Neurophysiology 2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is the central pattern generator involved in
rhythmic behaviours (e.g. walking, swimming, flying, ventilation)
what is reciprocity
muscle groups arranged in antagonistic pairs, when 1 fires the other is inhibited
what does the cellular oscillator do
generate temporary patterned activity itself
what is the network oscillator
network of neurones interact so output is temporarily patterned
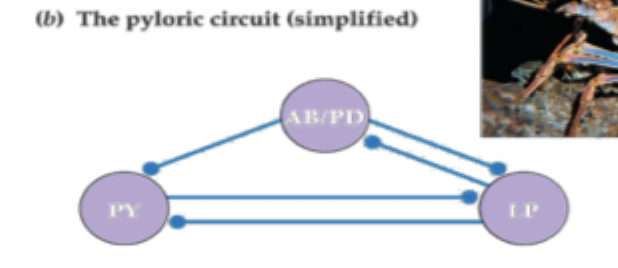
what do the letters represent
AB = anterior burst neurone, PD = pyloric dilator neurone, LP = lateral pyloric neurone, PY = pyloric neurone
what happens in the hybrid oscillator
AB bursts of action potentials, PD electrically coupled to AB, LP and PY inhibit each other
what is synaptic plasticity
change in synaptic strength over time, allows nervous system to adapt
what is synaptic strength measured as
amplitude of postsynaptic potential
what is facilitation in synaptic plasticity
increased amplitude in response to successive impulses
what is antifacilitation in synaptic plasticity
decreased amplitude in response to successive impulses
what does synaptic plasticity result from
amount of neurotransmitter released per presynaptic impulse
what is habituation
decrease in intensity of a reflex response to a stimulus when it occurs repeatedly
what is sensitisation
prolonged enhancement of a reflex response to a stimulus that results from a 2nd stimulus
which 2 glutamate receptors does long term potentiation depend on
NMDA and AMPA
what does NMDA require
postsynaptic cell to be strongly depolarised, so is blocked by Mg2+ unless conditions are met
what happens in long term potentiation when then the postsynaptic cell is depolarised
Ca2+ enters, phosphorylation of AMPA receptors, new receptors delivered in membrane
what does long term potentiation cause
structural change in neurone, effects learning and memory