides
What’s the functional group for esters?
-COO-
How are esters named?
In 2 sections:
The first bit is named from the alcohol used
The second bit is named from the carboxylic acids (-oate)
Give 3 uses of esters and why they’re suitable
Perfumes and food flavourings - may have sweet smells
Solvents - they are polar, also have low bp + evaporate easily
Plasticisers - make plastics more flexible during polymerisation
How are esters hydrolysed?
Using water but can be sped up using an acid (acid hydrolysis) or a base (base hydrolysis)
How does acid hydrolysis of esters work?
Use a dilute strong acid (H2SO4 or HCl) under reflux to split an ester into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
How does base hydrolysis of esters work?
Use a dilute base (eg NaOH) under reflux to split an ester into into a carboxylate ion and an alcohol
What is the advantage of base hydrolysis?
Reaction is not reversible so goes to completion due to neutralisation-more product formed
What is the difference between oils and fats?
Oils are liquid at room temperature, fats are solids
Fats are usually saturated, oils are not
How are fats and oils hydrolysed and what do they form?
They are hydrolysed by heating them with NaOH.
They form glycerol and sodium salts (soap)
How does soap do its job?
The polar COO- end is hydrophilic and mixes with water.
The long non-polar hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic and mixes with grease.
This allows the grease and water mix and be washed away.
What is biodiesel?
A mixture of fatty acids made from methyl esters
How is biodiesel made?
By reacting oils (eg vegetable oils) with methanol (KOH catalyst)
Write the reaction which forms biodiesel
Oil + Methanol + (KOH catalyst) → glycerol + methyl ester
What’s the functional group for acyl chlorides?
COCL
How are acyl chlorides named?
Find the longest carbon chain
Add -oyl chloride on the end
The carbon on the acyl group is always carbon 1
What 4 substances do acyl chlorides react with?
Water
Ammonia
Alcohol
Primary amines
Write the reaction for an acyl chloride and water
Acyl chloride + Water → carboxylic acid + HCl(g)
Write the reaction for an acyl chloride and ammonia
Acyl chloride + Ammonia → Amide + HCl(g)
Write the reaction for an acyl chloride and an alcohol
Acyl chloride + Alcohol → Ester + HCl(g)
Write the reaction for an acyl chloride and a primary amine
Acyl chloride + Primary amine → N-substituted amide +HCl(g)
What are acid anhydrides?
Molecules made from 2 carboxylic acids that are the same
How are acid anhydrides named?
Know the carboxylic acids it is made from
Remove -acid and add -anhydride on the end
Are acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides more reactive?
Acyl chlorides
Write the reaction for an acid anhydride and water
Acid anhydride + Water → 2x Carboxylic acid
Write the reaction for an acid anhydride and ammonia
Acid anhydride + Ammonia → Amide + Carboxylic acid
Write the reaction for an acid anhydride and an alcohol
Acid anhydride + Alcohol → Ester + Carboxylic acid
Write the reaction for an acid anhydride and a primary amine
Acid anhydride + Primary amine → N-substituted amide + Carboxylic acid
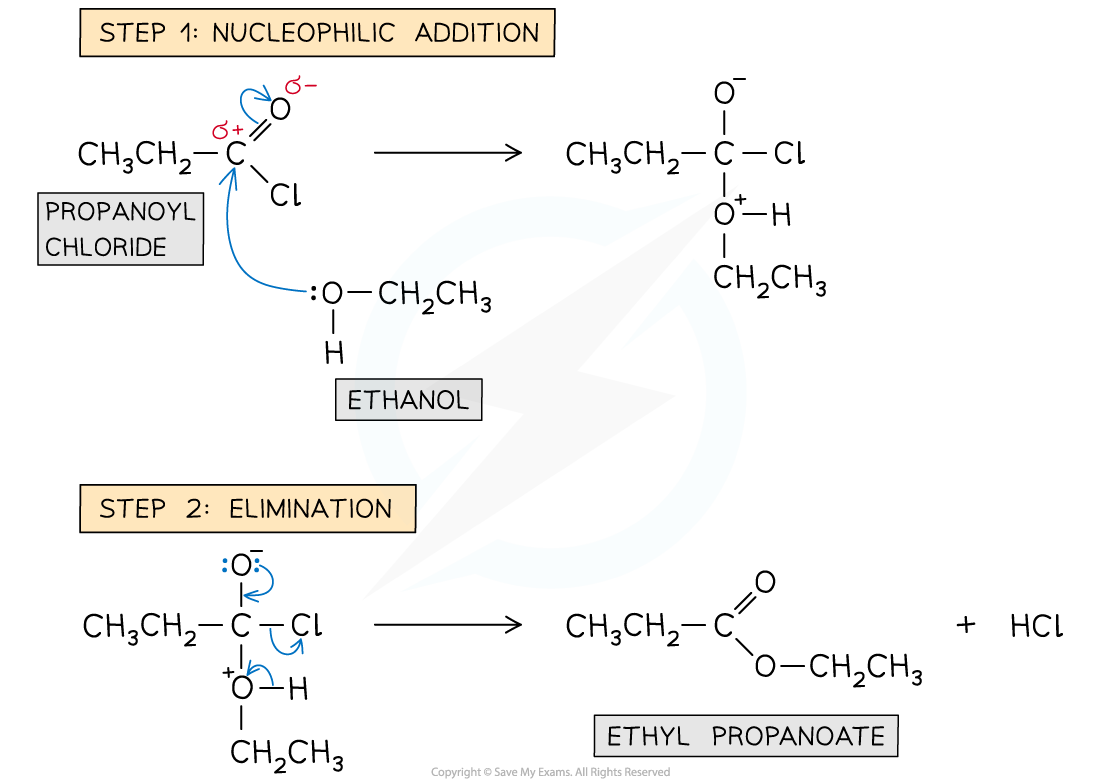
What type of reaction does an acyl chloride undergo and why?
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Because they have a strong delta + charge on the carbon which is susceptible to attack from nucleophile
Draw the mechanism for ethanol reacting with propanoyl chloride
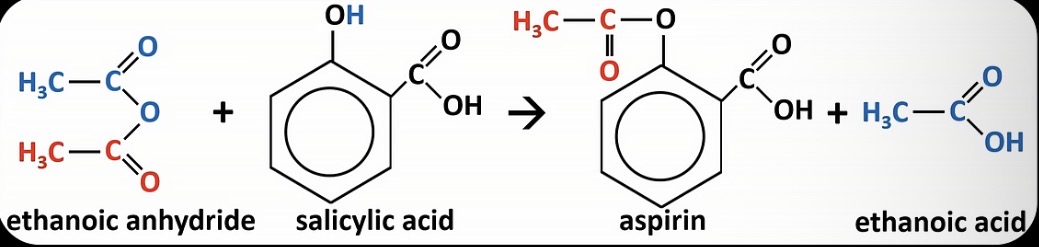
What is aspirin?
An ester made by reacting ethanoic anhydride or ethanoyl chloride and salicylic acid
Give 4 reasons why ethanoic anhydride is used instead of ethanoyl chloride in industry to make aspirin
It is safer as it is less corrosive
It is cheaper
It is safer as it does not produce harmful HCl gas
It is safer as it does not react vigorously with water
Show the reaction that forms aspirin
What is reflux and when and why is it used?
A technique that is used when you want to heat volatile liquids
It allows strong heating without losing volatile reactants and products as they evaporate and condense back into the flask
What pieces of equipment are use when heating under reflux and why are they suitable?
Liebig condenser has cold water running through the wall. Hot evaporating substances turn back into a liquid when they hit the cold condenser and return back to the round bottomed flask to react further
Heating is done via a water bath or electric heater called a mantle as the liquids are flammable so this is safer than using a naked flame
When is distillation used?
When we want to separate substances with different boiling points
When is redistillation used?
When we want to purify volatile substances which can be purified further using separation