Endocrine 3 - Adenohypophysis, GH, Prolactin
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Blood supply of the anterior pituitary
Superior hypophyseal artery - goes into the median eminence
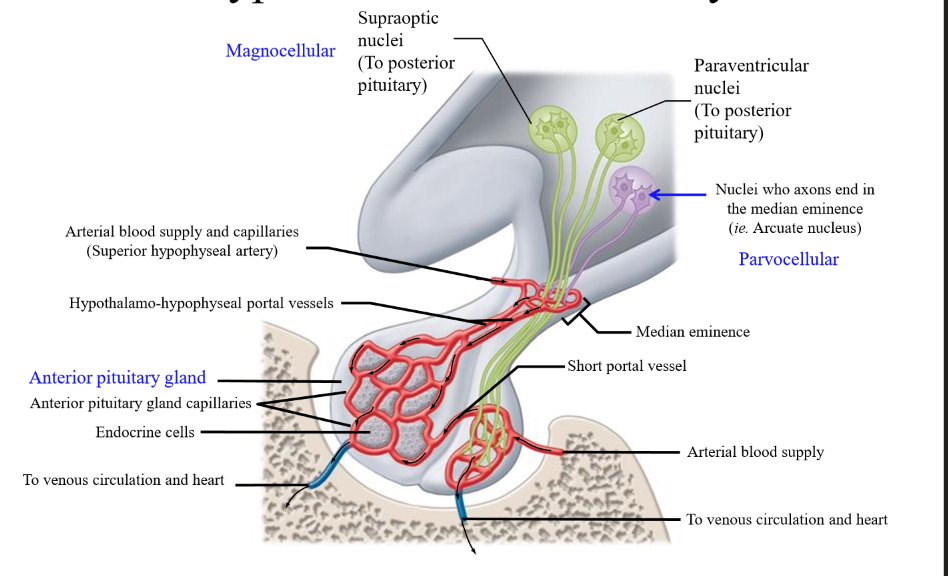
Median eminence
Midline feature on the base of the brain marking the point at which the pituitary stalk exits the hypothalamus to connect to the pituitary. Allows for hypothalamic hormones to be transported to the anterior pituitary
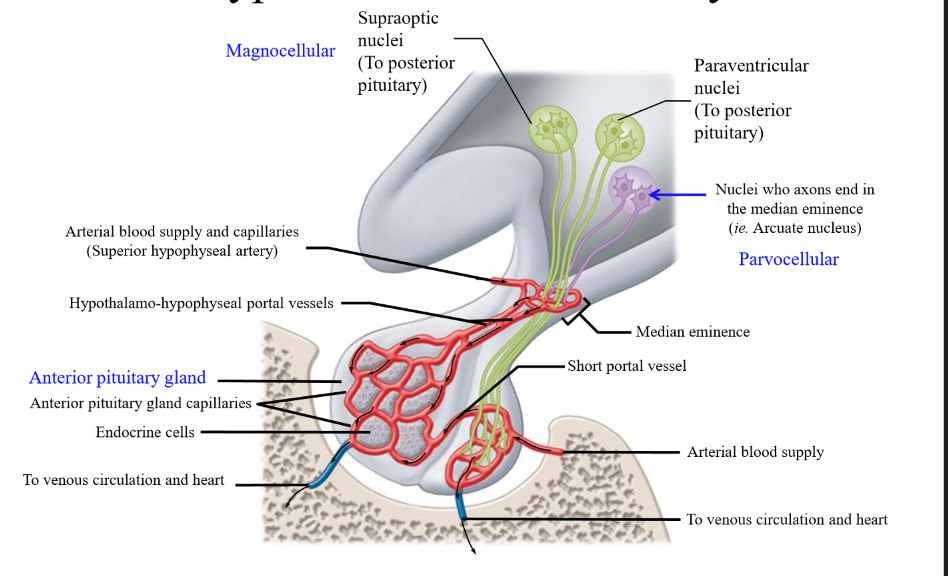
hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal vessels
vessel traveling from the median eminence to the anterior pituitary lobe that carries hormones
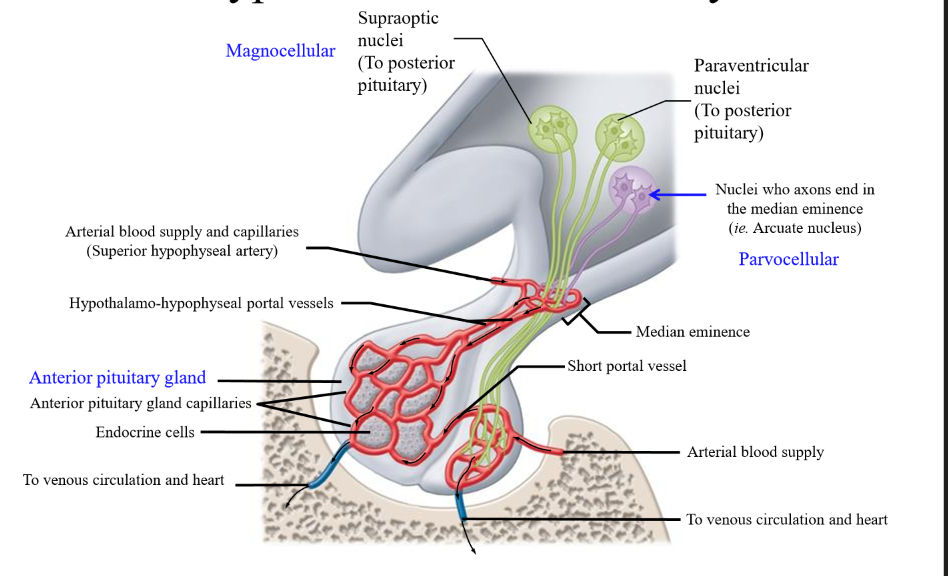
Features of the Arcuate nucleus
Small cell bodies, short axons (parvocellular neurons)
Role of parvocellular neurons
Produce neural secretions that are released into blood vessels to anterior pituitary
Magnocellular neurons
Include the supraoptic nuclei and the paraventricular nuclei that secrete oxytocin and ADH to the posterior pituitary
Trophic hormone
a hormone that results in production of a second hormone in a target gland
Role of Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Stimulate FSH and LH production
Role of Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
Stimulate GH production
Role of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
Stimulate TSH and Prolactin secretion
Role of prolactin releasing factors (PRFs)
Stimulate prolactin secretion
Role of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
Stimulate ACTH secretion
Somatotropin releasing inhibiting factor (SRIF)
Inhibits GH and TSH
Prolactin inhibitory factors (PIFs)
Inhibit TSH and PRL release
Most abundant PIF in the body
Dopamine
Role of TSH
Induces thyroid gland to release T3 and T4
Role of ACTH
Induces adrenal cortex to release cortisol
Role of Prolactin
Acts on mammary glands to stimulate milk secretion and breast growth
Role of GH
Acts on various tissues for intermediary metabolism, or acts on the liver to produce somatomedins (IGF-1), causing bone and soft tissue growth
Role of LH
Acts on gonads for sex hormone secretion (estrogen in women, testosterone in men)
Role of FSH
Acts on gonads for gamete production (sperm, ova)
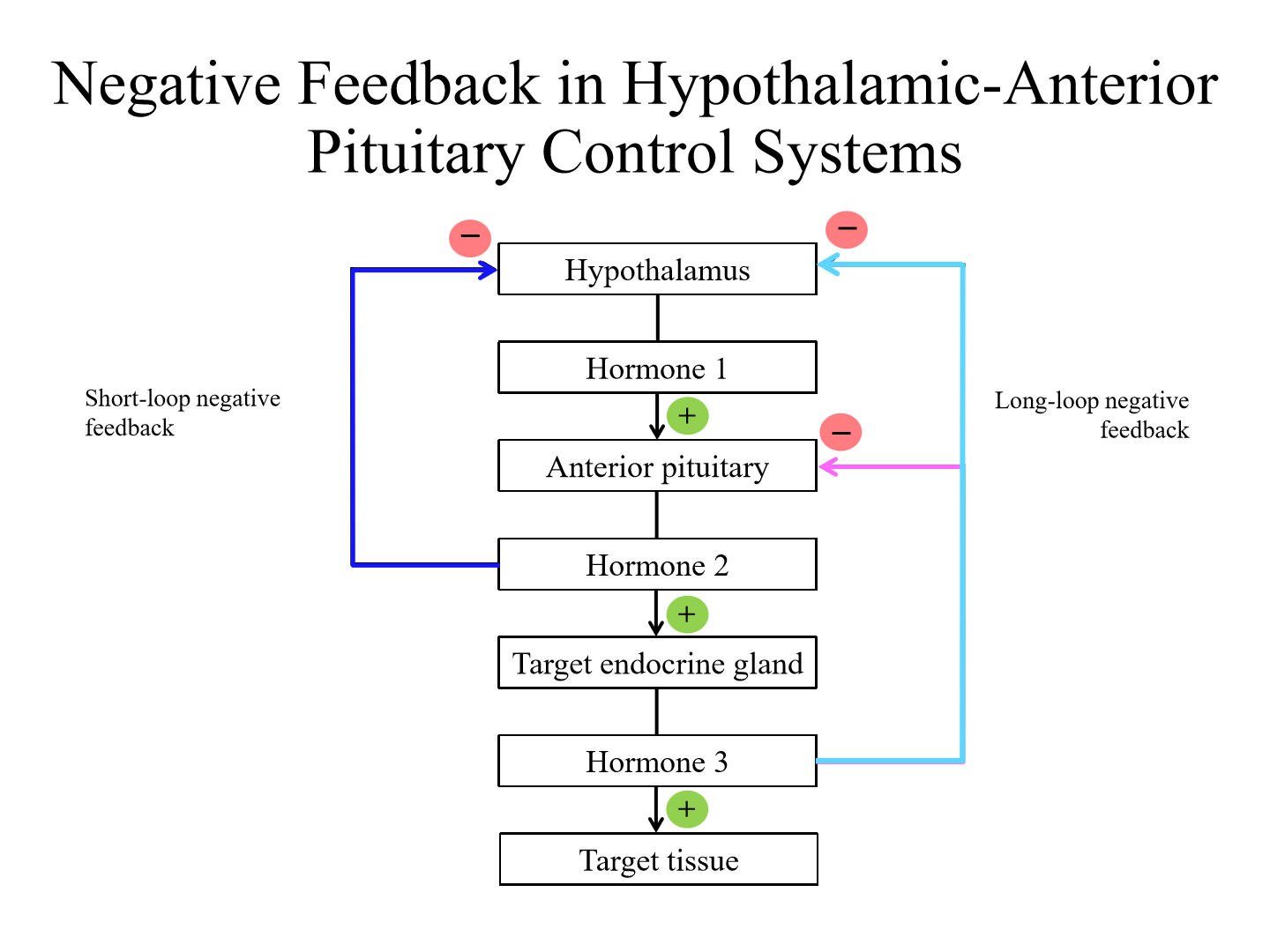
general steps of negative feedback in hypothalamic anterior pituitary axis
1. Hypothalamus secretes hormone 1, that acts on anterior pituitary
2. Anterior pituitary releases hormone 2. This can act on target endocrine gland or cause negative feedback on hypothalamus (short loop)
3. Target endocrine gland releases hormone 3, which can act on target tissue or inhibit anterior pituitary and hypothalamus (long-loop negative feedback)
Role of GH on muscle
- Increased protein synthesis
- Decreased glucose uptake
- Anabolic = increased muscle mass
Role of GH on adipose tissue
- Decreased glucose uptake
- Increases lipolysis (increased blood FFAs)
- Decreased adiposity
Role of GH on the liver
- Increased protein synthesis
- Increased gluconeogenesis
- Increased somatomedin production (IGF-1)
What are the somatomedins
Insulin like growth factors: IGF-1, IGF-II
Effect of IGF-1
Effects bone chondrocytes
- Increased collagen synthesis
- Increased protein synthesis
- Increased cell proliferation
Increased linear growth
Effect of IGF-II
Effects many tissues and organs
- Increased protein synthesis
- Increased RNA synthesis
- Increased DNA synthesis
- Increased cell size, number
Increased tissue growth, increased organ size
Main regulators of GH secretion
Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (somatostatin)
Growth hormone releasing hormone
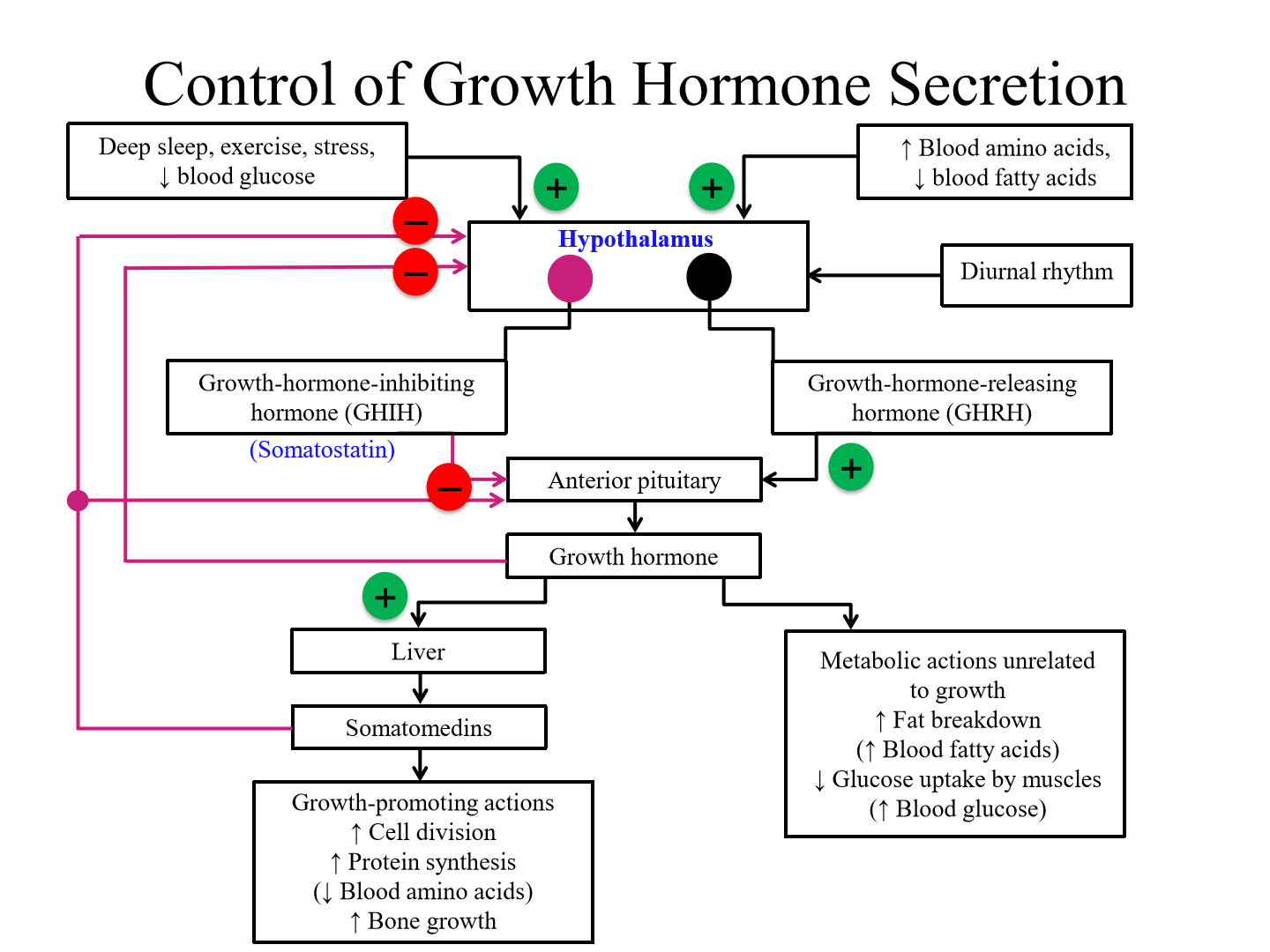
Somatomedins effect on the anterior pituitary, hypothalamus, and GH
Inhibitory effect
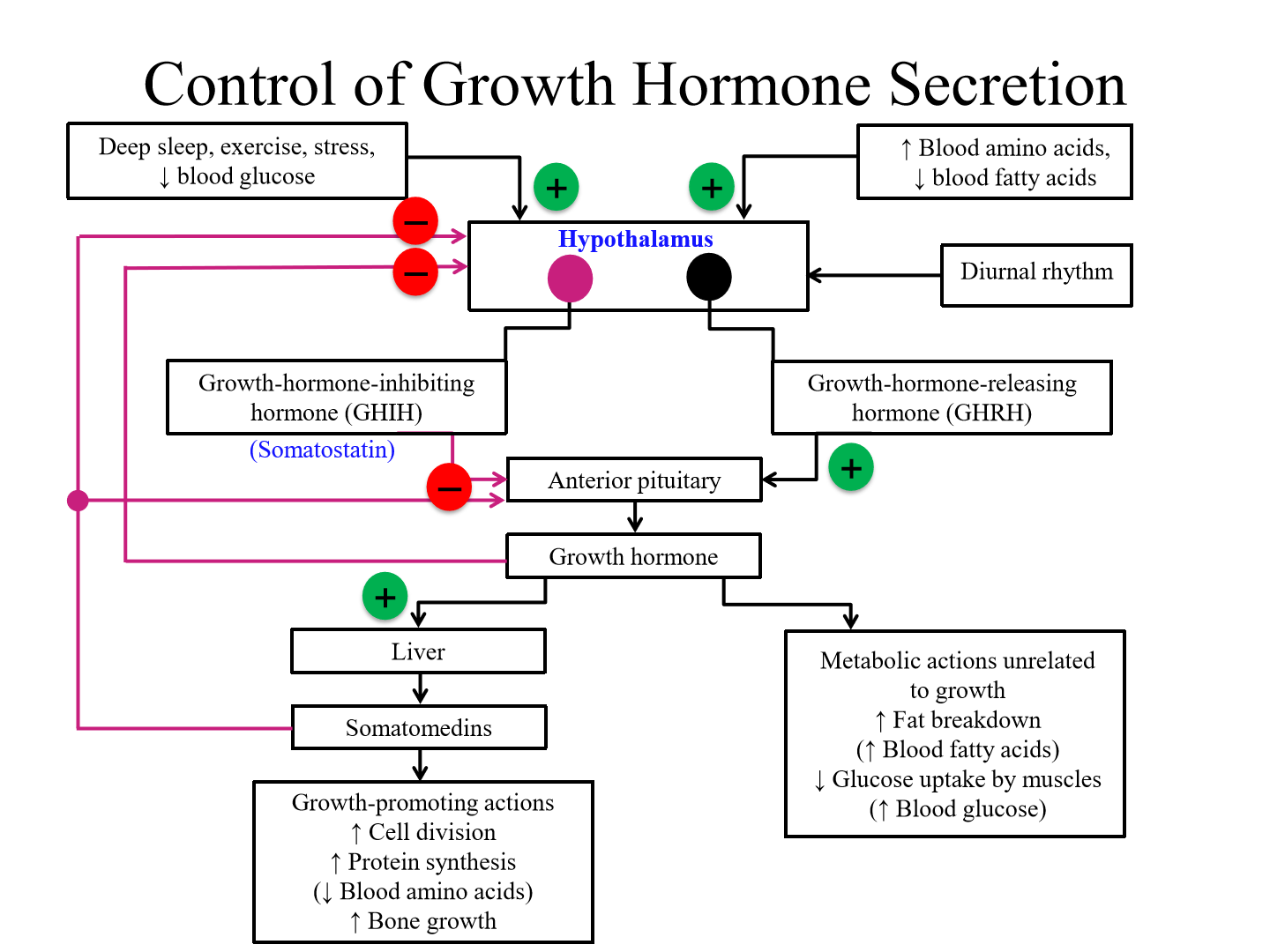
Positive regulators of GHRH secretion from hypothalamus
- Increased blood amino + fatty acids
- Deep sleep, exercise, stress, decreased blood glucose
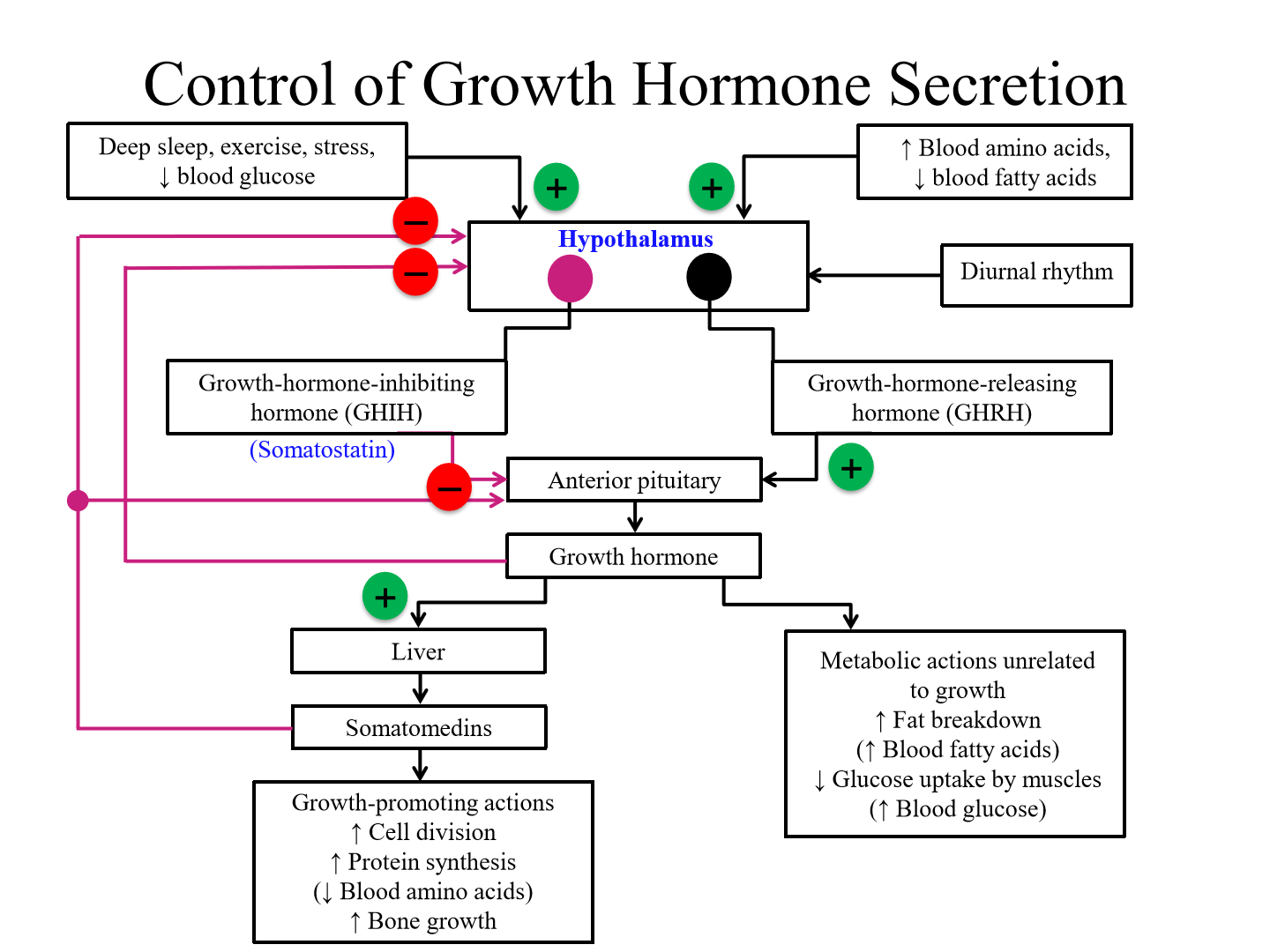
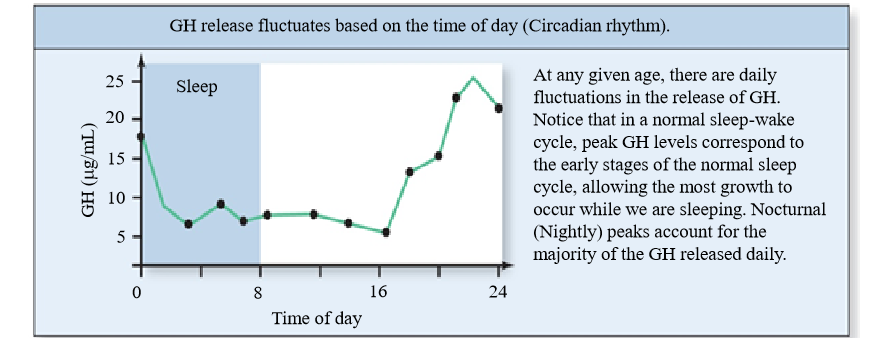
Diurnal pattern of GH release (24H cycle)
Episodes increases in the dark and increased during sleep
GH release changes in response to blood nutrinet levels
- Fasting increases GH secretion
- Meals high in glucose and fatty acids suppress growth
- Meals high in amino acids increase GH
What cells synthesize GH
Somatotrophs
Secretion of GH
Episodic, more during stress/sleep
- Decreased due to age
- Reflects balance of GHRH and SRIF balance
GH deficiency in juveniles
Dwarfism
GH deficiency in adults
Somatopause (gradual and progressive decrease during age - similar to menopause)
Isolated GH deficiency (Type I dwarfism)
defect in GH production
Laron-type dwarfism
- Defect in GH action: GH receptor dysfunction
- Since GH cannot work, IGF-1 is low
Characteristics of GH deficiency in juveniles
Normal body proportions for age, no intellectual disability, mature sexually
Difference between GH dwarfs and hypothyroid dwarfs
Different body proportions
Somatopause
GH deficiency in adults
Impacts of somatopause
- Increased fat/ decreased lean mass
- Metabolic disturbances
- Impaired immune function (as GH drives immune system) - thymus is lost
How to treat somatopause
Exogenous hormone therapy (risky) - can induce gigantism or acromegaly
Effects of gigantism
Large organs
Issue with blood glucose management (diabetes)
Acromegaly
Excess GH production, causing increased size of face, hand, feet, jaw
- Internal organs can increase
- Increased glucose release = diabetes
Acromegalic features
- Large orbital ridges
- Broad, flat nose
- Large, fleshy lips
- Extensive spaces between teeth
- Thicky, oily, acne prone skin
- Prognathism (protruding jaw)
- Visual filed problems
- Osteoarthritic changes
- Hirsutism
- Large hands and feet
- Gynecomastia
Actions of prolactin
- Gonadal modulation (pro-gonadal when gonadal activity low, opposite when high)
- Mammary gland development
- Lactation (milk production)
Prolactin releasing factors
Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
Oxytocin (promotes milk let down)
Gonadal steroids that cause prolactin secretion
- Increase in testosterone or estrogen
- Progesterone decrease
Mammary stimulation that causes prolactin secretion
Suckling
Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia
Gonadal dysfunction, amenorrhea, reduced libido
Treatment of hyperprolactinemia
Dopamine agonist, tumor removal
Symptoms of hypoprolactinemia
Gonadal dysfunction, impaired lactation
Pituitary diabetes
Hypersecretion of GH, TSH - causes hyperglycemia
Hypopituitarism
Failure of pituitary gland to produce one or more of its hormones partially or completely
Panhypopituitarism
Inadequate or absent production of all anterior pituitary hormones