Exam #2 - Vibrio, Aeromonas, Plesiomonas, Campylobacter, Helicobacter
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
General characteristics of Facultative Gram-Negative Rods
Ferment glucose
Oxidase positive
Grow on Blood Agar and MacConkey Agar
When motile – polar flagella
Vibrio Organisms
V. cholerae
V. alginolyticus
V. parahemolyticus
V. vulnificus
Vibrio General
Almost all are pathogenic to humans
Commonly found in aquatic environments
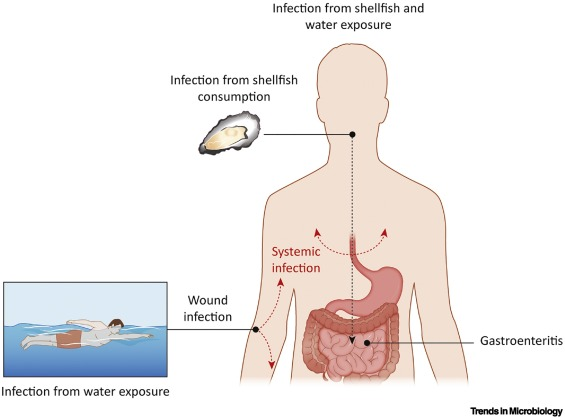
Clinical infections: Gastroenteritis, Wound infections, Septicemia
All (except V. cholerae) are halophilic = require addition of salt to grow
Vibrio abbreviated morphology and biochemical
Motile
Oxidase positive
Nitrate positive
Curved GNB
Vibrio
String Test
Most species exhibit a positive “string test.” after being emulsified in 0.5% sodium deoxycholate
Helps distinguish Vibrio from Aeromonas and P. shigelloides
Vibrio – Culture Media
Grows on BA and usual differential media for stool cultures
May be hemolytic on BA
NLF on MAC (except V. vulnificus)TCBS Agar
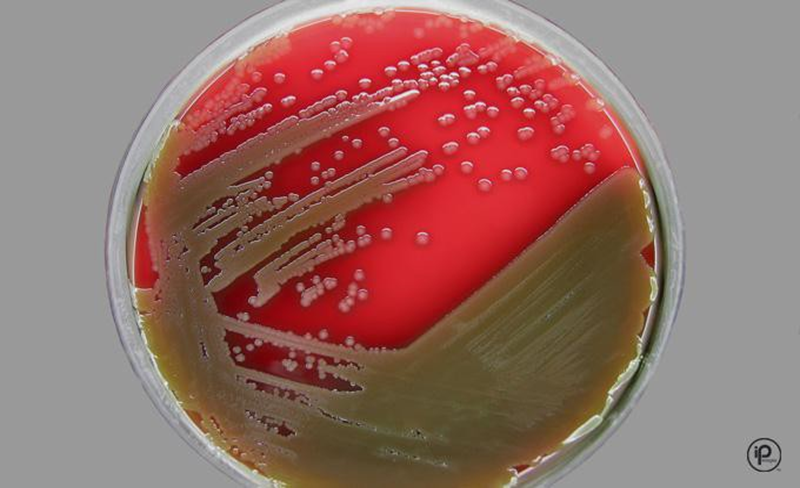
TCBS Agar
Thiosulfate Citrate Bile salts Sucrose
Selective media…gram pos and LF GNB inhibited
Some Vibrio grow poorly on this media
Those that grow: Yellow or Green colonies
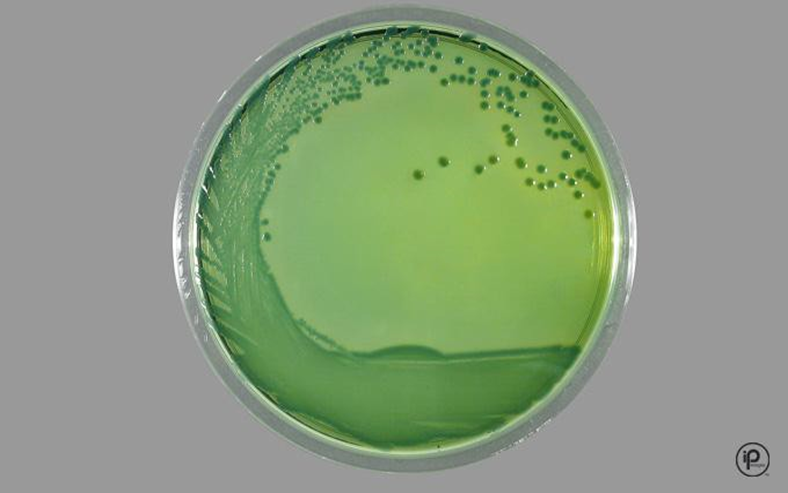
Vibrio media TCBS
Results
V. cholerae and V. alginolyticus will be yellow (ferments sucrose
V. parahemolyticus and V. vulnificus will produce green colonies (do not ferment sucrose)
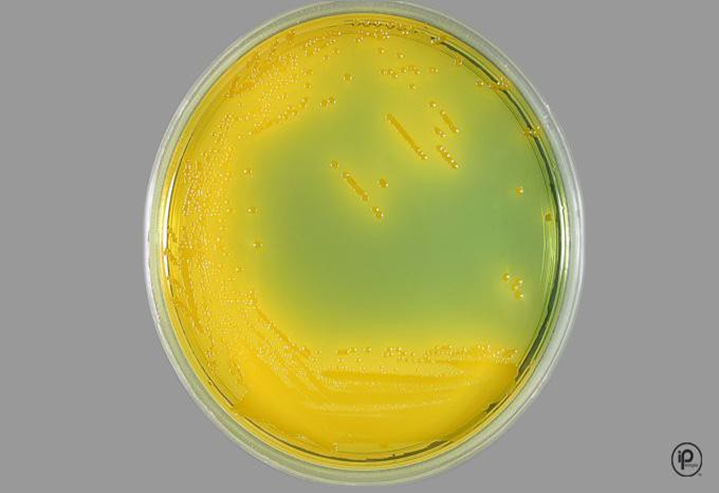
Vibrio cholerae
Morphology and characteristics
BAP – may be beta hemolytic
MAC – NLF
TCBS – yellow (sucrose fermenter)
Identification
Sucrose fermenter
0% NaCL = Growth
6% NaCL = Variable growth
Vibrio cholerae – Disease
Cholera
Rice water stools (10-30/day w/ mucous)
Enterotoxin production – ‘cholera toxin’
Affects absorptive ability of GI tract
Can lead to death if untreated
Spread mainly from water, food contaminated with organism
7 major cholera pandemics since 1817
Two major biotypes: O1 classic and El Tor
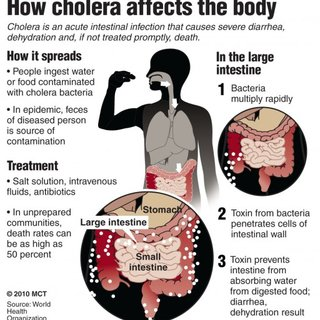
Cholera Treatments
Fluids …. A Lot of FLUID!
Electrolytes
Maybe antibiotics
Vibrio parahemolyticus
Morphology and characteristics
Morphology and characteristics
BAP – May be beta hemolytic (not all)
MAC – NLF
TCBS – Green (sucrose -)
Halophilic – requires at least 1% NaCl for growth….tolerates up to 8% NaCL
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Identification
Sucrose non-fermenter
ODC and LDC = Positive
0% NaCL = no growth
6% NaCl = growth
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Disease states
Gastrointestinal disease – self limiting
Raw or improperly cooked seafood
Wound infections
Open wound exposed to contaminated water or seafood
Vibrio vulnificus
Morphology and Characteristics
BAP = Non hemolytic
MAC = LF (usually)
Isolate on TCBS – colony color is usually green
Vibrio vulnificus
Identification
Lactose = Fermenter (usually)
Sucrose = variable (usually non-fermenter)
ODC = variable
LDC = positive
0% NaCL = no growth
6% NaCL = Growth
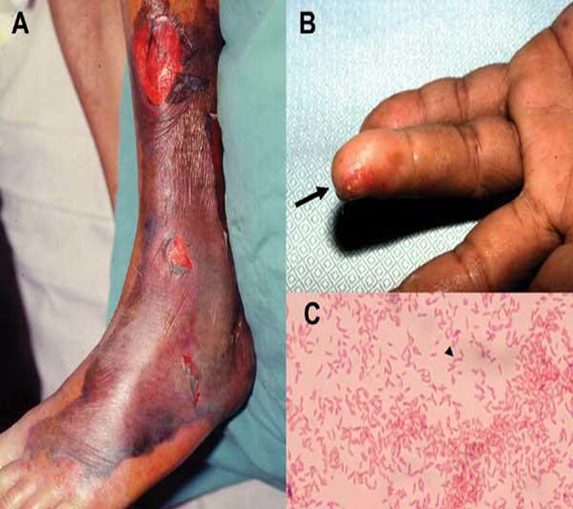
Vibrio vulnificus
Disease States
Disease States
Highly invasive and virulent
Intestinal….raw oysters
Invades intestinal mucosa and reaches blood stream
Wound infections
Most often have a history of a traumatic aquatic wound
Aggressive tissue infection
Vibrio alginolyticus
Morphology & Characteristics
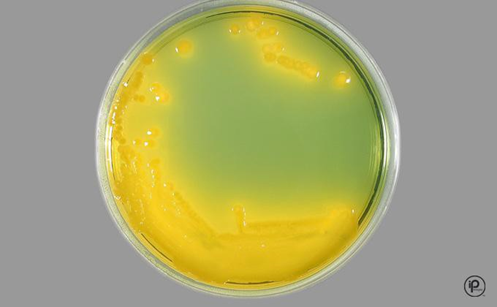
Morphology and characteristics
BAP – nonhemolytic
MAC – NLF
TCBS – yellow colony
Vibrio alginolyticus
Id
Sucrose = Fermenter
LDC = Positive
ODC = Positive
0% NaCL = No growth
6.5% NaCL = Growth
Vibrio alginolyticus
Disease States
Least pathogenic species
Occupational exposures – fishing, sailing, etc.
Wound, ear, eye, burn
Aeromonas hydrophila
Morphology & Characteristics
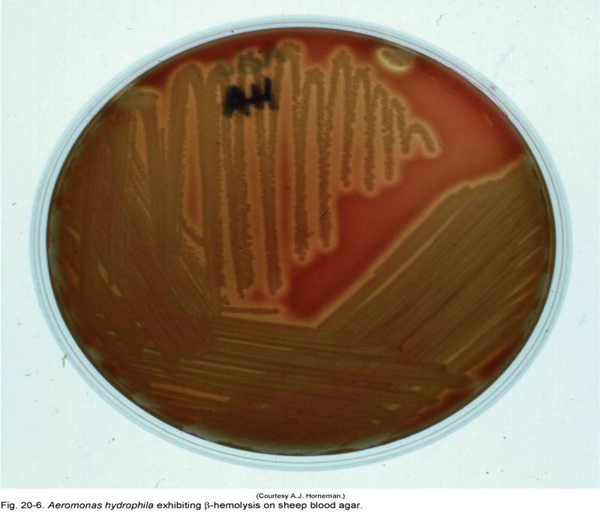
Morphology and characteristics
Beta-hemolysis on BA
MAC = NLF or LF
Large, round, raised opaque colonies, smooth mucoid surface
CIN agar = growth of pink colonies
Aeromonas hydrophila
Biochemicals
Gram stain = Straight gram negative rod
Identification
Lactose = variable
Sucrose Fermenter
Inositol = non-fermenter
LDC and ADH = Positive
ODC = Negative
Indole = Positive
Dnase = Positive
0% NaCL = Growth
6% NaCL = No Growth
Aeromonas hydrophila
Disease States
Gastroenteritis
Wound infections
Septicemia…hepatic, biliary, pancreatic malignancy
UTI
Osteomyelitis
FOUND IN WATER AND SEWAGE
Plesiomonas shigelloides
Morphology & Characteristics
Morphology and Characteristics
BAP = Non-hemolytic
MAC = Both LF and NLF
Gram Stain = pleomorphic gram-negative rod
NOTE: Considered a member of the Family Enterobacteriaceae even though Oxidase positive
Plesiomonas shigelloides
Identification
Identification
Lactose = variable, delayed fermenter
Sucrose= non-fermenter
Inositol = Fermenter
LDC, ADH, and ODC = Positive
Indole = Positive
Dnase = Negative
0% NaCL = Growth
6% NaCL = No Growth
Plesiomonas shigelloides
Habitat & Disease States
Habitat
Fresh or brakish water in tropical areas
Disease States
Gastroenteritis
Ingestion of contaminated water or food
Shares antigenic structures with Shigella but less virulent
Microaerophilic GNB
Species and Id
Species
Campylobacter
Helicobacter
Gram Negative Rods
Oxidase Positive
Glucose = Asaccharolytic
Microaerophilic
Curved Bacilli
Campylobacter species
Infections
Infections
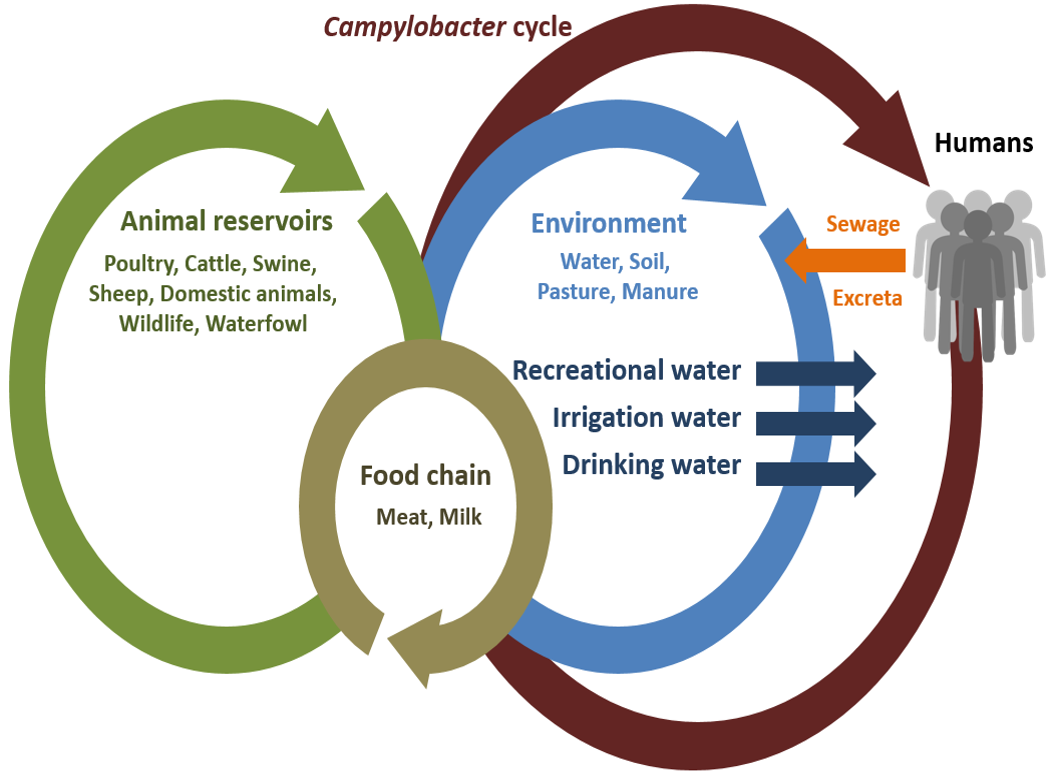
Found in intestinal tract of animals (poultry, cattle, etc.)
Associated with diarrhea and systemic infections
Humans infected when consuming contaminated food, milk, water
Has been associated with Guillain-Barre syndrome
Auto immune disorder characterized by acute paralysis due to damage to the peripheral nerve system possibly due to Campylobacter antibodies cross-reacting with nerve cells
We’ll hear about these from public health. Beware of contaminated meats (mostly chicken) & Raw milk.
Campylobacter species
Most are microaerophilic and capnophilic
Most are slow growing
Gram Stain
Small, curved GNB….S shapes or ‘sea gull wings’
Carbolfuschin counter stain improves GS
Urease Negative
Darting motility in fresh stool, Allegedly
Campylobacter jejuni ssp jejuni
Morphology
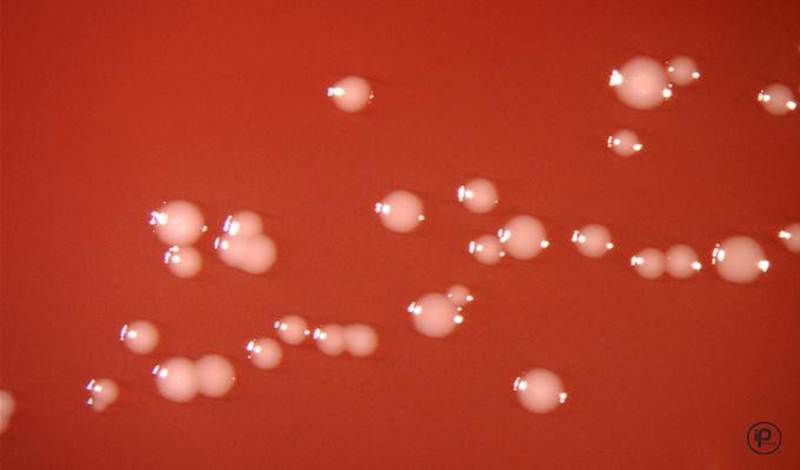
BAP: Gray to pink-tan flat colonies, moist, runny, spreading
Selective media – used to prevent overgrowth by faster growing enteric organisms
Campy-BAP: Brucella agar base, 10% sheep blood, antibiotics
Skirrows media: Columbia agar base, 7% horse blood, antibiotics
Grows best at 42C
Microaerophilic and capnophilic
Don’t like too much Oxygen, But not anaerobic

Campylobacter jejuni
ID
Identification
Characteristic gram stain and motility
Oxidase positive
Catalase positive
Hippurate hydrolysis positive
Growth at 42C
Nalidixic acid: Susceptible
Cephalothin: Resistant
MAC = no growth
Campylobacter jejuni
Disease States
Disease States
Leading cause of diarrhea world-wide (self-limiting)
As few as 500 organisms can cause enteric disease
Penetrates the intestinal epithelium, multiplies and destroys cells causing diarrhea that contains RBCs and WBCs
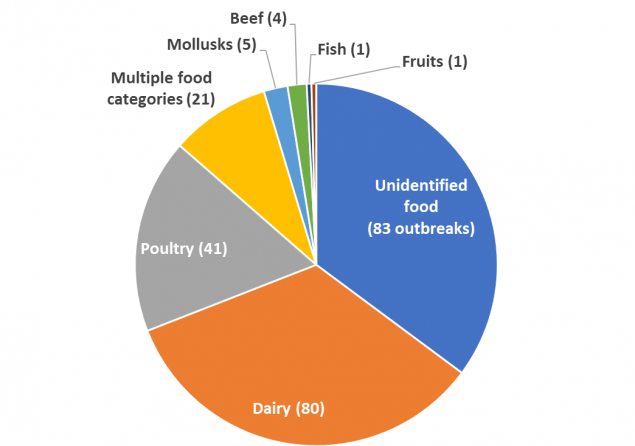
Food contaminants are the major route of transmission. Dairy, unknown, and then poultry
Other Campylobacter sp.
C. Coli
Grows at 42C
Hippurate hydrolysis: Negative
Cephalothin: Resistant
Nalidixic Acid: Susceptible
C. Fetus
Animal pathogen
Variable growth at 42C
Hippurate hydrolysis: Negative
Cephalothin: Susceptible
Nalidixic acid: Resistant
Grows on MAC
These are uncommon and more commonly seen in vet clinics
Helicobacter pylori
General
Associated with gastric, peptic, and duodenal ulcers
Colonizes 20%-40% of adults in the United states
Possibility that groundwater is the source of infections
Person to person??
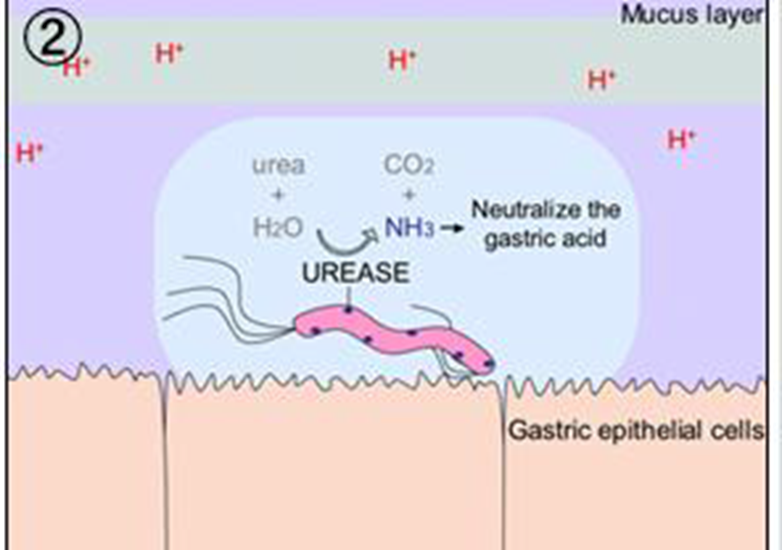
Survives the highly acidic environment of the human stomach
Produces urease which breaks down urea to ammonia and neutralizes stomach pH
Helicobacter pylori
Disease States
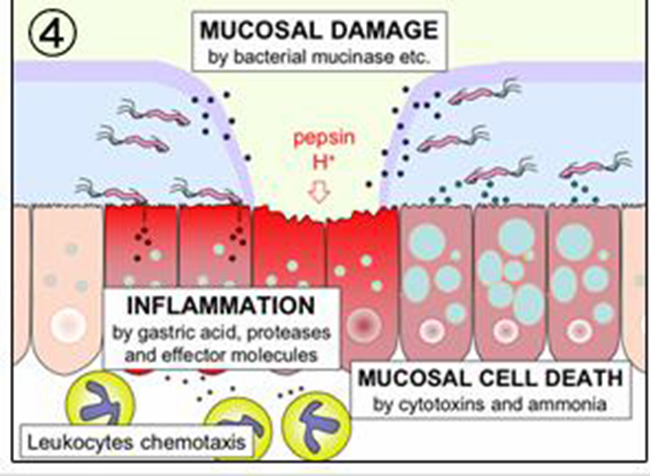
Produces a low-grade inflammatory response
Damaged tissue resulting in ulcers
Continued damage has been associated with the development of gastric carcinoma
Difficult to treat
Helicobacter pylori
characteristics and identification
Organism is strongly urease positive
Usually detected using non-culture methods
Presumptively identified from gastric biopsy specimen by testing for the presence of urea
Proteus miribilis is also urease pos
Helicobacter pylori
Id
•Serologic testing also available—serum antibody test
•Stool Antigen detection kits
Also have Breath test that are available.
Given a pill with radioactive urea. If H. Pylori present, they are able to break it down into ammonium and blow into a balloon→ look for Co2