biomechanics final exam (material from first exam)-Phillips
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
251 Terms
what is the term for the study of motion or human movement?
kinesiology
what is the term for the study of the human musculoskeletal system and musculotendinous system?
anatomical
what is the term for the study of muscles as they are involved in science of movement (both skeletal and muscular structures are involved)?
structural
what is the term for the application of mechanical physics to human motion?
biomechanics
what is the basis from which to describe joint movements?
reference positions
what is the anatomical position?
-head, gaze of eyes, and toes are directly anteriorly (forward)
-arms to the side with palms facing forward
-lower legs are close together, feet parallel, and toes are directed anteriorly (forward)
what is a level, flat surface, that is often imaginary?
plane
what is the point or line about which something rotates?
axis
what are the three primary planes of motion?
sagittal, frontal, and horizontal (transverse) plane, cardinal
which primary plane of motion passes through the body from front to back and divides the body into left and right? what is a movement that occurs primarily in this plane?
sagittal plane; flexion and extension
which primary plane of motions divides the body into anterior and posterior? what is a movement that occurs primarily in this plane?
frontal; abduction and adduction
which primary plane of motion divides the body into superior and inferior (top and bottom)? what is a movement that occurs primarily in this plane?
horizontal (transverse); pronation and supination or horizontal flexion/extension
which plane of motion divides the body into equal halves?
cardinal plane
which anatomical term described to position of something relative to a surface or other structure as being closer to the surface?
superficial
which anatomical term described to position of something relative to a surface or other structure as being in between two structures?
intermediate
which anatomical term described to position of something relative to a surface or other structure as being farthest away from the surface?
deep
which anatomical term describes something being closer to the median plane?
medial
which anatomical term describes something being farther away from the median plane?
lateral
which anatomical term describes something being closer to the center of an object (inside)?
internal
which anatomical term describes something being farther away from the center of an object?
external
which anatomical term describes something being on the back surface of the body?
posterior (dorsal)
which anatomical term describes something being on the front surface of the body?
anterior (ventral)
which anatomical term is used in describing the brain and is the nearer anterior part of the head?
rostral
which anatomical term describes something being nearer to the sole of the foot?
inferior
which anatomical term describes something being nearer to the top of the cranium?
superior
which anatomical term describes something being towards the tail region?
caudal
which anatomical term describes being towards the head?
cranial
which anatomical term describes being nearer to the attachment of a limb or central aspect of a linear structure?
proximal
which anatomical term describes being farther from the attachment of a limb or central aspect of a linear structure?
distal
which anatomical term means occurring on one side?
unilateral
which anatomical term means having right and left members?
bilateral
which anatomical term means occurring on the same side?
ipsilateral
which anatomical term means occurring on opposite sides of the body?
contralateral
which movement can be described as decreasing the angle at a joint?
flexion
which movement can be described as increasing the angle at a joint?
extension
which movement can be described as flexion toward the top of the foot?
dorsiflexion
which movement can be described as flexion toward the bottom of the foot?
plantar flexion
which movement can be described as movement toward the median plane?
adduction
which movement can be described as movement away from the median plane?
abduction
which movement can be described as distal end circular movement?
circumduction
what can be described as the muscles used for purposeful movement?
the agonist muscles
what can be described as the muscles that work in opposition to the muscles used in purposeful movement?
the antagonist movement
what is the term for movement revolving around the longitudinal axis?
rotation
what is the term for rotation toward the median plane
medial/internal rotation
what is the term for rotation away from the median line?
lateral/external rotation
what is the anatomical term for when the palm of the hand faces posteriorly and the dorsum (back of the hand) faces anteriorly?
pronation
what is the anatomical term for when the palm of the hand faces anteriorly and the dorsum (back of the hand) faces posteriorly?
supination
what is the term for movement of the sole of the foot away from the median plane?
eversion/foot abduction
what is the term for movement of the sole of the foot toward the median plane?
inversion/foot adduction
what is the term for movement superiorly?
elevation
what is the term for movement inferiorly?
depression
what is the movement of the first digit (thumb) to another digit?
opposition
what is the movement from opposition back to anatomical position?
reposition
what is the term for movement forward of the chin, lips, and tongue?
protrusion
what is the term for movement backward of the chin, lips, and tongue?
retrusion
what is the term for the anterior movement of the shoulder?
protraction
what is the term for the posterior movement of the shoulder?
retraction
what are some examples of combined anatomical terms?
inferomedial and superolateral
what does the skeletal frame provide?
support and protection
what is a first class lever?
the fulcrum is in between the effort (force) and the load (resistance)
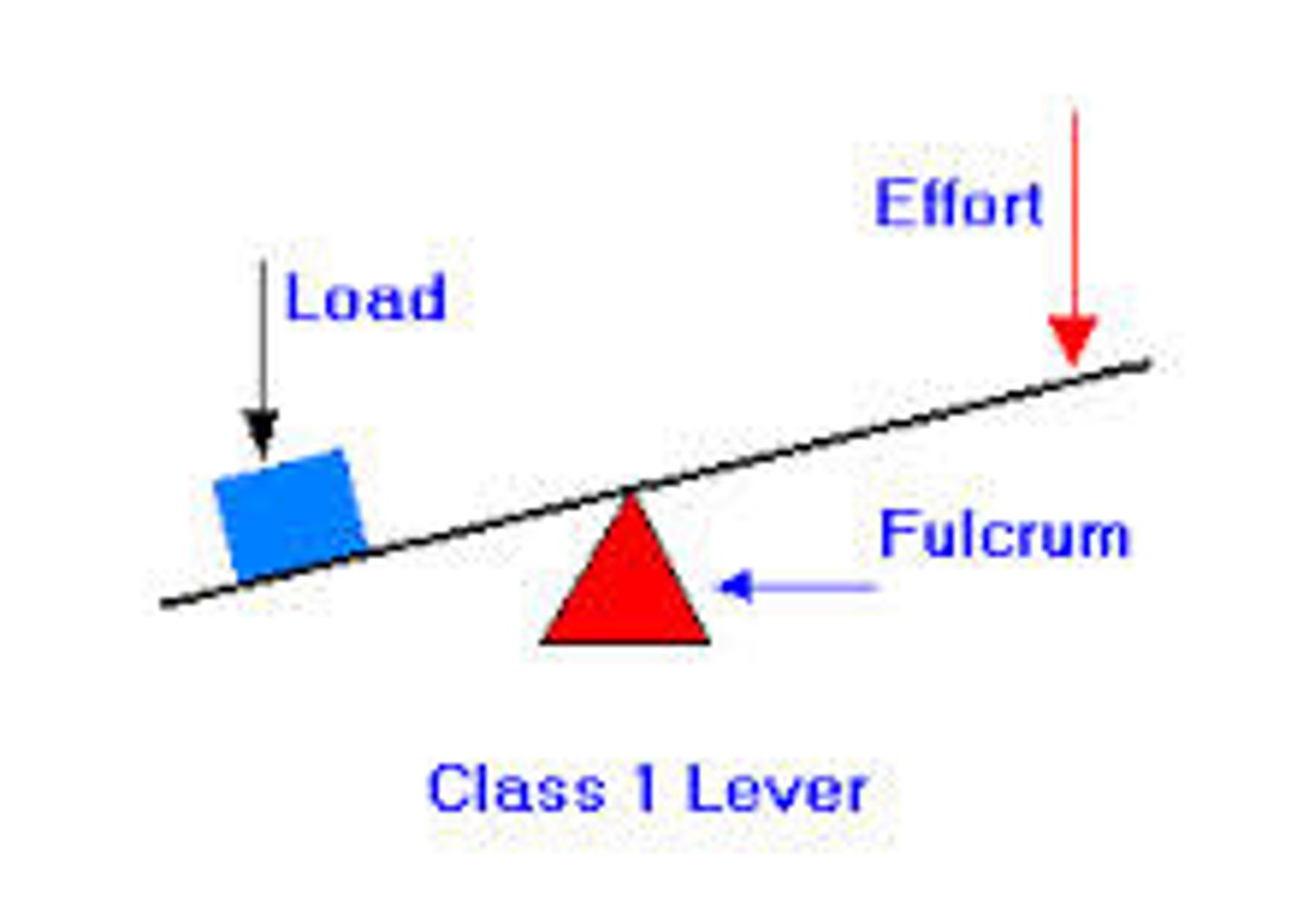
what is a second class lever?
the load (resistance) is in between the fulcrum and the effort (force)
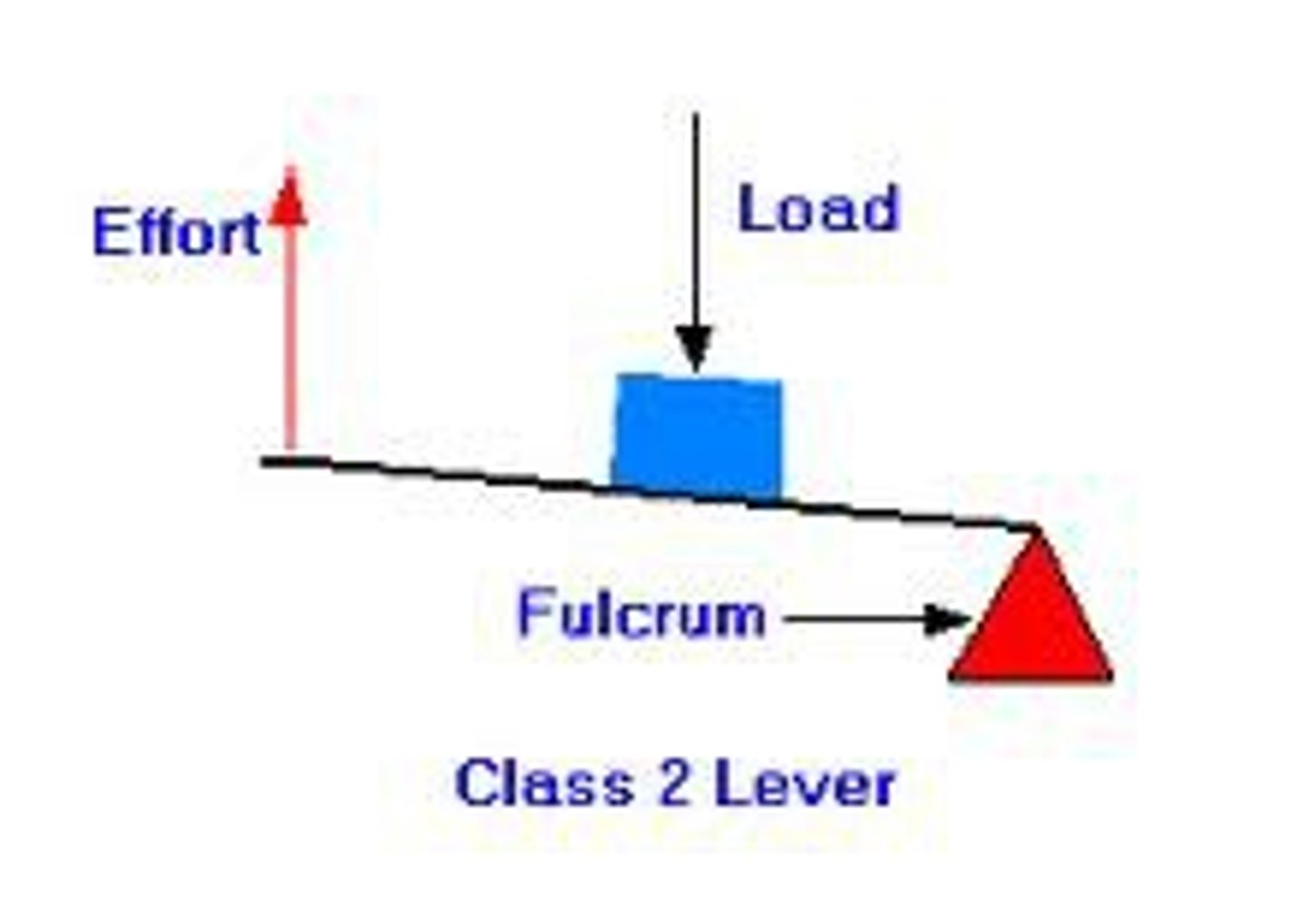
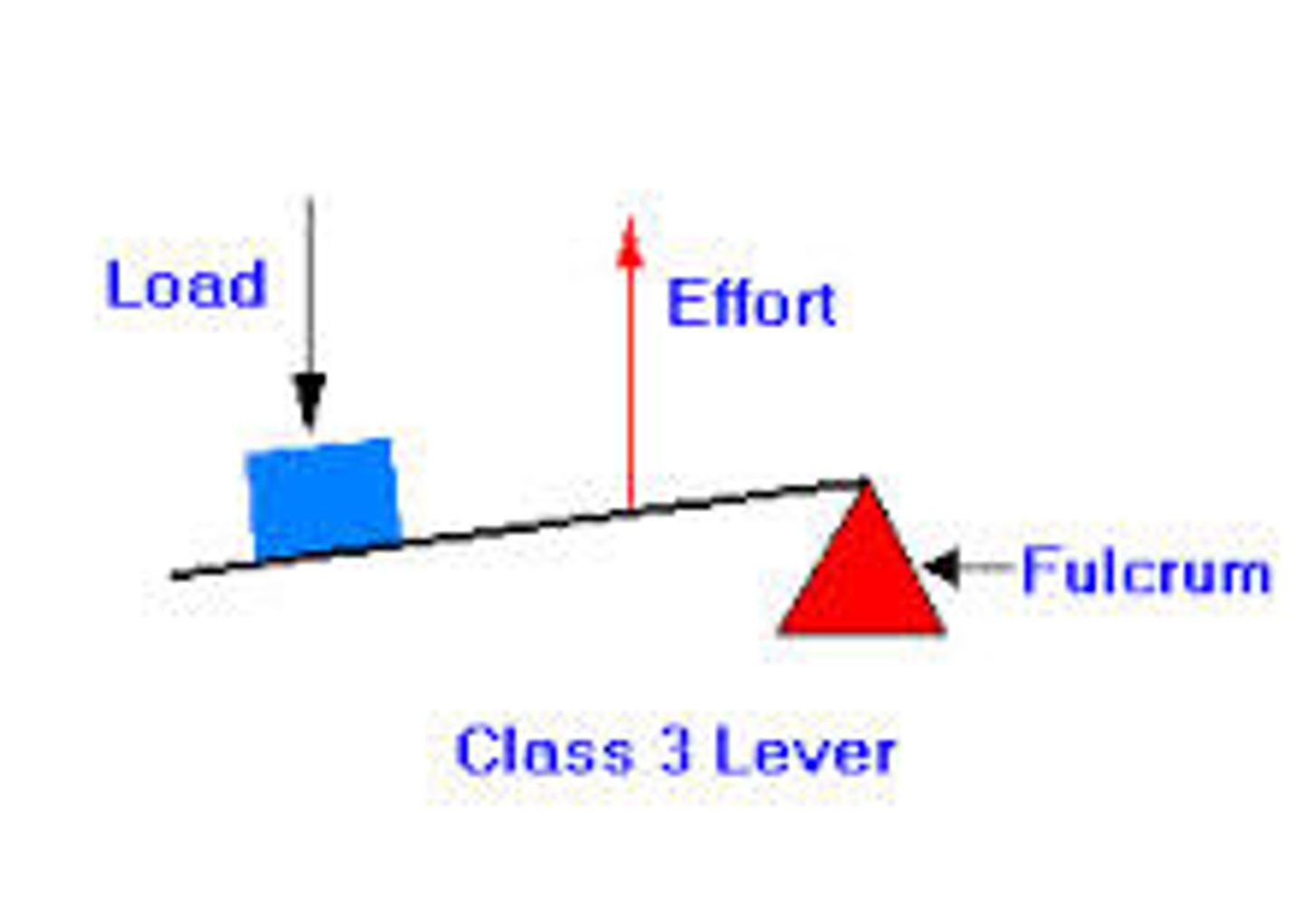
what is a third class lever?
the effort (force) is in between the load (resistance) and the fulcrum
what are the components of bone composition?
-calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate
-collagen protein
-water
what amount of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate makes up bones? what is the purpose of this component?
-60-70%
-it provides rigidity and compressive strength
what is the purpose of collagen in bone?
to provide flexibility and tensile strength
what amount of water that makes up bone weight? what is the purpose of this component?
-25-30%
-contributes to strength
what are the two types of bone in the body?
cortical and trabecular bone
which type of bone makes up 5-30% of bone volume non-mineralized tissue, is referred to as "compact bone", and makes up as much as 80% of skeletal mass?
cortical bone
which type of bone makes up 30-90% of bone volume non-mineralized tissue and has vertical and horizontal bars for cells (pores) that are filled with marrow and fat?
trabecular bone
what is the ability to resist a squeezing force?
compressive strength
what is the ability to resist a stretching force?
tensile strength
what is the distribution of force divided by the area over which the force acts?
stress
what is the amount of deformation divided by original length of the structure?
strian
which type of bone can withstand more stress but not as much strain?
cortical bone
which type of bone can withstand more strain but not as much stress?
trabecular bone (it can move in more directions because of the pores)
what is the term that describes how bones have different mechanical properties in response to loads from different directions?
anisotropic
which type of force are bones strongest against?
compression force
which type of force are bones the weakest against?
sheer force
what are the two parts of the skeleton?
axial and appendicular
which part of the skeleton contains the center and the skull?
axial skeleton
which part of the skeleton contains the limbs, pelvic girdle, and shoulder girdle?
appendicular skeleton
what are the four types of bones?
short, flat, irregular, long
what is an example of a short bone?
carpals and tarsals
what is an example of a flat bone?
sternum, scapula
what is an example of an irregular bone?
vertebrae and facial bones
what is an example of a long bone?
humerus, femur
what are the two types of how bones grow?
longitudinal and appositional growth
what is longitudinal bone growth?
increase in length
what is appositional bone growth?
increase in width
true or false:
appositional growth is accomplished when the inner layer of periosteum (osteoblasts) build new concentric layers of bone
true
which cells form bone?
osteoblasts
which cells reabsorb bone?
osteoclasts
how does bone change in adults?
loss of collagen (makes bones more brittle), loss of bone density (especially in post-menopausal women), loss in both structure and strength of trabecular bone
which type of bone is most affected with age?
trabecular bone
true or false:
during the aging process, the loss of collagen results in bone becoming more brittle
true
true or false:
research suggests that activities involving impact force is necessary to increase bone mass
true
what percentage of trabecular bone is remodeled each year?
25%
what happens to bones in response to stress (generally)?
bone hypertrophy
what does a greater load on the bones habitually cause?
an increase in bone density
what ratio of post-menopausal women are at risk for fractures due to osteoporosis?
1/2 of all post-menopausal women (due to changes in estrogen and progesterone