biology- igcse revision (not topical)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
State the name given to a length of DNA that codes for a protein.
gene
State features of all prokaryotes.
unicellular
asexual reproduction
ribosomes
cell wall
cytoplasm
circular DNA (free in cell)
Describe what is meant by the term decomposer.
organisms that get energy from dead organism or waste organic material
state the function of mitochondrion.
aerobic respiration
Enzymes are involved in chemical digestion which produces small ................................................ molecules that can be absorbed into the blood.
soluble
Two examples of protease enzymes are pepsin and trypsin. Pepsin is produced by the ................................................ and requires acidic conditions. These conditions are created by the release of ................................................ , which provides the optimum pH for pepsin activity and also kills harmful ................................................ .
stomach
hydrochloric acid
pathogens
The ................................................ produces trypsin which breaks down protein in ................................................ pH conditions. These conditions are created by a substance called ................................................ , which neutralizes the gastric juices and also has an important role in the ................................................ of fats and oils.
pancreas / small intestine
alkaline
bile / bile salts
emulsification
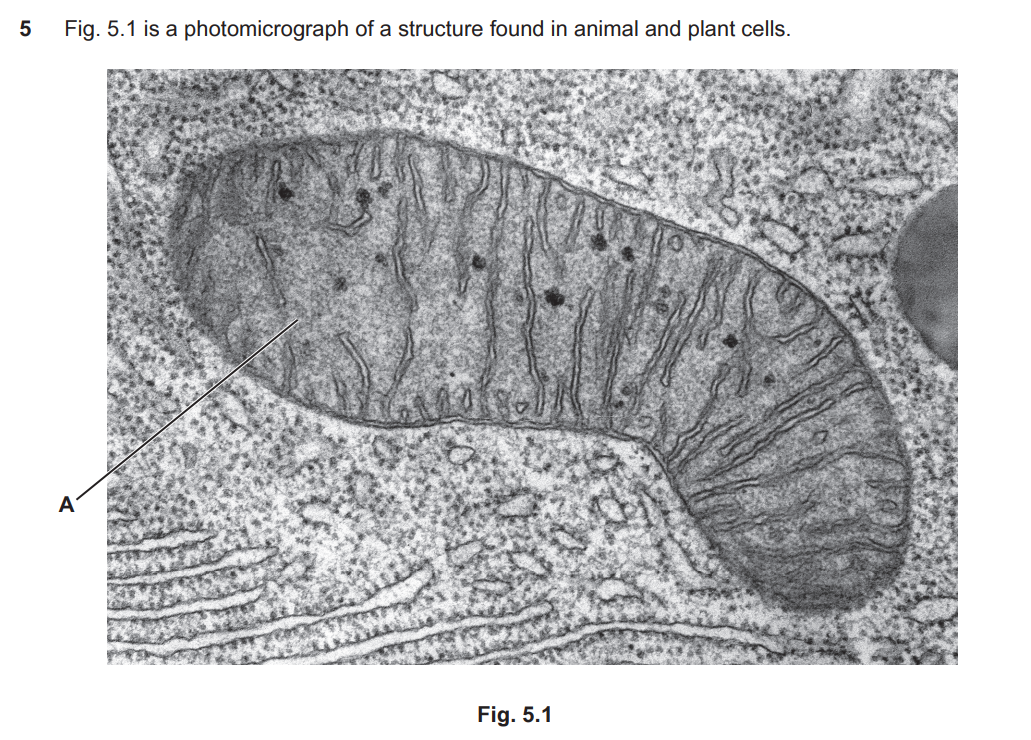
State the name and function of the cell structure labelled A in Fig. 5.1
mitochondrion
(aerobic) respiration
features of incisors
Rectangular shape, sharp for cutting and biting
Explain the reasons for changes in pressure seen in arteries
caused by contraction of muscles (of the heart/ventricle)
pressure increases when the heart/ ventricles contract/pump
pressure decreases when the heart/ventricles relax
describe the structure of capillaries
One cell thick wall for easy diffusion
Highly branched; large surface area
Capillary beds constantly supplied with fresh blood, so diffusion occurs
equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast
Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
what is a synapse
a junction between two neurones, consisting of a gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neurotransmitter
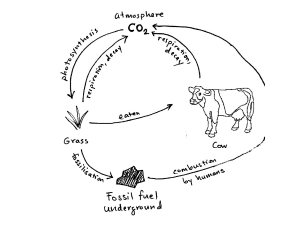
describe the carbon cycle
Carbon is taken from the atmosphere by photosynthesis (plants)
It is passed on to animals and decomposers by feeding. It is returned by respiration in plants and animals and decomposed by microorganisms.
state the features of arachnids
Two body segments – cephalothorax and abdomen
Four pairs of legs (8 legs)