3.2.2.6 DETERMINANTS OF LONG-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Define normal capacity level of output
The level of output at which the full production potential of the economy is being used
In the short run, what does the aggregate supply of real output depend on?
The average price level in the economy
What is the word used to explain when all other variables stay the same?
Ceteris Paribus
How does this change in the long run?
Aggregate supply is not influenced by the price level, long run supply reflects the economy's production potential
Explain where yN is?
YN goes where Y1 is n the x axis
What is yN?
Perfectly inelastic - full capacity of the economy
This can be called - natural rate of unemployment OR natural rate of output
The natural rate of unemployment = full employment (3%) - all of those wanting a job, has a job
Supply of workers = demand for labour
(Provided by workers) - (Provided by firms)
What does an outward shift of LRAS mean?
An outwards shift means the economy's productive potential has increased
Explain the factors which shift the LRAS curve outwards
the state of technical progress - improvements means firms can produce more output with the same level of inputs
the quantities of capital and labour - an increase in the quantity of of inputs raises the economy’s capacity
the productivity of the factors of production - more can be produced from the same resources
peoples attitudes hard work - increased work ethic, increases labour input - increasing output
personal enterprise - encourages investment - increasing productive capacity
What is the difference between SRAS and LRAS?
SRAS
Shows the level of output firms are willing to supply in the short run, when at least one factor of reduction (wages) is fixed
it is upward sloping as higher prices increase profits when costs are too slow to adjust
What is the difference between SRAS and LRAS?
LRAS
Shows the level of output the economy can produce in the long run, when all factors of production are variable
it is vertical as output depends on productive capacity, not the price level
How does the UK's productivity compare to others?
The UK works longer hours and generates less money than other countries
The UKs productivity ranks in the bottom half of the G7 countries
In macro, is productivity a long term problem?
Long run
How can you describe productivity?
Output per worker overtime
What are 3 things that could be don't to improve productivity in the UK?
more work place incentives such as profit related pay or output based on
better ‘on the job’ training such as apprenticeships to ensure that staff are as efficient as possible
refocus education to ensure that school leavers are able to meet the skills needed of the modern global economy
What does workplace incentives mean?
Commission or bonuses - encourages individuals to work harder and faster
What does the introduction of tech do? In terms of prices and output
decreased prices and increases output
Keynes diagram
What is the main thing that can improve productivity n the LRAS?
Technology, AI, automation
Why does tech lead to better productivity?
Workers work for less time and generate more output
Examples of countries that are very productive?
Scandinavian counties - Norway and Sweden

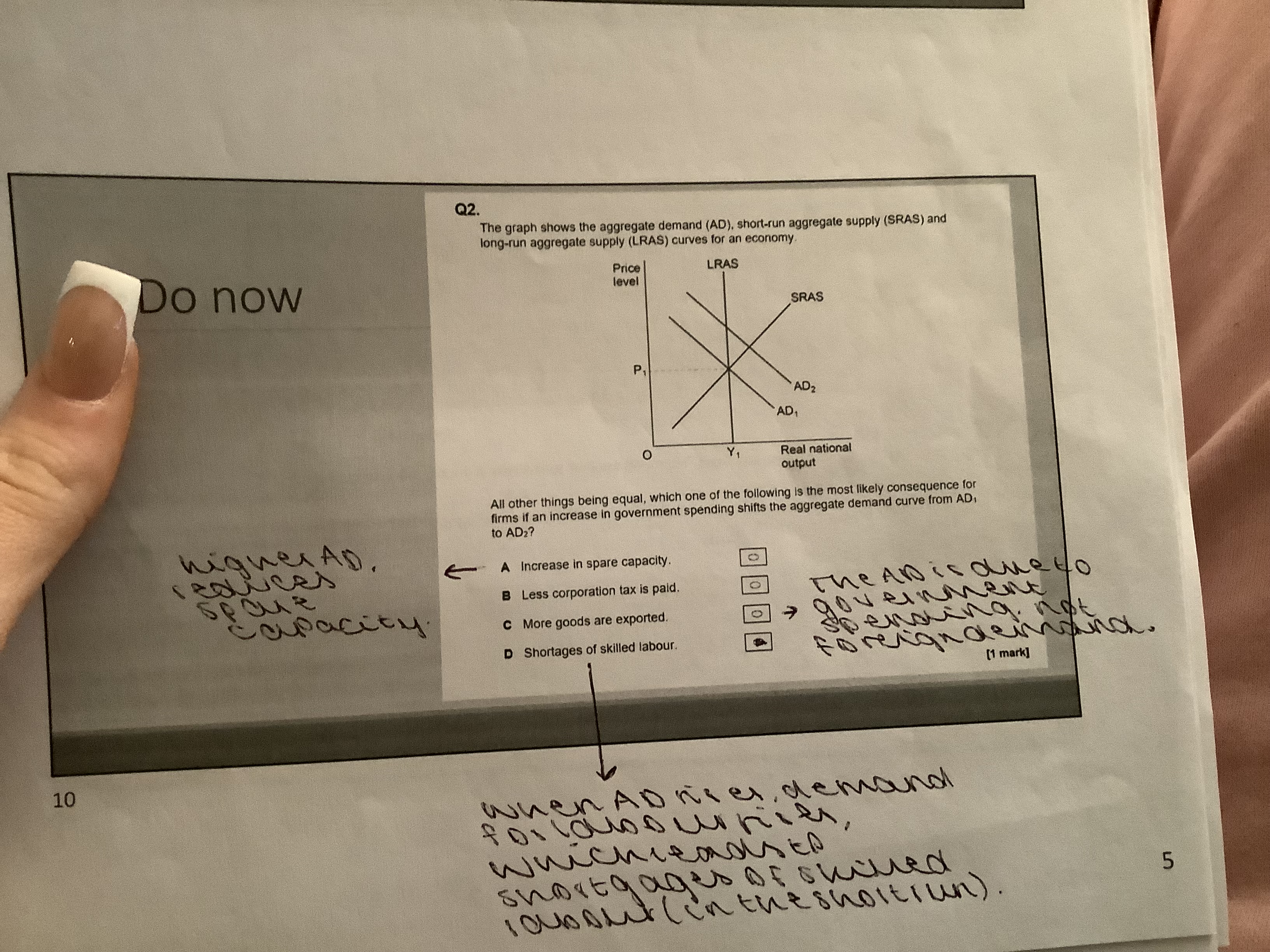
MCQ