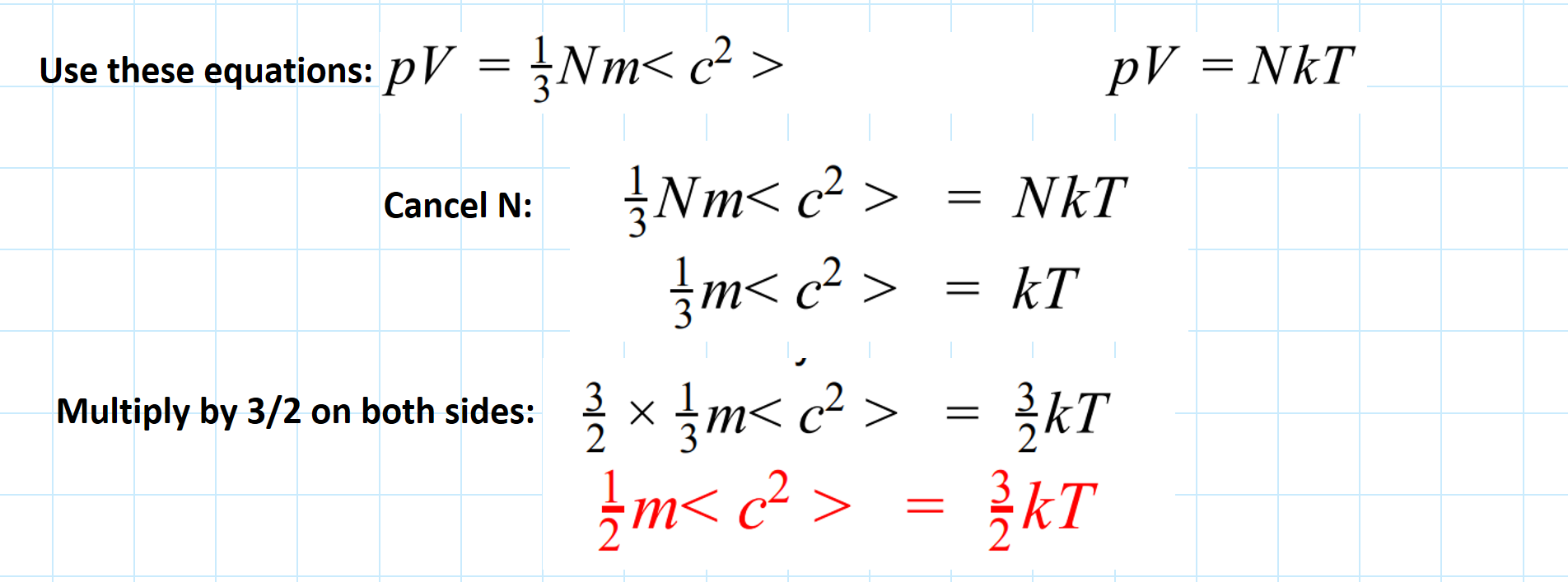A Level Pearson Edexcel Physics Topic 9 Thermodynamics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Define what is meant by the internal energy of a body
The sum of potential energy contained within the inter-atomic bonds
Define temperature
Is directly related to the mean, random, kinetic energy of the vibrating atoms of a body
Define potential energy
The stored energy
Define kinetic energy
A form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion
Define heating
The process by which energy is transferred by conduction
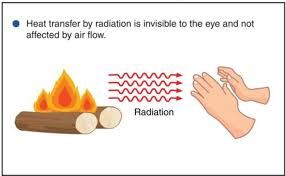
Define radiation
The emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium
Define conduction
The transfer of energy in the form of heat or electricity from one atom to another in an object due to direct contact

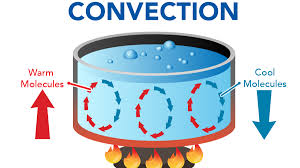
Define convection
Process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water.
Formula for energy required to change the temperature of a substance
Where:
c is the specific heat capacity
delta theta is the change in tempreture
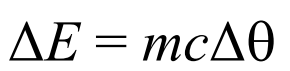
Formula for the amount of energy required to change the state of a substance
Where:
L is the specific latent heat
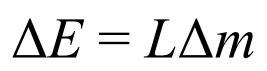
Define specific heat capacity (c)
It is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1 degrees Celsius/1 Kelvin, without changing its state
Define specific latent heat capacity (L)
Is the amount of energy required to change the state of 1kg of material, without changing its state
What are the two kinds of specific latent heat
Specific latent heat of fusion
Specific latent heat of vaporisation
What is the specific latent heat of fusion
When a solid changes to liquid
What is the specific latent heat of vaporisation
When liquid changes to gas
Define internal energy
Of a body is equal to the sum of all of the kinetic energies and potential energies of all its particles.
Kinetic and potential energies of a body are randomly distributed.
True or False | Is the kinetic and potential energy of a body are randomly distributed
True, the kinetic and potential energy of a body are randomly distributed
Define Absolute zero
The lowest possible temperature and is the temperature at which particles have no kinetic energy and the volume and pressure of gas are zero
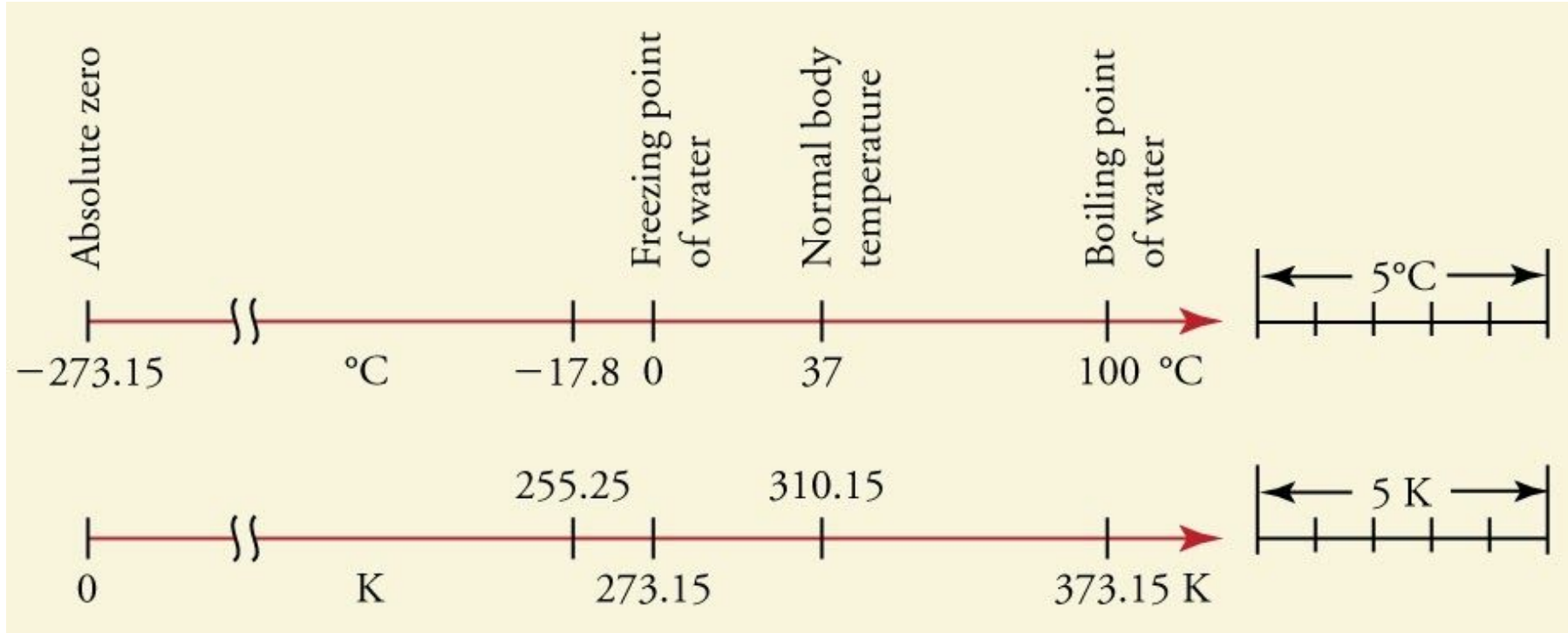
What is the number of absolute zero (so temperate in degrees and kelvin)
-273 Degrees Celsius or 0 Kelvin
How does average kinetic energy of molecules relate to the absolute temperature
Average kinetic energy of molecules in a substance is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the substance

Kelvin formula
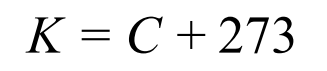
Kelvin and degrees Celsius graph
Define what is an ideal gas
In an ideal gas:
All interactions are perfectly elastic collisions meaning no intermolecular forces
Has no potential energy meaning its internal energy is equal to the sum of the kinetic energies of all its particles
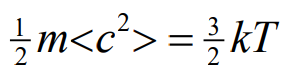
Derive this equation