OCR Gateway Chemistry: C4
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is another name for Group 1?
Alkali metals
What is the electronic structure of Group 1 metals?
1 electron in outer shell so forms +1 ion
Describe reactivity in group 1
Reactivity increases down the group.
This is because the atoms are larger further down the group and it is easier for the outer electron to be lost. The atom is oxidised more easily
What are some physical features of Group 1 metals? (3)
They are solids but soft and easy to cut
They are shiny but tarnish quickly
They have typical metal properties (conduct electricity, malleable etc.)
Describe the reactions of Group 1 metals
They react rapidly with air and water so are stored under oil
React with water to form an alkali and all follow the same pattern
2Na(s) +2H20(l) -> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Describe the melting point of Group 1 metals
Melting point decreases down the group
What are features of Group 0 gases? (Melting point, reactivity, state of matter)
-Non-metal gases
-Weak forces of attraction between atoms so they have low melting and boiling points
-Melting point increases down the group as atoms get larger so there is a stronger attraction between the atoms
-Inert (unreactive)
What is another name of Group 0
Noble gases
Describe atomic structure of Group 0 gases
-Exist as monatomic single atoms
-8 electrons on outer shell so very unreactive
What is an alternative name for Group 7 atoms?
Halogens
What are features of Group 7 atoms? (properties, melting point, reactions)
Typical non- metal properties (don't conduct electricity, brittle when solid)
Melting point increases down group as molecules get larger so they have stronger intermolecular forces
They react vigorously with Group 1 metals to produce salts
Describe reactivity of Group 7
Reactivity decreases down group.
This is because atoms are larger further down the group and it is harder for them to gain an outer electron. The atom is reduced less easily.
Cl2 +2e- -> 2Cl-
Describe atomic structure and forces of group 7
- 7 electrons in outer shell so form -1 ion
- Exist as diatomic molecules
- Strong covalent bond within the molecule but weak intermolecular forces between molecules so low melting/boiling point
What is the colour and state of fluorine?
Pale yellow, Gas
What is the colour and state of chlorine?
Pale green, gas
What is the colour and state of bromine?
Orange-brown, liquid
What is the colour and state of iodine?
Grey, solid
What is a halide?
A compound containing a halogen as an ion e.g. NaCl,HBr
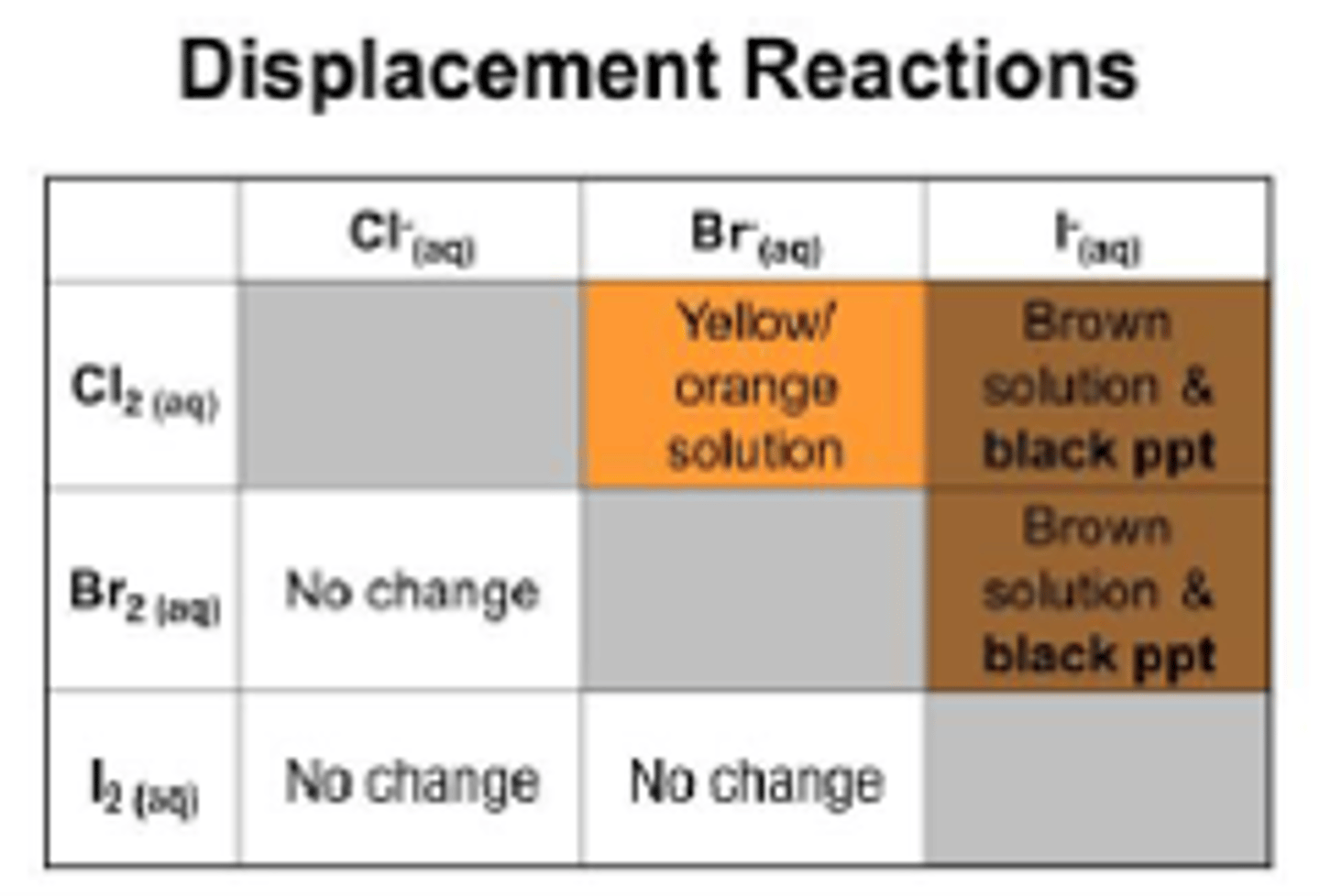
How do halogen displacement reactions work?
A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive hallogen from it's solution if it is a halide
Show an example of bromine being displaced by chlorine
Cl2 (aq) +2NaBr (aq) -> 2NaCl (aq) + Br2 (aq)
Show a half equation for the displacement reaction between chlorine and bromine
Reduction: Cl2 (aq) + 2e- -> 2Cl-
Oxidation: 2Br- -> Br2 +2e-
Show an ionic equation for the displacement reaction between chlorine and bromine
Cl2(aq) + 2Br- -> 2Cl- + Br2
What can you see in a halogen displacement reaction?
What are the features of transition metals
-Typical metal properties (conduct electricity, strong, malleable etc) but harder, more dense and with higher melting points than Group 1
- Good catalysts
- Platinum, palladium and rhodium are used in catalytic converters in cars to turn harmful vehicle fumes into less harmful ones
Describe reaction of transition metals
- Produce coloured compounds when they react
- Iron reacts with water and oxygen to form rust
- 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) --> 2Fe2O3 (s)
- Form more than one type of ion e.g. Fe(II) and Fe(III)
What does the rate at which a reaction takes place show?
relative reactivity of a substance
When can metals react with acid or water and why?
If they are more reactive than hydrogen they can react with acid or water as they are able to displace it out of the acid or water
What is the reactivity series?
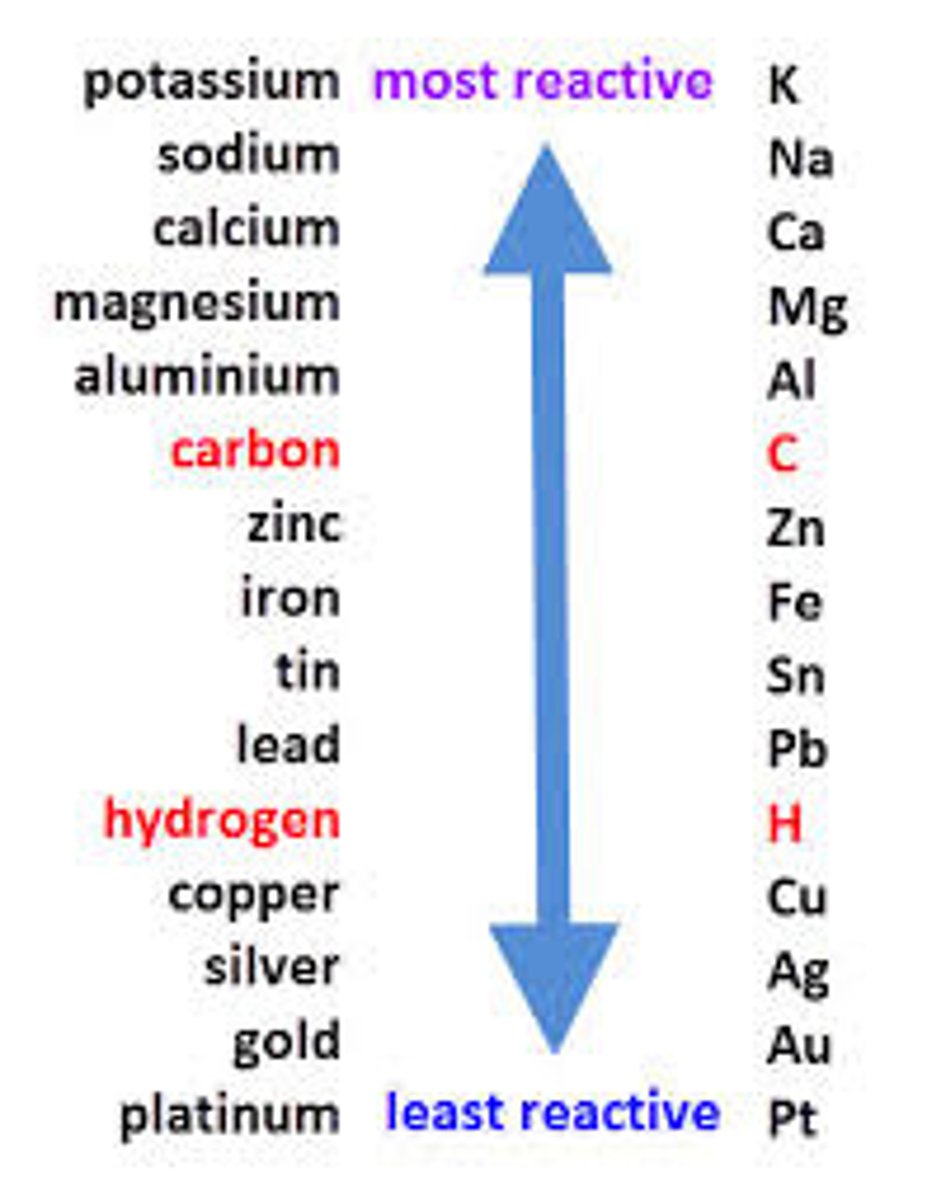
How can you tell if one metal displaces another
Colour change
If the metal is not more reactive then there is no colour change
Describe what you can see when copper displaces silver
Copper is more reactive than silver so it can displace it.
You would see the solution turn blue as blue copper nitrate solution is produced and a silver coating appear on the surface of copper peices.
What are trends in reactivity?
Reactivity increases down the metal groups
Reactivity decreases down the non-metal groups
Francium and Fluorine are most reactive
How can you test for oxygen?
It will relight a glowing splint
How can you test for hydrogen?
Squeaky pop test with a lit splint
How can you test for carbon dioxide?
Bubble it through limewater, Ca(OH)2- it will go cloudy
If you carry on bubbling CO2 through the limewater the CaCO3 dissolves so the cloudy appearance disappears.
Describe testing for limewater in terms of an equation
The water in limewater reacts with CO2 to make carbonic acid H2CO3:
H2O(l) + CO2(g) --> H2CO3(aq)
H2CO3 (aq) + CaCo --> Ca(HCO3) (aq)
How do you test for chlorine?
Bleaches damp blue litmus paper
OR
Damp starch-iodide paper turns blue/black
How do you test for cations?
Flame test
OR
Hydroxide precipitate test
What happens in a flame test?
1. Dip nichrome wire in conc HCl to clean it
2. Dip into substance to be tested
3. Hold it in a blue flame
What colour does calcium go in a flame test?
orange/red
What colour does copper go in a flame test?
green/blue
What colour does potassium go in a flame test?
lilac
What colour does lithium go in a flame test?
red
What colour does sodium go in a flame test?
yellow
How does a hydroxide precipitate test work?
1. Add a few drops of NaOH and you will see a coloured precipitate as a hydroxide forms
2. If you see a white precipitate, add more NaOh and see if the precipitate dissolves
Why does a hydroxide precipitate test not work with group 1 ions?
They form a hydroxide that dissolves so there is no precipitate
What colour precipitate does Fe(II) have?
green
What colour precipitate does Fe(III) have?
orange/brown
What colour precipitate does Cu(II) have?
blue
What colour precipitate does Ca(II) have?
White
Need to add excess NaOH, it does not dissolve with excess NaOH so stays white
What colour precipitate does Mg(II) have?
White
Need to add excess NaOH, it does not dissolve with excess NaOH so stays white
What colour precipitate does Zn(II) have?
White
Need to add excess NaOH, it does dissolve with excess NaOH so does not stay white
What colour precipitate does Al(III) have?
White
Need to add excess NaOH, it does dissolve with excess NaOH so does not stay white
How do you test of sulphate ions? (SO4 2- (aq) )
1. Add a few drops of HCl (aq) and then a few drops of BaCl2 (aq)
2. If sulphate ions are present then a white precipitate of BaSO4 (s) will appear, this is insoluble in HCl
Ionic equation:
Ba 2+ + SO4 2- -->BaSO4 (s)
How do you test of carbonate ions? (CO3 2- (aq) )
1. Add a few drops of HCl (aq)
2. If CO3 2- ions are present then you will see effervesence as CO2 is produced.
3. This can be confirmed by using limewater
What is the ionic equation for testing for carbonate atoms?
2H+ (aq) + CO3 2- --> CO2(g) + H2O (l)
How do you test for Cl-, Br- and I- ions?
1. Add a few drops of HNO3 (aq) to make sure no carbonate ions are present
2. Add a few drops of AgNO3 (aq)
3. If a halide ion is present you will see a precipitate
Cl- :is a white precipitate
Br- :is a cream precipitate
I- :is a yellow precipitate
What is instrumental analysis?
Where a machine carries out analysis of a sample rather than a person
What's the advantages of instrumental analysis?
More accurate
Faster
More sensitive ( means they can analyse very small amounts of a sample e.g. from a crime scene)
What can a gas chromatograph tell you?
-The number of compounds in a mixture = the number of peaks
-How much of each compound is in the mixture = area under graph
- Retention time = time taken for a substance to travel through the chromatography column and is different for different substances
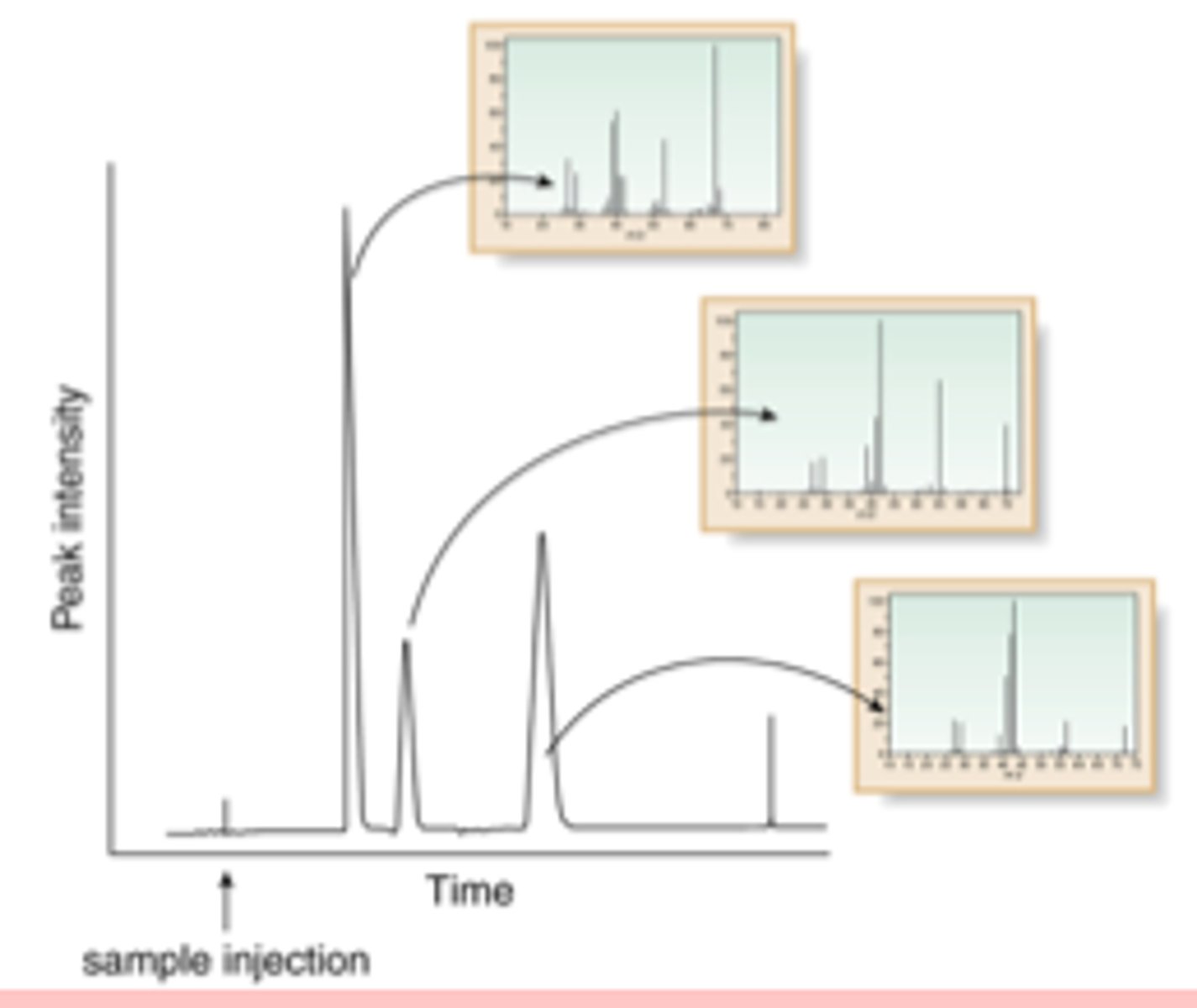
What can a mass spectrometer tell you?
-Mass of atoms or molecules
- Amount of isotopes for an element
- Structure of molecules
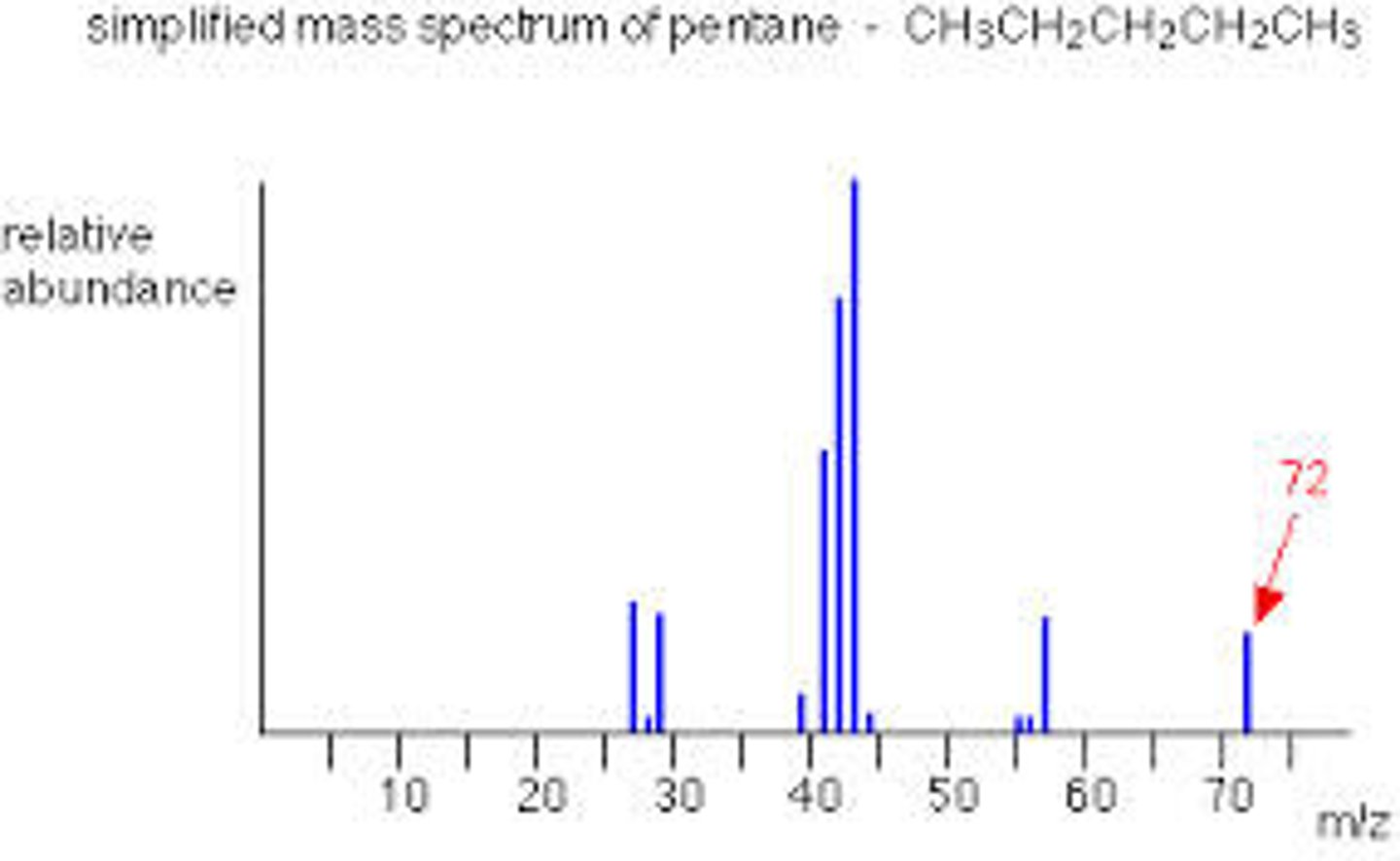
How does a mass spectrometer work?
1. Sample is ionised to form a molecular ion
2. This breaks up into fragments of molecules which are then detected
3. Far right peak is the molecular ion peak and the value = Mr
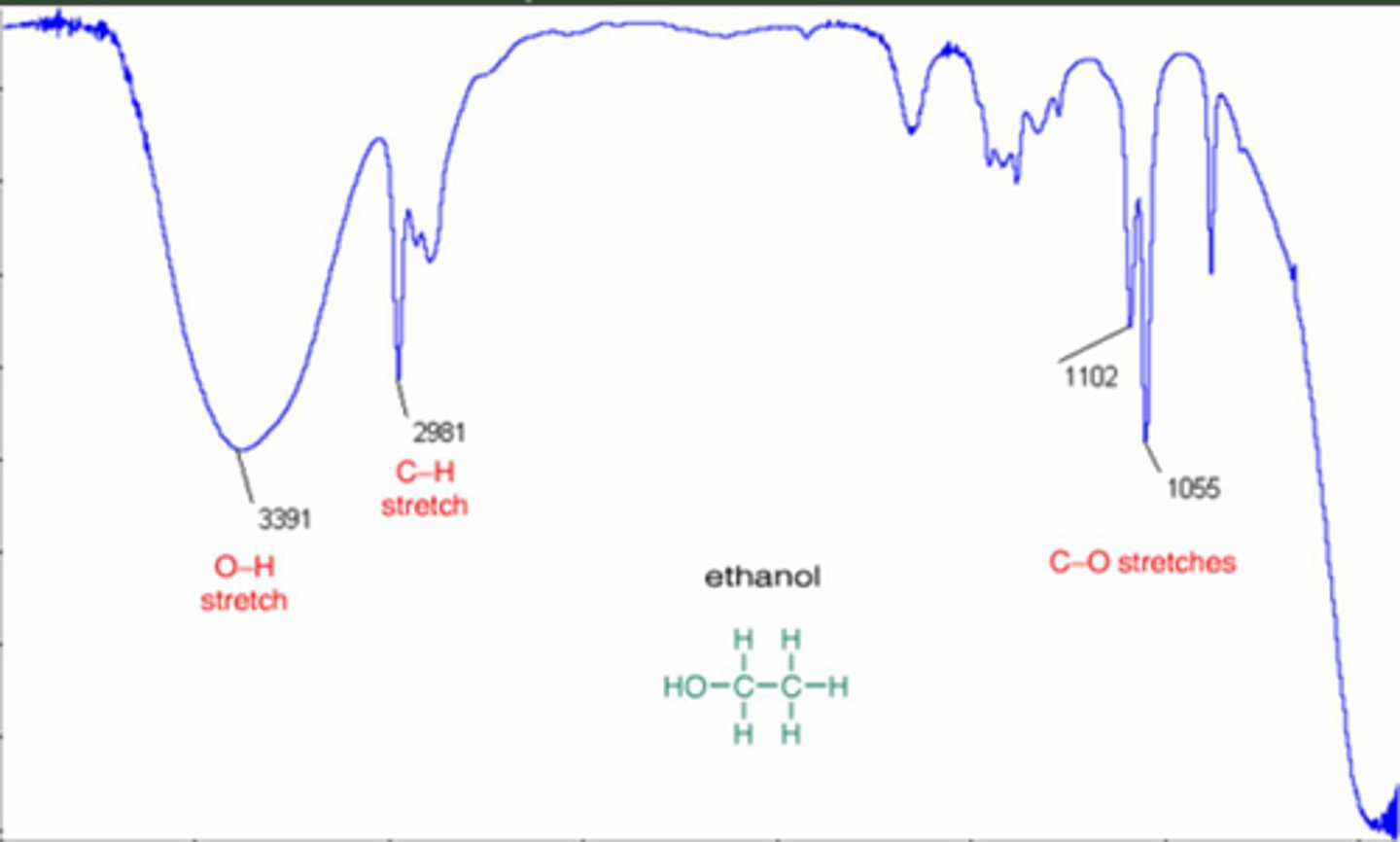
What can infrared spectroscopy tell you?
Covalent bonds in a sample by looking at the graph and looking up values in the table
(they have a graph and table)