IB BIO SL MIDTERM 2025
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Osmosis Definition
the passive movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane, from a region of low concentration to high concentration, no energy required
Osmosis in cells (Hypertonic solution)
solution has a higher solute concentration than cell
water moves out
plant = plasmolysis
animal = shrinks
Osmosis in cells (Hypotonic solution)
solution has a lower solute concentration than cell
water moves in
plant = turgid
animal = burst (lysis)
Osmosis in cells (Isotonic solution)
same solute concentration in cell and solution
no net movement of water
How Osmosis Happens
Aquaporins - water can pass through phospholipid bilayer (slow), but mostly passes through protein channels (aquaporins) (fast)
Real-World Examples
plant cells taking up water from soil
Polarity of Water
Polar molecule
oxygen carries a partial negative charge
hydrogen carries a partial positive charge
this allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonding
form between + hydrogen of one water molecule and - oxygen of another
individually weak, but collectively strong
cohesion
attraction between water molecules
causes by hydrogen bonding
results in: high surface tension (water droplets)
important for: transport of water in plans (xylem)
adhesion
attraction between water and other substances
water stick to polar/charged surfaces
important for: water moving along xylem walls in plants (capillary action)
thermal properties
high specific heat capacity - water has to absorb lots of heat before its temperature increases
results in: stable temperatures in organisms
high latent heat of vaporization - large amount of energy needed to evaporate water
used in: sweating to cool organisms
solvent properties
excellent solvent
dissolves - ionic substances, and polar molecules
forms hydration shells around ions
important for: transport of substances in blood and cytoplasm, and biochemical reactions
water as a medium
most biochemical reactions occur in aqueous environments
allows molecules to move and collide for reactions
What is DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
stores genetic information
found in: nucleus, mitochondria/chloroplasts, nucleoid region
Nucleotides
building blocks of DNA/RNA
made up of
phosphate group
deoxyribose sugar
nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous bases
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine → uracil (RNA)
sugar-phosphate backbone
nucleotides join by phosphodiester bonds (between phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next)
strong covalent bonds
double helix
2 polynucleotide strands
twist to form a double helix
backbone is on the outside
bases face inwards
complementary base pairing
A→T(2 hydrogen bonds)
C→G(3 hydrogen bonds)
antiparallel structure
2 strands run in opposite directions
strand 1 - 5→3
strand 2 - 3→5
stability of DNA
hydrogen bonds allow strands to separate
phosphodiester bonds give strength and stability
double helix protects base sequence
Prokaryotic cells
no nucleus
DNA is free in cytoplasm
ex. Bacteria
Eukaryotic cells
has nucleus
DNA enclosed in a nuclear envelope
ex. animal, plant, fungus
ribosomes
pro - 70s
euk - 80s
DNA and genetic material
prokaryotes - single circular chromosome
in nucleoid region
may have plasmids
no histone proteins
eukaryotes - multiple linear chromosomes
inside nucleus
associated with histones
organelles
prokaryotes - not membrane bound
eukaryotes - membrane bound
metabolism and respiration
pro - on cell membrane
euk - in mitochondria
cell division
pro - binary fission
euk - mitosis (meiosis)
Paramecium
unicellular eukaryote
found in freshwater
protists
all life functions in one cell
nutrition
heterotrophic
feeds on bacteria and small organisms
food enters in oral groove
digestion occurs in food vacuoles
movement
uses cilia
allows: movement through water
directing food towards oral groove
reproduction
asexual reproduction (binary fission)
sexual reproduction (conjugation)
involves genetic exchange
results in genetic variation
Polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) linked by glycosidic bonds
they are carbohydrates used for energy storage/structural purposes
they are macromolecules, insoluble in water, often branched or unbranched
formation
condensation reactions
longer chains = polysaccharides
broken down my hydrolysis (addition of water) to release monosaccharides for energy
main polysaccharides
starch (m = glucose) - sometimes branched - energy storage (plants) - ex. potatoes
glycogen (glucose) - highly branched - energy storage (animals) - liver
cellulose (glucose) - unbranched - structural support (plant walls)
chitin (N-acetylglycosamine) - structural support in fungi cell walls
more branched =
faster energy release
humans cannot digest
cellulose
functions
energy storage - starch + glycogen
branched allows for rapid hydrolysis to glucose
structural support - cellulose + chitin
straight chains form strong fibers
amylose vs. amylopectine
amylose = unbranched = slow energy release
amylopectine = branched = rapid energy release
both are forms of startch
Condensation reaction
two molecules join together
one water molecule is released
covalent bond is formed
build polymers from monomers
in carbohydrates
forming a disaccharide
two monosaccharides join together
forms glucosidic bonds
water is released
condensation chart
carbohydrate - monosaccharides - glycosidic bond
proteins - amino acids - peptide bond
lipids - fatty acids + glycerol - ester bond
nucleic acids - nucleotides - phosphodiester bond
Fatty acids
long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group at one end
key components of lipids
used for energy storage, insulation, and membrane stucture
types
saturated - no carbon-carbon double bonds
carbon atoms are fully saturated with hydrogen
straight chains - pack tightly
solid at room temp
unsaturated - contains one or more C=C double bonds
fewer hydrogen atoms
bent chains
liquid at room temp
unsaturated types
monounsaturated - one carbon=carbon double bond
cause a single bend
polyunsaturated - two or more double bonds
multiple bends
increase membrane fluidity
cis vs trans
cis - hydrogen atoms on same side of double bond
creates a kink
most natural unsaturated fats
trans - hydrogen atoms on opposite sides
chain is straighter
often artificially produced
linked to health risks
structure - feature
saturated/straight - pack tightly - solid fats
unsaturated/kinked - pack loosely - liquid oils
more double bonds - greater membrane fluidity
cis vs trans - kinked vs straight structure
peptide bond
covalent bond that links 2 amino acids
forms between - carboxyl group (COOH) and the amino group (NH2)
formed by condensation reaction
releases one water molecule
picture

formation
2 amino acids align
OH is removed from carboxyl group
H is removed from amino group
OH + H = H2O
remaining atoms form peptide bond
dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins
dipeptide - 2 amino acids
polypeptides - many amino acids
protein - one or more polypeptide chains folded into a functional shape
importance
allows formation of - enzymes
hormones
structural proteins
sequence of amino acids determines protein structure and function
why membrane transport needed
membranes are selectively permeable
transport allows cells to obtain nutrients, remove waste, maintain internal conditions (homeostasis)
diffusion
movement from high to low concentration
no energy needed
occurs for - small, non polar molecules (oxygen)
facilitated diffusion
passive
uses channel or carrier proteins
for - ions, polar molecules (glucose)
moved down the concentration gradient
osmosis
diffusion of water
through partially permeable membrane
from high water potential to lower water potential
active transport
moves substances against concentration gradient
uses carrier proteins
requires ATP
endocytosis + exocytosis
endo - substances enter cell in vesicles
required ATP
exo - vesicle fuses with membrane to release substances
used for secretion
structure - function
hydrophobic bilayer - blocks ions/polar molecules
channel proteins - allows ions to pass
carrier proteins - change shape during transport
ATP - provides energy for active transport
fluid mosaic model
fluid - phospholipids and proteins can move sideways
mosaic - proteins are embedded throughout the membrane

phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic (polar) phosphate head
hydrophobic (non-polar) fatty acid tails
heads face aqueous environments
tails face inwards
membrane proteins
integral - spans the bilayer, inside
functions: transport (channel, carrier) , receptors, enzymes
peripheral - attached to membrane surface, outside
functions: structural support, cell signaling
cholesterol
located between phospholipids
regulated membrane fluidity
not become too rigid at low temps
prevents excessive fluidity at high temps
carbohydrates
glycoproteins (protein + carbohydrate)
glycolipids (lipid + carbohydrate)
functions: cell recognition, cell adhesion, receptor sites
found on external surface only
membrane fluidity factors
unsaturated fatty acids → increase fluidity
shorter fatty acid chains → increase fluidity
higher temperature → increase fluidity
cholesterol → stabilizes fluidity
phospholipid
made up of - glycerol
2 fatty acid chains
1 phosphate group
nucleus
contains genetic material
controls gene expression
controls cell activities (protein synthesis)
nuclear envelope
double membrane
continuous with the rough ER
separates nuclear contents from cytoplasm
function: protects DNA
controls movement of substances in and out
Nuclear Pores
protein-lined openings in nuclear envelope
allows selective transport of: mRNA
Ribosomal subunits
proteins
active transport is often involved
chromatin
DNA + histone proteins
condenses into chromosomes during cell division
nucleolus
not membrane bound
dense region in nucleus
function: synthesizes rRNA
assembles ribosomal units
large nucleolus = high protein synthesis
structure-function
double membrane - protects DNA
nuclear pores - regulate gene expression
chromatin organization - controls transcription
nucleolus - ribosome production
stem cells
undifferentiated cell that
can divide by mitosis
can differentiate into one or more specialized cell types
potency
range of cell types a stem cell can differentiate into
types of stem cells
totipotent
pluripotent
multipotent
totipotent stem cells
can differentiate into all cell types
can form a whole organism
ex. zygote
pluripotent stem cells
can differentiate into almost all cell types
cannot form a whole organism
found in: embryonic stem cells
multipotent stem cells
can differentiate into a limited range of cell types
found in adult tissues
ex. bone marrow stem cells → blood cells
Embryonic vs adult stem cells
F - E - A
potency - pluripotent - multipotent
source - embryo - adult tissue
SA:Vol important?
exchange of substances occurs across the cell surface
metabolic reactions occur inside the cell volume
high SA:Vol allows faster and more efficient diffusion
small or large?
smaller cells have a higher SA:Vol ratio
allows uptake of nutrients
efficient removal of waste
fast cell division and metabolism
what happens as cells get larger
volume increases faster than surface area
SA:Vol decreases
diffusion becomes less efficient
cells will need to divide
activation energy
the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction
break existing bonds
allow new bonds
energy difference between reactants and the peak (higher peak = higher activation energy)
role of enzymes
lower activation energy
do not change: overall energy released, products of the reaction
increase reaction rate
how they lower activation energy
form enzyme-substrate complexes
correctly orient substrates
strain bonds
provide an alternative reaction pathway
why it matters in cells
many metabolic reactions have high activation energy
without enzymes, reactions would be to slow at body temp
enzymes allow reactions to occur at 37 degrees
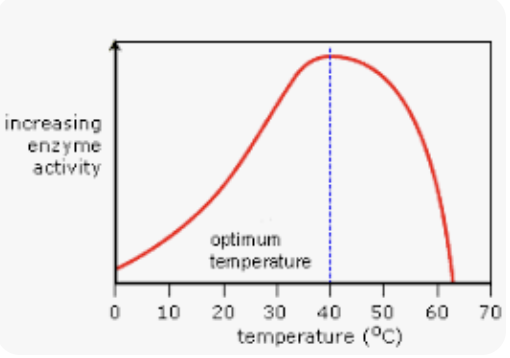
enzyme temp effects
low - reaction rate is slow
increasing - kinetic energy is increasing
reaction rate increases
optimum temp - humans = 37c
high temp - active site changes shape
enzyme becomes denatured
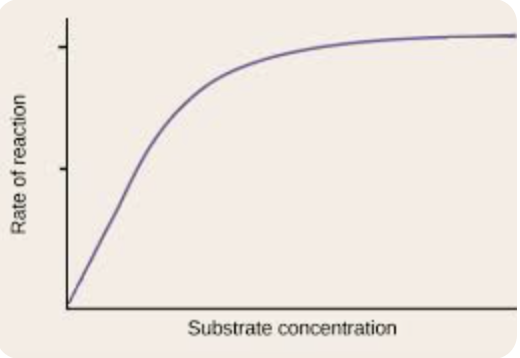
effect of substrate concentration on enzymes
low - less substrate molecules available
rate of reaction is low
increasing - more frequent collisions
rate of reaction increases
high - all enzyme active sites are occupied
rate reaches a max and stops increasing
anaerobic respiration
breakdown of glucose without oxygen to release energy in form of ATP
releases less energy than aerobic respiration because glucose is not fully broken down
in animals
glucose → lactic acid + ATP
occurs in muscle cells
happens during vigorous exercise
effect: causes muscle fatigue, leads to oxygen dept
in yeast and plants
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide + ATP
called fermentation
carbon dioxide causes bread to rise (waste product)
oxygen dept
the extra oxygen required after exercise to break down lactic acid
transported to liver
compare aerobic and anaerobic
F - A - AN
oxygen - required - not required
ATP yield - high - low
Products - CO2 and H2O - lactic acid/ethanol
location - mitochondria - cytoplasm
Taq Polymerase
a heat-stable DNA polymerase enzyme used in the polymerase chain reaction
why is it needed in PCR
high temps (95c) to separate DNA strands
lower temps for primer binding and DNA synthesis
Taq does not denature at high temps (found in hot water springs)
role of taq
extends DNA strands by adding free nucleotides to primer and synthesizing new DNA strands
optimally works at 72c
advantages
does not need to be replaced after each cycle
allows rapid/efficient DNA amplification
makes PCR practical
DNA profiling
a technique used to identify individuals by analyzing specific regions of DNA that vary between people
steps
extract DNA from cells
apply STR’s using PCR (taq)
separate DNA fragments by size using gel electrophoresis
visualize bands to produce a DNA profile
compare profiles
Gel electrophoresis
dna is negatively charged
moved towards the positive electrode
smaller fragments move faster and further
patter of bands = DNA profile