Digestive System
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiology Exam 3 Material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
four major layers of the digestive tract
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa
mucosa layer
nerves, blood and lymph vessels
submucosa layer
connective tissue, plexus
muscularis externa layer
two layers of smooth muscle, plexus
serosa layer
continuation of peritoneal membrane
portions of the stomach
fundus
body
antrum
pyloric valve
rugae
permits stomach expansion
relaxed rugae
mucosa forms numerous muscular ridges
stretched rugae
less prominent rugae
regions of the small intestine
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
duodenum
10 inches long, receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas, bile from the liver and gall bladder
jejunum
8 feet long, most of the digestion and absorption occurs here
ileum
12 feet long
lining of the small intestine
surface area is increased by fingerlike villi and invaginations called crypts
structures within the villi
capillaries and lacteals
villi function
absorb the digested nutrients from the lumen of the small intestine into the capillaries
lacteal function
absorb material that cannot be absorbed by the capillaries
sections of the pancreas
endocrine and exocrine
endocrine cells
islet of langerhans, alpha cells (glucagon), beta cells (insulin)
exocrine ells
acting cells (zymogens), duct cells (bicarbonate)
gall bladder function
stores and concentrates bile
bile composition
bile salts: facilitate enzymatic fat digestions
bile pigments: bilirubin
cholesterol
liver functions
produces bile
stores glycogen
inactivates xenobiotics
inactivates many hormones
how does the liver inactivate xenobiotics?
modifies their structures to make them water-soluble for excretion by the kidneys
liver microstructure
organized into lobules centered on central vein; within each lobule, ~70% of the surface area of each hepatocyte faces the sinusoids, maximizing the exchange between the blood and the cells
hepatic portal vein
absorbed nutrients from gut and Hb breakdown products from spleen
hepatic artery
oxygenated blood
what type of vascular supply does the liver have?
dual vascular supply
biological filter
absorbed materials go directly to the liver
liver as a storage organ
stores fat-soluble vitamins A, and several months supply of E and K
stores vitamin B12
stores iron and copper
macronutrient metabolism of liver
carbohydrate metabolism
amino acid metabolism
fatty acid metabolism
protein metabolism
carbohydrate metabolism in liver
involved in glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis
amino acid metabolism in liver
catabolize amino acids or use them for gluconeogenesis
synthesizes much of the body’s non-essential amino acids
fatty acid metabolism in liver
produces triglycerides
metabolizes fatty acids through beta-oxidation and makes ketones
synthesized cholesterol
protein metabolism in liver
synthesizes the majority of plasma proteins
gluconeogenesis
synthesis of glucose from amino acids, lactate, glycerol
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen into glucose
glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose
four major classes of the circulating plasma lipoproteins
chylomicrons: produced in small intestine
very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs): majority produced in the liver
low-density/high-density lipoproteins (LDLs/HDLs): produced in plasma and the liver also produces a small amount
anatomy of the large intestine
cecum w/ appendix, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anus
basic functions of GI tract
digestion
secretion
motility
absorption
digestion function
chemical and mechanism breakdown of foods into absorbable units
secretion function
transfer of water, ions and enzymes into lumen from ECF
motility function
moves food through GI tract
absorption function
movement of nutrients from lumen to ECF and blood
propulsion functions and locations
swallowing: oropharynx
peristalsis: esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
mechanical digestion functions and locations
chewing (mouth)
churning (stomach)
segmentation (small intestine)
motility
contractions in the GI tract; migrating motor complex: “housekeeping”
motility contractions in the GI tract
segmental contractions: mixing
peristalsis: forward movement
secretions
ions and water: Na+, K+, Cl-, HCO3-, and H+
acids: parietal cells
bicarbonate: duct cells of pancreas, small amount of duodenal cells
digestive enzymes: zymogens (pancreas)
mucus: mucous cells (stomach) and goblet cells (intestines)
saliva
phases of processing food
cephalic
gastric
intestinal
cephalic processing
sight, smell, thoughts of food > brain activates feedforward response
gastric processing
foods combine with acid and enzymes to form chyme
intestinal processing
majority of digestion and absorption
what role does the mouth play in cephalic digestive processing?
site of chemical and mechanical digestion
how is saliva secretion controlled?
through the autonomic (parasympathetic) nervous system
saliva function
soften and lubricate food
chewing
mastication
enzymes involved in cephalic chemical digestion
salivary amylase and other lipases
types of saliva
stimulated saliva
unstimulated saliva
stimulated saliva
70-90% of saliva produced
99% water
1% proteins and minerals
unstimulated saliva
background saliva
viscous, elastic, sticky: mucins
forms protective film on teeth
stomach functions in the gastric phase
storage
receptive relaxation of upper stomach
regulates entry into SI
digestion
acid, enzymes and signal molecules
formation of chyme
protection
destroys ingested bacteria/pathogens
protects itself with mucous-bicarbonate layer
secretory cells
parietal cells
chief cells
g cells
parietal cell function
secrete intrinsic factor and gastric acid (HCl)
intrinsic factor: facilitates the absorption of vitamin B12
HCl: kills microorganisms and activates pepsinogen
chief cell functions
secrete pepsinogen, which is converted to pepsin via action of HCl
g cell function
produce hormone gastrin which causes the parietal and chief cells to release their products
key intestinal secretions for digestion
bicarbonate: neutralizes gastric acid
goblet cells: secrete mucus for protection and lubrication
isotonic NaCl: mixes with mucus for lubrication
bile: fat digestion
digestive enzymes: secreted by intestinal epithelium and pancreatic acinar cells
gallbladder functions
stores and secretes bile
expels bile into duodenum
contraction stimulated by CCK (fats in meals)
lipid digestion in the mouth
mechanical digestion
mixing with saliva
limited enzymatic digestion (lingual lipase)
lipid digestion in the stomach
mixing/churning
limited enzymatic digestion (gastric lipase)
lipid digestion in the small intestine
emulsification (bile)
enzymatic digestion (pancreatic lipases)
micelles help with absorption
micelles
small disks with bile salts, phospholipids, fatty acids, cholesterol, and mono- and diglycerides
carbohydrate digestion in the mouth
enzyme salivary amylase begins breaking down starch into shorter polysaccharides
carbohydrate digestion in the stomach
salivary amylase is inactivated and no further carbohydrate digestion takes place
carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine
majority of starch digestion and breakdown of disaccharides occurs here, enzymatic pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into monosaccharides, disaccharides and oligosaccharides, digestion is completed by enzymes attached to the brush border of the villi
carbohydrate digestion in the large intestine
fiber and other indigestible carbohydrates are partially broken down by bacteria to form short chain fatty acids and gas, remaining fiber is excreted in the feces
carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine diagram
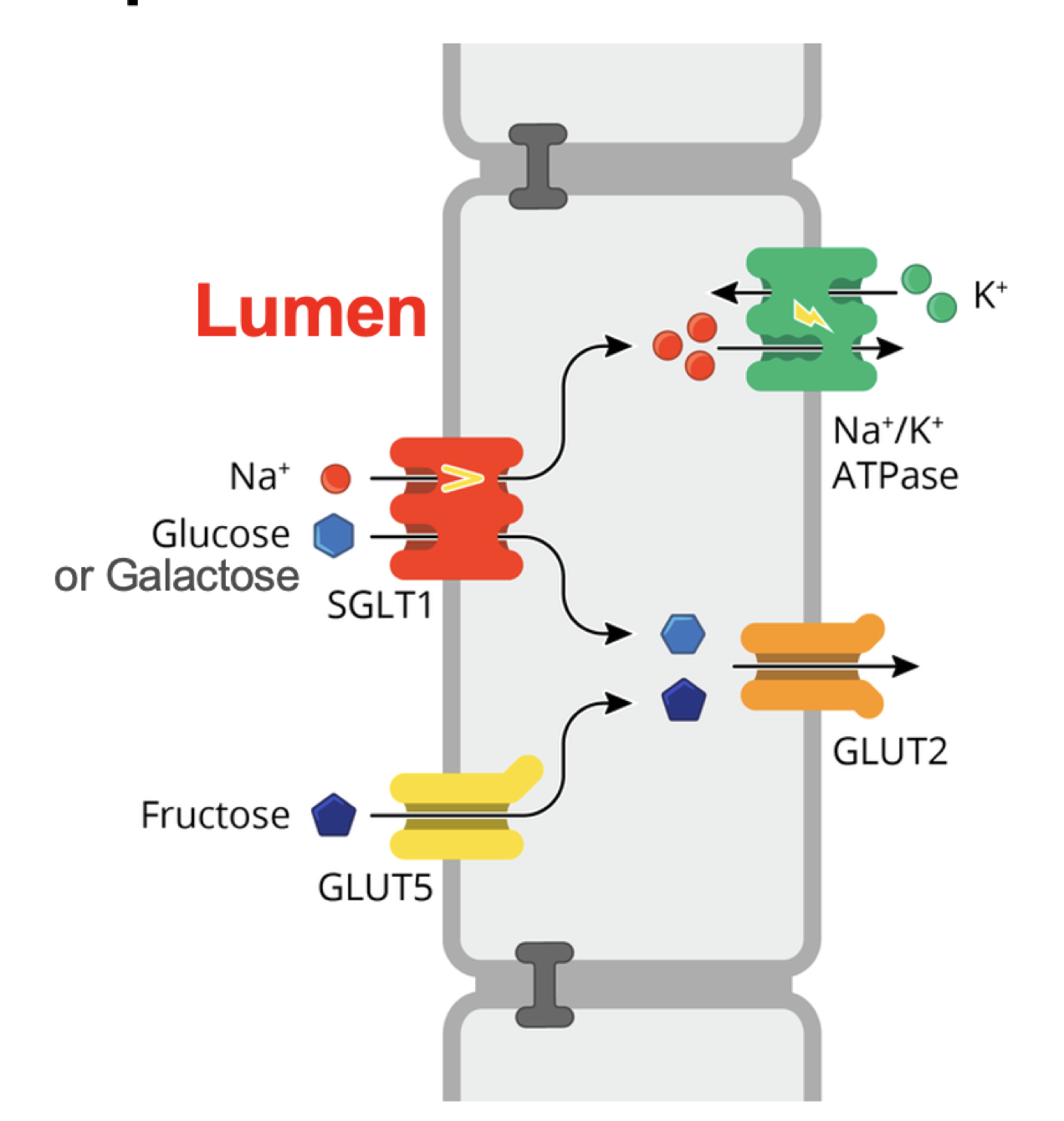
endopeptidase fucntion
digests terminal peptide bonds to release amino acids
endopeptidase examples
pepsin (stomach)
trypsin (small intestine)
chymotrypsin (small intestine)
peptide absorption
di- and tri-peptides: cotransport with H+
amino acids: cotransport with Na+