Binocular Summation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Alternation/suppression theory
theory of binocular combination stating that monocular images formed from the right and left eyes are alternated in perception and mutually inhibit each other. Occurs when there are dissimilar images presented to each eye. Does not occur under natural viewing conditions.
Fusion theory
theory of binocular combination stating that images to the right and left eye are perceived and processed simultaneously. The resulting binocular percept is additive, and therefore binocular thresholds are lower than monocular thresholds. Occurs when there are similar images presented to each eye. Occurs under natural viewing conditions.
Binocular summation
an additivity of the information from each eye to yield binocular visual performance that exceeds monocular performance. Ie) better VA, CS, CV, light detection, etc. Can only occur if both eyes are stimulated within a short interval of time at corresponding areas.
Neural summation
aspect of binocular summation where signals sum between the right and left eye, but neural noise differs between the two eyes and fails to sum. The signal to noise ratio improves by the square root of the number of detectors.
Temporal synchrony of <100 ms, corresponding points or points within Panum's area, similar stimuli
three requirements for neural (binocular) summation.
Probability summation
aspect of binocular summation where there is a benefit of two eyes even if they are independent of each other.
Binocular facilitation
degree of binocular summation where visual performance is better with both eyes than the sum of each eye.
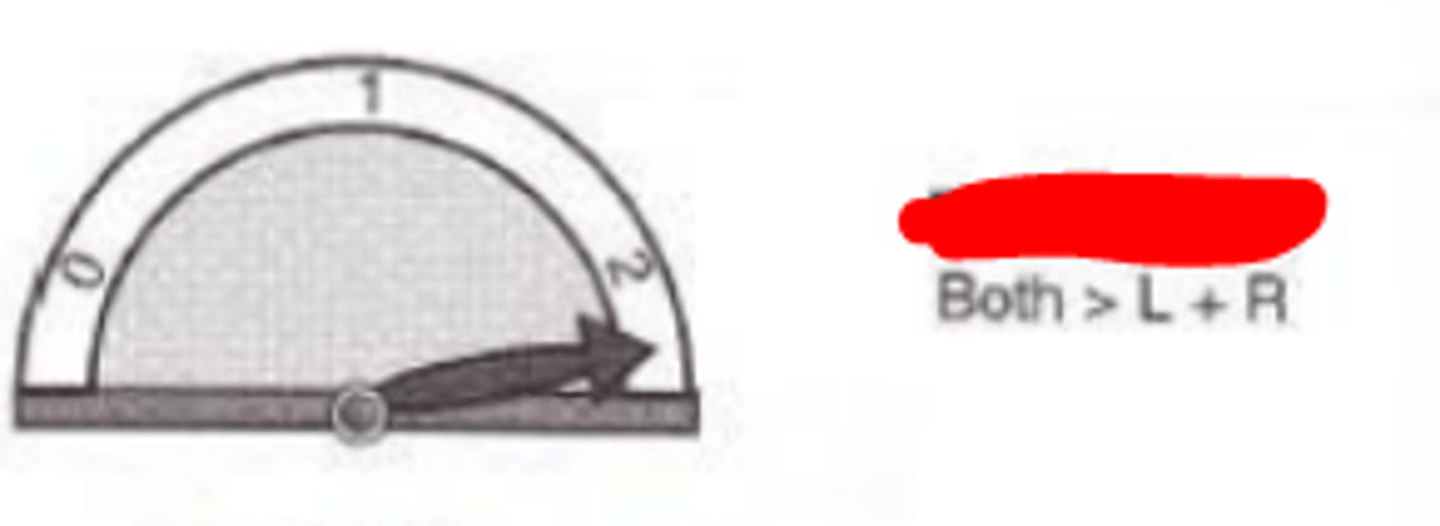
Complete summation
degree of binocular summation where the binocular performance is equal to the sum of monocular performance. Is relatively rare. Ie) VA does not improve 2x with both eyes open

Partial summation
degree of binocular summation where there is an incomplete summation of each eye's visual performance to binocular performance. The binocular view is less than the sum of the two eyes, but is still greater than using a single eye individually.
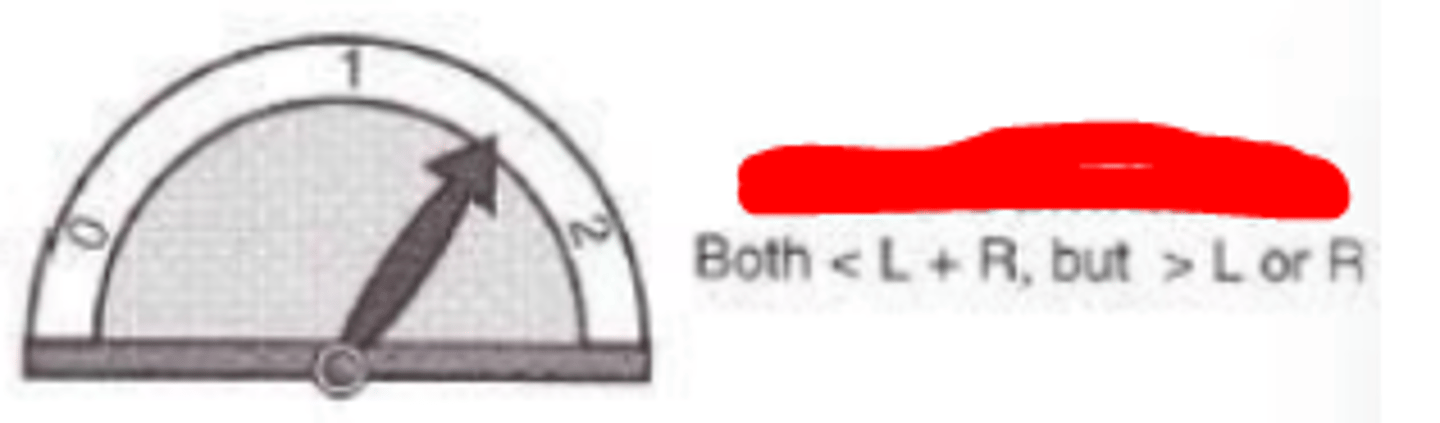
Light detection, visual acuity
two visual functions that undergo partial summation
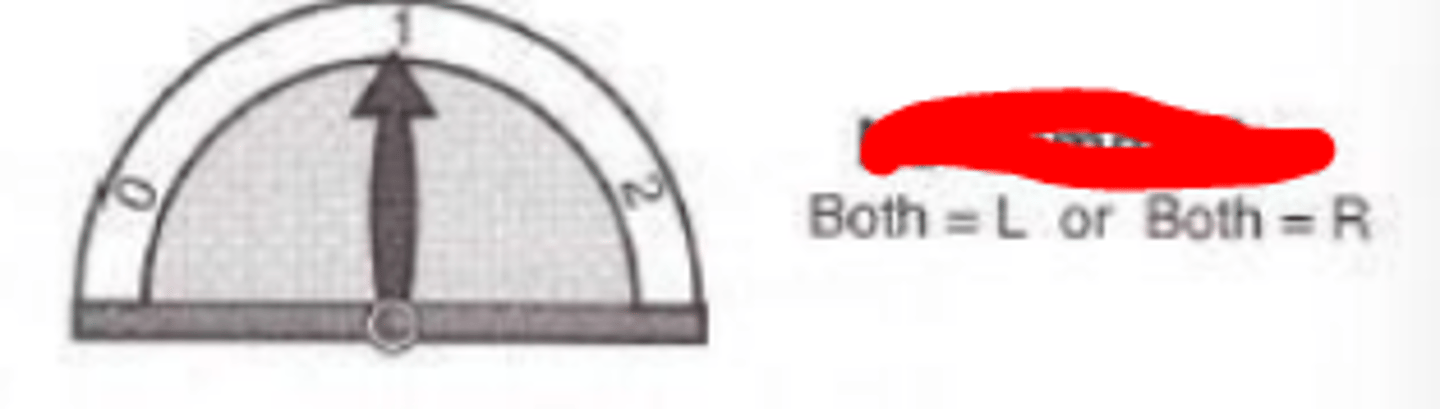
No summation
occurs when the visual performance of the two eyes is no better, but no worse, than one
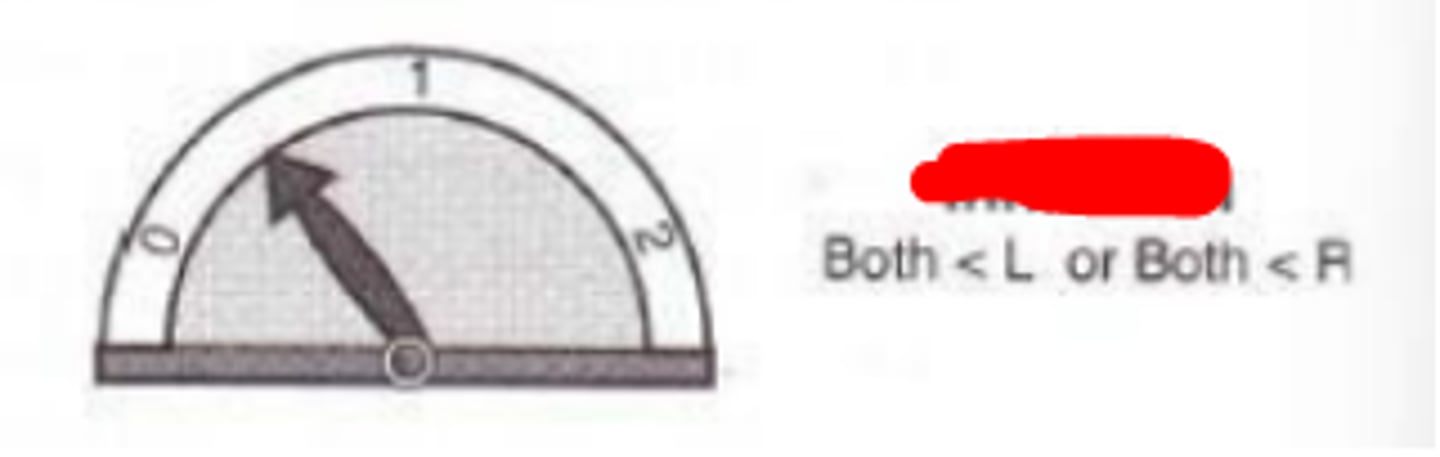
Binocular inhibition
degree of binocular summation where the performance of one eye is degraded by the other eye, and the binocular visual performance with both eyes is less than the monocular visual performance.
in phase, out of phase, monocular
Studies show that sensitivity is greatest for _____ signals between two eyes, is lowest for _____ signals, and _____ perception has sensitivity midway between these two.
1.4, 40
Binocular viewing has a constant factor of improvement of ___ higher sensitivity. This is equivalent to ____% improvement
Independence theory (probability summation)
theory stating that even if the eyes work perfectly independently, we can still expect some degree of lowered thresholds under binocular conditions. Ie) a monocular threshold of 0.60 in each eye, results in a probability of 0.84 of detecting a stimulus binocularly. Applies even when the image of one eye is degraded, as seen in amblyopia

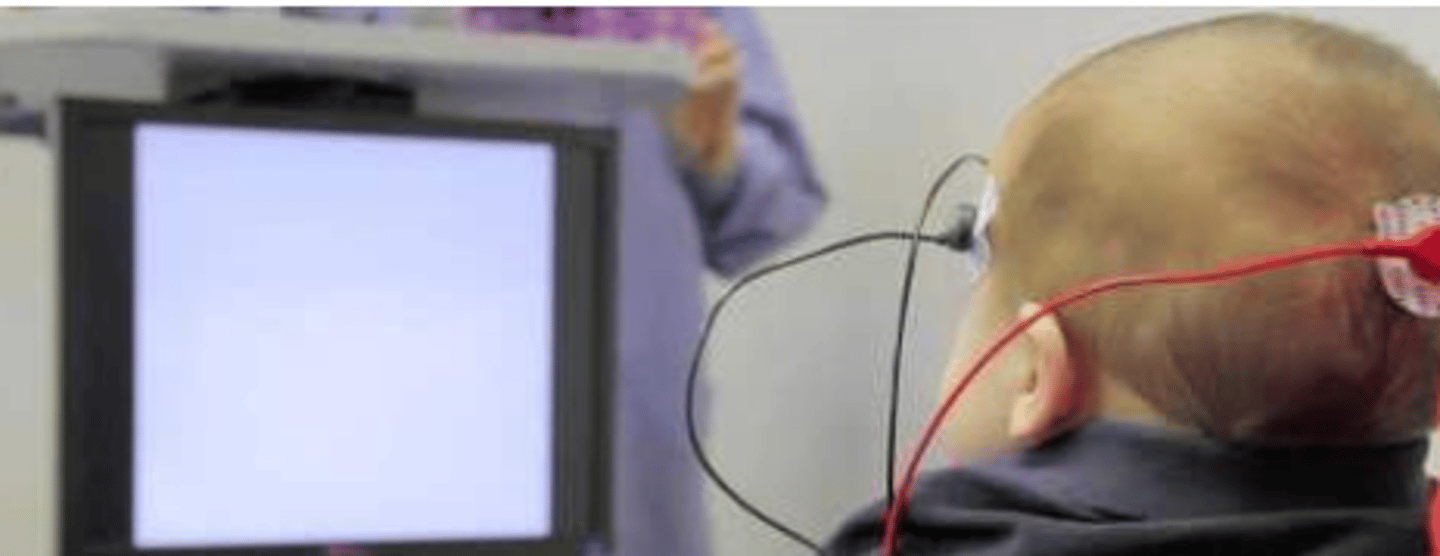
Binocular vision problems, visually evoked potentials (VEP)
_____ may be indicated by a loss of binocular summation over a wide range of stimulus conditions. It is important to detect this early in life in order to encourage proper binocular vision development. In infants, ______ can be used to evaluate their binocular summation capabilities.

suprathreshold, threshold
Studies show that there is still a benefit of having two eyes under _____ conditions, but the benefit is greater at or near _____
Fechners paradox
an apparent increase in brightness of a figure caused by the closing of one eye, or decreased brightness upon binocular viewing. Demonstrates binocular brightness averaging where when one eye sees a target as brighter than the other eye, and the binocular image appears less bright with both eyes open.
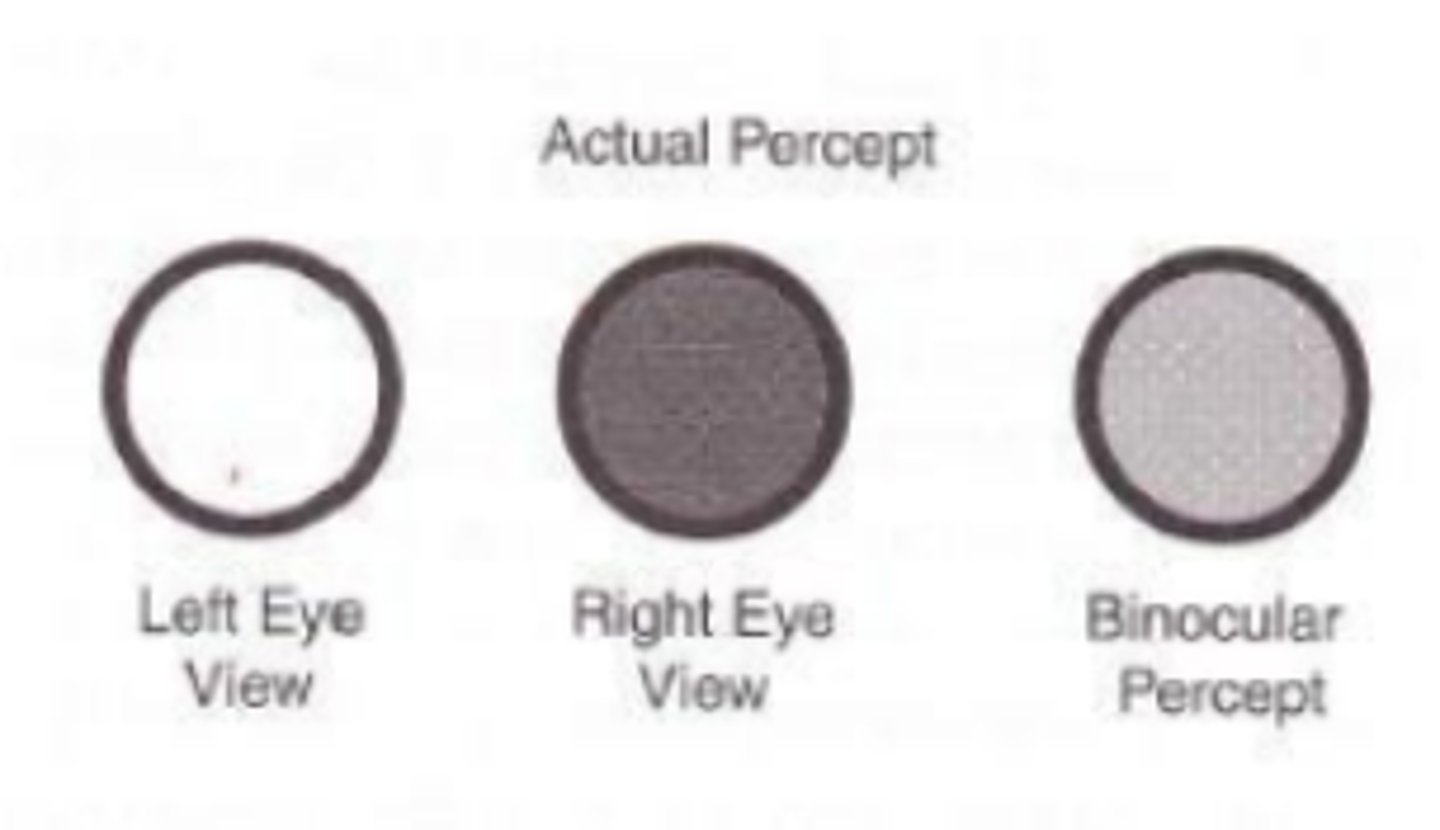
Independence hypothesis
hypothesis of Fechners paradox stating that the eyes are acting independently, and that the eye with the brighter image determines the brightness of the binocular percept.

Summation hypothesis
hypothesis of Fechners paradox stating that binocular brightness of an image is the sum of the monocular brightness, and that the binocular percept is brighter than both monocular percepts.
Averaging hypothesis
Hypothesis of Fechners paradox stating that the visual system averages the perceived brightness of each eye, and that the binocular percept has a brightness that is midway between the brightness of the monocular percepts. Correctly describes what occurs.

Aftereffect
a biased perception of a target to be seen by fatiguing tuned visual neurons with an adapting stimulus. Is a cortically mediated phenomenon resulting in interocular transfer. Occurs monocularly as well, but to a lesser extent. Ie) motion, tilt, and size. Demonstrates that the two eyes are not independent of one another. May be lost in patients having binocular vision problems.
V1 (monocular), V2 (binocular), MT (motion)
three areas of the brain involved in aftereffect
Dichoptic masking
occurs when test stimulus is presented to one eye and a masking stimulus to the fellow eye.
Visual masking
degradation of a test stimulus percept by a masking stimulus presented before, with, or after the test stimulus. Effect is stronger when presented to the dominant eye.
Crowding Effect
a form of simultaneous masking where nearby contours of a target reduce its visibility. Ie) vernier acuity testing
Metacontrast masking
a reduction in target visibility occurring due to a subsequently presented mask that reduced target visibility. Effect is strongest when the mask is presented to the dominant eye.
poorer
Stereoacuity and binocular summation is usually (better or poorer) in patients having strabismus versus patients having anisometropic amblyopia
subthreshold binocular summation, dichoptic masking
Amblyopic patients excitatory and inhibitory binocular interactions may be impacted differently by their condition. For example, they do not exhibit ______ (an excitatory function), but still may exhibit _____ (an inhibitory function)