Lecture 5 - Electric Charges
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Static Electricity
objects can be charged by rubbing
plastic ruler rubbed with a cloth becomes negatively charged
when two unlike materials are rubbed together, they become charged
combing hair, sliding in car seat, walking on carpets
what is charging
transfer of electrons from one material to another material
what is a conductor
materials in which free electron can move within the material
what is an insulator
materials in which electron cannot move within the material
two types of electric charges
positive
possessed by protons
negative
possessed by electrons
like charges repel, opposite charges attract
electron transfer equation
number of electrons transferred = Amount of charge/charge of one electron
Coulomb’s Law (1780)
Electric force between two point charges is given by Coloumb’s law
F = k (q1 * q2) / r²,
k is the electrostatic constant
q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges
r is the distance between the charges.
An electron and a proton are held at a distance of 0.5m, if released which partial would have greater acceleration at any one instant
both experience the same force but the mass of electron is much smaller than a protons and therefore to compensate, it has greater acceleration
Electric Field: contact forces
charges apply force without any physical contact to push or pull the other charges - force at a distance
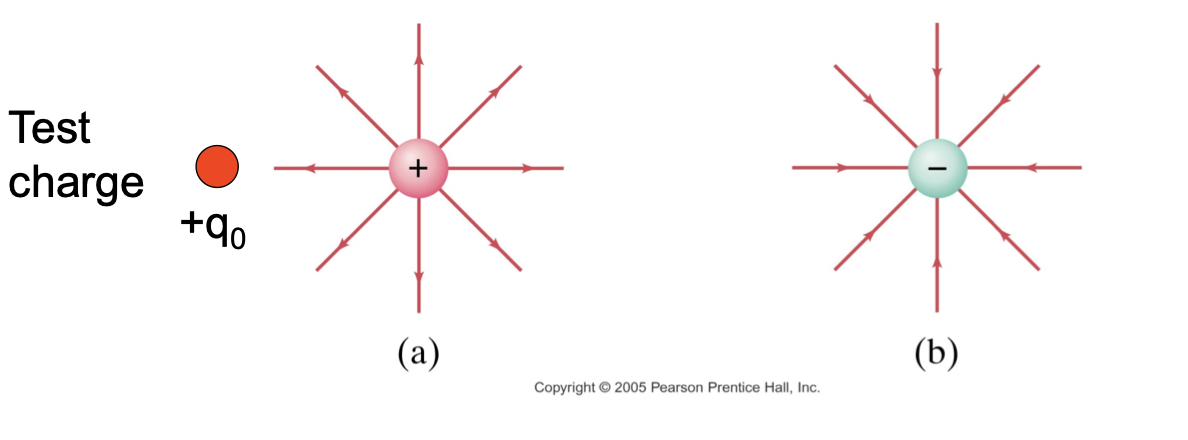
Electric Field Lines
Electric field around a charge can be represented by field lines. They start on a positive charge and end on a negative charge.
When another charged object called the test charge enters the electric field, electric force acts upon it
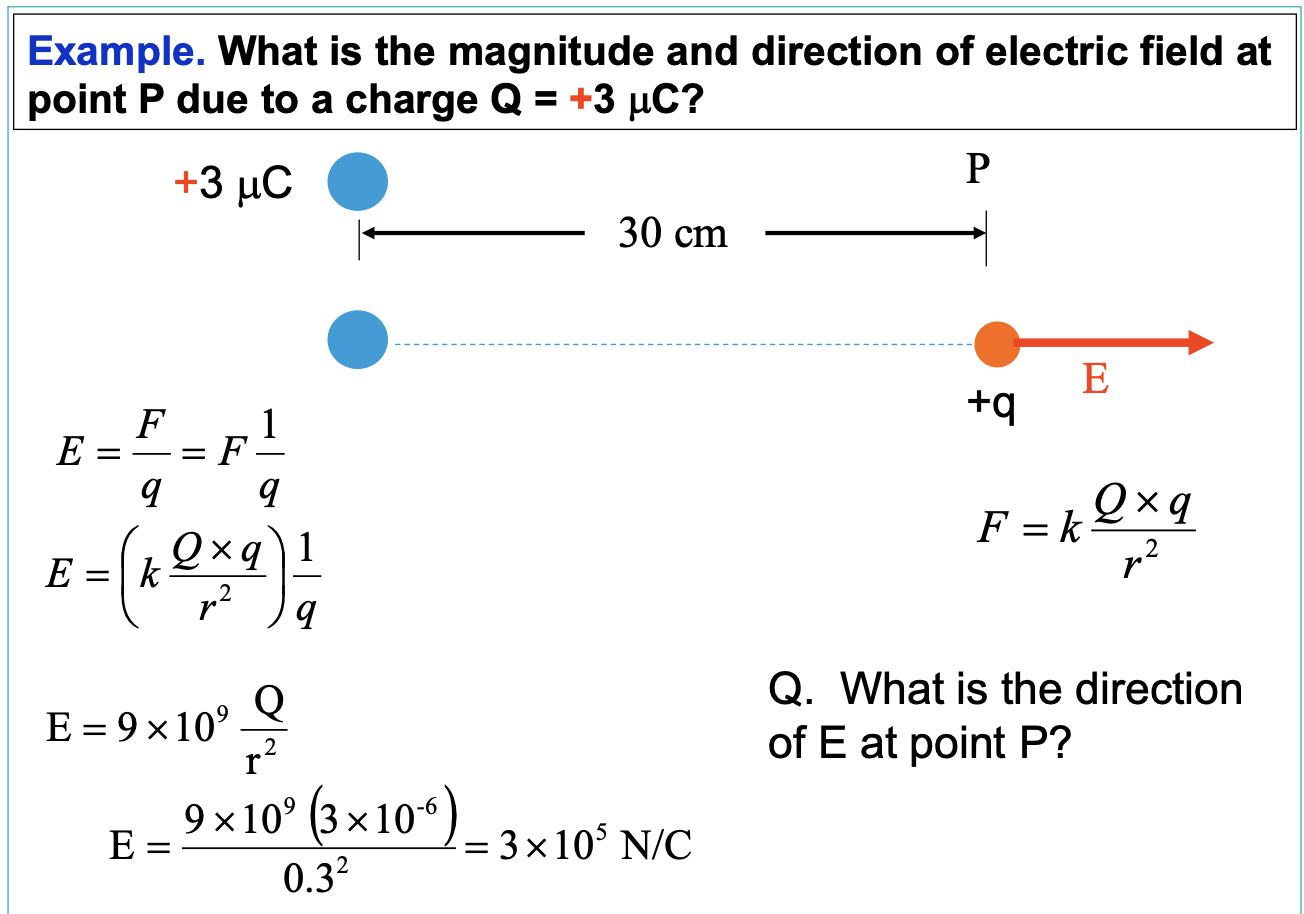
Electric field at a point equation
E = F/q
F = force on a small charge
q = charge of the small charge
Electric Shielding
the charges induced on the two surfaces of the box produce an electric field inside the box
the field opposes the external field, causing a zero net field in the box