Genetic Expression: BISC120 Units 17.1-17.5
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
proteins are the…
links between genotype and phenotype
What is gene expression
the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis. This includes 2 stages: transcription and translation
When can translation begin for prokaryotes?
before transcription has finished
What is the difference between translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
in prokaryotes translation of mRNA can begin before transcription has finished (transcription and translation can happen simultaneously because there is nothing separating where the processes happen)
In eukaryotes translation happens within the nuclear envelope
Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through…
RNA processing to yield the finished mRNA
What is the Central Dogma?
the concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command (DNA→ RNA→ Protein)
What does transcription do?
synthesize mRNA from DNA (copy a DNA segment into messenger RNA)
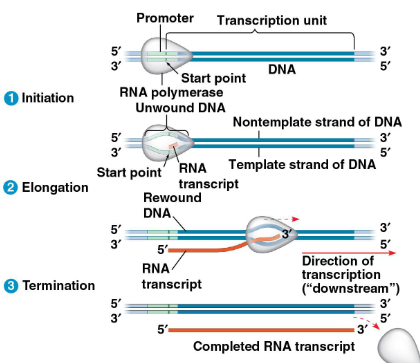
What are the three stages of transcription?
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
What is a template strand?
the strand of DNA that provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript
non-template strand aka…
coding strand
what are promoters
DNA regions that initiate the transcription of a gene
signal the transcription start point
eukaryotes have a promoter called a TATA box
what are transcription factors?
proteins that help guide the binding of RNA polymerase
what is RNA polymerase?
an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from DNA template
a specialized protein
what does RNA polymerase do?
it unwinds the double helix 10-20 nucleotides at a time
how is a template strand read?
3’-5’
how is a RNA strand built?
5’-3’ nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule
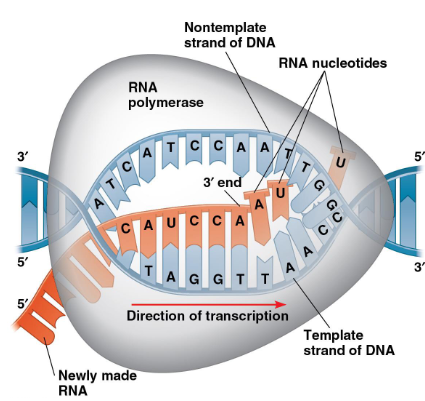
what is the last step of RNA synthesis?
the RNA strand is released from the RNA polymerase, which is signaled by the terminator
what are the steps involved in transcription?
initiation - Promoter initiates the start of transcription, transcription factors guide the construction of RNA polymerase
elongation - RNA polymerase untwists the DNA (separates the template and non-template strands), RNA strand is being built on the template DNA
Termination - RNA strand is released from the RNA polymerase
What do ribosomes do?
take info from DNA to make proteins (ribosomes build protein in the cytosol and outside the endoplasmic reticulum)
how are proteins constructed?
through nucleotide sequences of genes in DNA (code for constructing a protein)
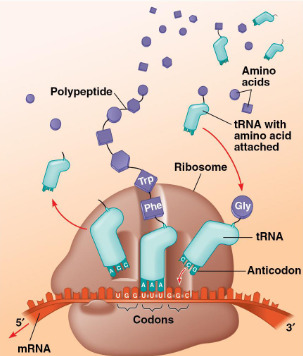
What does translation involve?
the conversion of the nucleic acid language to the polypeptide (protein language)
takes in this language through a triplet code (3 nucleotides), which are organized and stored in codons
what is the genetic code?
the set of rules that dictates the amino acid translations of each of the mRNA nucleotide triplets
what are the three phases of translation?
initiation- the small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA and a special initiator tRNA, the special initiator tRNA carries the amino acid methionine, then the unit moves along the mRNA until it reaches the start codon
Elongation- translation proceeds along the mRNA in a 5’-3’ fashion
Termination- a tRNA with a complementary anticodon pairs with each codon, elongation continues until a stop codon is reached
point mutations are…
changes in just one nucleotide pair of a gene
nucleotide-pair substitutions replace..
one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides
missense mutations are when…
the mutation codes for an amino acid, just not the correct one
Nonsense mutations are when a..
change causes an amino acid codon to turn into a stop codon
a silent mutation is..
when the mutation that occurred has no effect on the amino acid produced (more than one codon for each amino acid)