BIOL2325 U of U Exam 1
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Organization of Living Matter
Chemistry, Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism
Name, Basic Structure, Distribution, Function
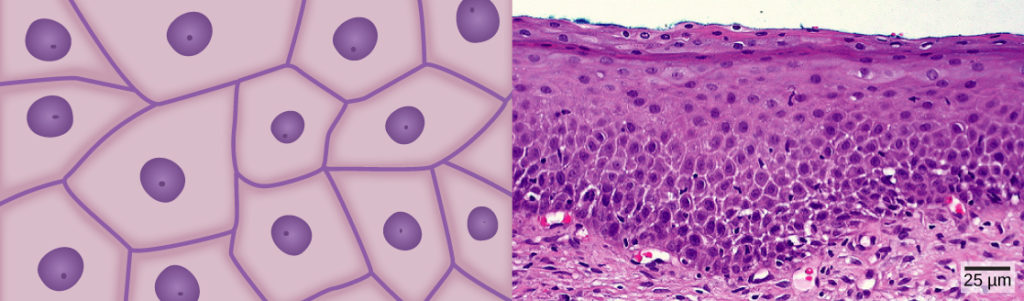
Epithelial Tissue
tightly packed, avascular cells
covers body surfaces, lines cavities
protection, absorption, excretion, secretion
Name, Basic Structure, Distribution, Function
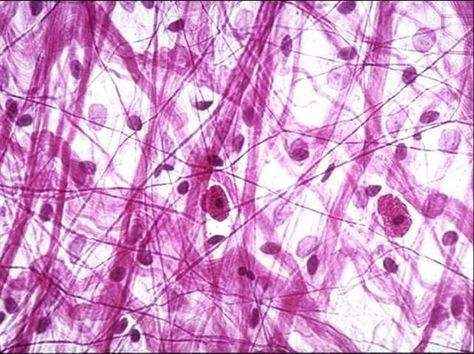
Connective and Supporting Tissue
few, scattered cells with lots of fibers and extracellular matrix and highly vascular
Everywhere in the body
connect and support
Name, Basic Structure, Distribution, Function
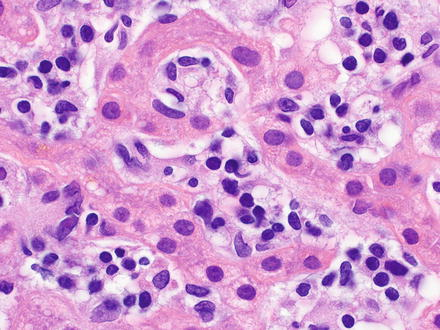
Hematolymphoid Complex
Liquidy Tissue, cells are separated by plasma
blood and lymph
produce and maintain blood and immune cells
Name, Basic Structure, Distribution, Function
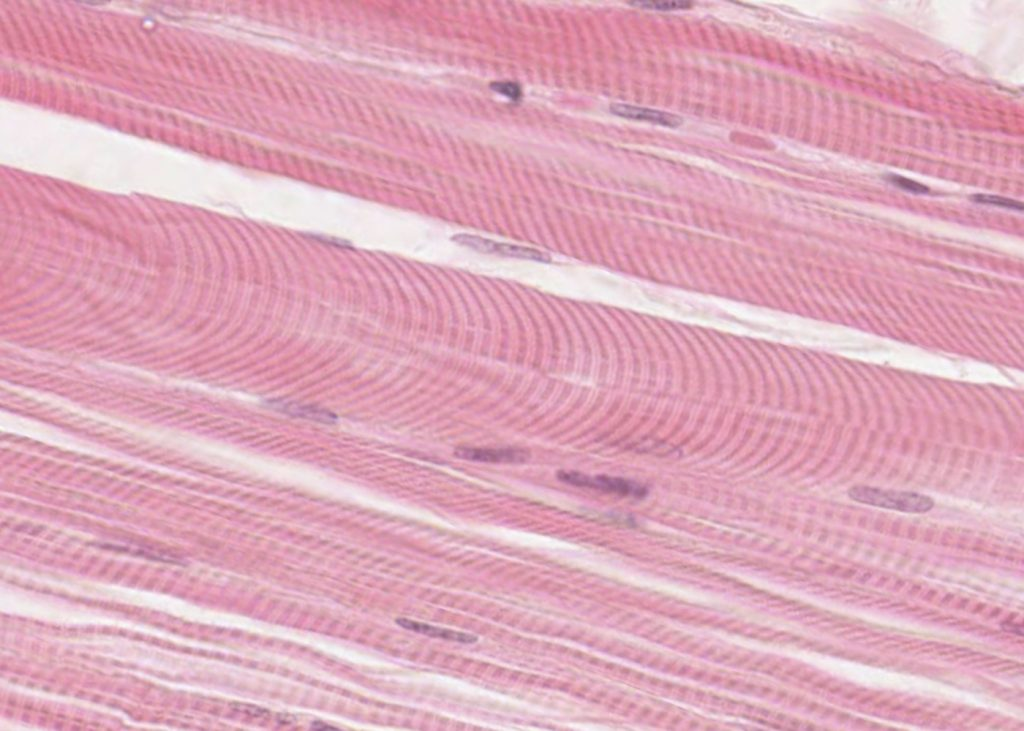
Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
long, slender cells
contraction (movement, posture, heat, transport, protection)
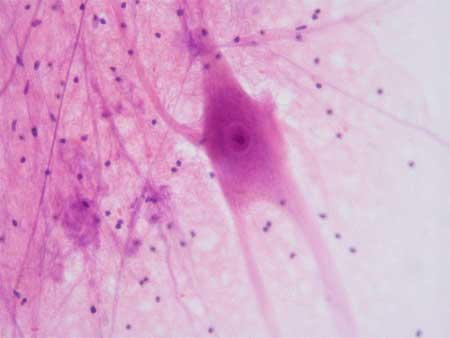
Name, Basic Structure, Distribution, Function
Nervous Tissue
neurons and glial cells surrounded by lots of extracellular matric
nervous system
communication (relaying signals)
Contrast epithelial & connective and supporting tissue
Epithelial - tightly packed cells, avascular
Connective - few, scatter cells w/ large extracellular matrix, highly vascular
Clearly & concisely define the term epithelial tissue.
tightly packed, avascular cells meant for protection, absorption, secretion, and excretion and covers body surfaces and cavities.
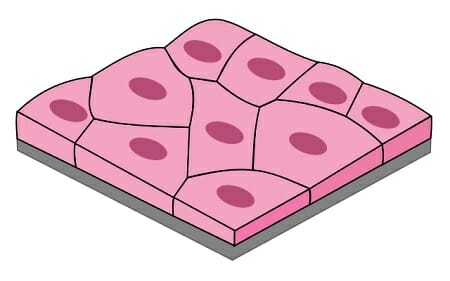
Name, Types & Distribution, Function
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Endothelium - Inner Lining of Cardiovascular System
Mesothelium - covering organs and lining body cavities
Exchange & Friction Reduction
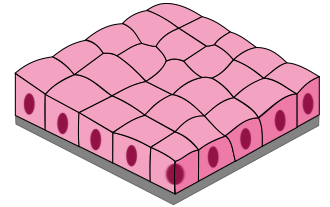
Name, Distribution, Function
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Lining Glands
Secretion
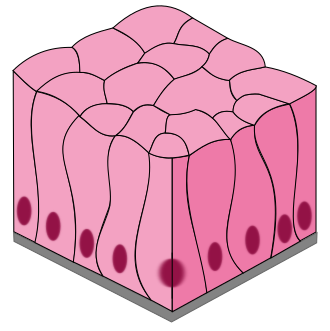
Name, Types, Distribution, Function
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Nonciliated (more common) and ciliated
lining inside of digestive tubes
absorption, protection, mucous production
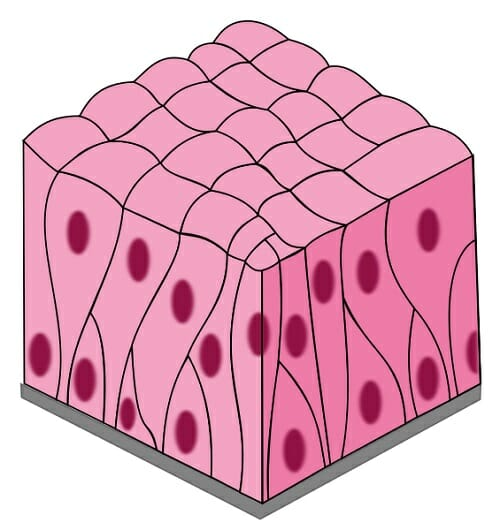
Name, Types, Distribution, Function
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
nonciliated and ciliated (more common)
in big respiratory tubes
mucous production, movement, filtering
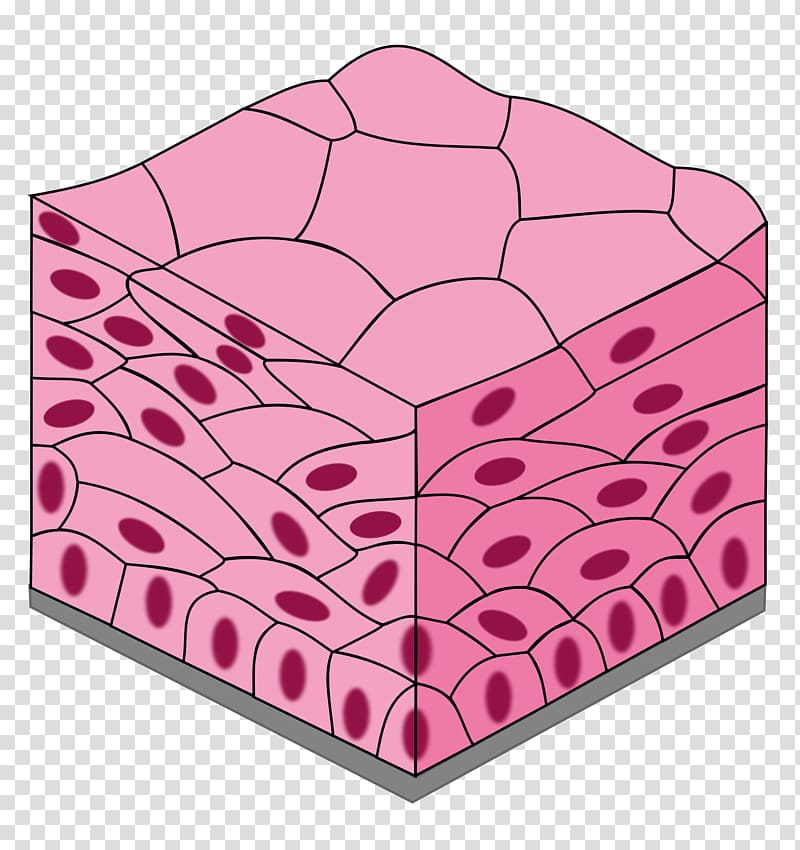
Name, Types & Distribution, Function
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Nonkeratinized - Mucousy Areas
Keratinized - Everywhere on epidermis
Protection
Name, Distribution, Function
Urothelium
Urinary system
Protection
Endothelium v. Mesothelium
Mesothelium covers organs and lines body cavities while endothelium is only in the cardiovascular system.
Compare Connective and Supporting Tissue
they both have large extracellular matrices made of collagen fibers
Different Categories of Connective and Supporting Tissue
connective - connective tissue proper, reticular tissue, adipose tissue
supporting - cartilage, bone
2 Categories of Cells in Connective Tissue
Fixed/Resident Cells and wandering/migrant cells
Fixed/Resident Cells - Name & Function
Mesenchymal Cell - early stem cell, can become specified (some options being fibroblast or adipocyte)
Fibroblast/Fibrocyte - builds fibers (become fibrocytes when dormant)
Adipocyte - fat cell
Wandering/Migrant Cells - Name & Function
Macrophage/WBCs - defenders (engulf pathogens and cellular debris)
Mastocyte - pathogen detection and inflammation
Lymphocyte - identify, attack, and remember pathogens
Plasma Cell/Plasmocyte - produce antibodies and participate in immune response
Define the term “ground substance”.
A thing, gel-like substance w/ lots of water that fills spaces between cells and fibers and facilitates nutrient exchange
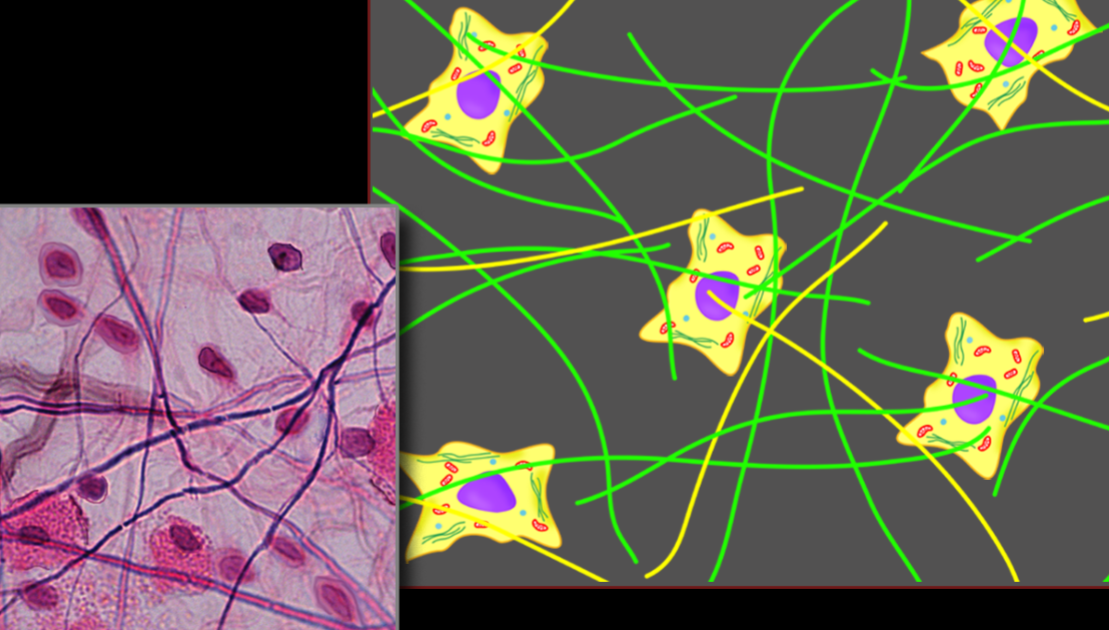
Principle Fibers of Connective Tissue - Name & Function
Collagen Fibers - protein ropes good at resisting tension
Elastic Fibers - Able to recoil, good at resisting tear
Name, Distribution, Function
Loose Connective Tissue
Potentially everywhere (under epithelium)
General glue of body, provides vascular supply
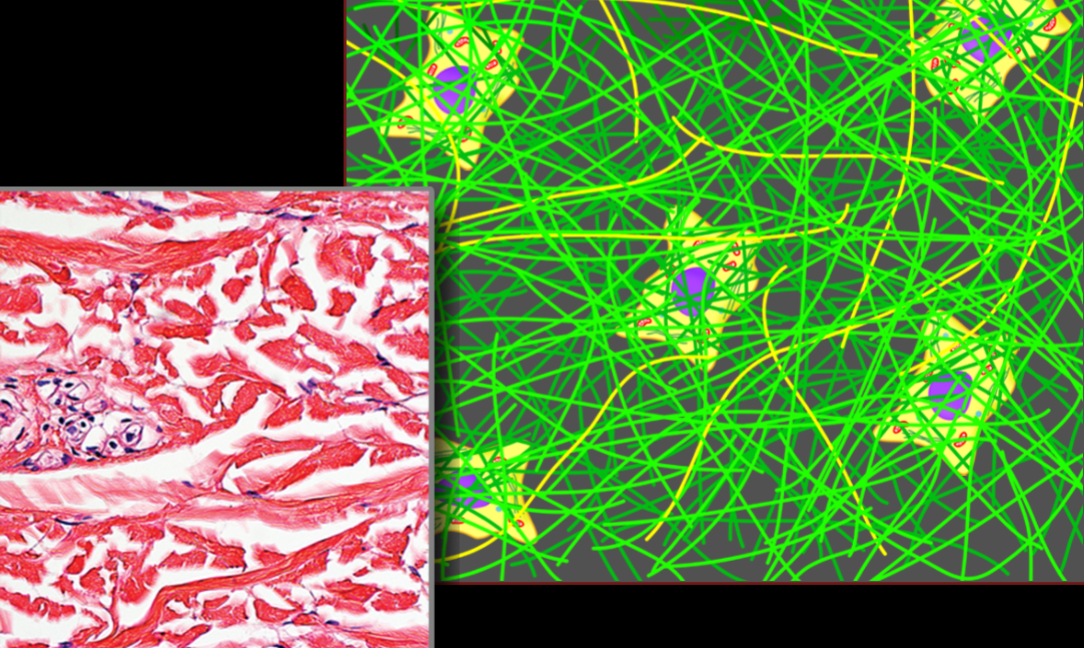
Name, Distribution, Function
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
ligaments, fascia, dermis
resists tension in all directions
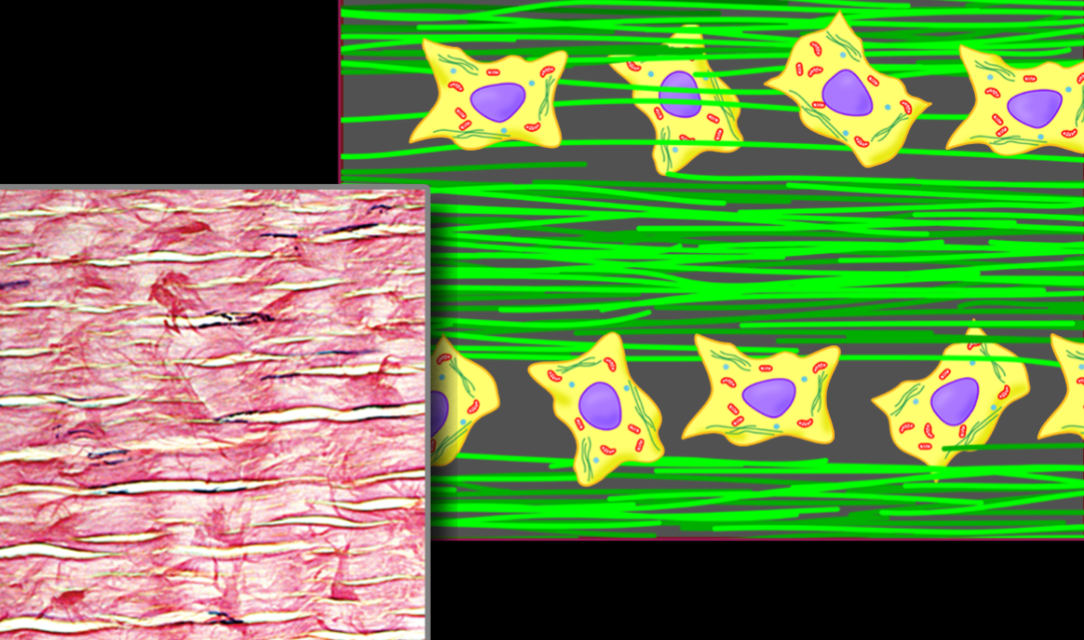
Name, Distribution, Function
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
tendons of muscles
resists tension in one direction
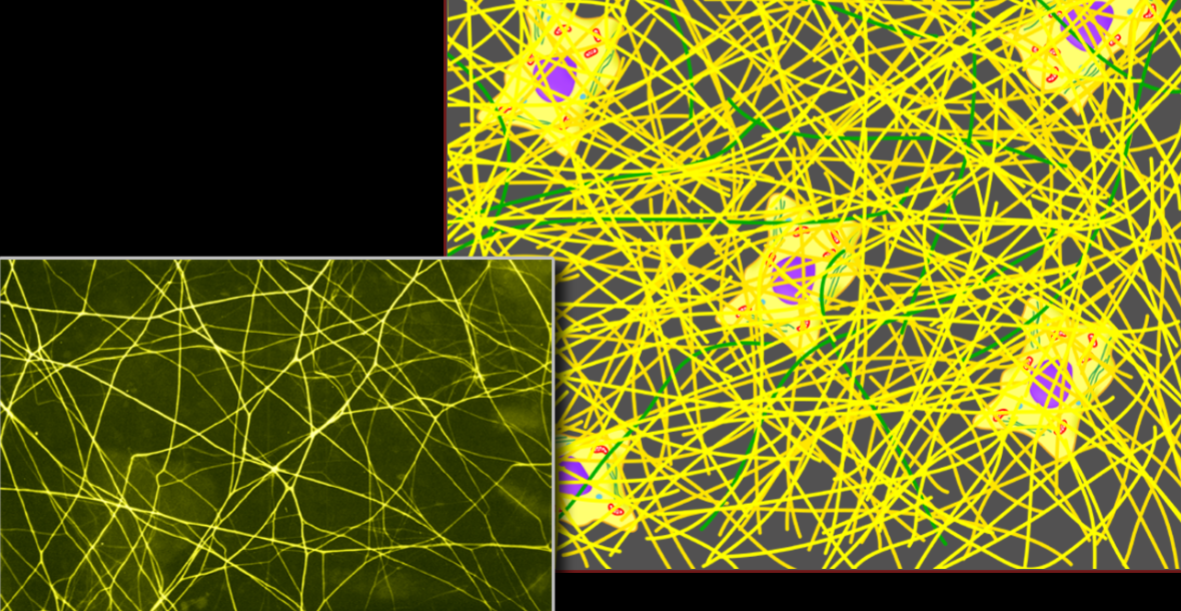
Name, Distribution, Function
Elastic Connective Tissue
large arteries
stretch and recoil
Name, Distribution, Function
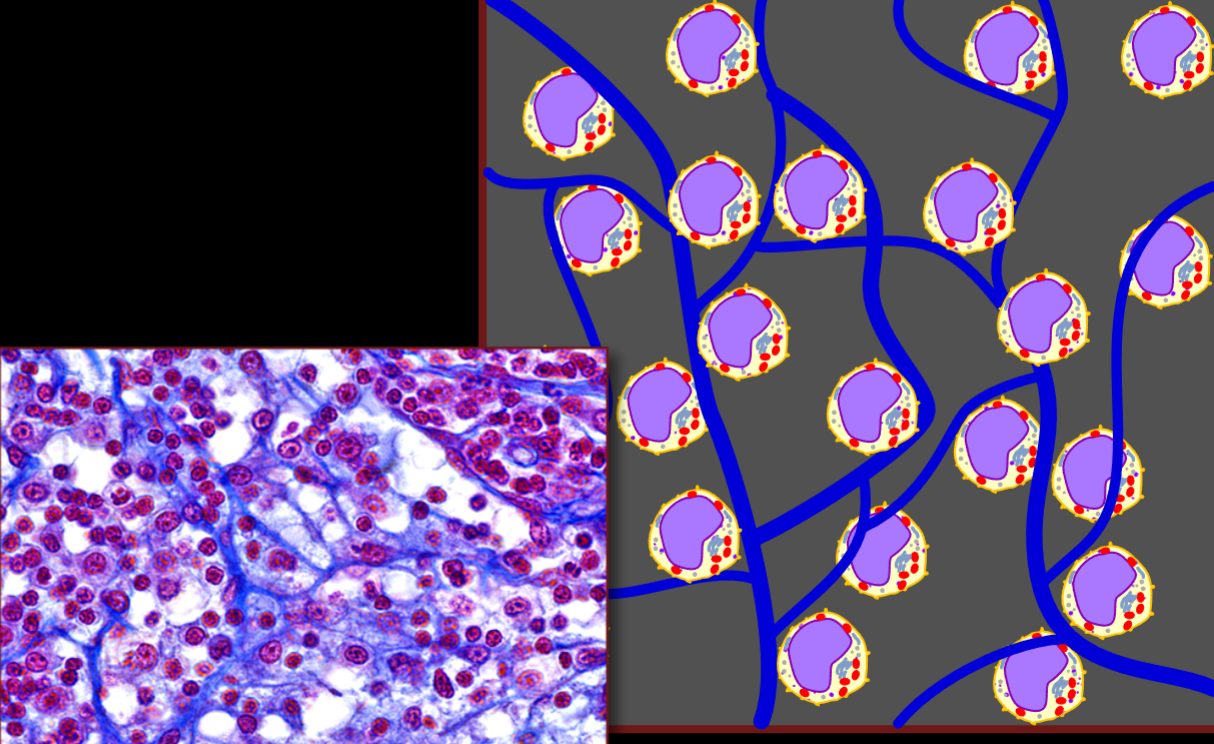
Reticular Tissue
Lymph nodes, red bone marrow
allow other cells to adhere to it and provides support
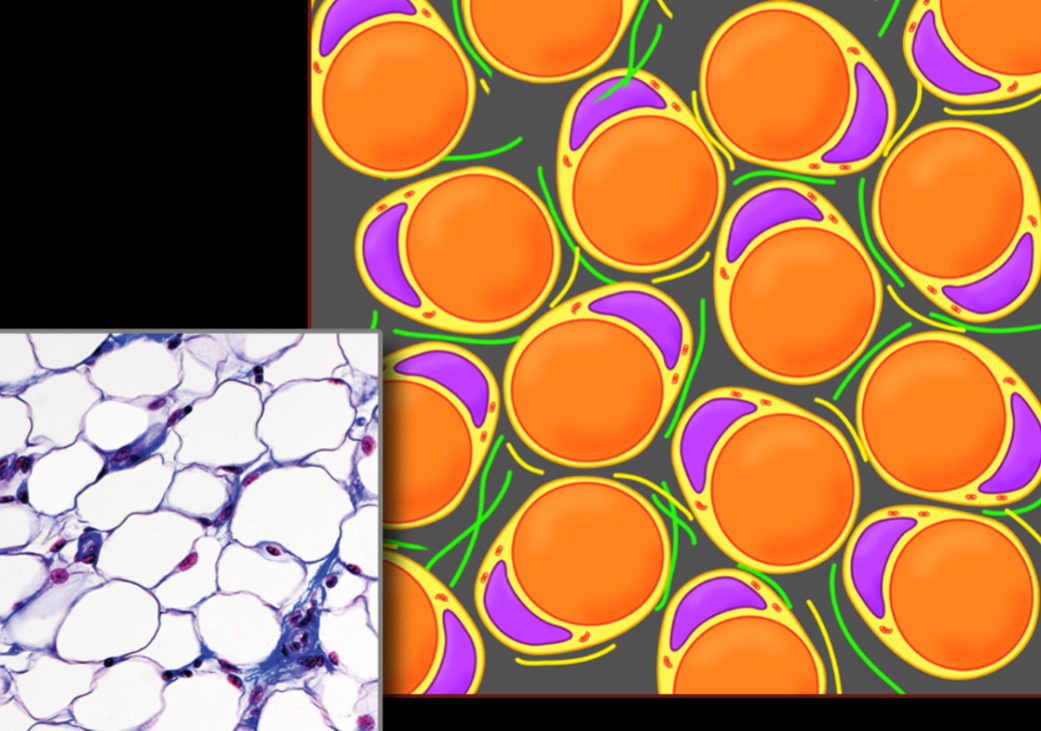
Name, Distribution, Function
Adipose Tissue (type of loose connective tissue)
potentially everywhere (+hypodermis and around organs)
stores energy
What type of tissue(s) is the cartilage of the nasal septum?
hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the oral cavity?
stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is a capillary?
simple squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is the costal cartilages?
hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue(s) is the epidermis?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica muscularis of the esophagus?
Striated skeletal muscle and smooth muscle
What type of tissue(s) is endocardium?
endothelium and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the urinary bladder?
urothelium
What type of tissue(s) is an intervertebral disc?
fibrocartilage
What type of tissue(s) is the cricoid cartilage?
hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue(s) is myocardium?
striated cardiac muscle, dense irregular, and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the synovial membrane of bursa?
loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is an epiphysial growth plate?
hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the trachea?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium, and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the dermis?
dense irregular connective tissue and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the vagina?
stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica intima of a blood vessel?
endothelium and elastic lamellae
What type of tissue(s) is the periosteum?
dense irregular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica media of an arteriole?
smooth muscle and elastic connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the hypodermis?
adipose and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica serosa of the stomach?
Mesothelium (simple squamous) & loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the epiglottal cartilage?
elastic cartilage
What type of tissue(s) is a ligament?
dense regular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the lining of a sebaceous gland?
simple cuboidal epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the esophagus?
stratified squamous epithelium & loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the small intestine?
simple columnar epithelium, loose connective tissue, smooth muscle
What type of tissue(s) is the alveoli?
simple squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica externa of a blood vessel?
dense irregular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is a sutural ligament?
dense irregular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the arrector pili muscle?
smooth muscle
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica muscularis of the small intestine?
smooth muscle
What type of tissue(s) is a tendon?
dense regular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica fibromusculocartilaginea of the trachea?
hyalin cartilage, smooth muscle, and dense irregular connective tissue.
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica mucosa of the ureters?
urothelium and loose connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the lining of the hair follicle?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue(s) is fascia?
loose & dense irregular connective tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica media of the aorta?
elastic and smooth muscle tissue
What type of tissue(s) is the tunica adventitia of the lobar bronchus?
dense irregular connective tissue
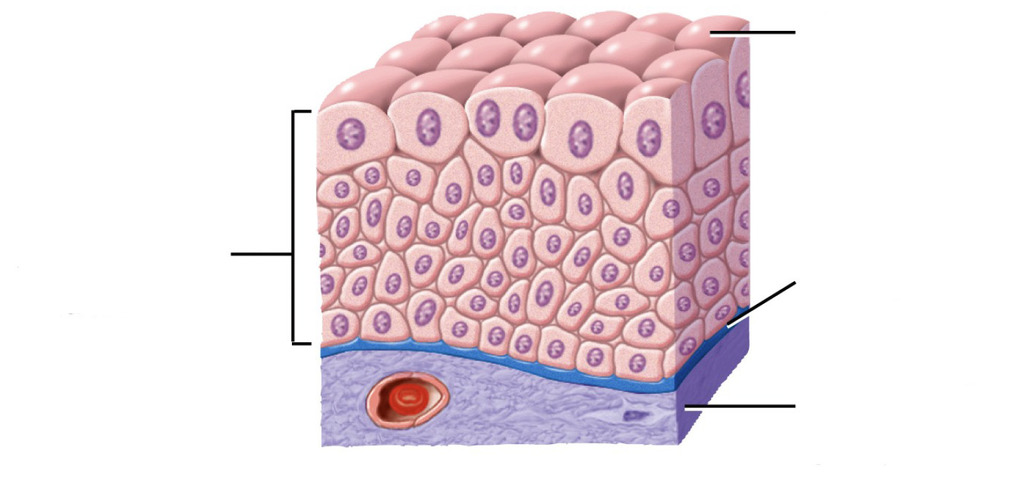
tissue of epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
tissue of dermis
dense irregular connective tissue
tissue of hypodermis
adipose or loose connective tissue
5 functions of integument
protection, thermoregulation, sensory perception, vitamin D production, excretion

Stratum Name & Function
Stratum Basale - mitosis of keratinocytes (skin regeneration)
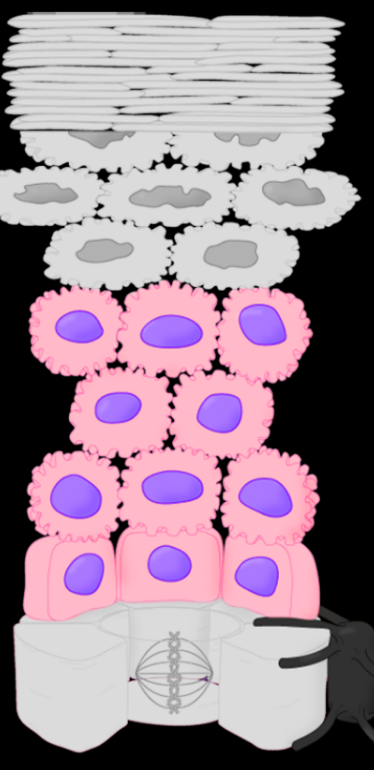
Stratum Name & Function
Stratum Spinosum - protection from tearing
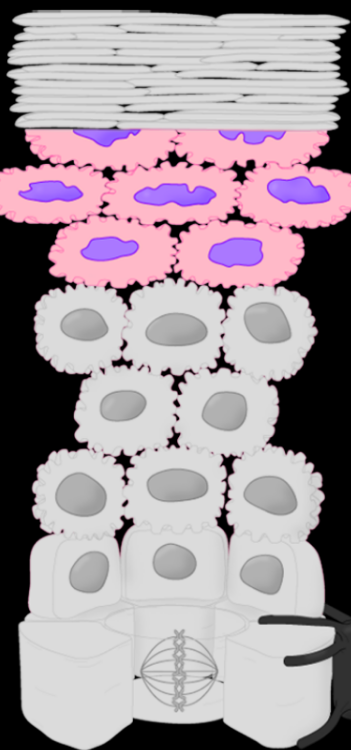
Stratum Name & Function
Stratum Granulosum - resists tear and waterproofing (to keep water both in and out)

Stratum Name & Function
Stratum Lucidum (almost impossible to differentiate from corneum) - protection from abrasion and water loss
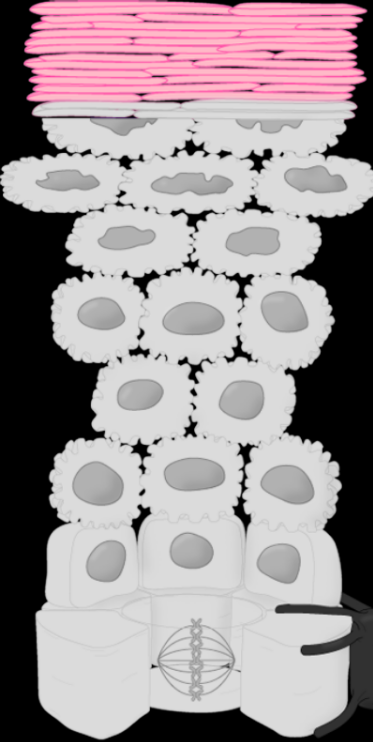
Stratum Name & Function
Stratum Corneum - protection from abrasion and water loss
Most common cell in epidermis & how it differs between levels.
Keratinocytes, become more dead as they are pushed towards the skin and away from a vascular supply, allowing for their regeneration and sloughing off. They also become more squished (squamous) as they are pushed towards the surface.
Cells responsible for skin color, their relationship with keratinocytes, and how they distribute pigment.
Melanocyte, attached to keratinocytes through branching arms. The melanin pigment produced goes through these arms and engulfs the keratinocytes, producing a UV protectant umbrella over the keratinocyte.
2 different dermal strata, their locations, & their differences.
stratum papillare (papillary layer) - found at sites of thin, hairy skin.
stratum reticular (reticular layer) - found between the stratum papillare and hypodermis
Stratum papillare is more prominent on areas with less hair.
Structure & function of dermal papilla.
hilly, nipple-like structure. it increases surface area to allow for more diffusion of nutrients
structure of papillae in palms and soles
papillae are taller and arranged into rows, causing finger prints, friction ridges, and better cohesion.
How are cleavage lines related to stretch marks and cleavage tears of skin?
cleavage lines tear parallel to the predominant direction of underlying collagen fibers
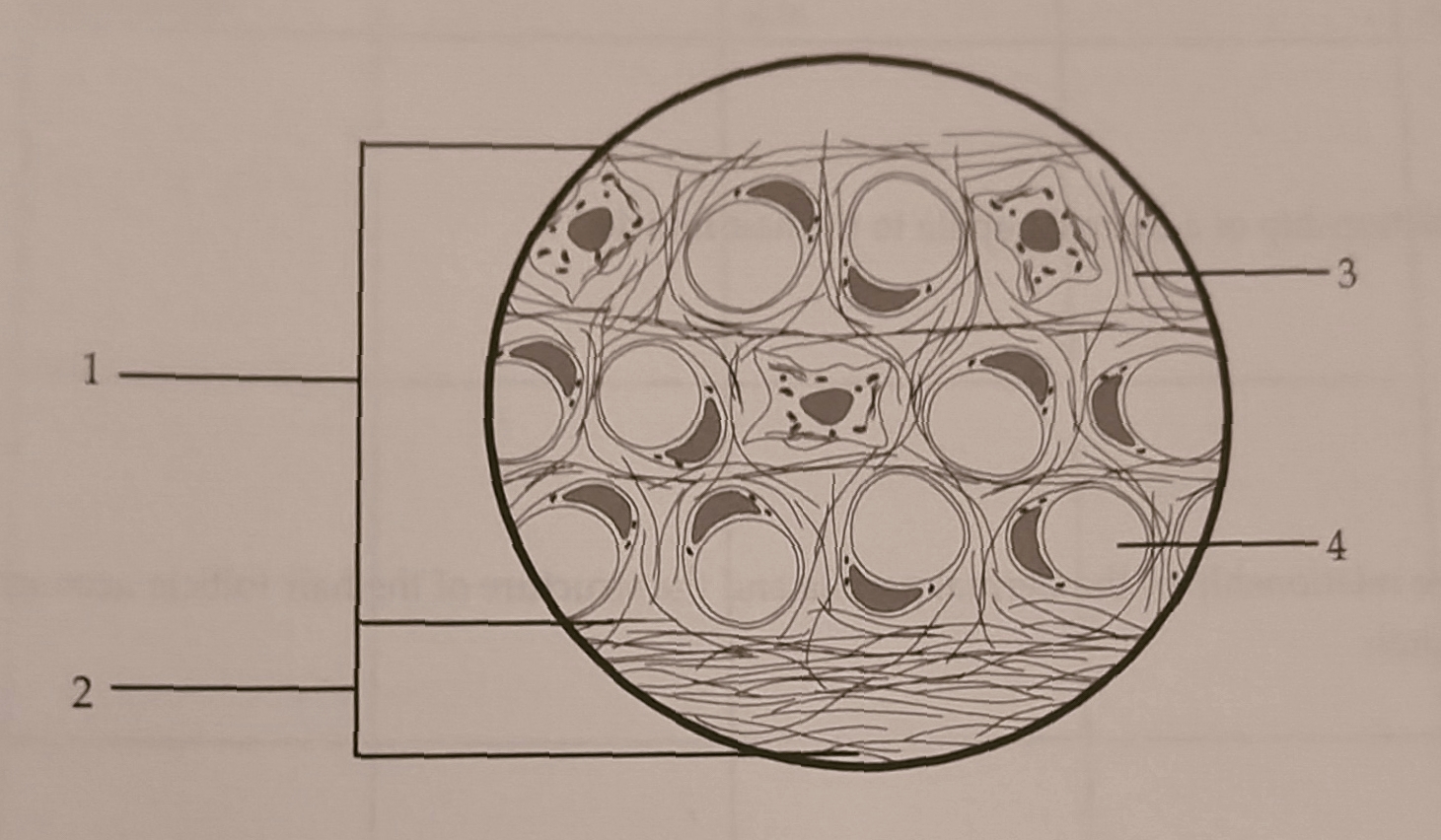
Fatty Layer 2. Fibrous Layer 3. Lipid Droplet of Adipose Cell 4. Fibers (mostly collagen)
Which hypodermis layer is most variable throughout different integument regions and why?
Fatty layer because if the lipid droplets are very full, the adipose tissues are dominant, but if the lipid droplets are shriveled, it is more of a loose connective tissue.
Define the process of invagination and describe its structural importance in the skin.
during embryonic development, the epidermis undergoes rapid cell division. This pushes cells deeper, into a cord, because of the crowding. As they push into the dermis, the cords become hollow tubes because the inner cells lose nutrient sources and slough off. This is how hair follicles and glands are created (and some cavities).
Structure of a hair follicle.
a hollow structure made of stratified squamous epithelium
relationship of dermal papilla to hair follicle & how this accounts for hair growth
the dermal papilla brings nutrients & a vascular supply to the hair follicle. the dermal papilla is at the base of the hair. the dermal papilla contains capillaries which bring nutrients to the stratum basal at bottom of the hair follicle. The stratum basal uses nutrients to grow and divide keratinocytes and create hair from keratinocytes.
Describe the structure & attachments of arrector pili muscle.
smooth muscle that attaches at the bottom of the epidermis and extends down to the bottom of the hair follicle.
describe the two changes in the skin from an arrector pili contraction
hair standing up and skin pulling down (goosebumps)

Name, Structure, Distribution, Secretion, and Function
Sebaceous Gland
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
everywhere you have skin (except palms and soles)
secretes sebum
moisturizes skin

Name, Structure, Distribution, Secretion, and Function
Eccrine Sweat Gland
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
everywhere w/ skin
secretes water
thermoregulation

Name, Structure, Distribution, Secretion, and Function
Apocrine Sweat Gland
simple cuboidal epithelium
hair follicles of armpits, genitals, & anal region
secretes oily sweat and pheromones
emotional sweating and sexual stimulation signaling
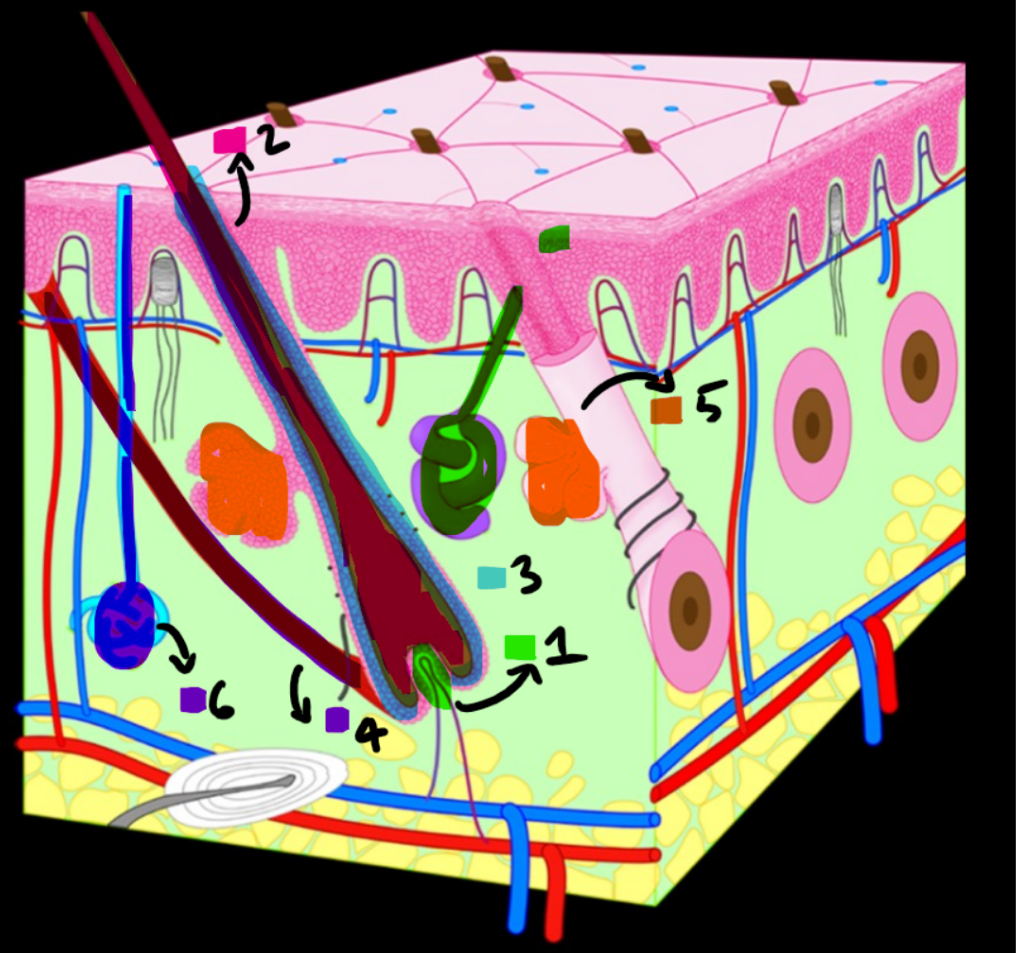
Forgot to label 7
dermal papilla 2. hair 3. hair follicle 4. arrector pili muscle 5. sebaceous gland 6. eccrine sweat gland 7. apocrine sweat gland
cartilage v. other connective tissue & associated problems
cartilage is avascular and cannot heal itself
key extracellular structures of cartilage
proteoglycan, collagen, and elastic tissue
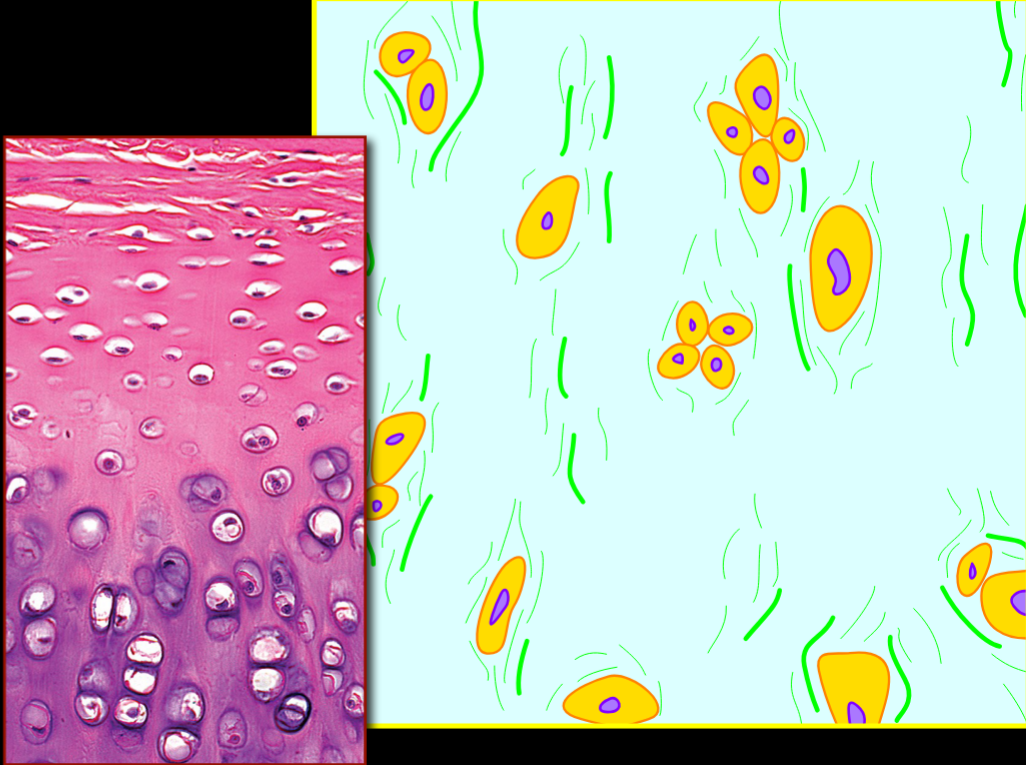
Name, Structure, Distribution, Function
Hyaline Cartilage
Firmer, Smooth, Glass-Like & Few, Scattered Collagen Fibers
Between Joints (and Nose)
Structural Support & Friction Reduction
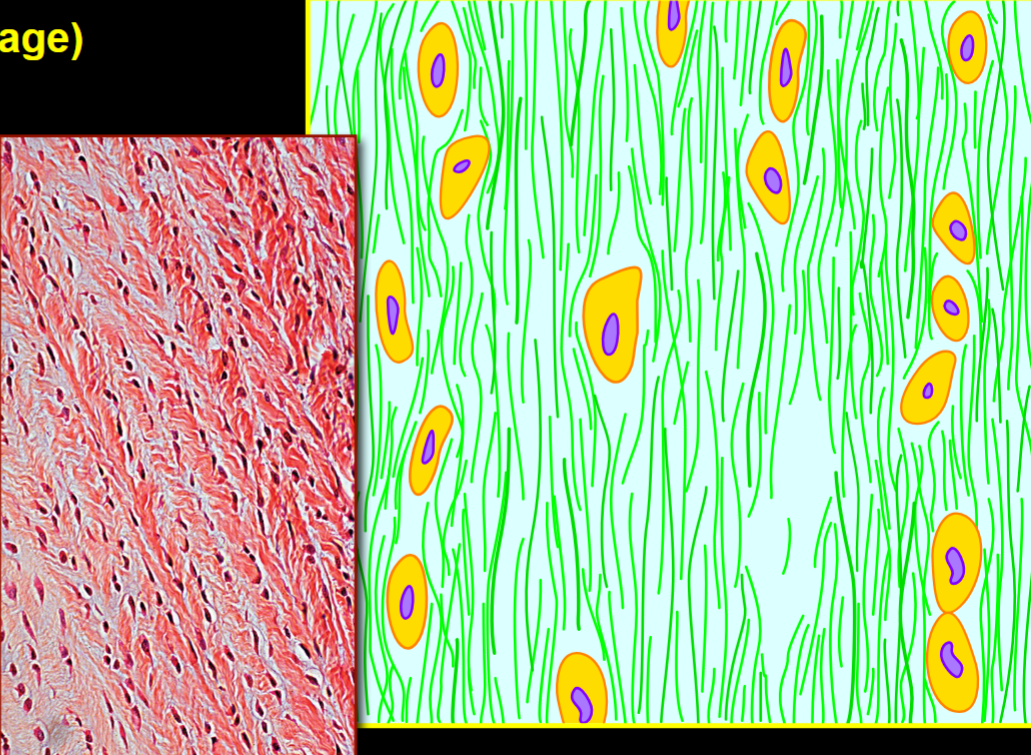
Name, Structure, Distribution, Function
Fibrocartilage
Few cells, lots of collagen in uniform arrangement
down midline (intervertebral disks, menisci)
resisting tension & absorbing shock
Name, Structure, Distribution, Function
Elastic Cartilage
elastic fibers, few cells
outer ear & epiglottis
structure, stretch & recoil
Similarities & Differences of Bone Tissue v. Other Connective & Supportive Tissues
similar: more extracellular matrix than cells & highly vascular
different: hard
3 Physical Properties of bone tissue & the structural features that cause this
Resists Tension - Collagen fibers able to resist force in one direction
Resists Compression - hydroxyapatite makes bone hard
Able to Remodel - cells, osteoclasts reabsorb bone not being used and osteoblasts build new bone
4 Cells of bone tissue with functions
Osteoprogenitor Cell - bone stem cells
osteoblast - makes bone
osteocyte - mature, encased in matric
osteoclast - breaks down bone matrix (WBC lineage)