GCSE AQA Geography- Living World
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the Information that you will need for Living World. This is based off the specification for GCSE AQA Geography. These Flashcards cover ‘Tropical Rainforests’ and ‘Hot Deserts’, please check if this is what your school has selected.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
A natural system made up of plants, animals and the environment, includes both living and non-living features.
Define ‘biotic’
A living feature within an ecosystem.
Define ‘abiotic’
A non-living feature within an ecosystem.
Give a general example of a small scale ecosystem.
A pond
Give a general example of a global scale ecosystem.
A tropical rainforest
What are producers?
Organisms that convert energy from the environment (sunlight) into sugars (glucose).
What are consumers?
Organisms that get energy from sugars produced by producers
What is a decomposer?
An organism that breaks down plant material and returns the nutrients to the soil.
What is a food chain?
A diagram showing the direct link between producers and consumers in the form of a simple line
What is a food web?
A diagram that shows all the connections between producers and consumers in a rather more complex way.
What are the two main sources of nutrients?
Rainwater, releasing chemicals out of the atmosphere, and Weathered rock, releasing nutrients into the soil.
What is the nutrient cycle?
The decomposition of dead plants or animals, resulting in the nutrients from the organism recycled and made available again for living organisms.
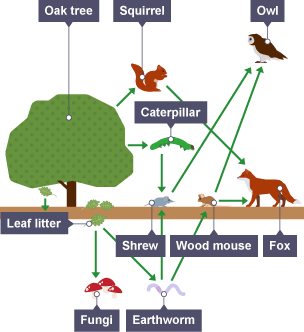
What is this an example of?
A food web
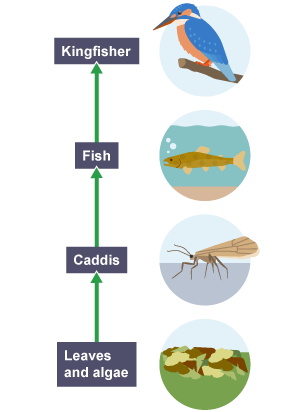
What is this an example of?
A food chain
Ecosystems can take ________ to __________ of years to develop
Hundreds to thousands
If an ecosystem is to be sustainable, it needs to be in _________.
Balance
Why does a change in one component of an ecosystem potentially impact the entirety of it?
As each component is reliant on the others in order to maintain balance, and therefore sustainability.
Give the two main causes of change to an ecosystem, with examples.
Global scale changes- e.g climate change.
Local scale changes- e.g changes to a local habitat.
What speed must change be in order for an ecosystem to adapt?
Slow
Give two example of changes to ecosystems due to human activity.
Deforestation- reducing biodiversity and affecting nutrient cycle.
Fertilisers- Increasing algae in ponds, killing fish as they are depleted of oxygen.
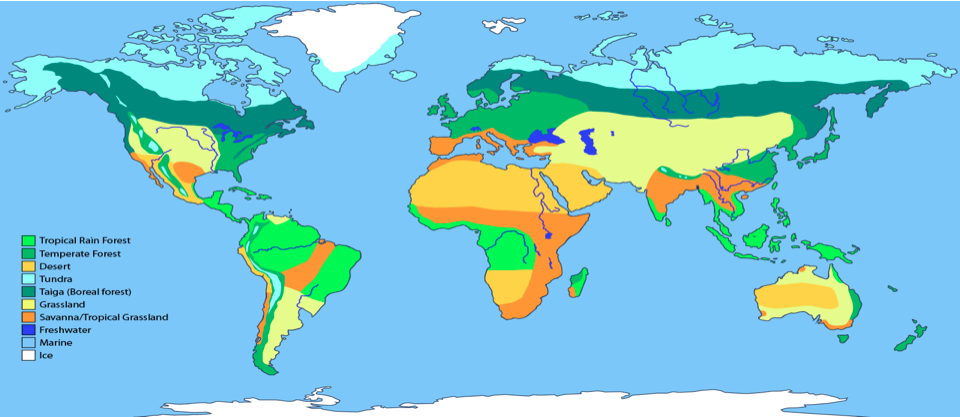
How are global ecosystems generally distributed on a large scale?
In broad belts across the world, parallel to the lines of latitude.
Why are global ecosystems distributed on a large scale as they are?
As the climate and characteristics of ecosystems are determined by the global atmospheric circulation model.
What percentage of the world’s plants and animals live in the Rainforest?
50%
What fraction of the earth’s surface is desert?
1/5
What are the conditions like in the Polar Ecosystems? Why is this?
Low temperatures and cold conditions, can be below-50 degrees, due to cold air sinking at the poles.
What are deciduous forests?
Forests made up of trees that shed their leaves in winter to retain moisture.
What are coniferous forests?
Forests made up of cone-bearing evergreen trees, retaining their leaves to maximize photosynthesis in summer months.
Describe Temperate grasslands.
A habitat with warm, dry summers and cold winters, with grasses that can tolerate this.
Describe Mediterranean conditions?
Hot, sunny and dry summers, with mild winters.
Describe the Savanna (Tropical Grassland)
Distinct wet and dry seasons due to low latitude. Potentially causes wildfires in dry season and thunderstorms in wet seasons.
Describe the Tundra?
A very fragile ecosystem made up of low growing plants adapted to retain heat and moisture in cold, windy and dry conditions.
What are the two global ecosystems that we must learn in detail?
Rainforests and Hot Deserts.
Where are Tropical Rainforests located?
Around the equator, between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
What is the largest area of tropical rainforest, located in South America, called?
The Amazon Rainforest
What are the four main components of the tropical rainforest ecosystem?
Climate, soil, vegetation and animals
In relation to the Tropical Rainforest’s climate, describe the temperature through the year.
Temperature is high and constant
In relation to the Tropical Rainforest’s climate, describe the rainfall throughout the year.
There is a distinct wet season, 6 months in length. Rainfall is very high.
Why is rainfall very high in the TRF, especially in the wet season?
Due to the equatorial low.
Tropical rainforests soil is surprisingly in_______.
Infertile
Where is the bulk of the nutrient rich soil located in the Tropical Rainforest? Why?
it is in the thin top layer of soil due to the nutrient cycle.
What is the name of the infertile, acidic red soil in the tropical rainforest?
Latosol
What is leaching (think about the fertile layer of soil)?
When the rich fertile layer of soil is washed away by heavy rain.
The nutrient cycle in the tropical rainforest is a _____ process as it is hot and wet, encouraging decomposition.
Rapid
Why is removing vegetation from the tropical rainforest harmful for the soil?
The soil will quickly become infertile and vulnerable to erosion, as the fertile top layer of soil can easily be washed away.
How is removing vegetation from the tropical rainforest harmful for the local climate?
As transpiration is reduced, causing precipitation to decrease, an integral part of the rainforest.
Describe ‘Buttress Roots’ an adaptation of trees in the tropical rainforest.
Buttress roots are vast ridges which provide stability for tall trees. They are also very shallow in order to soak up nutrients from the fertile top layer of soil.
Describe ‘Red Leaves’ an adaption of plants in the tropical rainforest.
The red leaves provide protection from the sunlight for young plants that are still developing, by reflecting red light.
Describe ‘Epiphytes’ an adaption of plants in the tropical rainforest.
These are plants that have their roots in the ground but use other trees to climb into the forest canopy to maximize their sunlight exposure.
Describe ‘Drip Tips’ an adaption of plants in the tropical rainforest.
These are leaves that have a waxy surface and pointed tips, to allow excess rainwater to run off, preventing algae growth, which would block sunlight.
Describe ‘Leaf angling’, an adaption of trees in the tropical rainforest.
Trees have leaves that are each angled differently to prevent shading it’s own leaves below.
Give three adaptations of a sloth, an animal living in the rainforest.
Green Algae growing on their fur to create camouflage.
Slow metabolism to save energy
Specialized tendons to keep feet and hands in place on the trees.
Give three adaptions of the Asian Elephant.
A long trunk to help reach food sources high and low
Big floppy ears to help cool blood in capillaries, thus cooling the whole body.
Tough tusks to strip bark, and bore down the earth to find water.
The rainforest is home to around __% of the world’s species, it is hugely diverse.
50%
What is reducing the rich biodiversity in the rainforest?
Human exploitation of the rainforest’s ecosystem.
What does the rainforest act as, helping us fight climate change?
A carbon sink, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
The rainforest provides __% of all medicines.
25%
The rainforest is also home to __________ ______,who live in harmony with the forest, using it’s resources sustainably.
Indigenous tribes
Over the last century, deforestation has had a serious impact on the TRF. It is estimated to be clearing at the rate of __________ per second
1 hectare
What is deforestation?
The conversion of forest to another land use or the long-term reduction of tree canopy cover below 10% threshold.
What is our Tropical Rainforest Case Study for deforestation?
Malaysia
What are the 6 cause of deforestation in Malaysia?
Logging, Subsistence farming, mineral extraction, commercial farming, population pressure and energy development.
What is logging?
Cutting down trees in order to collect the timber and sell it.
What has mostly replaced clear felling (logging)?
Selective logging
What is subsistence farming?
The hunting and gathering of food from the forest for tribes to sustain themselves.
Is subsistence farming sustainable?
When performed traditionally and on a small scale.
Where in Malaysia have they begun drilling for oil causing habitat loss?
Borneo
Give three types of extraction which has caused habitat loss in Malaysia?
Drilling for oil, tin mining and smelting.
Why has commercial farming caused deforestation in Malaysia?
The exportation of palm oil, enouraged by 10 year tax incentives, causes huge amounts of habitat loss.
How has energy development caused habitat loss in Malaysia?
Hydro electric power, generated from dams, flood frequently and severely, causing damage and habitat loss.
What is the name of the dam reservoir created in 2011 in Sarawak, Malaysia?
Bakun dam.
What size was the area that the Bakun dam flooded in Malaysia?
700 km²
How has population pressure caused deforestation?
Overcrowded cities have caused people to move away, and clear forest to live in.
Give the four main environmental impacts of deforestation.
Reduction of biodiversity, contribution to climate change, exposure to soil erosion, contribution to greenhouse effect.
Why does deforestation contribute to soil erosion?
As the tree canopy act as as an umbrella to protect the soil from full rain exposure, and the roots help to hold the soil together.
What does soil erosion cause, which can be fatal?
Frequent landslides
Why does deforestation contribute to global warming?
It reduces the amount of carbon dioxide that would be absorbed in the trees. Increased Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contributes to the greenhouse effect.
Why does deforestation contribute to higher temperatures?
As deforestation causes reduces evaporation.
Why does deforestation contribute to drier conditions?
As it reduces transpiration, meaning that there is less moisture in the air.
What are the 5 main economic losses of deforestation?
Water shortages, devastation to farming, medicine loss, adaption to a warmer world and tourist decreases.
How does deforestation cause water shortages?
As deforestation can cause polllution of water sources, and therefore water shortages.
How could deforestation devastate farming?
Some forms of farming such as tea, fruit and flowers would struggle due to rising temperatures.
What are 4 economic gains of deforestation?
Creates jobs, provides cheap and plentiful energy, extraction of valuable minerals (e.g gold) and improved public services.
How does deforestation potentially lead to improved public services?
Taxes from companies to the government can be used for education and water supply for example.
What percentage of oxygen comes from the tropical rainforest?
28%
What are the two reasons that tropical rainforests must be managed sustainably?
To ensure rainforests remain a lasting resource for future generations and to prevent long term damage to the environment.
What are the 6 ways that the TRF can be managed sustainably?
Conservation and education, ecotourism, international agreements, debt reduction and selective logging.
What are conservation areas and what can they be used for?
Conservation areas are national parks or nature reserves for example. They can be used for education, scientific research and tourism.
Why is ecotourism a more sustainable option that deforestation?
As ecotourism creates a much more long term source of profit, as communities can gain income whilst protecting the rainforest trees.
Why are international agreements made over the tropical rainforests?
As they are of global importance, as they are a carbon sink, and provide oxygen, water and medicines.
What is debt reduction in relation to deforestation known as? Describe this.
It is known as ‘debt for nature swapping’ whereby countries with TRFs that are in debt that usually fund this repayment through deforestation, are told by donor countries that they will reduce the debt, if they stop deforesting their TRF.
Define a desert.
A desert is an area that receives less than 250mm of rainfall per year. The resulting dryness or aridity is the main factor controlling life in the desert.
Where are hot deserts located?
30 degrees North and south of the equator, away from coasts.
Name three main abiotic parts of a desert.
Soil, underlying rocks and water supplies.
Describe the climate in hot deserts. Why is it like this?
There is a lack of cloud and rain due to a consistent belt of high pressure. This lack of cloud cover leads to very varying temperatures across the seasons and between day and night. Rainfall is low to non existent at times.
Describe the soil in hot deserts. Why is it like this?
The soils are sandy and stony. There is little organic matter due to a lack of leafy vegetation. They are infertile.
Give two adaptions of camels in the desert.
Two rows of eyelashes to protect against the sun and blowing sand
Fat stored in humps to survive long periods without food and water.
Give two adaptions of snakes and lizards in the desert.
Waterproof skin in order to retain water.
Minimal urine production to retain water.
Give two adaptions of cacti in the desert.
Spikes to deter consumer species
Small, waxy leaves to minimize transpiration
Give two adaptions of flowering plants in the desert.
Have seeds that only germinate after heavy rainfall
Brightly coloured to attract insects.
What is our case study for hot deserts?
Thar Desert