Exam 1 - General Characteristics of the Spine
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
what does the spine protect
spinal cord and nerve roots
what does the spine provide a passageway for
spinal nerves to and from spinal cord
what is the spine the developmental origin of
ribs
the spine provides ___, ___, ___, and ___ of the body
support, stabilization, shape, and position
the spine allows for movements of the ___ and ___
trunk and limbs
the spine provides horizontal orientation for ___ and ____
eye (vision)
vestibular apparatus (balance)
what gives rise to 3 types of somites
paraxial mesoderm
what are the 3 types of somites
sclerotome, myotome, and dermatome
which somite gives rise to the vertebral column
sclerotome
which somite gives rise to muscle
myotome
which somite gives rise to skin
dermatome
what is the order of vertebral columns formed during development
membranous --> cartilaginous --> skeletal (osseous)
what occurs around day 22 of embryological development
sclerotomes surround the notochord to form the perichordal blastema
what does the perichordal blastema form
2 vertebrae
what lies between the sclerotomites of a perichordal blastema
intrasclerotomal fissure
what does the intrasclerotomal fissure give rise to
perichordal disc
what is the location of the adult intervertebral disc
perichordal disc
during week 6, what undergoes chondrification
membranous vertebral blastema (perichordal blastema)
mesoderm is replaced with cartilage from ___ to ___ ends
cranial to caudal
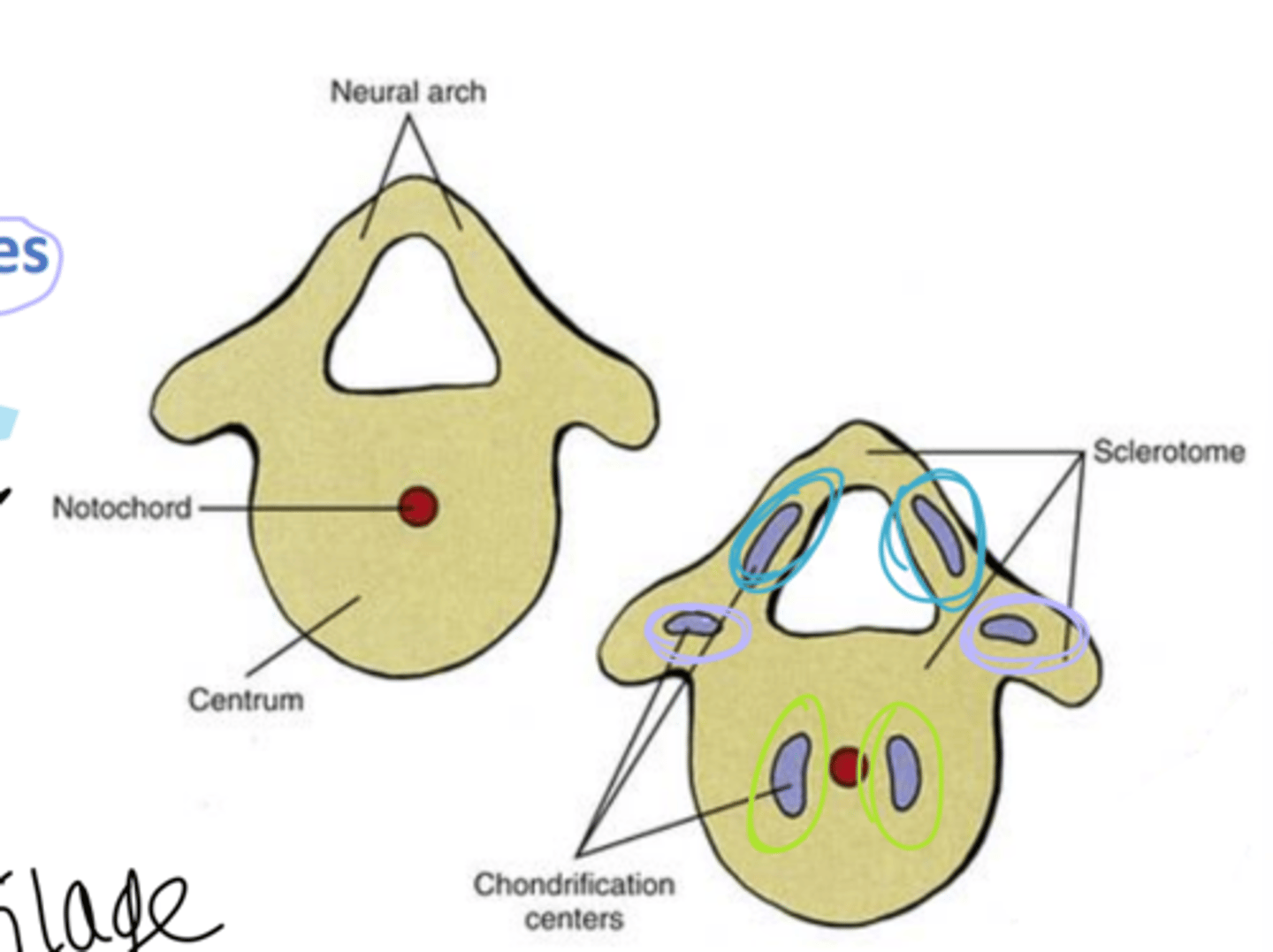
How many chondrification centers are there in the developing vertebra
6
how many pairs of chondrification centers are there in a developing vertebra
3
where are the centers of chondrification
1 pair in centrum (body)
1 pair in right and left neural arch
1 pair in right and left transverse processes
when are primary centers of ossification developed
before birth
when are secondary centers of ossification developed
puberty to age 25
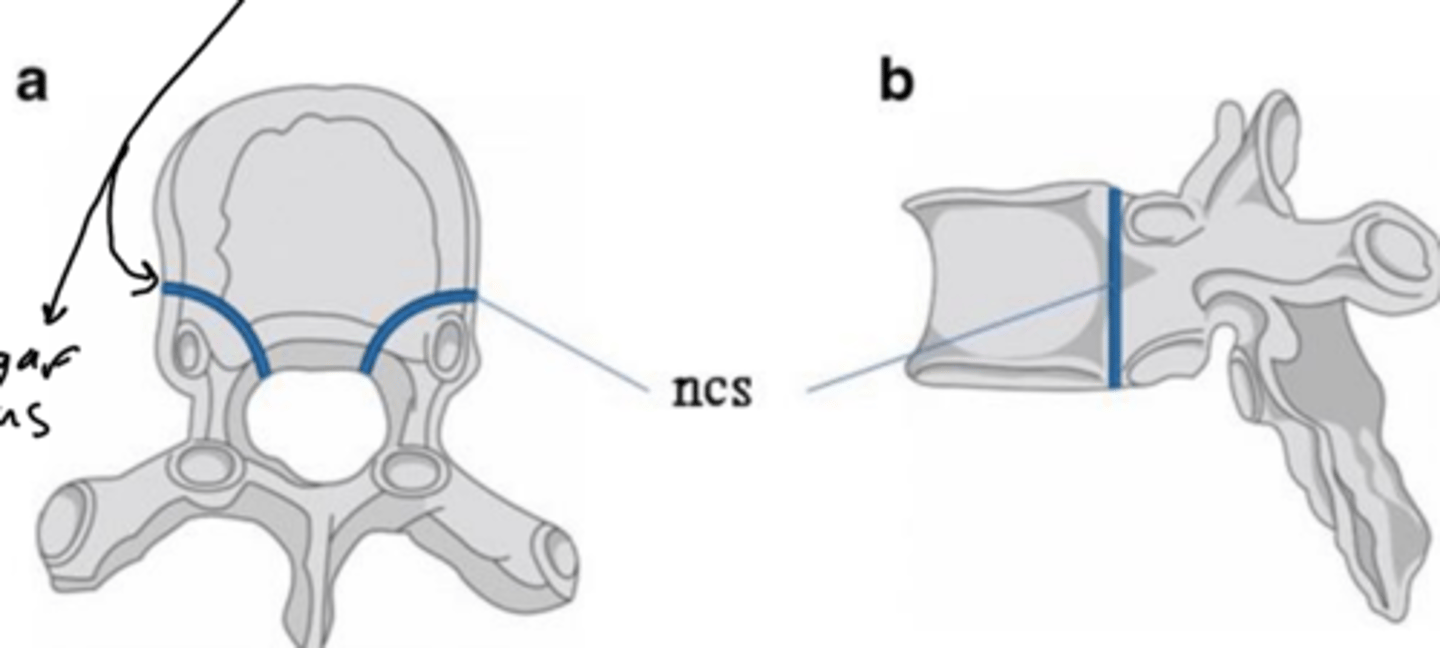
how many primary centers of ossification are there in each vertebra
3
what are the 3 primary centers of ossification
1 vertebral body (centrum)
2 in vertebral arch (neural arch)
what forms between the centrum and neural arch of primary centers of ossification
neurocentral synchondrosis
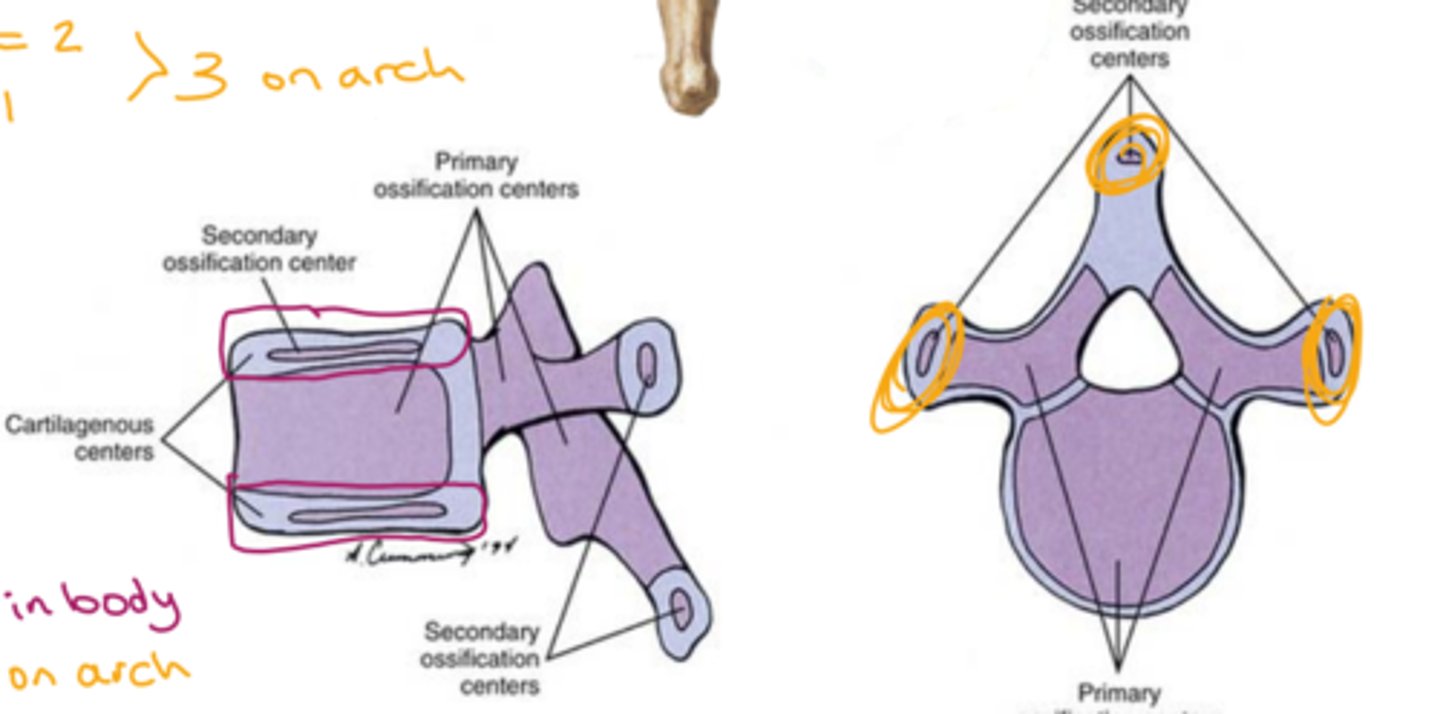
how many secondary centers of ossification are there in each vertebra
5
what are the secondary ossification centers
superior and inferior epiphyseal rims, 2 on tips of transverse process, 1 on spinous process tip
primary curvature of the spine is also referred to as ___
posterior
secondary curvature of the spine is also referred to as ___
anterior
kyphotic refers to what curvature
primary, posterior
lordotic refers to what curvature
secondary, anterior
in a primary, posterior, kyphotic curvature, there is a greater ___ height of intervertebral discs than ___
posterior, anterior
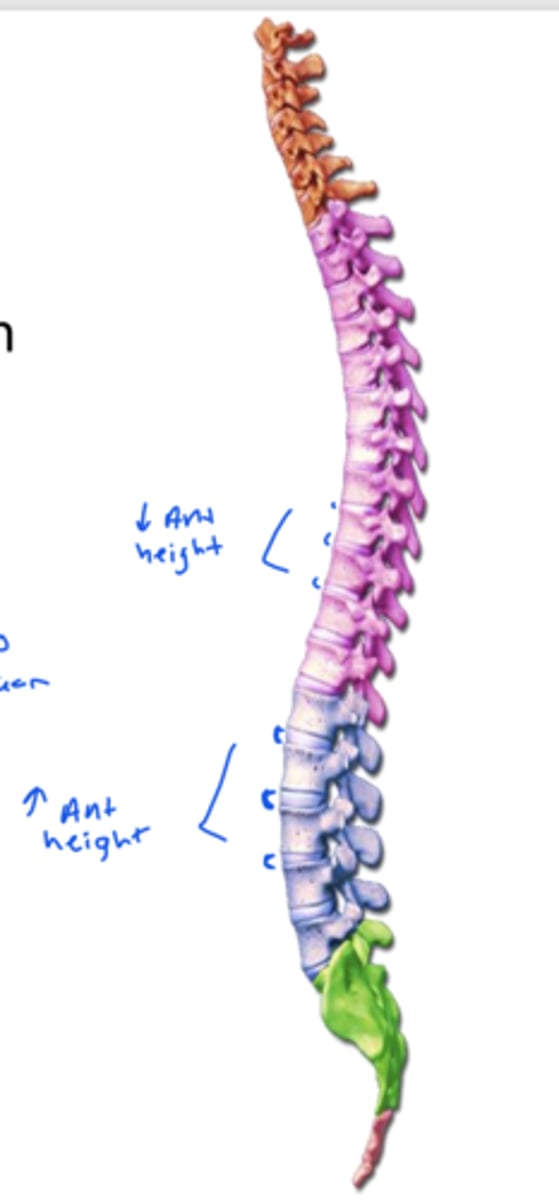
where are kyphotic, posterior, primary curves found
thoracic and sacrococcygeal
where are lordotic, secondary, anterior curves found
cervical, lumbar
which curves are significant for developmental milestones
secondary
which curve becomes more defined first: cervical or lumbar?
cervical
which curve is last to develop in infants and is fully extenuated when toddler begins to walk
lumbar
in secondary, lordotic, anterior curves, there is a greater ____ height of IVD than ___
anterior, posterior
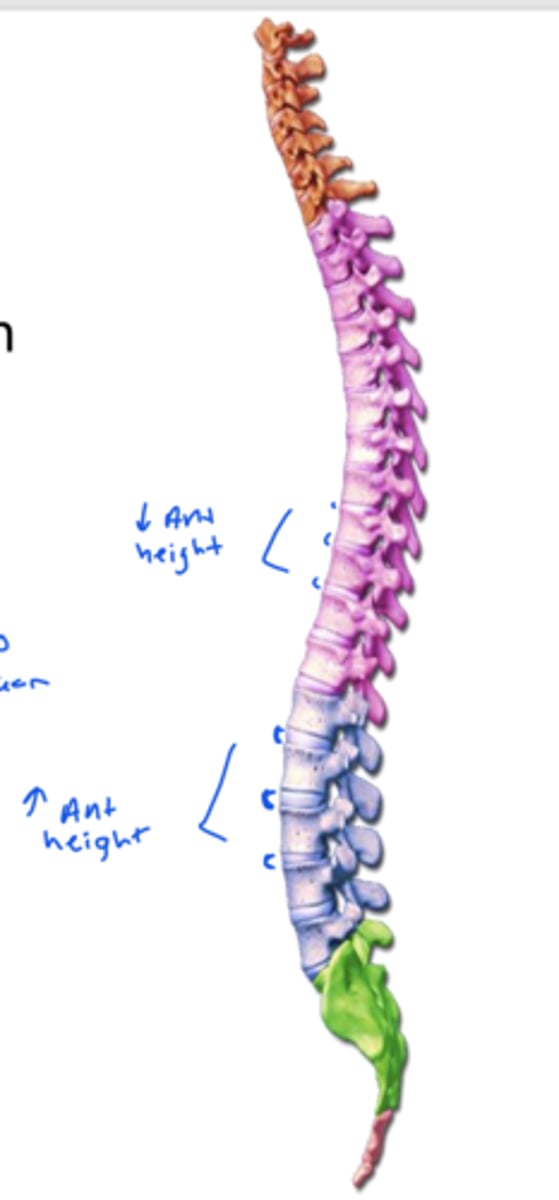
which curves allow for the erect posture of the body
secondary, lordotic, anterior
the cervical and lumbar curvatures are formed by the height difference of the ___
IVD
The thoracic curvature is formed by the height difference of the ____
vertebral bodies
there is a slight lateral curvature in what regions of the spine
thoracic and lumbar
when do typical lateral curvatures occur
after age 6
Typical lateral curvatures are associated with ___ and may have __ or __ factors as well
handedness, genetic, environmental
left-handed people will have a typical lateral deviation to the ___. Why?
left, muscles used more often so they pull more frequently than the right side
intervertebral discs attach and separates what to/from each other
vertebral bodies
intervertebral discs help to shape the ___
spine
intervertebral discs act as a powerful ___
ligament
what do intervertebral discs form the borders of
anterior border of vertebral canal
anterior border of IVF
T/F
intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers
true
what causes a slight decrease in the height of IVD throughout the day? what replenishes this?
water loss, 8 hours horizontal
what part of the IVD is C shaped and not a full circle and is made of collagen
Annulus Fibrosus
what part of the IVD restricts movement
annulus fibrosus
what part of IVD allows movement and retains water
nucleus pulposus
what is the nucleus pulposus composed of
water, collagen, and proteoglycans
what is the IVD made of
proteoglycan gel and collagen fibers
IVD height diminishes with age because _____
the nucleus pulposus gets more fibrous and there is less water and proteoglycans
which IVD component pushes vertebral bodies away from one another
nucleus pulposus
term for a small round projection or protuberance on a bone
tubercle
term for a projection or outgrowth tissue from a larger body
process
term for a small flat surface on a bone
facet
term for a something that is of, at, or relating to the joints of the body
articular
term for something that relates to the area near ribs
costal
what make up the superior and inferior border of the IVF
superior and inferior vertebral notches
what is the thin, flat portion of the vertebra that is an attachment site for the ligamentum flavum
lamina
does lamina have good blood supply
NO
the vertebral foramen refers to the
spinal canal
what is the attachment site of IVD on the body of each vertebra
superior epiphyseal rim
at the end of each process, there is a ___
EX: the spinous process has a spinous ___ at the end
tubercle
what come together to form the facet joint
superior articular facet and the inferior articular facet
intervertebral foramina located between T6 and T7 is formed from
inferior vertebral notch of T6 and superior vertebral notch of T7
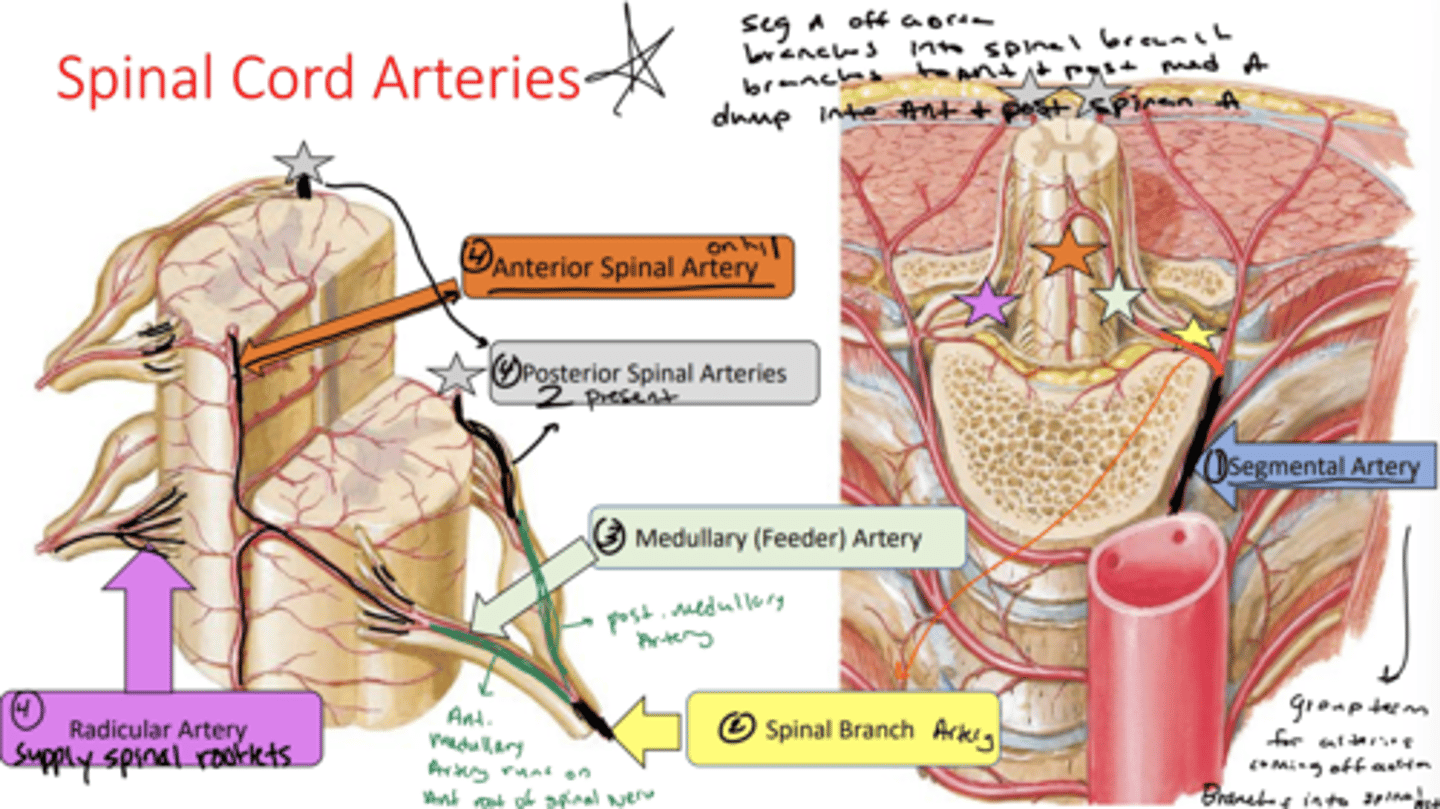
what is the name of the arteries that come off the aorta
segmental arteries
segmental arteries branch into the ___
spinal branch Artery
spinal branch artery splits into
anterior and posterior medullary feeder artery
the anterior medullary feeder artery runs on the anterior root of the spinal nerve and supplies the
anterior spinal artery
how many anterior spinal arteries are there
only 1
the posterior medullary feeder artery supplies the
posterior spinal arteries
how many posterior spinal arteries are there
2
what do the radicular arteries supply
spinal rootlets
arteries in spinal cord image
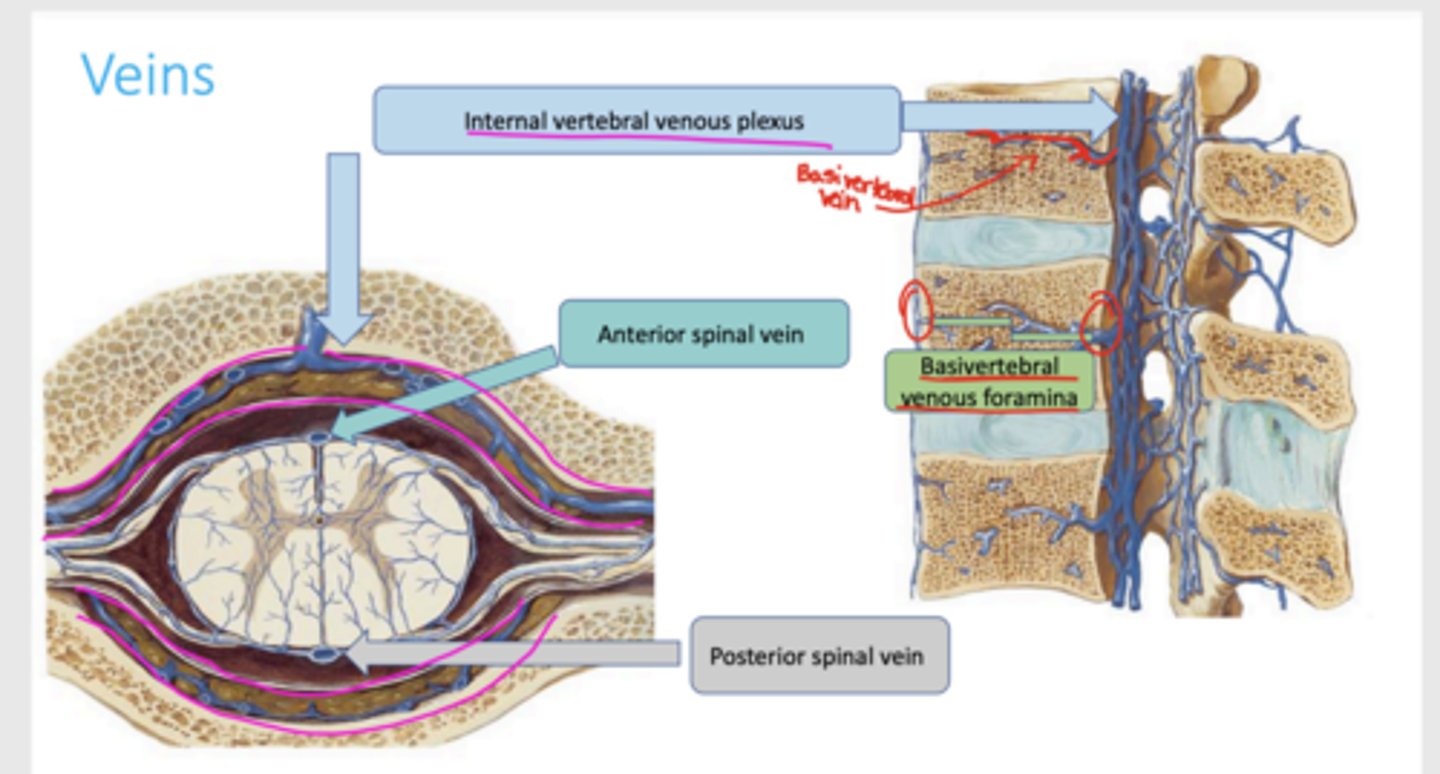
what provides an alternate route for venous return and surrounds vertebral foramen in the epidural space
internal vertebral venous plexous
which veins are found on the anterior and posterior surface of the spinal cord
anterior and posterior spinal veins
how does the internal vertebral venous plexus exit the vertebral body
through basivertebral venous foramina
venous flow diagram
what spinal ligament form the anterior boundary of the spinal canal
posterior longitudinal ligament
what spinal ligament form the posterior boundary of the spinal canal
ligamentum flavum
what does the posterior longitudinal ligament prevent
hyperflexion, posterior herniation
what does the posterior longitudinal ligament attach to
vertebra and IVD
TIGHTLY
what does the ligamentum flavum do
preserve upright posture, straighten spinal column after flexion, and prevent hyperflexion
what does the ligamentum flavum attach to
lamina
Running along the posterior boundary of the spinal canal is an important ligament that assists in maintaining our upright posture and preventing hyperflexion of the vertebral column. Identify the ligament and its attachment site:
ligamentum flavum, lamina
the denticulate ligament is an extension of ___
pia
the denticulate ligament prevents ___ movement
lateral
what anchors the spinal cord laterally to dura
denticulate ligament
the filum terminale is an extension of ___
pia
what anchors the spinal cord to the sacrum and coccyx
filum terminale
what movement does the filum terminale prevent
vertical
which real space is between arachnoid and pia and is filled with CSF
subarachnoid space