AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Ultimate Guide
4.3(3)Studied by 533 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
Electric-Charge
Coulomb's-Law
Electric-Charge
Conservation-of-Charge
Conductors
Insulators
Law-of-Electrostatics
Electric-Potential-Difference
Electric-Potential-Difference
Charging-and-Discharging
Gauss'-Law
Electric-Field-Strength
Electromagnetism
Magnetic-Flux
Magnetic-Flux
Maxwell’s-Equations
Faraday's-Law
Lenz's-Law
Ampère's-Law
Biot-Savart-Law
Right-Hand-Rule
Right-Hand-Rule
Resistance
Ohm's Law
Circuits
Capacitors
Kirchhoff's-Voltage-Law
Kirchhoff's-Current-Law
Electric-Shielding
Capacitance
Parallel-Plate-Capacitor
12th
Last updated 11:19 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
Charge
It is a fundamental property of matter that describes the amount of electrical energy present in an object.
2
New cards
Coulomb
SI unit of charge
3
New cards
Electric charge
It is a fundamental property of matter that arises from the presence or absence of electrons in an atom.
4
New cards
Conductors
These are materials that allow electric charge to flow freely through them.
5
New cards
Insulators
These are materials that do not allow electric charge to flow easily.
6
New cards
law of electrostatics
a set of fundamental principles that govern the behavior of electric charges at rest.
7
New cards
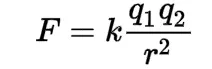
Coulomb's law
This law states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
8
New cards
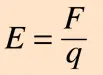
Electric field
A region in space where an electric charge experiences a force.
9
New cards
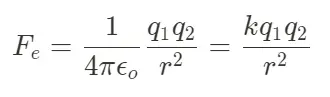
Electric potential difference
It is the difference in electric potential between two points in an electric field. It is measured in volts (V).
10
New cards
Charging
It is the process of adding electrical energy to a system.
11
New cards
Discharging
It is the process of releasing electrical energy from a system.
12
New cards
Electrostatic force
It is the force that exists between electrically charged particles.
13
New cards
Electrostatic Force Formula
14
New cards
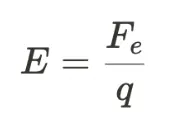
Electric field strength
It is the force per unit charge experienced by a test charge placed in an electric field. It is a vector quantity and is denoted by E.
15
New cards
Capacitors
devices that store electric charge and energy.
16
New cards
Electric motors
devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
17
New cards
Particle accelerators
devices that use electric fields to accelerate charged particles to high speeds.
18
New cards
Electrostatic precipitators
devices that use electric fields to remove pollutants from the air.
19
New cards
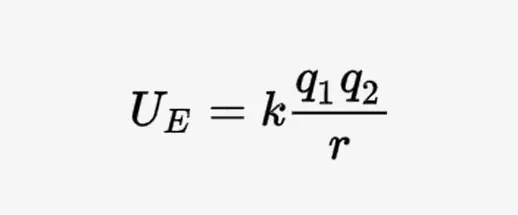
Electric potential energy
It is the energy that a charged particle possesses due to its position in an electric field. It is defined as the amount of work required to move a charged particle from infinity to a point in the electric field.
20
New cards
Joule
SI unit of electric potential energy
21
New cards
Potential difference
It is the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points in an electric circuit.
22
New cards
Gauss' Law
It is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed within that surface. It is named after the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss.
23
New cards
Flux
It is the amount of a physical quantity passing through a given surface.
24
New cards
Extended charge distributions
This refer to the distribution of electric charge over a three-dimensional object.
25
New cards
Continuous Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed continuously over a volume or surface.
26
New cards
Spherical Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of a sphere.
27
New cards
Cylindrical Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of a cylinder.
28
New cards
Planar Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over a flat surface.
29
New cards
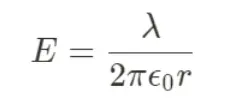
Gauss law in Line of Charge
30
New cards
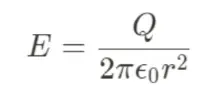
Gauss law in Point, Hoop, or Sphere (fully enclosed)
31
New cards
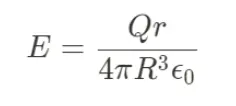
Gauss law in Sphere (not fully enclosed)
32
New cards
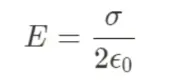
Gauss law in Insulating Sheet of Charge
33
New cards
Electric field
It is a vector quantity that describes the force experienced by a charged particle in an electric field.
34
New cards
zero
The electric field inside a conductor is \_____, and any excess charge resides on the surface of the conductor.
35
New cards
surface of a conductor
The electric field on the \______ is perpendicular to the surface and is proportional to the surface charge density.
36
New cards
outside the surface
The electric field just \______ of a conductor is perpendicular to the surface and is equal to the electric field inside the conductor.
37
New cards
inside the surface
The electric field just \_____ of a conductor is perpendicular to the surface and is equal to the electric field outside the conductor.
38
New cards
curved
The electric field on the surface of a conductor is strongest where the surface is most \____, and weakest where the surface is most flat.
39
New cards
Electric shielding
It is the process of reducing the electric field in a space by surrounding it with a conductive material.
40
New cards
Faraday cage
It is a type of electric shielding that completely surrounds a space with a conductive material, creating a barrier that prevents electromagnetic waves from entering or leaving the space.
41
New cards
Capacitor
An electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material.
42
New cards
Capacitance
It is the ability of a capacitor to store charge.
43
New cards
Parallel plate capacitor
It is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field between two parallel conducting plates. It consists of two parallel plates separated by a dielectric material.
44
New cards
\= εA/d
capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
45
New cards
E \= V/d
electric field between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor
46
New cards
U \= (1/2)CV^2
energy stored in a parallel plate capacitor
47
New cards
Ceramic capacitors
These are the most commonly used type of capacitor.
48
New cards
Electrolytic capacitors
These are polarized capacitors that use an electrolyte as the dielectric.
49
New cards
Film capacitors
These are non-polarized capacitors that use a thin plastic film as the dielectric.
50
New cards
Tantalum capacitors
These are polarized capacitors that use tantalum metal as the anode.
51
New cards
Variable capacitors
These are capacitors whose capacitance can be adjusted.
52
New cards
E \= 1/2 * C * V^2
energy stored in a capacitor
53
New cards
Dielectrics
These are materials that do not conduct electricity easily.
54
New cards
Polar dielectrics
These have a permanent dipole moment due to the presence of polar molecules.
55
New cards
Non-polar dielectrics
They do not have a permanent dipole moment. They are made up of non-polar molecules and do not align themselves in an electric field.
56
New cards
Dielectric strength
It is the maximum electric field that a dielectric material can withstand before it breaks down and conducts electricity. It is measured in volts per meter (V/m).
57
New cards
Voltage
It is the difference in electric potential between two points in a circuit. It is measured in volts (V) and is represented by the symbol "V".
58
New cards
Current
It is the flow of electric charge through a circuit. It is measured in amperes (A) and is represented by the symbol "I". It is the rate at which charge flows through a circuit.
59
New cards
Resistance
It is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and is represented by the symbol "R". It is determined by the material and dimensions of the conductor.
60
New cards
Power
It is the rate at which energy is transferred in a circuit. It is measured in watts (W) and is represented by the symbol "P". Power is calculated by multiplying voltage and current.
61
New cards
Frequency
It is the number of cycles per second in an alternating current (AC) circuit. It is measured in hertz (Hz) and is represented by the symbol "f". It determines the speed at which the AC signal alternates.
62
New cards
Impedance
It is the total opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and is represented by the symbol "Z". It is a combination of resistance, capacitance, and inductance.
63
New cards
Current
It is the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
64
New cards
Direct current (DC)
Current flows in one direction only.
65
New cards
Alternating current (AC)
Current changes direction periodically.
66
New cards
Ohm's Law
It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.
67
New cards
V \= I * R
Ohm's Law Formula
68
New cards
Resistance
it is the opposition that a material or a circuit offers to the flow of electric current.
69
New cards
Fixed resistors
These have a fixed resistance value and cannot be changed.
70
New cards
Variable resistors
These have a variable resistance value and can be adjusted.
71
New cards
Thermistors
These have a resistance that varies with temperature.
72
New cards
Light-dependent resistors
These have a resistance that varies with light intensity.
73
New cards
Circuit measuring tools
These are used to measure various electrical parameters in a circuit.
74
New cards
Multimeter
A versatile tool that can measure voltage, current, and resistance. It is used to troubleshoot circuits and check the continuity of wires and components. They come in both analog and digital versions.
75
New cards
Oscilloscope
Used to measure and display voltage signals over time. It is used to analyze waveforms and diagnose problems in circuits. They come in both analog and digital versions.
76
New cards
Function generator
Used to generate various types of waveforms such as sine, square, and triangle waves. It is used to test circuits and simulate different types of signals.
77
New cards
Logic analyzer
Used to capture and analyze digital signals in a circuit. It is used to troubleshoot digital circuits and analyze the behavior of digital signals.
78
New cards
Power supply
Used to provide a constant voltage or current to a circuit. It is used to test circuits and power electronic devices.
79
New cards
LCR meter
Used to measure the inductance, capacitance, and resistance of a circuit. It is used to test and design circuits that use inductors, capacitors, and resistors.
80
New cards
Series circuit
It is a circuit in which the components are connected in a single loop, so the current flows through each component in turn.
81
New cards
Parallel circuit
It is a circuit in which the components are connected in separate branches, so the current divides between them.
82
New cards
Electrical circuits
These are often used to convert electrical energy into other types of energy.
83
New cards
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
It is a fundamental law in electrical engineering that states that the sum of all voltages around a closed loop in a circuit must be zero. This law is based on the principle of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one form to another.
84
New cards
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
it is a fundamental law in electrical engineering that states that the total current entering a node or junction in a circuit must be equal to the total current leaving that node or junction.
85
New cards
Electromotive forces
the voltage generated by a battery or other source of electrical energy.
86
New cards
1/C_total \= 1/C_1 + 1/C_2 + ... + 1/C_n
Capacitors in Series Formula
87
New cards
C_total \= C_1 + C_2 + ... + C_n
Capacitors in Parallel Formula
88
New cards
RC circuits
These are circuits that contain a resistor and a capacitor. These circuits are used in a variety of applications, including filters, timing circuits, and oscillators.
89
New cards
Magnetic fields
These are created by moving electric charges.
90
New cards
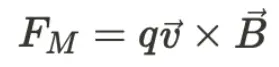
force from a magnetic field
91
New cards
F \= q(v x B)
Lorentz force (When a charged particle moves through a magnetic field, it experiences a force perpendicular to both the direction of motion and the magnetic field. )
92
New cards
F \= qE
When both magnetic and electric fields are present, the particle experiences a combined force that is the vector sum of the two individual forces.
93
New cards
F \= I L x B
When a wire carrying current is placed in an external magnetic field, it experiences a force.
94
New cards
B_perp \= B sin(theta)
If the wire is not perpendicular to the magnetic field, then only the component of the magnetic field perpendicular to the wire will cause a force.
95
New cards
T \= F * r * sin(theta)
When a wire is twisted, a torque is applied to it.
96
New cards
k \= T / theta
torsional stiffness
97
New cards
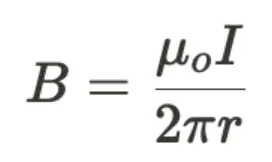
internal magnetic field created by a very long current-carrying wire
98
New cards
F \= μ₀I₁I₂L / 2πd
force between the wires
99
New cards
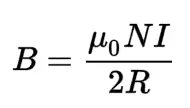
Biot-Savart Law
it states that the magnetic field at a point is proportional to the current density and the distance from the point to the current element.
100
New cards
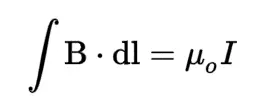
Ampère's Law
The law states that the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed loop is equal to the current passing through the loop multiplied by a constant known as the permeability of free space.