AP Biology Unit 7
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals
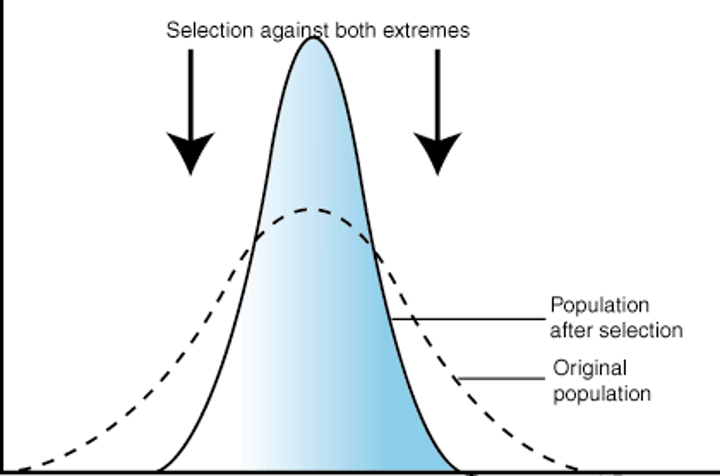
directional selection
a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction
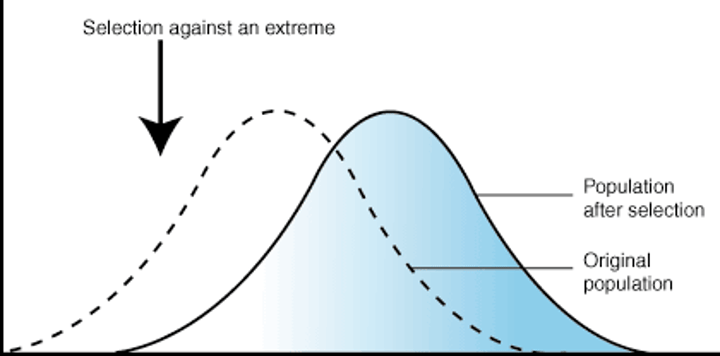
diversifying / disruptive selection
extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values
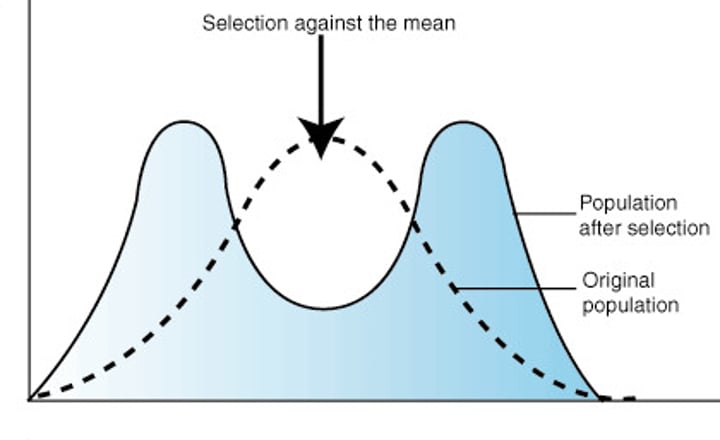
stabilizing selection
genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilizes on a particular trait value
artificial selection
Selectively breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with desirable traits.
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection.
founder effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
gene flow
Movement of alleles into or out of a population due to the migration of individuals
polygenic traits
traits controlled by two or more genes
fitness
measure of relative reproductive success
Microevolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations.
Macroevolution
large-scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time
mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change
adaptation
A characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment
evolution
The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is supported by multiple lines of evidence
genetic variation
Genotypic and phenotypic differences in a population
Selective pressures
Any biotic or abiotic factors influencing survivability
analogous structures
Structures evolved independently in different species due to similar environment/selective pressures
homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry
vestigial structures
remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species
Endosymbiosis
A process by which the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells probably evolved from symbiotic associations between small prokaryotic cells living inside larger cells
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
A model for describing and predicting allele frequencies in a non evolving population
5 requirements to use Hardy-Weinberg
-Large population (no genetic drift)
-Absence of migration (no gene flow)
-No net mutation (no modified gene flow)
-Random mating (no sexual selection)
-Absence of selection (no natural selection)
What is the H-W equation to calculate genotype/phenotype?
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
What is the H-W equation to calculate alleles?
p + q = 1
p in H-W equation
dominant allele
q in H-W equation
recessive allele
Speciation
process by which new species form. - occurs when groups in a species become reproductively isolated and diverge
allopatric speciation
groups from an ancestral population evolve into separate species due to a period of geographical separation
sympatric speciation
groups from the same ancestral population evolve into separate species without any geographical separation
gene pool
collection of gene variants
prezygotic barriers
prevent members of different species from mating to produce a zygote, a single-celled embryo
habitat isolation
Two species might prefer different habitats and thus be unlikely to encounter one another (prezygotic)
temporal isolation
Two species might reproduce at different times of the day or year and thus be unlikely to meet up when seeking mates (prezygotic)
behavioral isolation
Two species might have different courtship behaviors or mate preferences and thus find each other "unattractive" (prezygotic)
gametic isolation
Two species might produce egg and sperm cells that can't combine in fertilization, even if they meet up through mating (prezygotic)
mechanical isolation
Two species might have bodies or reproductive structures that simply don't fit together (prezygotic)
postzygotic barriers
keep hybrid zygotes—one-celled embryos with parents of two different species—from developing into healthy, fertile adults
Polyploidy
condition of having more than two full sets of chromosomes
Gradualism
When evolution occurs slowly over hundreds of thousands or millions of years.
punctuated equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change