Types of Joints
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
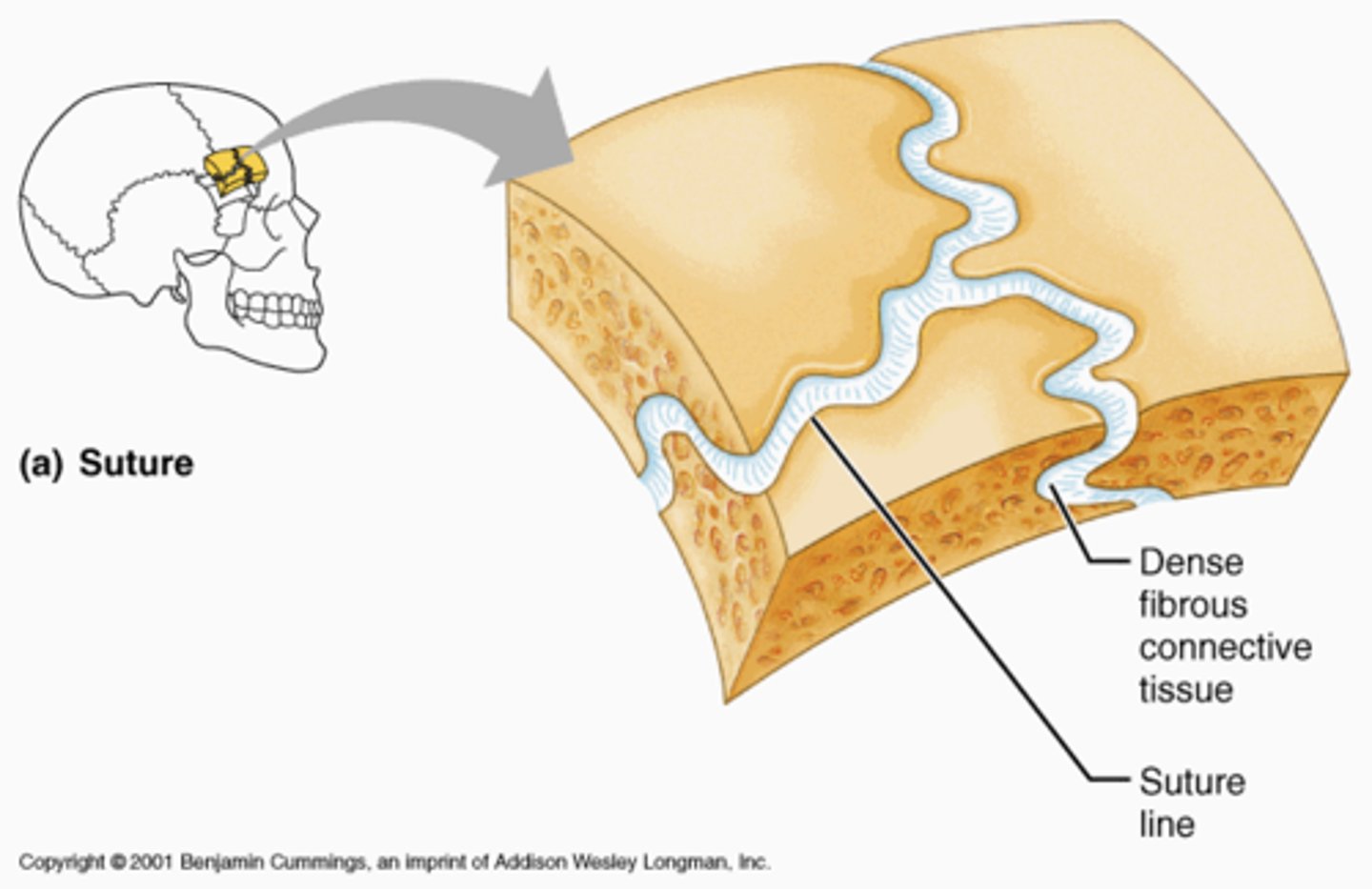
Synarthroses- Fibrous joint
immovable joints
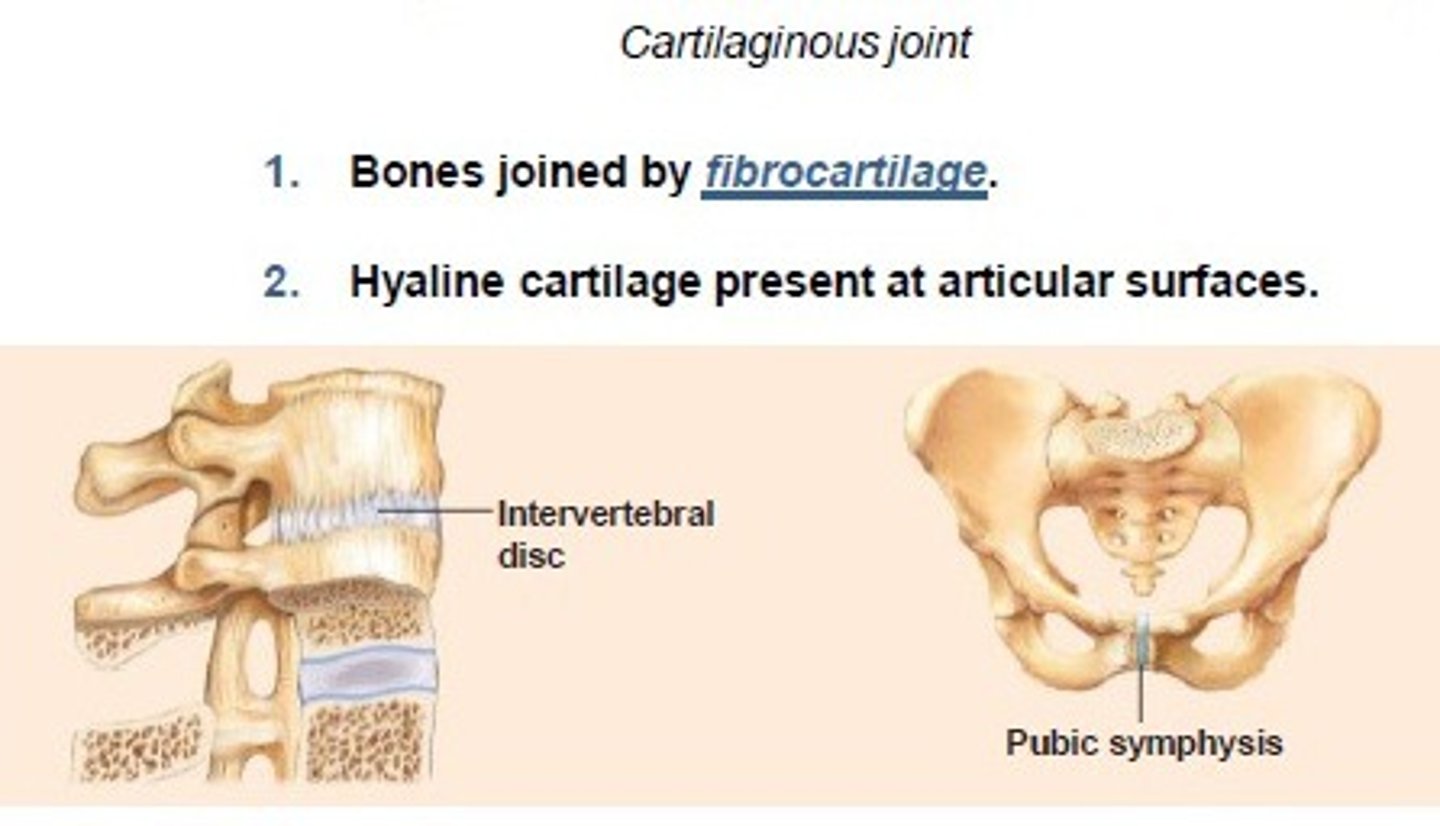
Amphiarthroses- Cartilaginous joints
Slightly moveable joints
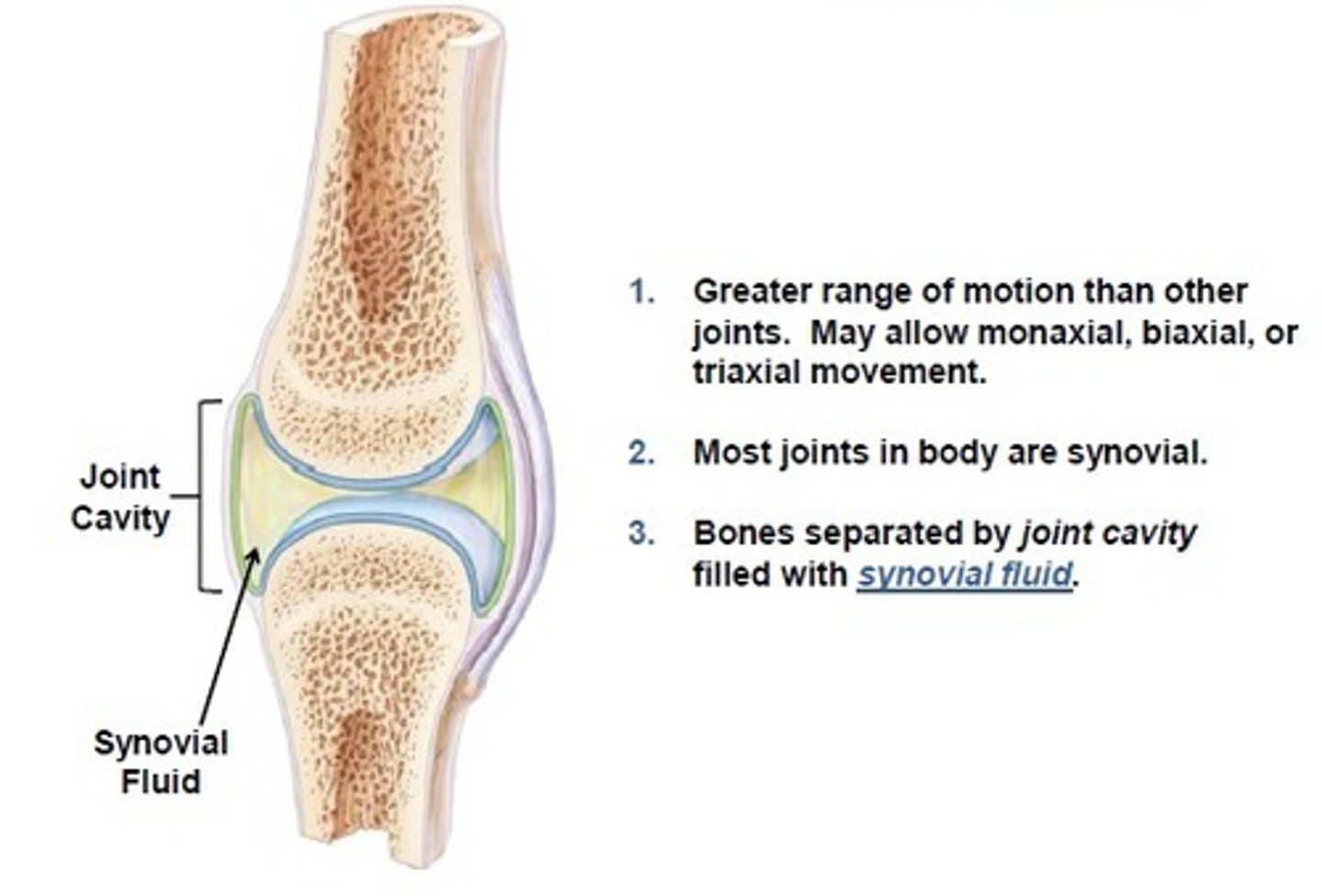
Diarthroses- Synovial joint
Freely movable joint
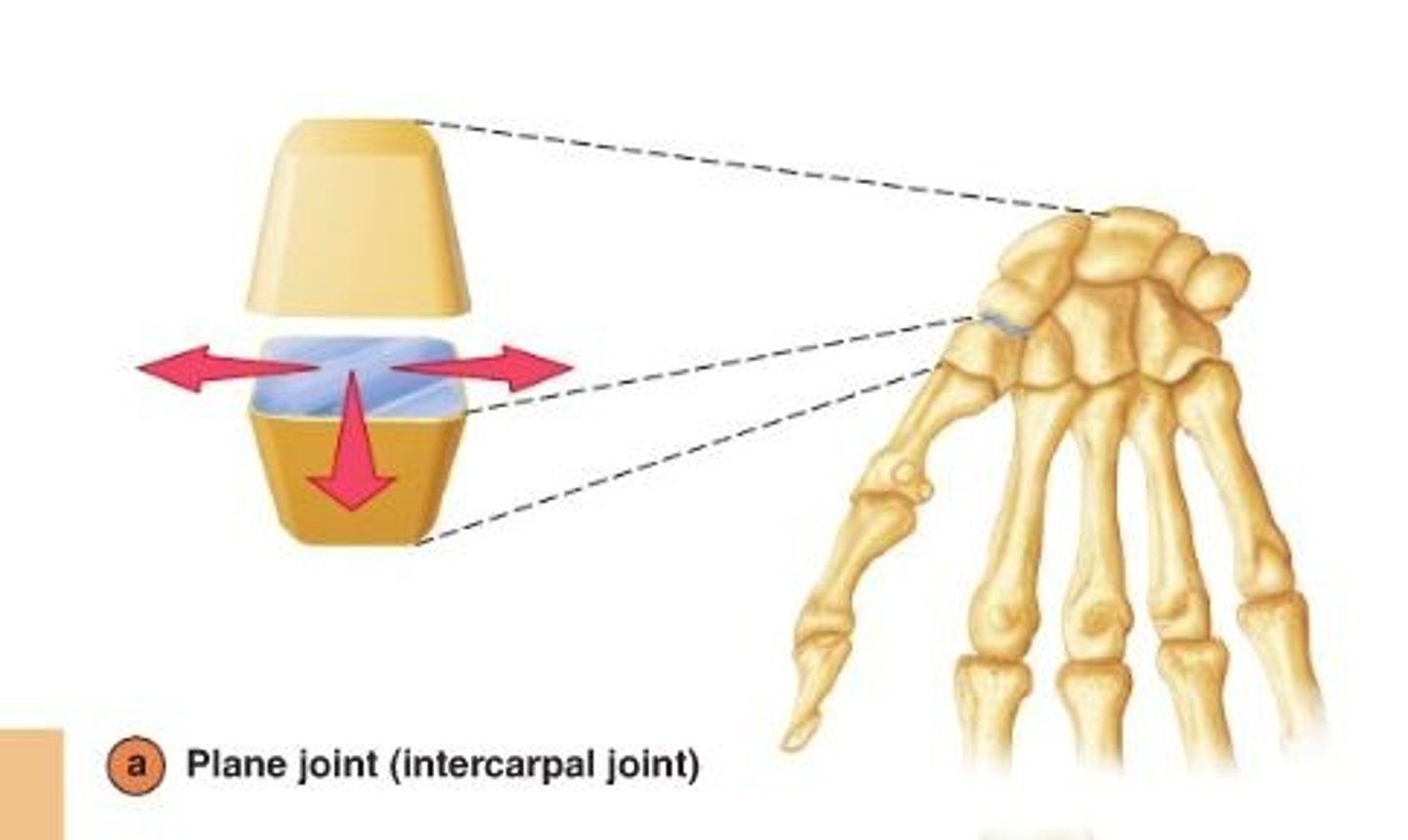
Plane joint
-Nonaxial movement
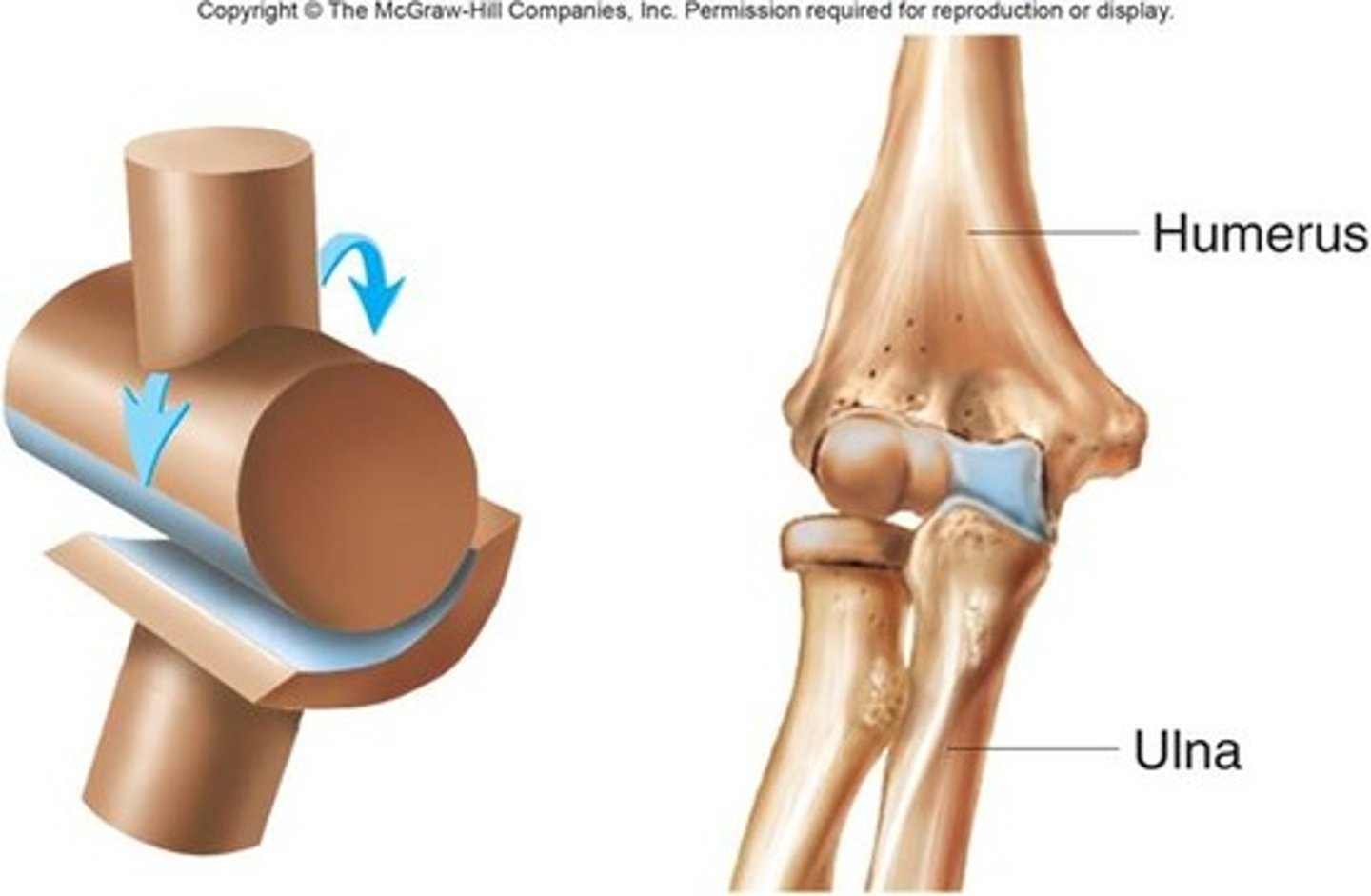
Hinge joint
-Uniaxial movement
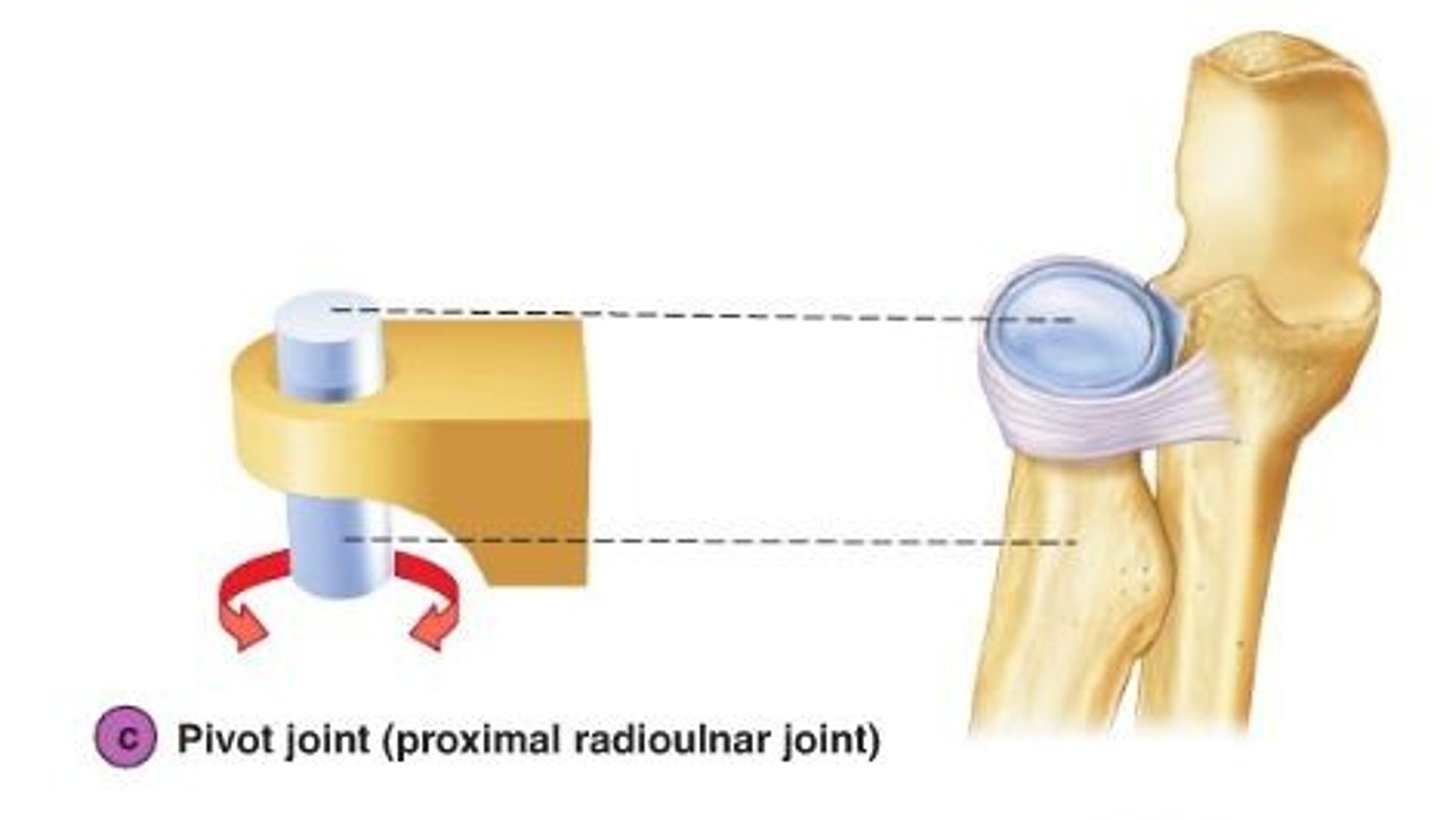
Pivot joint
-Uniaxial movement
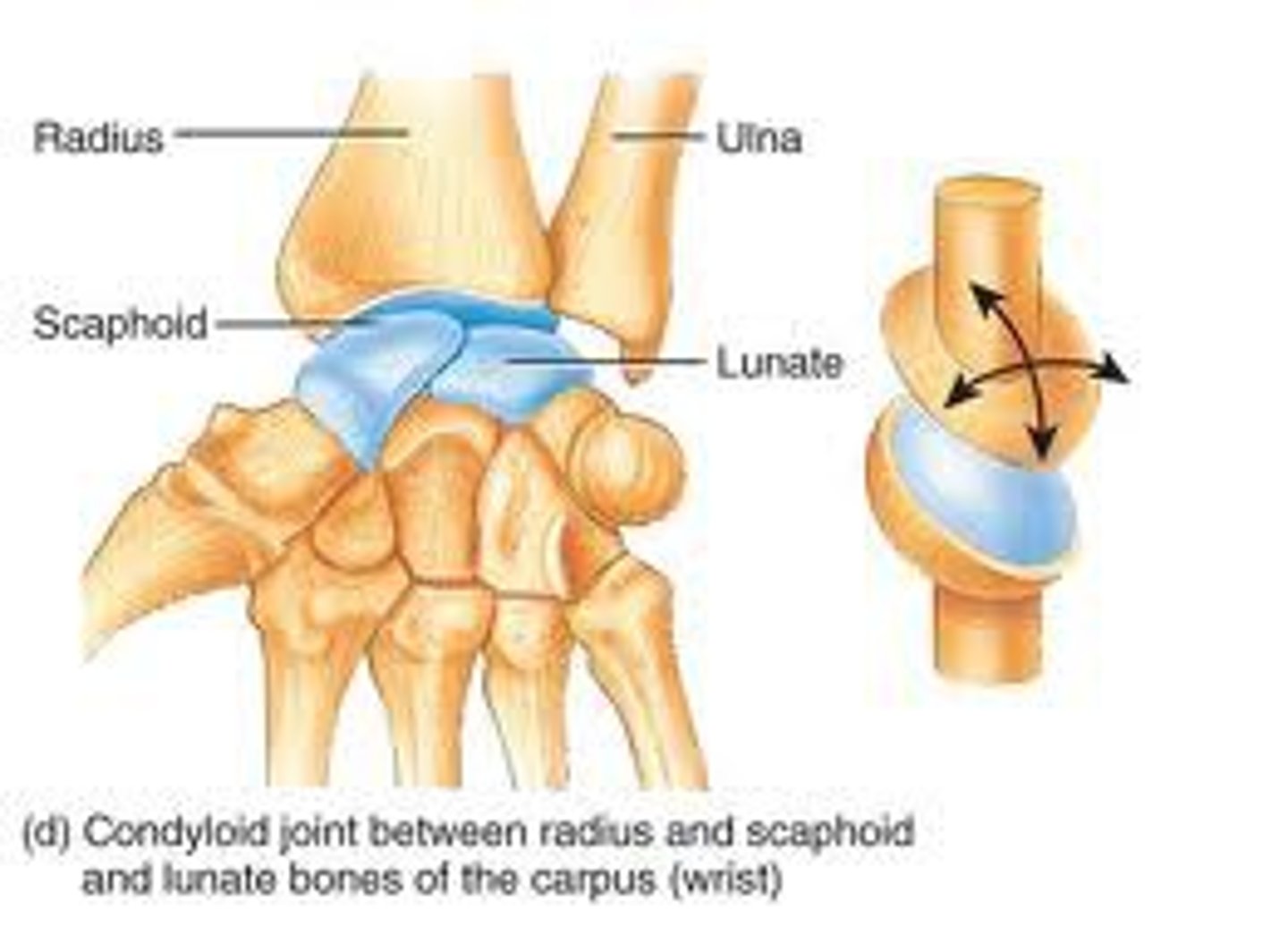
Condylar joint
-Biaxial movement
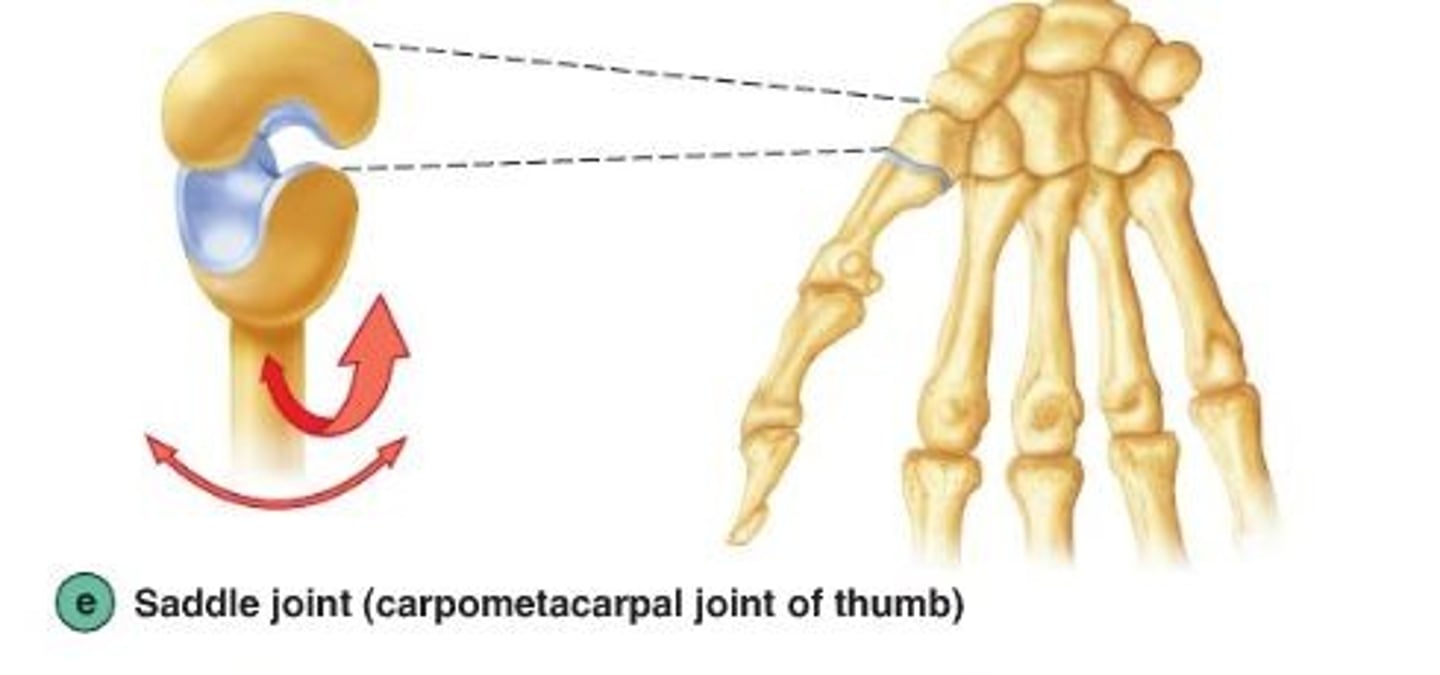
Saddle joint
-Biaxial movement
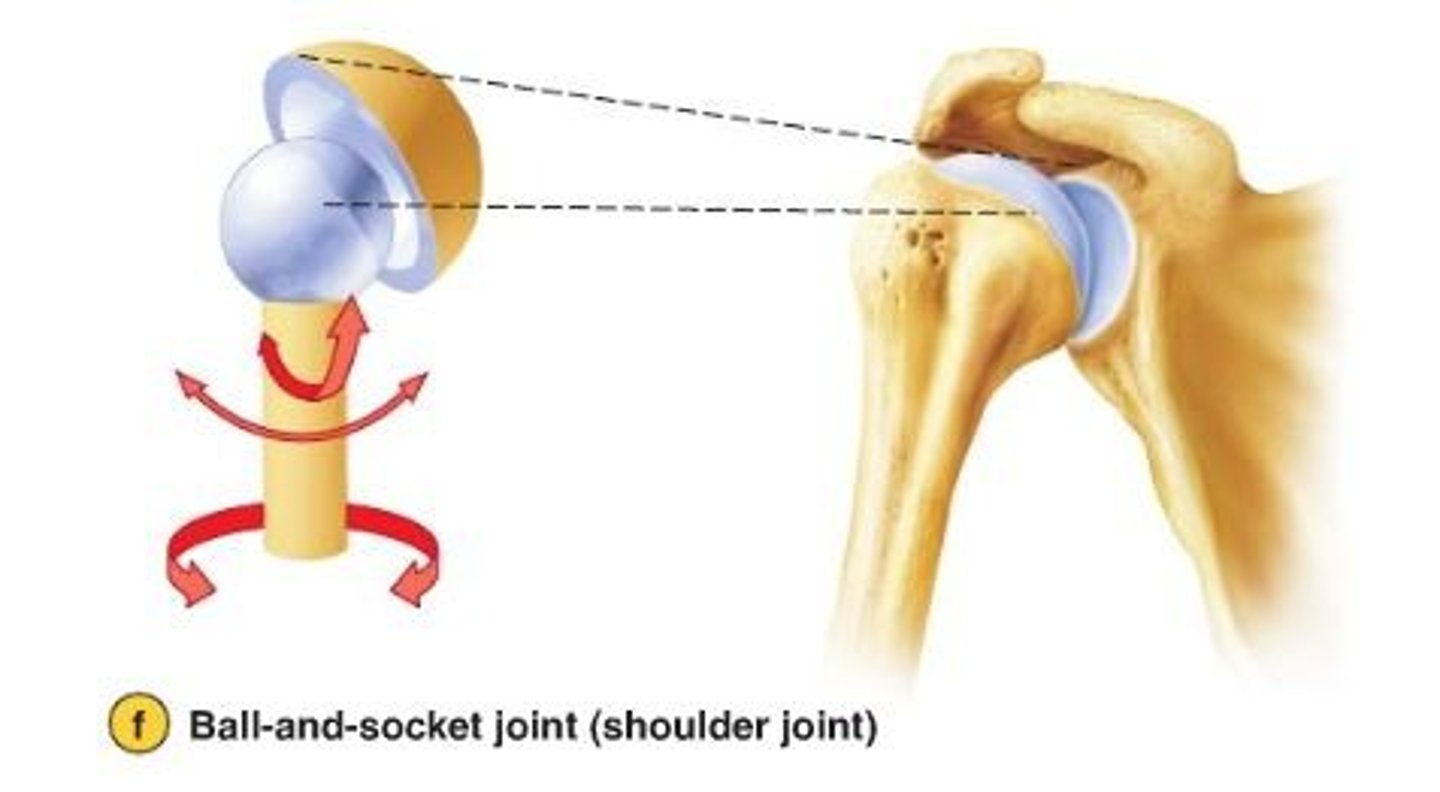
Ball-and-socket
-Multiaxial movement
Fibrous joints
joined by fibrous tissue
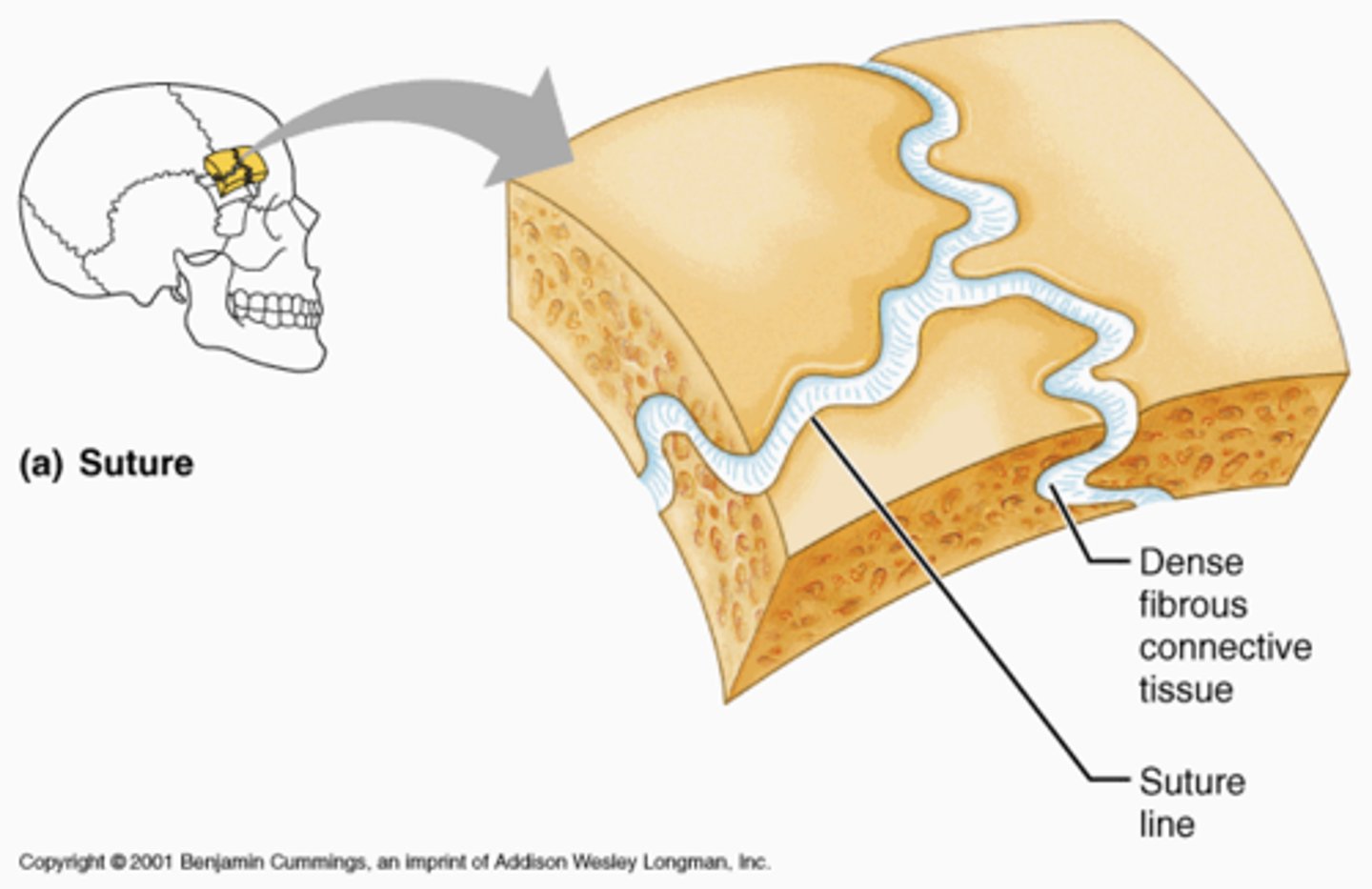
-Sutures
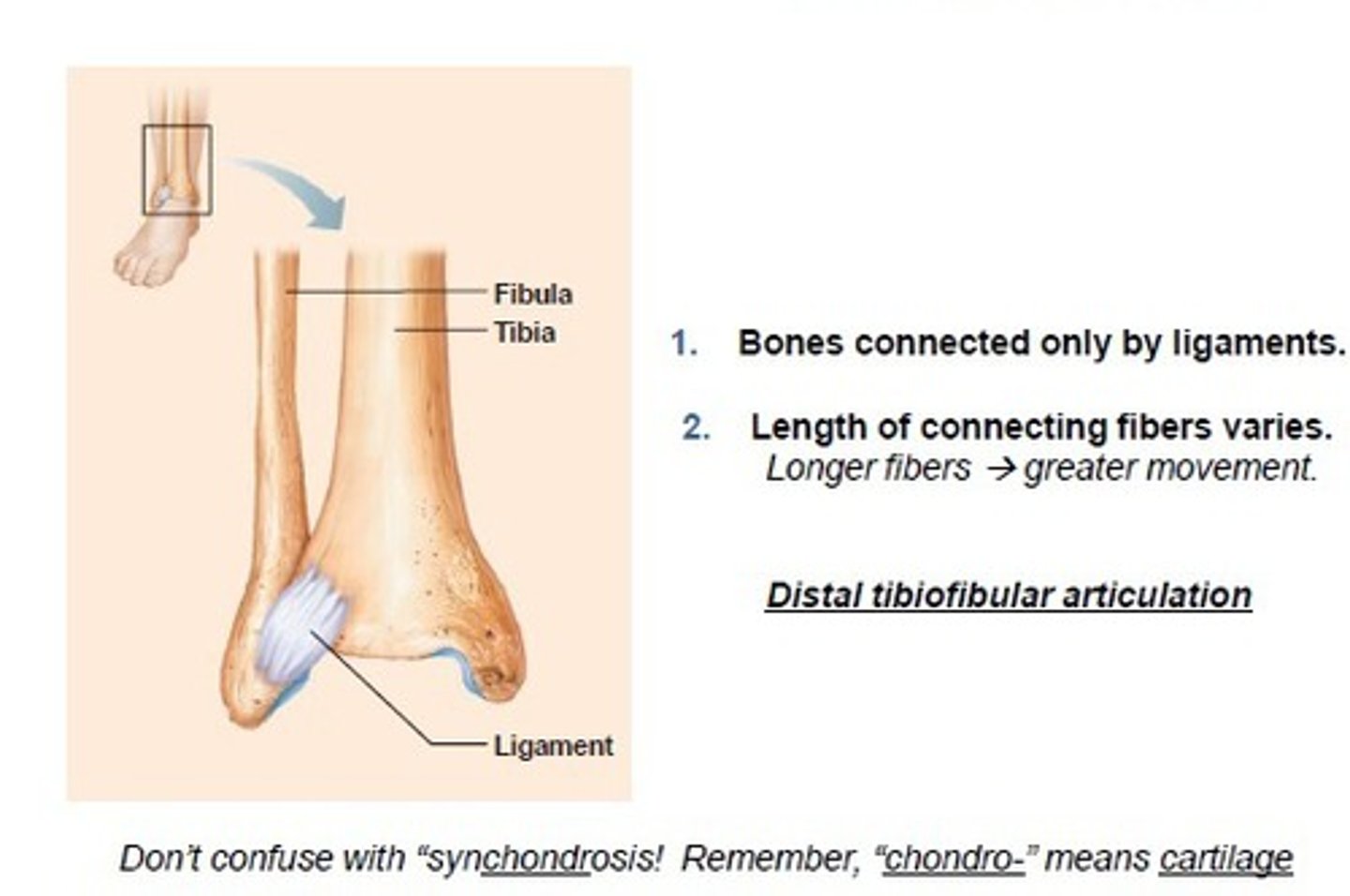
-Syndesmosis
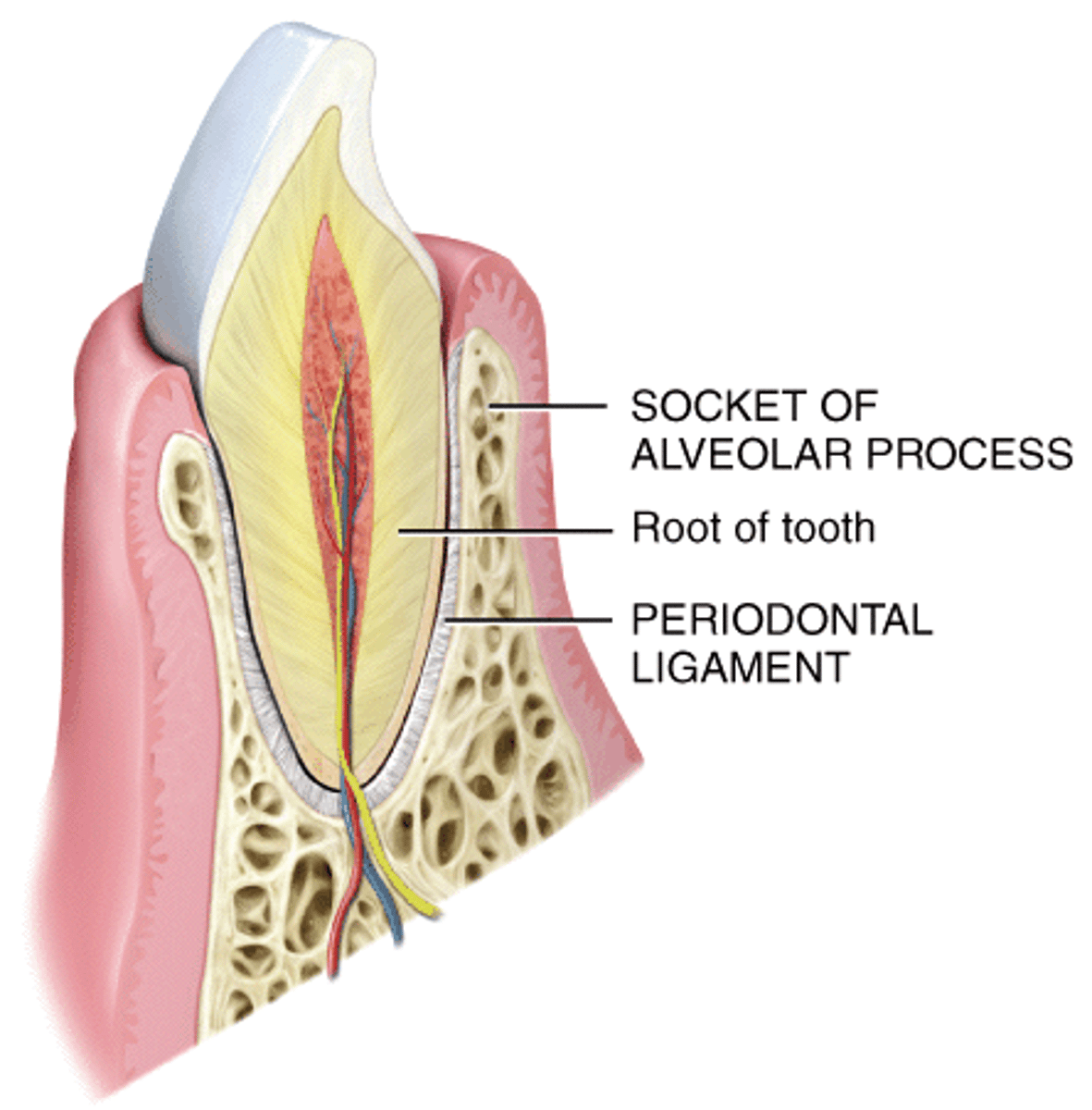
-Gomophosis
Suture
Syndesmosis
Gomophosis
Fibrous joint; Periodontal ligament holds tooth in socket
Cartilagenous Joints
Joined by cartilage
Synchondroses
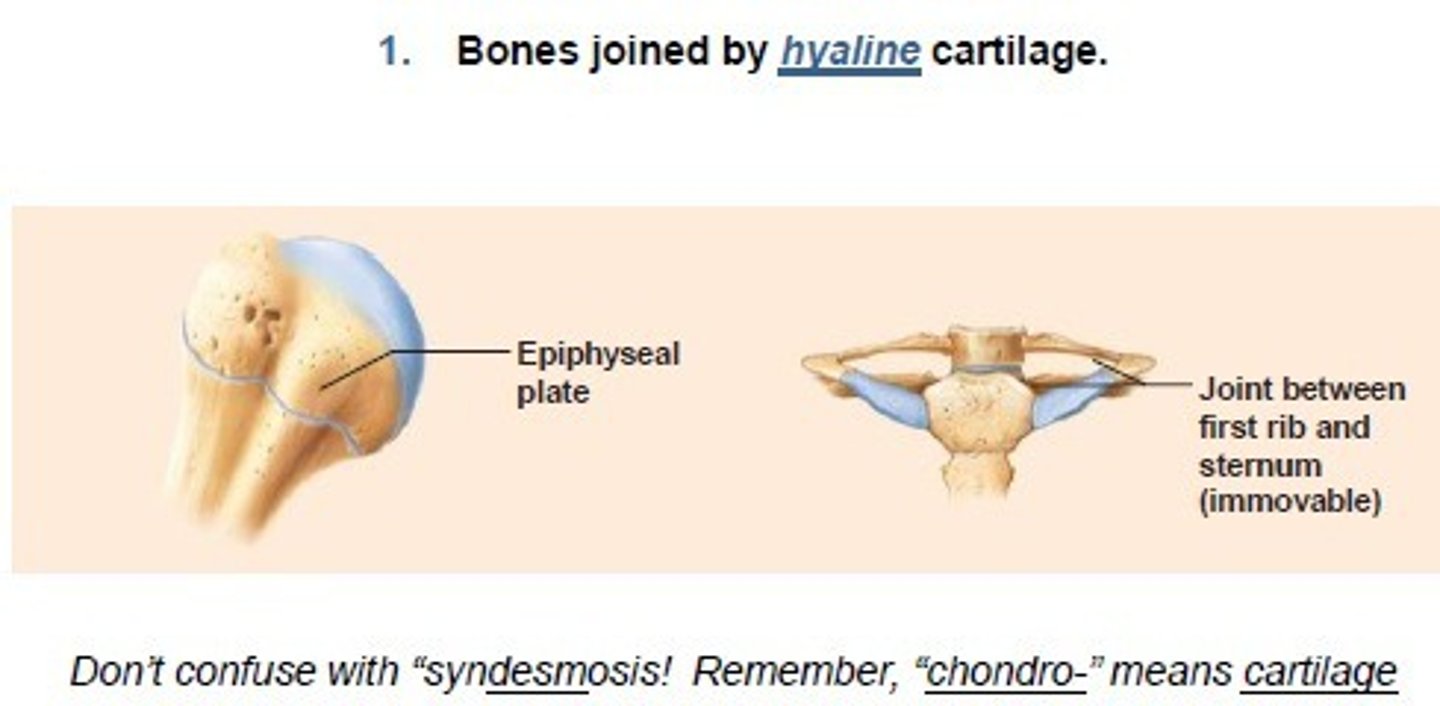
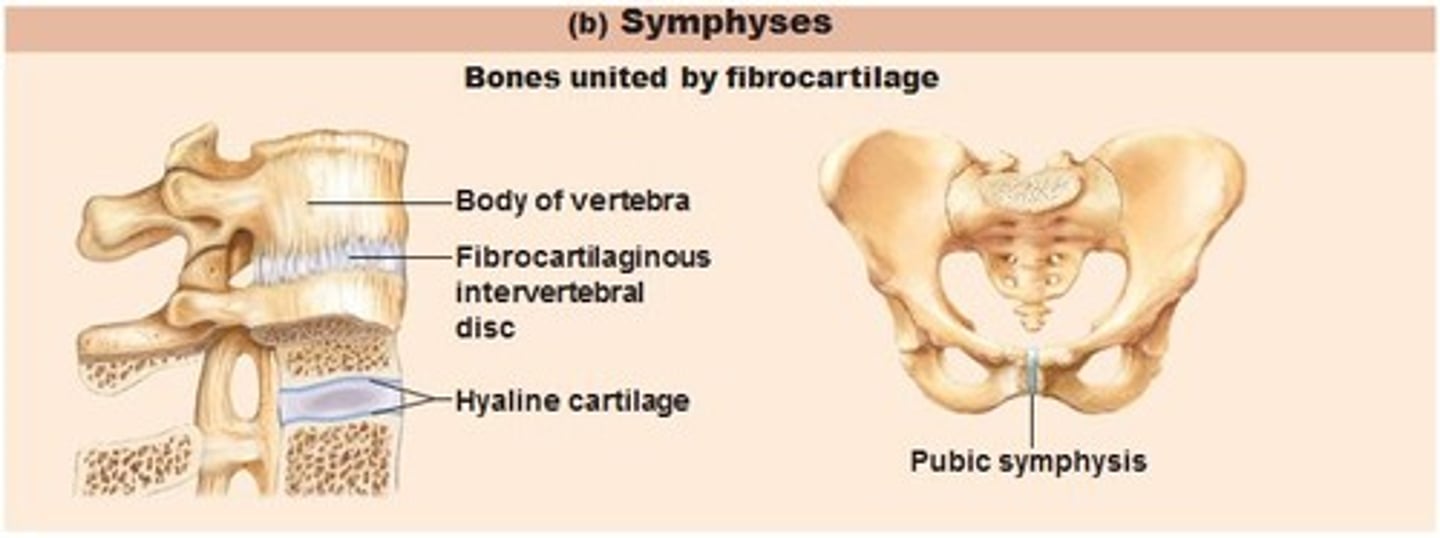
Symphyses
Synovial joint
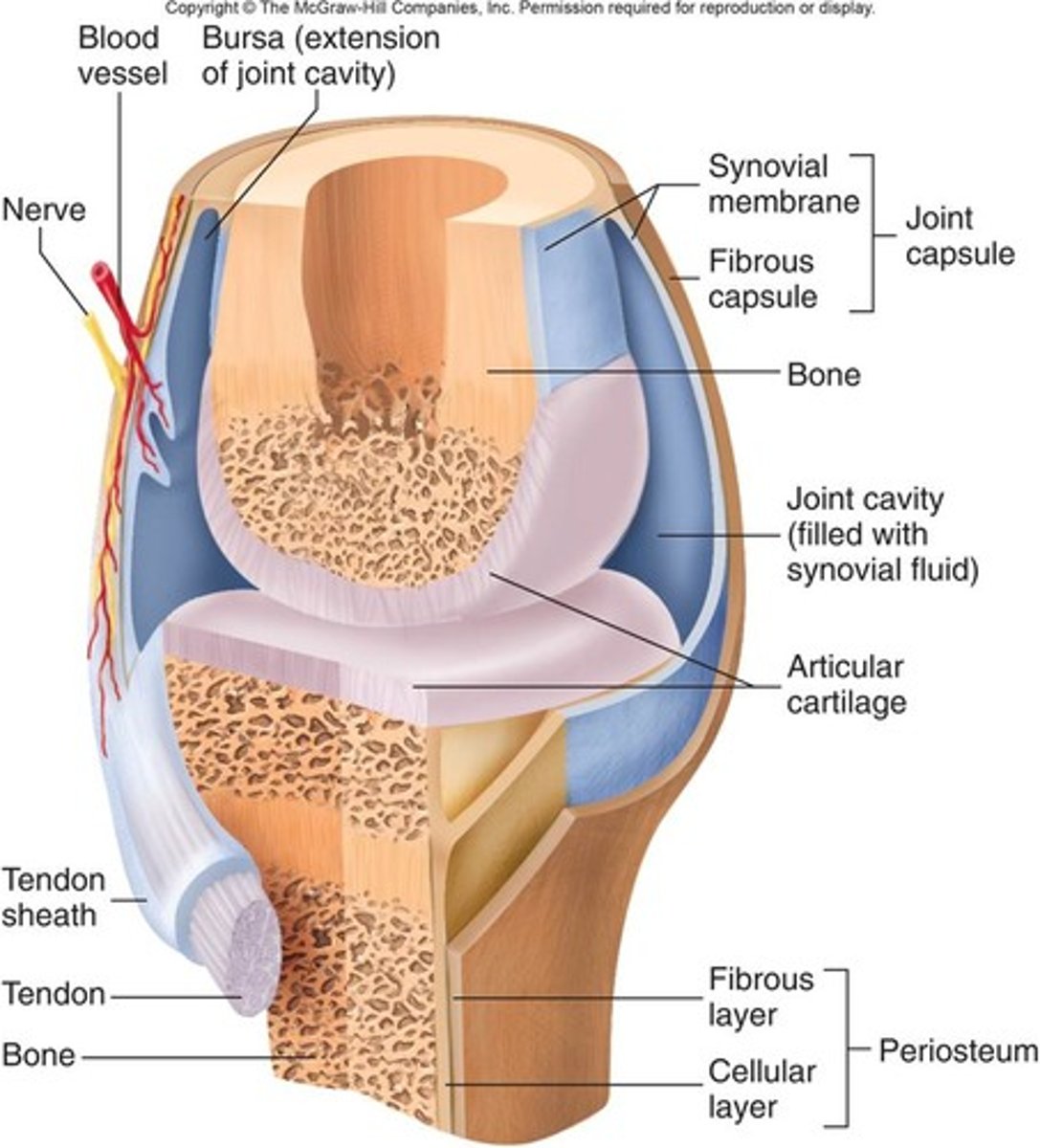
3 stabilizing factor at synovial joints
1. Shapes of articular surface (minor role)
2. Ligaments number and location (limited role)
3. Muscle tendons that cross joint (most important)
Synovial joints
Nonaxial- Slipping movements only
Uniaxial- movement in one plane
Biaxial- movement in two planes
Multiaxial- movement in or around all 3 planes
3 general types of movement at Synovial joints
1. Gilding
2. Angular movements
3. Rotation