Chapter 22
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Amines
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
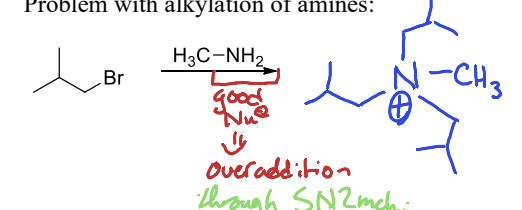
What is the problem with directly preparing an amine through an SN2 alkylation?
There can be overalkkylation of the amine because of the nucleophilicity of the amine, leading to multiple alkylation reactions.
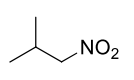
What are the reagents required to convert a nitro to a primary amine?
The reagents required are typically iron (Fe) or zinc (Zn) in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl) to reduce the nitro group to a primary amine.
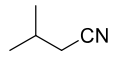
What are the reagents required to convert a nitrile to a primary amine?
The reagents required are typically lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)
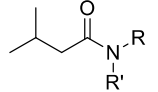
What are the reagents required to convert a amide to a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine?
The reagents required are typically lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or borane (BH3) in conjunction with acid or alkali to reduce the amide to an amine.
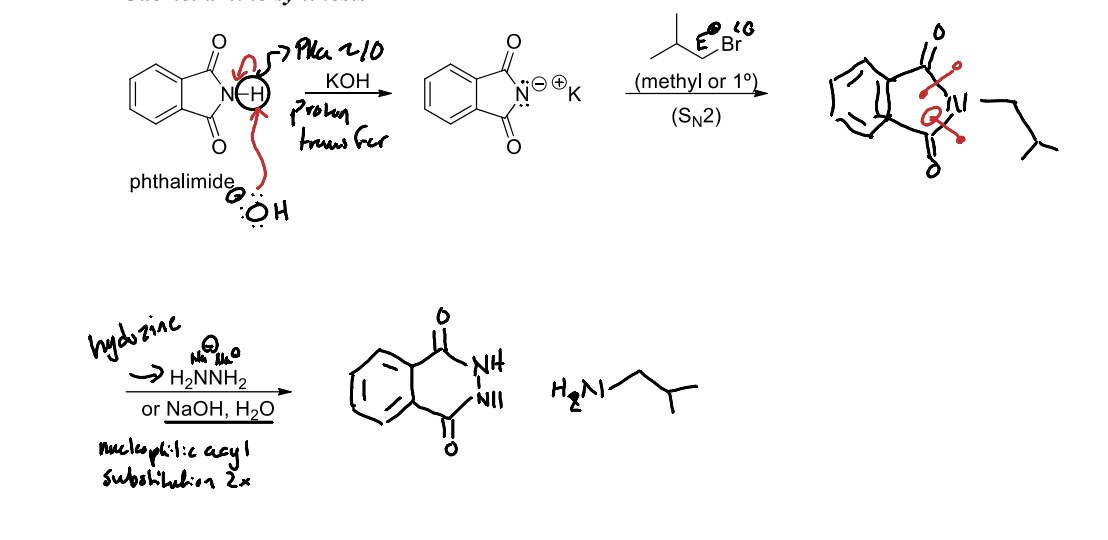
What is Gabriel Amine Synthesis?
A method for synthesizing primary amines via the reaction of phthalimide with an alkyl halide, followed by hydrolysis to yield the amine.
What is a reductive amination?
A chemical reaction that involves the conversion of a ketone or aldehyde into an amine through the reaction with ammonia or an amine in the presence of a reducing agent, such as sodium cyanoborohydride or lithium aluminum hydride.
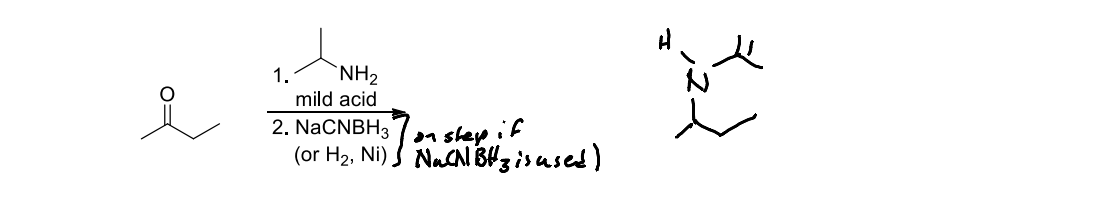
In a reductive amination what is the mild acid used in the first step as an acid catalyst?
A lewis acid or Bronsted acid
What is the typical reducing agent in a reductive ammination and why?
The typical reducing agent in a reductive amination is sodium cyanoborohydride, as it is mild and selective, allowing for reduction without further reaction of the functional groups.
When reacting an amine with an aldehyde or a ketone what forms?
An imine or enamine
When reacting an amine with acid chlorides or anhydrides what forms?
Amides
When reacting an amine in a Hoffmann elimination what forms?
An alkene *less substituted
When reacting a primary amine with an aldehyde or ketone?
an imine is formed.
When reacting a secondary amine with an aldehyde or ketone?
An enamine is formed.
What is required to reverse the imine or enamine formation?
An acid and water to hydrolyzer back to a ketone or aldehyde.
During there Hoffman elimination there are two steps an SN2 reaction and the Hoffman E2 reaction. Why is the SN2 reaction performed upon the amine?
Amines are poor leaving groups making it necessary to form an ammonium ion to act as a leaving group. This facilitates the subsequent elimination step, allowing for the formation of the desired alkene product.
Why is the Hoffman product formed with the ammonium ion?
The ammonium is a bulky leaving group meaning that internal protons are hard to get to for the base, therefore the external protons are utilized.
With a primary alcohol what is formed in a PCC reaction?
An aldehyde is formed.