fina vocal genetics
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
reciprocal cross
a breeding experiment that involves crossing two different strains of organisms twice, with the sexes of the parents switched in the second cross
codominance
where a heterozygote's phenotype displays the traits of both of the phenotypes of its two homozygote parents.
incomplete dominance
where a heterozygote's phenotype is intermediate between the phenotypes of its two homozygote parents.
haploinsufficient
when a gene is inactivated or deleted, and the remaining copy of the gene is not enough to produce the necessary gene product to maintain normal function
pleiotropy
a genetic phenomenon where a single gene or mutation influences multiple traits that appear to be unrelated
nondisjunction
the failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division, usually resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei.
pseudoautosomal
homologous nucleotide sequences on the X and Y chromosomes of mammals
hemizygous
a genotype where an organism has only one copy of a gene instead of the normal two
polar body
a small, haploid cell produced alongside the egg cell during meiosis
chiasmata
the point where crossing over occurs
bivalent
one pair of chromosomes (homologous chromosomes) in a tetrad
synaptonemal complex
a protein structure that forms between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I in eukaryotes
variable expressivity
when some individuals express varying severity of mutant gene traits
incomplete penetrance
when a mutant gene causes a mutant phenotype in some individuals but not others
complementation test
if +, mutations are on different genes (complement)
if -, mutations are on the same gene (not a complement)
Drosophila sex cascade

C. Elegans sex cascade
Tra-1 expression high, hermaphrodite
Tra-1 expression low, male

Genes that increase cell division
Ras - promotes proliferation
Bcl2 - blocks apoptosis
EF2 - transcription factor, promotes proliferation
lf decrease, gf increase
Genes that block cell division
P53 - tumor suppressor
P21 - blocks cell cycle
Rb - tumor suppressor
lf increase, gf decrease
FISH
a laboratory technique used to detect and locate specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. It uses fluorescently labeled probes that bind to complementary sequences, allowing researchers to visualize gene locations, chromosomal abnormalities, or structural changes in cells under a microscope.
Domain
blocks of conserved structure and function
Paralog
A paralog is a gene that arises through duplication within the same organism’s genome and evolves to perform a related but slightly different function.
Simple nucleotide polymorphism (snp)
a variation at a single position in the DNA sequence among individuals.
Simple sequence repeat (ssr)
An SSR is a short sequence of DNA (usually 2–6 base pairs) that repeats multiple times in a row.
Restriction fragment length
the size of a DNA segment generated when a DNA molecule is cut by a specific restriction enzyme.
Polymorphism (RFLP)
Polymorphism (RFLP) stands for Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. It is a variation in DNA sequence that changes the location of restriction enzyme recognition sites. This leads to differences in the lengths of DNA fragments when the DNA is cut by the enzyme.
Alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a process where a single gene can produce multiple different proteins. This happens because the gene's RNA can be "cut and pasted" in various ways, using different combinations of exons (coding regions). As a result, one gene can lead to the creation of multiple protein variants with potentially different functions.
Pseudogene
a non functional copy of a gene
Gene desert
a region of the genome that has very few or no genes. large, non-coding regions of DNA with little to no function in producing proteins.
Yeast two-hybrid screen
a laboratory technique used to study protein-protein interactions. It involves two key proteins being expressed in yeast cells. One protein is fused to a "bait" molecule, and the other to a "prey" molecule. If the two proteins interact, they bring together two components of a reporter system, leading to a detectable signal
Transposon
A transposon is a DNA sequence that can move or "jump" from one location to another within the genome
Retrotransposon
a type of transposon that moves within the genome by first being transcribed into RNA, then reverse-transcribed back into DNA, and finally inserted into a new location in the genome.
replicative transposition
a type of transposon movement where the transposon is copied and the copy is inserted into a new location in the genome, while the original copy remains in its original location.
DNA Transposon
A transposon that moves by "cut-and-paste" without an RNA intermediate.
conservative transposition
Conservative transposition is a process by which a transposon moves from one location in the genome to another without being copied
environmental mutagen
An environmental mutagen is a physical or chemical agent from the environment that can cause changes (mutations) in the DNA of organisms.
Oncogene
Gene associated with cancer, mutations usually dominant, activate gene/protein
Proto-oncogene
Normal gene that could turn into cancer, often function to control proliferation
Tumor suppressor
Genes whos products protect cells from becoming cancerous
Metastasis
Cells can spread to new sites
Cyclin
Protein whos level changes throughout cell cycle
CDK
Cyclin dependent kinase (kinases add phosphate to target proteins)
checkpoint
Cell determines if it ready for next phase in cell cycle
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Caspase
A protease that can mediate apoptosis
familial adenomatous polyposis coli
mutation in APC, protein degrades cytoplasmic B-catenin
Mutant APC, loses wild type, can’t degrade B-catenin, becomes cancerous
loss of heterozygosity
when an individual heterozygous for a cancer causing mutation loses the chromosome or segment of the chromosome that had the wild type copy of that gene in some cell
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Mutation in P53 gene, higher risk of many types of cancer
Can’t institute DNA damage checkpoint, can’t induce apoptosis if damage isn’t repaired
Sex determination
Sex determination is the biological process by which an organism’s sex is established, typically based on its genetic makeup. In many species, it is determined by specific sex chromosomes (e.g., XX for females and XY for males in humans). The presence or absence of certain genes, such as the Sry gene on the Y chromosome, influences the development of male or female traits.
SRY
Sry (Sex-determining region Y) is a gene located on the Y chromosome that plays a crucial role in determining male sex. It initiates the development of male characteristics by triggering the formation of testes, which produce male hormones (androgens) that lead to the development of male physical traits.
Dosage compensation
A process that equalizes gene expression form sex chromosomes in males and females
Morphogen
a signaling molecule that helps control the pattern of tissue development by diffusing across cells and triggering specific gene expression based on its concentration.
Gap genes
a group of genes that control the development of broad regions of an organism's body during early embryonic development. They define large segments along the anterior-posterior axis and help establish the basic body plan.
Segment polarity genes
genes that control the development of individual segments in the body of an organism, particularly during early development. They help establish the anterior-posterior polarity within each segment, determining the structure and identity of parts of the organism’s body.
Homeosis
the phenomenon where one body part is transformed into another, usually due to mutations in homeotic genes. These genes control the development of specific body regions, and their alteration can lead to the misdevelopment of structures, such as legs growing where antennae should be.
Equivalence group
a group of cells or tissues in early development that have the potential to develop into the same type of structure or organ, depending on signals they receive.
Population
A population is a group of individuals of the same species that live in a specific geographic area and interbreed, sharing a gene pool.
Subpopulation
A subpopulation is a smaller, distinct group within a larger population, often separated by geographic, environmental, or behavioral factors, but still belonging to the same species.
Gene pool
A gene pool is the total collection of genes and alleles present in a population or species, representing the genetic diversity available for inheritance.
Hardy-Weinberg
a principle that states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary forces (such as mutation, natural selection, genetic drift, or gene flow).
Mating system
the way in which a species mates, including how individuals pair up and reproduce.
Assortative mating (positive or negative)
Assortative mating is a mating pattern where individuals tend to mate with others that are similar (positive assortative mating) or different (negative assortative mating) from themselves in specific traits.
- Positive assortative mating: Individuals with similar traits (e.g., height, color) are more likely to mate.
- Negative assortative mating: Individuals with different traits are more likely to mate.
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is the mating of individuals that are closely related genetically, leading to an increased probability of offspring inheriting similar genetic material from both parents. This can result in a higher chance of genetic disorders and reduced genetic diversity.
Multi factorial traits
traits influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. These traits show continuous variation (e.g., height, skin color, and intelligence) rather than discrete categories. The interaction between genes and the environment determines the expression of these traits.
Quantitative traits
traits that vary in degree and are measured on a continuous scale, such as height, weight, or blood pressure.
Variance
Variance is a statistical measure of how much individual values in a dataset differ from the mean (average) of the dataset. It quantifies the degree of variation or spread in a set of values. High variance means the values are spread out, while low variance indicates they are close to the mean.
Total variance
Total variance is the overall measure of variability in a dataset, accounting for all sources of variation. It is the sum of genetic variance (variation due to genetic differences) and environmental variance (variation due to environmental factors) in traits. It represents how much individuals in a population differ from the overall mean for a particular trait.
Environmental variance
Environmental variance is the portion of total variance in a trait that is caused by differences in the environment rather than genetic differences.
Genetic variance
Genetic variance is the portion of total variance in a trait that is due to differences in the genetic makeup of individuals within a population.
Heritability
Heritability is the proportion of the total variation in a trait that is due to genetic factors. It quantifies how much of the variation in a trait within a population can be attributed to genetic differences, as opposed to environmental factors. Heritability values range from 0 (no genetic influence) to 1 (all variation is genetic).
Linkage equilibrium
a situation in a population where alleles at different loci are inherited independently of each other. In this state, the allele combinations at two or more loci occur at frequencies predicted by the product of their individual allele frequencies.
Genome wide association study
a research method used to identify genetic variants (like SNPs) associated with specific traits or diseases by scanning the entire genome of many individuals. It compares the genetic makeup of individuals with and without a particular trait to find correlations between certain genetic markers and the trait of interest.
positional cloning / chromosome walk use
use for tightly linked genes. prepare genomic library, perform colony lift using known gene as probe, make new probe from end of first clone and rescreen until you find the desired gene, must have some way to recognize the gene
functional complementation use
use for temperature sensitive or fungi. prepare cDNA library from wild type in a plasmid of the organism, transform mutant and look for rescued organism
antibody probe use
use if there is a synthesized antibody. prepare cDNA library using an expression vector and perform colony
lift using antibody as probe
nucleic acid probe use
use if DNA sequence is known. screen genomic library by colony lift with gene as probe
degenerate primers use
use if protein / amino acid sequence is known. screen cDNA or genomic library by colony lift using degenerate primers synthesized based on the amino acid sequence of the protein as your probe
making a mouse
Infect ES cells from black mouse, using vector shown above
Select for recombinants in neomycin and ganciclovir
Verify that recombinants had deletion by Southern blot or PCR
Mix engineered ES cells w embryo from white mouse
Implant into pseudopregnant mouse to produce chimeric mice
Cross Chimeric X white to find mice that produce all black offspring
Cross hets to get homozygotes
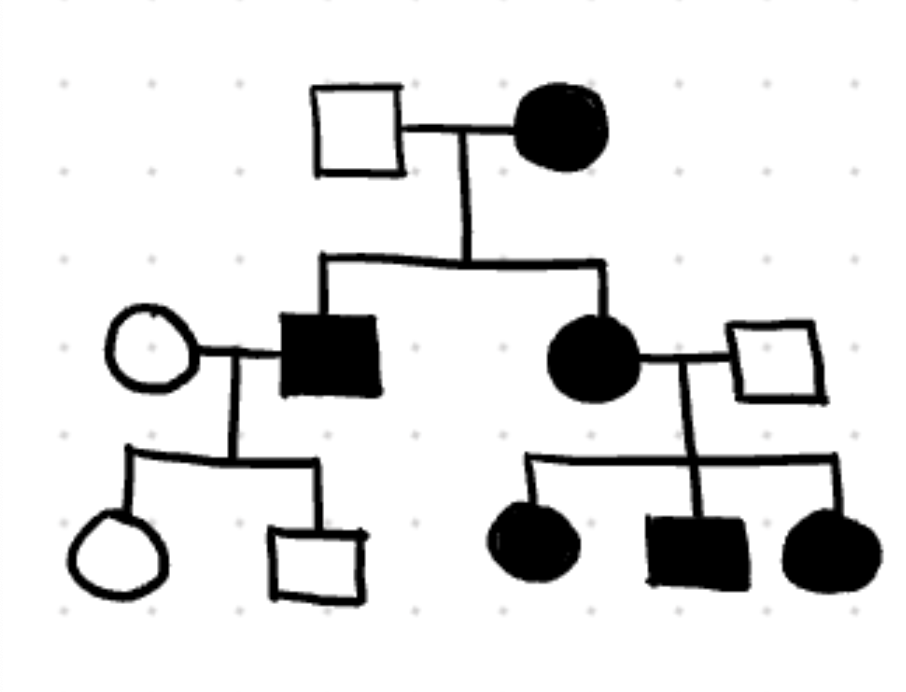
maternal effect
phenotype of offspring is based on moms genotype
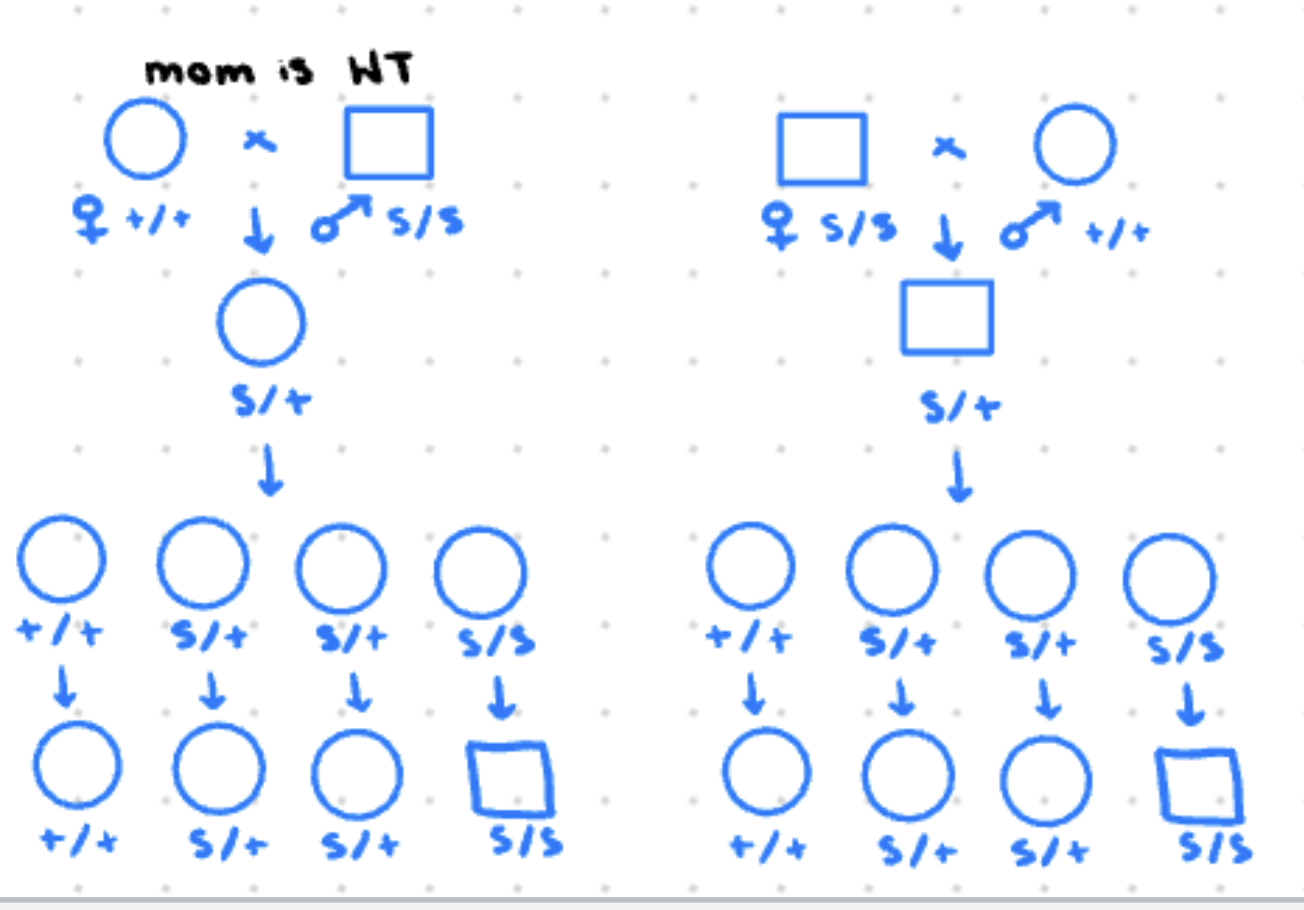
extranuclear inheritance
inheritance is determined by substances in the egg (all children of affected mother are affected)
pericentric inversion
includes centromere
paracentric inversion
does not include the centromere
deletion
removes part of a chromosome
Cri-du-chat syndrome
results from deletion of part of chromosome 5
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
results from deletion of part of chromosome 4
duplication
part of chromosome duplicated
balanced chromosome complement
a complete set of chromosomes where no genetic material is lost or gained, even if the arrangement of the chromosomes is altered through structural changes like translocations or inversions
reciprocal translocation
non homologous chromosomes exchange DNA
Robertsonian translocation
special type of non-reciprocal translocation that fuses 2 acrocentric/telocentric chromosomes
high frequency of spontaneous abortion and down syndrome
short arms of chromosomes lost
inversion
part of chromosome “flipped”
endopolyploidy
having extra sets of chromosomes in some cells of the body
euploidy
correct number of chromosomes
monoploidy
orgamism or cell with only one copy of each chromosome
autopolyploid
composed of multiple sets of chromosomes from the same species
allopolyploid
composed of multiple sets of chromosomes from different species
endoreduplication
replication without nuclear division
euploidy
a state where an organism or cell has the correct number of chromosomes, or a multiple of that number
aneuploidy
chromosome # differs from normal by less or more than a full chromosome set
polysomy
extra individual chromosome
trisomy
diploid with extra copy of 1 chromosome
kleinfelter (XXY)
trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
trisomy 13 (patau syndrome)
trisomy 18 (edwards syndrome)
triploid still have balance expression, but trisomy is unbalanced