Digital Society - Internet & Networks
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
network
a series of interconnected nodes that are able to transmit, receive and exchange data. The data may have various formats, including text, sound, images and video. The nodes include computers, servers and routers.
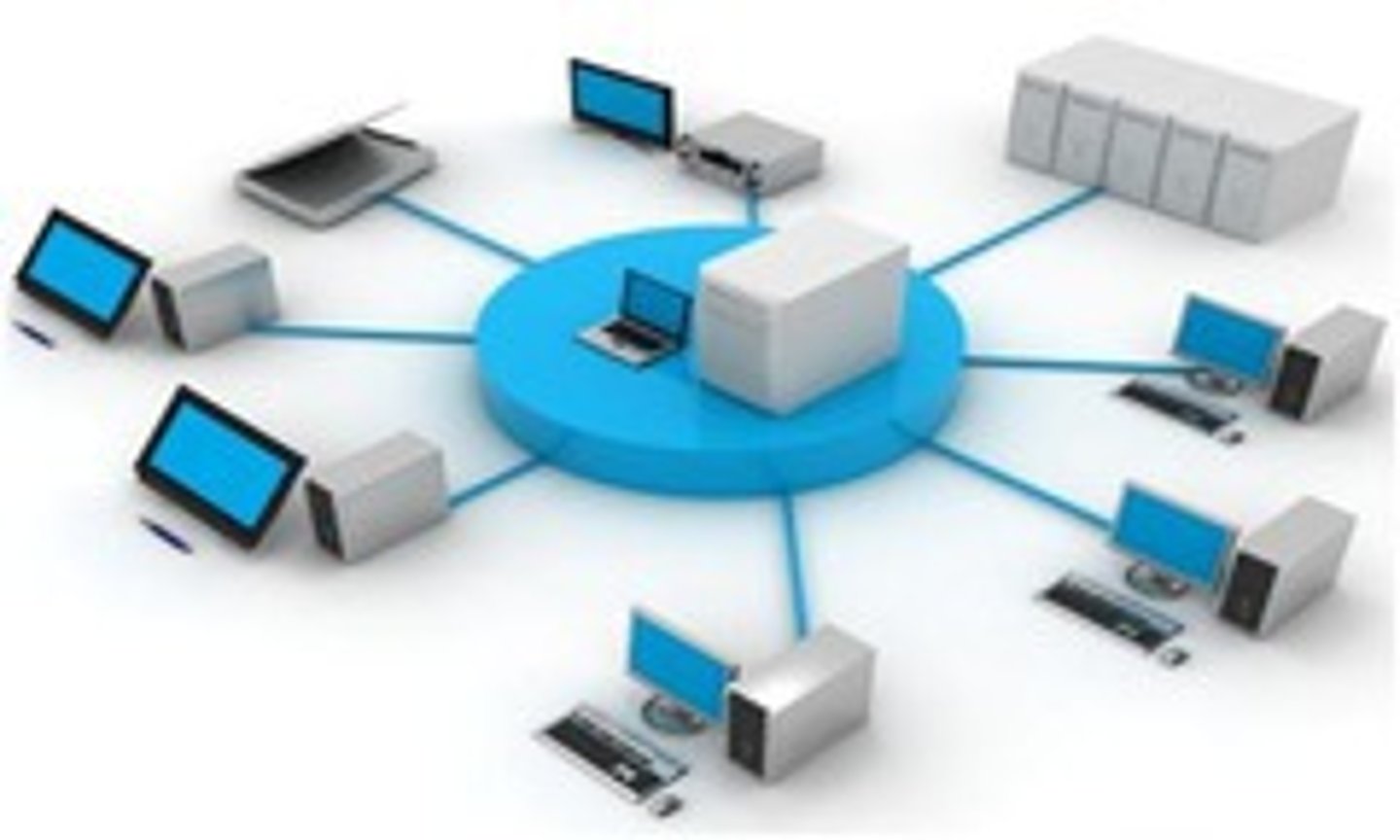
Local area network (LAN)
a group of computers or devices that are connected on a single site.

PAN (personal area network)
the smallest type of network, consisting of the connected devices that are close in proximity to an individual

Metropolitan area network (MAN)
A network that covers a larger geographical area, such as a city
Wide area network (WAN)
A national or international network; the largest example is the internet
Wired network
a traditional network of devices connected physically by ethernet cables and a port
Wireless network
use of wireless technologies to connect the different nodes from a network

client-server network
a set-up where data is stored centrally on a server and access is given to each device connected to the network.
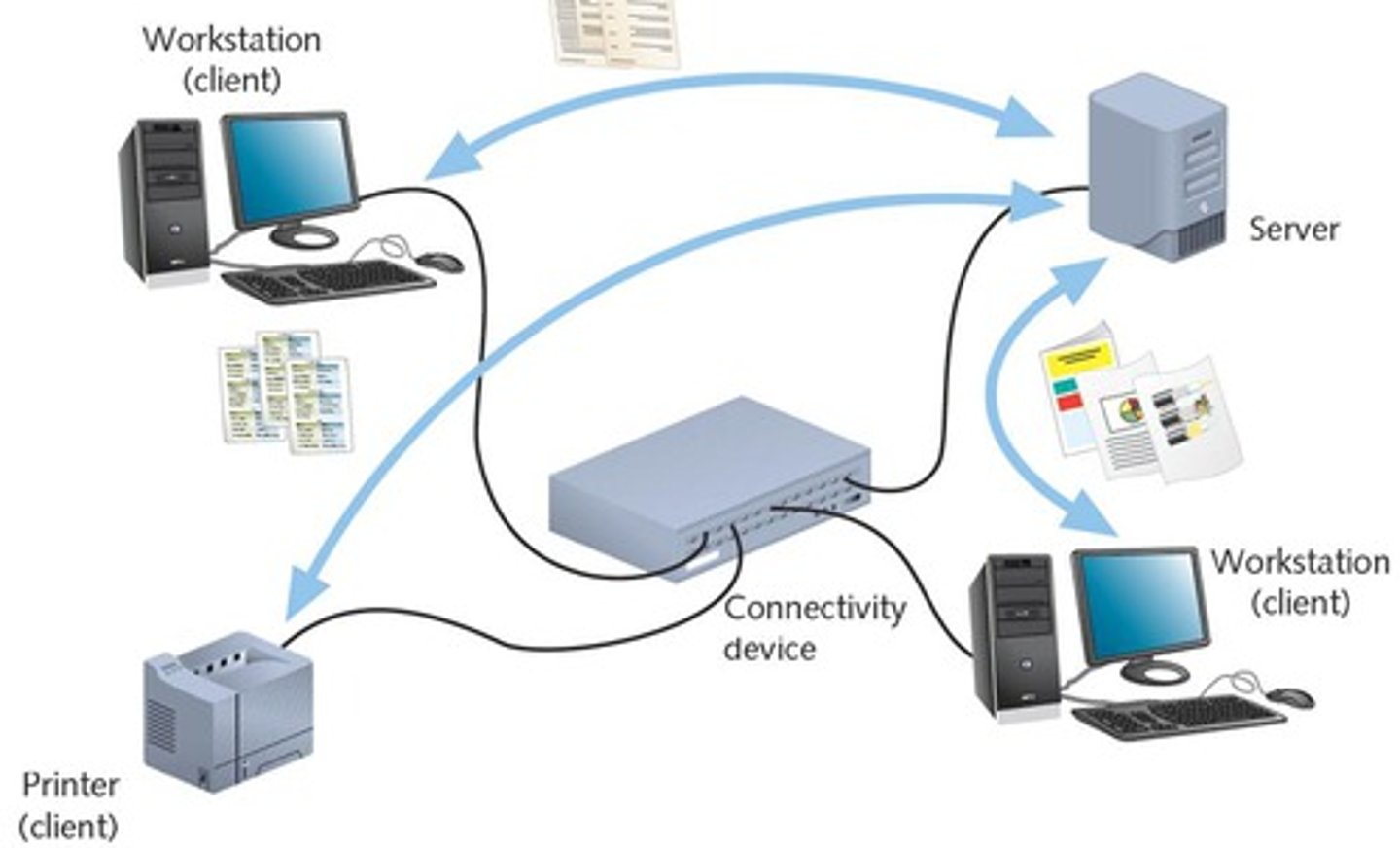
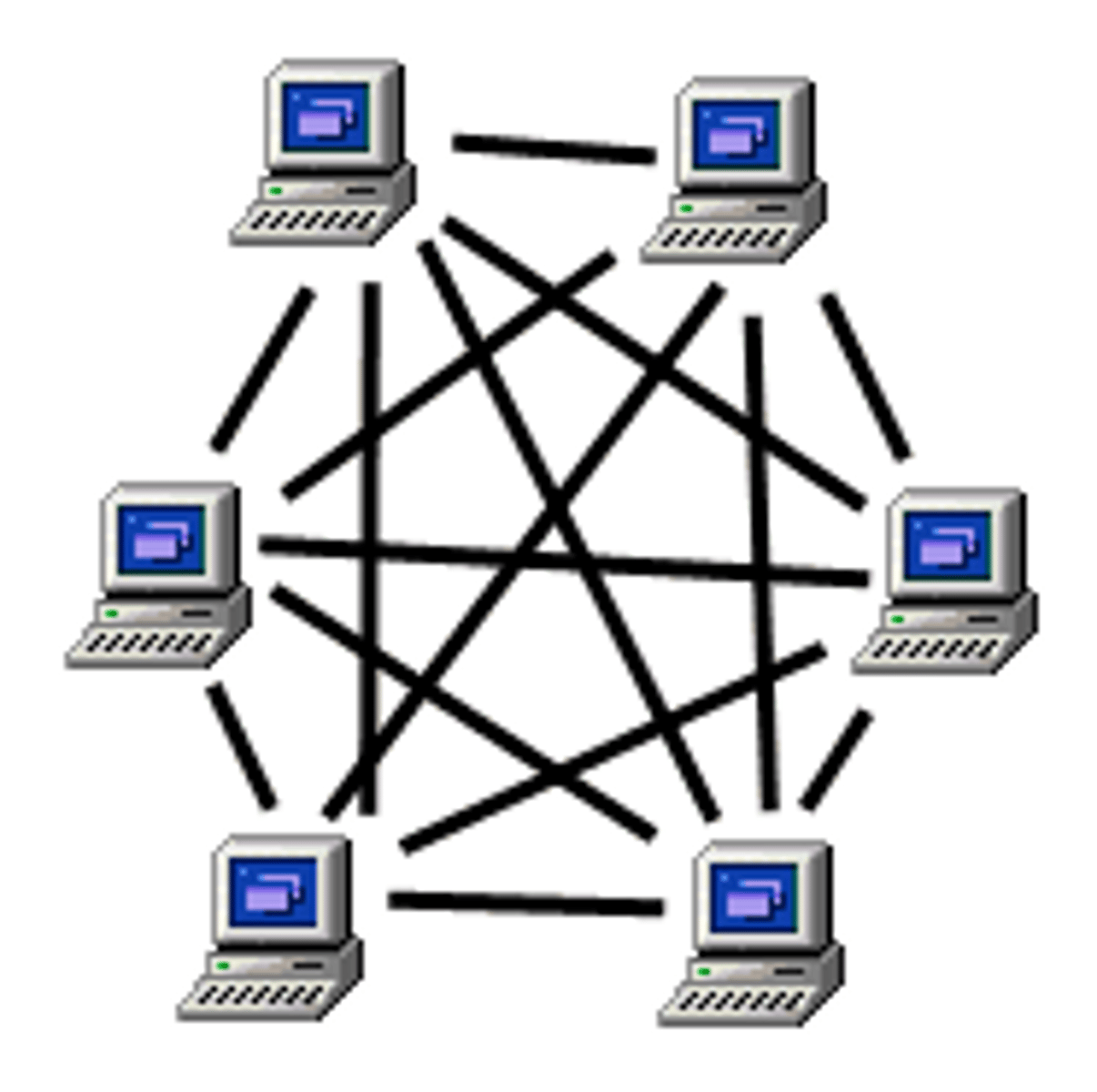
peer to peer (P2P) network
A decentralized network in which each computer is equally responsible for storing and sharing data
Network Interface Card
device responsible for converting data into a data signal and communicating this data to a network

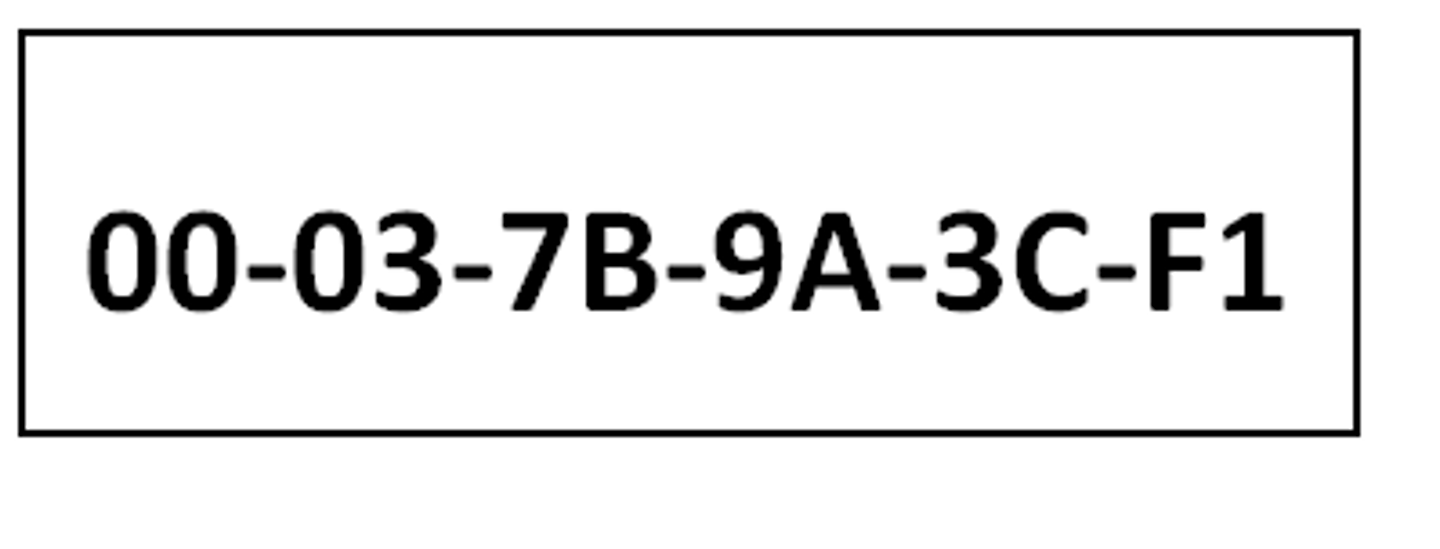
MAC address
A unique identifier assigned to every piece of hardware.
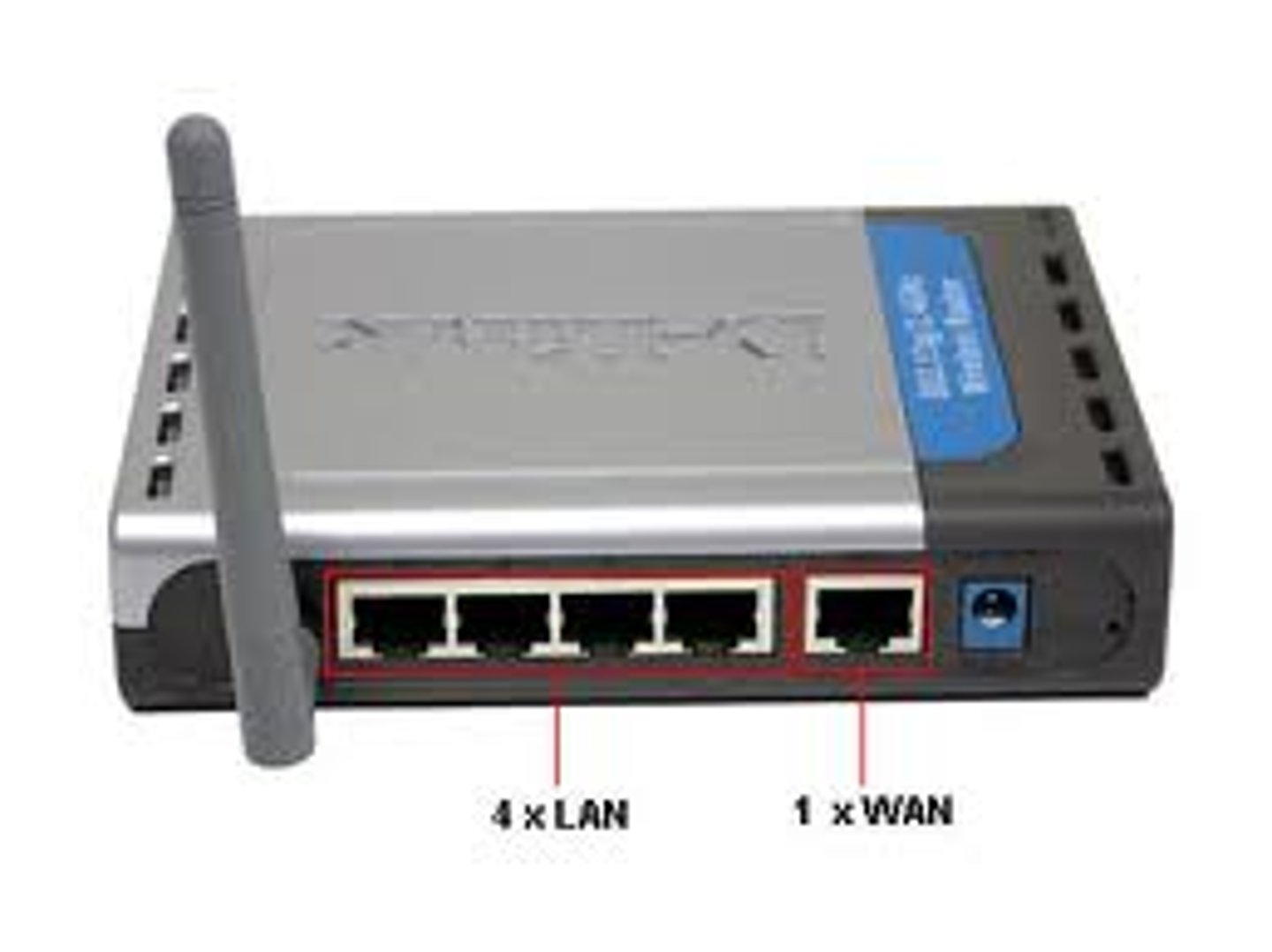
router
a networking technology that transfers data from one network to another by the most efficient path available

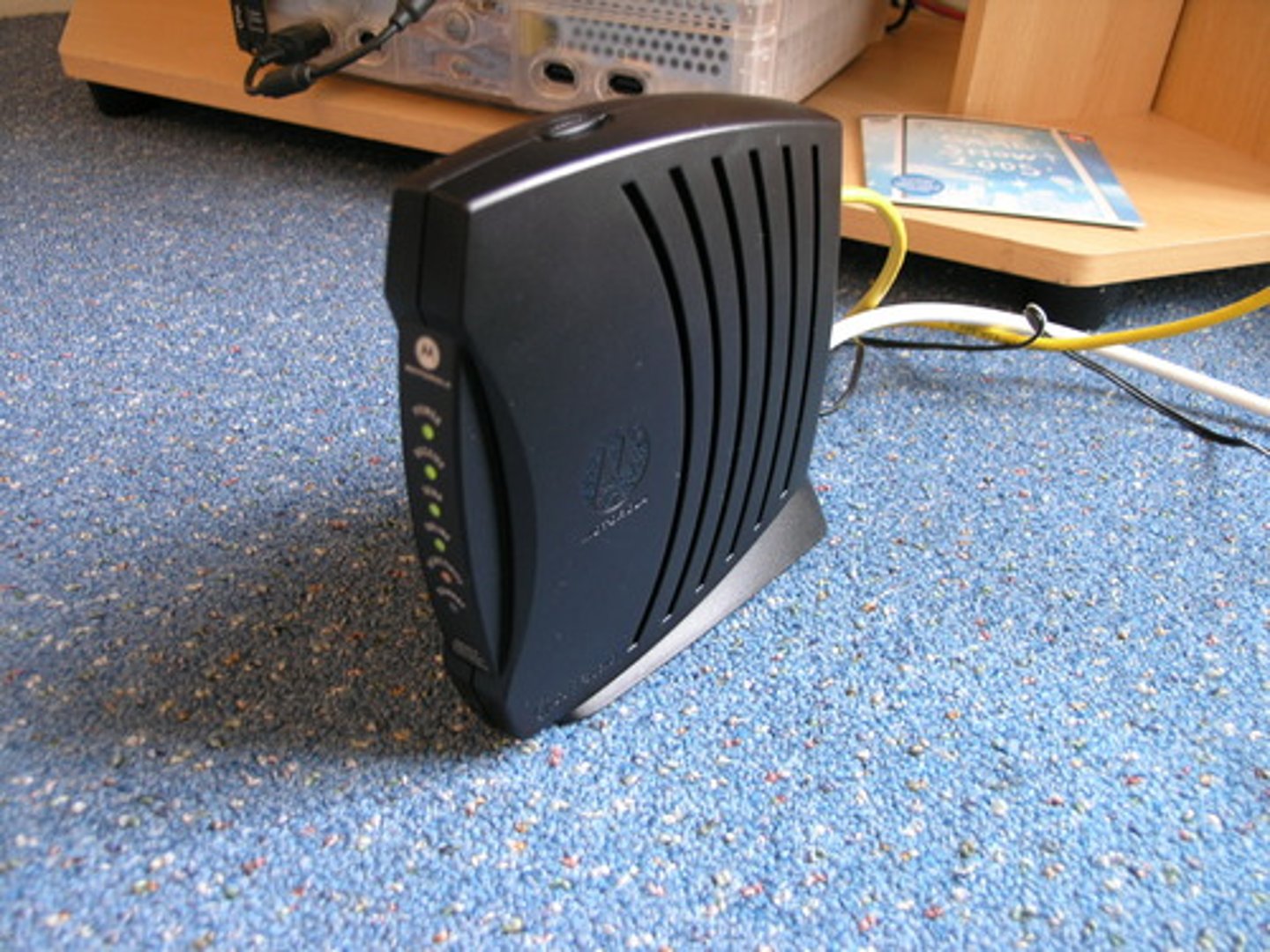
modem
a device that converts digital data into analog data so that it can be transmitted over a telephone line

wireless access point (WAP)
a device that creates a wireless local area network to improve coverage throughout a building

hub
a networking device that broadcasts data to all devices on the network

switch
a networking device that forwards data packets more efficiently than a hub
interoperability
allows different digital technologies or systems to connect and exchange data with one another without restrictions.

network protocol
a set of agreed rules that state how to format, send and receive data
transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP/IP)
protocol defines where data is to be sent to and from and how the data is to be broken down into packets before sending.
IP (internet protocol) address
A logical numeric address that is assigned to every node on a network
Domain name server (DNS)
a server that translates website names into IP addresses
Bandwidth
The maximum rate of data transfer at any one time, measured in Hz.
Speed
the length of time it takes for data to be transferred, measured in megabits per second (MBps)
Data compression
the process that reduces the size of a file by encoding it to use fewer bits of storage than the original file.

net partiality
the idea that all things are not equal on a network: priority can be given to a specific website
net neutrality
the idea that the internet should be free and without restriction
authentication
network access controls set up to control how users access physical resources and data

multi-factor authentication
the use of multiple methods of authentication to verify a user's identity

firewall
hardware or software designed to block unauthorized access to a network by inspecting incoming and outgoing network traffic

proxy server
computer server that acts as an intermediate between the client on the network and the internet providing an additional layer of security
mobile service provider (MSP)
a company that offers cellular connection to mobile phone subscribers
VoIP (voice over internet protocol)
allows users to make audible calls using a broadband internet connection instead of an analog phone line

internet service provider (ISP)
A company that provides internet access and other related services to its customers

the internet
the global collection of networks and networking technologies that link billions of users worldwide

World Wide Web (WWW)
the websites and web services that are hosted on web servers and identified by their URL

UrL (uniform resource locator)
the unique address of each resource on the web, which could be the address of a web page or the file hosted by a web server
http
determines how web resources are transmitted between the web browser and the server
https
a more secure way to transmit resources between the web browser and the server; it adds security certificates to the web servers so that when the users transfer sensitive data it is encrypted
IoT (Internet of Things)
all of the devices that are connected to the internet to collect and share data

spamming
sending unsolicited emails, mainly for the purpose of advertising

hacking
unauthorized access to a computer or network

social engineering
in internet security, this means to manipulate a user into sharing confidential or personal information with a fraudster

phishing
a type of social engineering that involves sending fraudulent emails designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information

virus
a type of malicious software comprised of small pieces of code, often attached to legitimate programs or emails

ransomware
malware that infects a coputer and effectively locks the user out of their own device and demands a payment to unlock it.

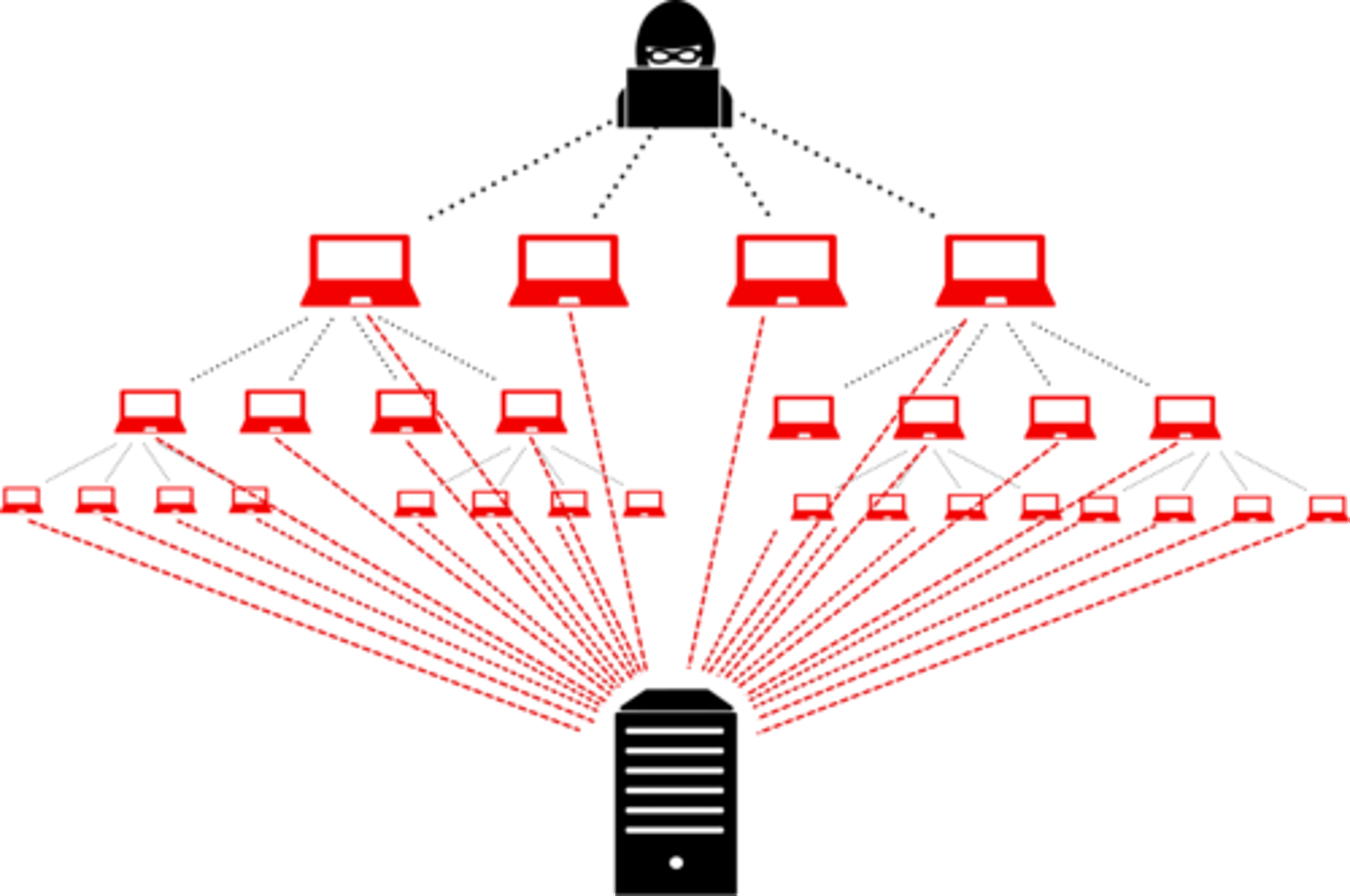
DDOS
overwhelming a site or service so that it is not available to its intended users
anonymity
the use of digital technology to conceal a person's true identity
internet trolls
people who leave intentionally provocotive or offensive messages online in order to get attention, cause trouble or upset someone

identity theft
when someone steals your personal information with the intention of committing fraud.
