The Brain
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Studying the Brain
Phineas Gage - case study - part of frontal lobe was destroyed and only his personality was impacted - shows importance of localization of brain functions
Phrenology
Thought up by Franz Gall - belief that bumps in the brain determine personality
Lesions
Destruction of brain tissue
Lobotomy
Removal of part of the brain
Plasticity
The brain’s ability to reorganize itself should it get damaged - explains phantom limb sensation
EEG Scan (Electroencephalogram Scan)
Amplified recordings of brain wave activity
CT/CAT Scan (Computerized Tomography Scan)
X-ray photos of slices of the brain; shows structures within the brain but not functions of the brain
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography Scan)
Visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose is being used while the brain performs certain tasks
MRI Scan (Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scan)
Technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to see structures within the brain
fMRI Scan (Functional MRI Scan)
Allows us to see where oxygen is being used in the brain while various tasks are being performed
Parts of the Brain
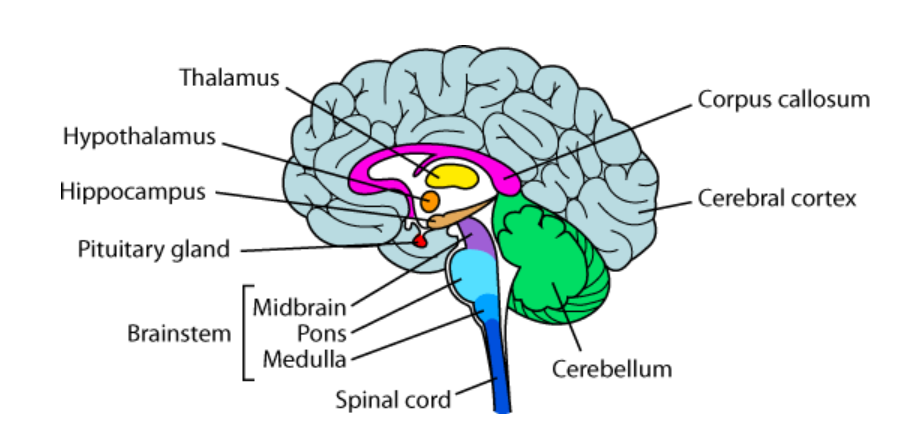
The Brainstem
Oldest area of the brain; also called the reptilian brain
Medulla
The base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Reticular Formation
A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep
Pons
Regulates sleep and balances movement for left and right sides of the body for reflexes
Thalamus
Sits on top of the brainstem; receives all incoming sensory information (except smell) and sends it to the appropriate part of the brain for further processing
Cerebellum
The “little brain” attached to the back of the brainstem; it helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance
The Limbic System
A doughnut-shaped structure between the brainstem and the cerebral hemispheres; it is considered the “seat of emotion” and is also involved in motivated behavior like eating, drinking and sex
Amygdala
Involved in rage and fear as well as emotional memories
Hippocampus
Involved in memory
Hypothalamus
Involved in drives (eating, drinking, sexual behavior); it also controls the endocrine (hormonal system) via the pituitary gland; it is sometimes referred to as the “pleasure center” of the brain
Pituitary Gland
Master gland in charge of the other endocrine glands; regulates growth
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the ultimate information-processing center of the brain
Frontal Lobe
Contains the motor cortex which controls voluntary movement; in the LEFT frontal lobe is Broca’s Area which controls our ability to speak
Parietal Lobe
Contains the somatosensory cortex which registers bodily sensations (touch)
Temporal Lobe
Contains the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense); the LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke’s Area which controls language comprehension and expression
Occipital Lobe
Contains the primary visual cortex
Association Areas
Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions; they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning and language; about 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas
Hemispheres of the Brain
Virtually all activities require BOTH hemispheres
Left Hemisphere
Controls right side of body; involved in language, science, math, etc…
Right Hemisphere
Controls left side of body; involved in music, artistic ability, spatial skills, etc…
Corpus Callosum
Hemispheres are connected via the corpus callosum; if it is cut due to epileptic seizures the patient would become split-brained
Split-Brained Patients
For split-brained patients anything in the right visual field goes to the left hemisphere and the patient is able to say what they saw; anything in the left visual field goes to the right hemisphere and the patient cannot say what they saw BUT they can draw it with their left hand