Week 9 - Magnetic Resolution Imaging
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are three components that an MRI uses?
Magnetic field
Radio-waves
Computer
How are patients kept still during MRI?
Sedation or GA
Why is GA or sedation needed for MRIs?
If a patient moves it messes with the image and generally have to restart
What is the Gauss line?
Perimeter of magnetic field
What must stay out of the gauss line?
Ferrous metal
What protons are used and where are they found in the body?
Hydrogen protons found in the tissues
What are 3 precautions to take with MRIs despite no ionising radiation?
Patients with metal implants
Operators with pace makers, implants or pregnant
Ear protection for high field unit as very noisy
How much water is the body made of?
70%
What is the magnetic property of hydrogen?
Protons
How is an image produced? - 7 steps
Magnetic field is applied to the structure
Spinning protons rotate to align with the magnetic
A series of radio frequency waves are applied
This forces the proton away from the magnet to 90-180 degrees
Transmission of RFW ceased, the protons return to their original position with the magnet
This movement and energy this causes is detected via sensors (RFC) within the system
These signals are then converted from analogue to digital images
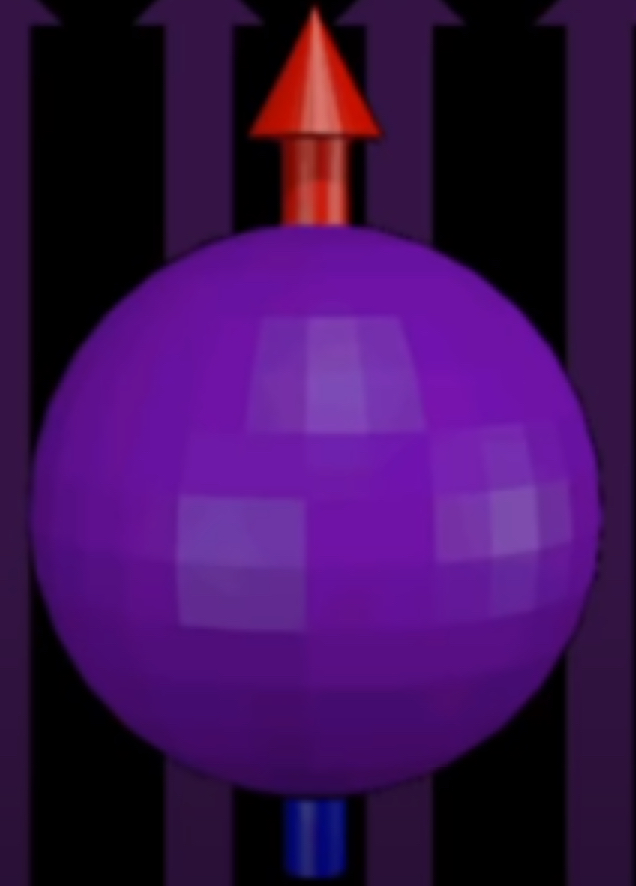

What does this picture show?
T1 relaxation
What does this picture show?
T2 relaxation
What collects the data in an MRI machine
Radiofrequency coil
What is the purpose of a radiofrequency coil?
Sends and receives radio waves
What is the job of the radiofrequency waves?
Sends the RF pulse that tips the protons
Listens for the MRI signal coming back
What is the purpose of a gradient coil?
Creates magnetic field variations
What is the job of the gradient coil?
Changes the magnetic field slightly in different directions
Allows the MRI to know where the signal is coming from
What is produced from an MRI?
Cross sectional images in three planes
What are the clinical application of MRI?
Predominately soft tissue
Inflammatory process in bones
Sensitive to bone density changes and remodelling
Pre-fractural plains
Single lobe damage to tendon and ligament tissue
What are do fields refer to?
The strength of the magnetic field?
3 main points about low field?
0.27 tesla
Temperature controlled by the environment
Less sensitive than high field but tolerates more movement
1 pro and 1 con of low field?
Cheap to install and maintain
Slight reduction to image quality BUT may tolerate more movement better
2 main points of high field
> 1 tesla
Uses liquid helium to enable superconducting
1 pro and 3 cons of high field
High image quality
Very sensitive - even to breathing
More expensive than low field
Artefacts increased around metal objects
What should the building/housing be cased in?
Copper lining
How does hygiene correlate with MRIs?
Keeps patients safe
Protects equipment
Improves image quality
Supports infection control