Linear Algebra
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
solution set
Set of vectors that satisfy a condition
if W is a subspace in Rn ,
W⟂ is also a subspace of Rn
(W⟂)⟂ = W
dim(W) + dim W⟂ = n
Row(A)⊥=
Nul(A)
Nul(A)⊥=
Row(A)
Col(A)⊥=
Nul(AT)
Nul(AT)⊥=
Col(A)
when 2 vec orthogonal
when the dot product of 2 vect is 0
if A is n x n, then the geometric multiplicity is alway…
less than or equal to the algebraic multiplicity
if A is n x n, then the Algebraic multiplicity is alway…
more than or equal to the geometric multiplicity
Characteristic polynomial equation
f(λ)=
det(A- λI) or
λ2−Tr(A)λ+det(A) (best for large Matricies)
finding the inverse of any size matrix A
write the matrix and then the standard basis vectors for the same dimension right next to it
RREF the matrix, and mimic all the steps on the standard basis vector matrix
subspace of a matrix m x n
Rm
A matrix is invertible if
Det(A) != 0 aka matrix is 1-1 and onto
Properties of Projection Matrices
Let W be a subspace of Rn, define T:Rn→Rn by T(x)=xW, and let B be the standard matrix for T. Then:
Col(B)=W.
Nul(B)=W⊥.
B2=B.
If WA={0}, then 1 is an eigenvalue of B and the 1-eigenspace for B is W.
If WA=Rn, then 0 is an eigenvalue of B and the 0-eigenspace for B is W⊥.
B is similar to the diagonal matrix with m ones and n−m zeros on the diagonal, where m=dim(W).
Properties of Orthogonal Projections
Let W be a subspace of Rn, and define T:Rn→Rn by T(x)=xW. Then:
T is a linear transformation.
T(x)=x if and only if x is in W.
T(x)=0 if and only if x is in W⊥.
T◦T=T.
The range of T is W.
geometric multiplicity
dim(eigenspace), aka # of lin ind eigenvector
algebraic multiplicity
the amount of times the eigenval appears in a sol when sol for the characteristic polynomial
ex:
f(λ) = (λ + 3) (λ + 3)
λ has an algebraic multiplicity of 2 for the sol -3
Trace of a matrix
the sum of the diagonal entries of a matrix
rank Nullity theorem
for any consistent system of linear equations, (dim of column span)+(dim of solution set)=(number of variables).
nullity
dimension of the null space
column space
the span of the columns of a matrix
span
Homogeneous system
When b = 0 in Ax = b, if there is >1 sol, there are infinite sols.
vector equation
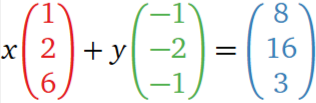
matrix equation
Ax = b
linearly independent
There is a pivot in each column
Ax = 0 is the only sol, has no free vars
Linear Dependents
rows > col (m>n) and/or
one of the vec in the set is a 0 vec
subspace
a subset of vectors that is:
not empty
closed under addition
closed under scalar multiplication
null space
the space containing the col of vectors (x in Ax = b) that make b = 0
are always subspaces
injective transformation (1-1)
transformation such that every y (point in the new transformed set) has at most 1 corresponding x from the untransformed set (T(x) = y)
Injective transformation (1-1) properties
Each vector in V has at most ONE corresponding vector in W
There is one pivot in every column and row
Not all vectors in W have to be a correspondent in V
must have at least as many rows as columns: m >= n
Sets must be linearly Independent
surjective (onto)
transformation where every point in the new transformation has at least 1 corresponding val in the old transformation
surjective (onto) properties
range of A is in T (all points in T have to be connected to some A)
Multiple Vs in A can be mapped to 1 point in T
There is a pivot in every row
transformation no-no’s
have a var being added to a const
have one or more of the resulting vars be a const
have one or more of the resulting vars be an absolute power
basis
the min # of vectors needed to get the same span as the subspace
ex of subspaces: sol set, column space, etc
the vectors in a basis are lin indep
found by writing the parametric form of a matrix and/or by using a linear combination of the vectors found using parametric form
Co-domain
the subspace of the vectors after they are transformed
rank
The rank of a matrix A, written rank(A), is the dimension of the column space Col(A)
dimension
The # of linearly independent vectors in the basis of a matrix
ex: if the sol set of a matrix is a plane in a 3D space, the dim is 2
trivial solution
the 0 vector
:
“such that”
∃
“there exists”
Closed under addition
If u and v are in V, then u+v is also in V.
unique sol
there is only 1 x in Ax=b that gets u a specific b
Closed under scalar multiplication
if u is in V, then uc, where c is any # in R1, is also in V
you can check this by multiplying a vector by a random real # and seeing if it is still in V
if there is even one situation where the system is not closed under addition, then the whole system is not closed
Invertible matrix
a square matrix transformation that can be multiplied by another square matrix to get the identity matrix
A matrix is invertible if:
matrix is square
A and B are commutable
commutable
the product of 2 matrices is the same no matter the order
invertible matrix theorem
All the following statements about the matrix transformation T(x)=Ax where T:Rn → Rn, are true
A is invertible.
T is invertible.
Nul(A)={0}.
The columns of A are linearly independent.
The columns of A span Rn.
Ax=b has a unique solution for each b in Rn.
T is one-to-one and onto.
det(A) and det(T) ≠ 0