Vascular Disorders: Arterial Embolism/Thrombosis - AV Malformation
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
emergency, thrombosis, A fib, superficial, popliteal
Arterial Embolism/Thrombosis: General Info
-Arterial embolism is considered a vascular __________
-Etiologies (many): native arterial ________, arterial injury, arterial embolism, thrombus following intervention, and vasoconstriction/vasospasm. The most common cause, however, is _ ___.
-Most common cause of upper extremity ischemia
-Most common in the ________ femoral or ________ artery in the lower extremities
acute, paresthesia, pulses, capillary, paralysis
Arterial Embolism/Thrombosis Clinical Manifestations:
Symptoms
-____ onset of extremity pain
-Skin color changes
-Neurovascular changes
___________
Physical Exam
-Decreased/absent ________
-Decreased __________ refill
-Coolness of the extremity
-Skin mottling
-Decreased sensation
-_________ in severe cases
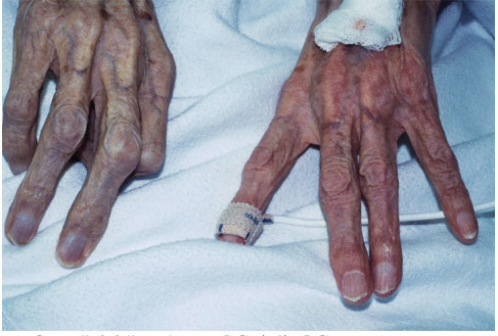
Paresthesia, pallor, paralysis
6 Ps of Arterial Embolism/Thrombosis
____________
Pain
______
Poikilothermic
Pulselessness
_________
clinical, angiography, heparin, IV, reperfusion, vascular
Arterial Embolism/Thrombosis Diagnosis and Management:
Diagnosis
-Usually ________, take a good history and exam
-Bedside arterial doppler
-CT ___________, as long as it won’t impede treatment
Management
-Unfractionated ________ + __ Heparin Infusion
-Pain control
-IV Fluids
-____________ is the mainstay of treatment, consult ________ team
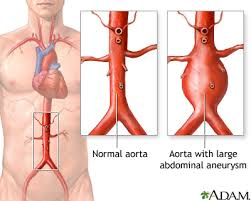
dilation, 3, males, degeneration, aortic, iliac
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: General Info
-Focal _______ of abdominal aorta > _ cm
-_______ > females
-Pathophysiology:
Proteolytic ____________ of _____ wall and connective tissue inflammation
Aortic bifurcation and common _____ arteries often involved
smoking, white, male, family, HTN, syphilis
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risk Factors
-________
-Age > 60 years
-_____
-______ sex
-________ history of AAA, ___, hyperlipidemia, connective tissue disorders, and ______
infrarenally, white, man
Common Presentation of AAA
-Found __________ and associated with atherosclerotic disease
-Old ______ ___ that smokes is your typical patient
asymptomatic, flank, bruit
Aortic Aneurysm Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms
-Most patients are __________, and their aneurysms are found incidentally
-Some patients may report abdominal, _____, or back pain
Physical Exam
-Abdominal _____
-Pulsatile mass
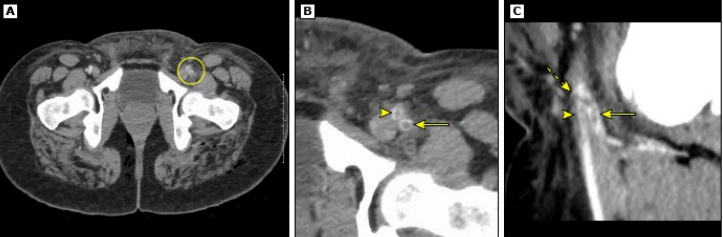
ultrasound, initial, CT, stable, 5.5
Aortic Aneurysm: Diagnosis
-Abdominal __________ is a great option for hemodynamically unstable patients at bedside
Great _____ test
-__ scan with IV contrast is the best test in symptomatic, hemodynamically _____ patients
Indicated when diameter reaches ~ _._ cm
65-75, 100, 10, annual, 6, refer, immediate
Aortic Aneurysm Screening / Management
-Screening Indication: men __-__ years with exposure to ___+ lifetime cigarettes
-Management
> 2-2.9 cm diameter = repeat imaging in __ years
3-4 cm = monitor with _______ ultrasound
4-4.5 cm = monitor with ultrasound every _ months
> 4.5 cm = _____ to vascular surgeon
> 5.5 cm or > 0.5 cm expansion in 6 months = _________ surgical repair
5.5, pain, open
Aortic Aneurysm Management
-Elective repair
Indicated with aneurysms > _._ cm, growing aneurysms, or patients with aneurysm + _____
-Surgical options
_____ surgery or endovascular
atherosclerosis, asymptomatic, cough, edema, widened
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: General Info
-Primary etiology = _____________
-Most are ____________, but some patients do present with varying symptoms
neck/back pain, dyspnea, dysphagia, hoarseness, or brassy _______
-Physical exam = stridor, ______ in neck/arms, distended neck veins
-Findings = ________ mediastinum on CXR
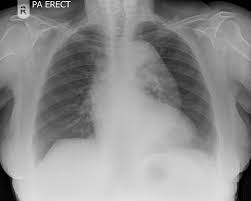
CT, contrast, cardiac, vascular
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: Diagnosis and Referral
-Diagnosis = __ scan with IV _______ is the test of choice
-Referral:
Ascending aorta → _______ surgeon
Descending aorta → _________ specialist
tear, lateral, hemorrhage, lumen, ascending, descending
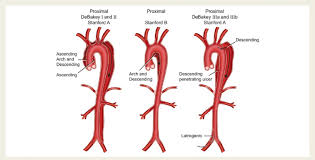
Aortic Aneurysm Dissection: General Info
-Circumferential or transverse ____ of the intima of aorta
-Often occurs along right _______ wall
-Initiating event could be primary intimal tear or medial ___________, both of which create a false _____ for blood to go into
-Stanford Type A = __________ aorta affected
-Stanford Type B = ___________ or transverse aorta affected
sudden, pain, back, hypotension, edema, neurologic
Aortic Aneurysm Dissection Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms
-_______ onset of chest pain, described as severe/tearing. Can radiate to the ______ or shoulder blades
-Usually associated with diaphoresis
-± syncope, dyspnea, weakness
Physical Exam
-Hyper/___________
-Loss of pulses
-Aortic regurgitation murmur
-Pulmonary ____
-________ findings: paraplegia, hemiplegia, hemianesthesia
D-Dimer, 500, LFT, mediastinum, left, normal, angiography
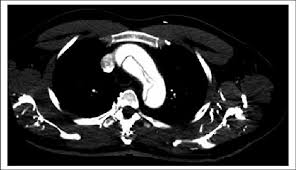
Aortic Aneurysm Dissection Diagnosis
-Elevated lab values = _-____ ( < ___ is unlikely to be a dissection), cardiac enzymes, ___, and lactate
-CXR = widened _________, ± ____-sided pleural effusion, or completely normal
-EKG = usually _______, helps you rule out MI
-CT __________ is the test of choice to rule out dissection, MI, and PE
admit, beta-blockers, 60-80, high, medical, surgical
Aortic Aneurysm Dissection Management
-_______ the patient, and immediately consult vascular or cardiothoracic surgery
-_____-________ like IV propranolol or metoprolol. Goal HR is __-__ BPM. Give with pain medicine.
-Nitroprusside if the BP is still _____ after managing HR and pain
-Uncomplicated Stanford Type B = ______ therapy
-Complicated Stanford Type B or Type A = _______ correction
nonatherosclerotic, thrombotic, males, 20-45, smoking
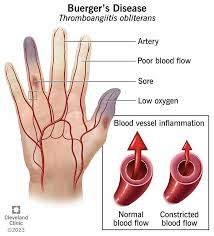
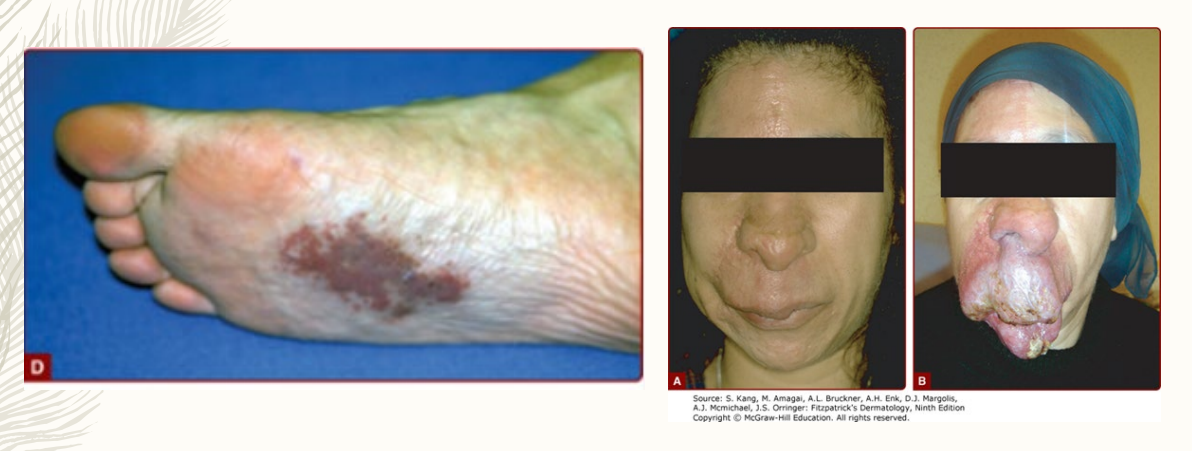
Thromboangiitis Obliterans: General Info
-____________, segmental, inflammatory, and ________ disease that affects small-medium size vessels of the upper and lower extremities
-_____ > females, most commonly in __-__ year old
-Risk Factors = ________ (rolling your own cigarettes) and severe periodontal disease
smoking, without, fibrosis, plantar
Thromboangiitis Obliterans Pathophysiology
-Pathophysiology is poorly understood, but _________ is an essential risk factor for each disease stage
-Acute = inflammatory thrombus development ________ necrosis
-Intermediate = progressive organization of thrombus in small-medium vessels
-Chronic = inflammation resolves, organized thrombus and ______ remains
-_______ and digital vessels are the most common
pain, ulcerations, superficial, ischemia, Raynaud’s, 3
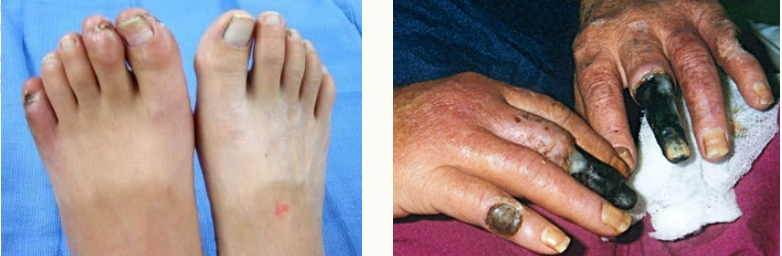
Thromboangiitis Obliterans Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms
-Rest _____ of the distal most extremity (toes), early manifestation
-_________/arthralgia in late disease
Physical Exam
-________ thrombophlebitis
-Distal extremity ________ to upper and lower extremities
-_______’_ phenomenon
-Check all extremities, for this is often present in _+ limbs
clinical, biopsy, corkscrew
Thromboangiitis Obliterans Diagnosis
-Typically ______ diagnosis using clinical criteria
-Labs obtained to rule out other disease process like scleroderma
-______: shows segmental vascular inflammation, confirms diagnosis
-Aortography: shows ________ collaterals
50, tobacco, exclusion
Clinical Criteria for the Diagnosis of Thromboangiitis Obliterans:
Age < __ years
Current or recent history of ________ use
Distal extremity ischemia
Typical arteriographic findings of TAO
________ of autoimmune disease, thrombophilia, diabetes, and proximal embolic sources
smoking cessation
Thromboangiitis Obliterans Management
-_______ _________ is the cornerstone of management, nothing is as effective in stopping disease progression
-Wound care
-IPC
-Iloprost
-CCBs (Nifedipine)
panarteritis, 70-80, women, age, menopause
Giant Cell Arteritis: General Info
-Systemic __________ (inflammation) affecting medium and large size vessels
-Frequently coexists with polymyalgia rheumatica
-Peak incidence in patients __-__ years old
-_______ > men
-Risk Factors: increased ___, genetic predisposition, history of smoking, early ________, and lower BMI
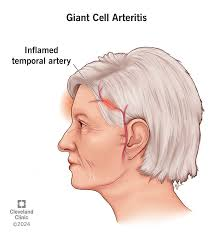
headache, jaw, visual, scalp, pulses, fundoscopic
Giant Cell Arteritis Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms
-___________ is the most common, classic symptom
Be concerned about new onset headache and localized pain
-___ claudication with mastication, _______ changes, _____ tenderness, fever, fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, malaise
Physical Exam
-Temporal artery abnormalities, decreased peripheral _______
-Aortic regurgitation murmur
-Supraclavicular/axillary bruits
-Abnormal ________ exam
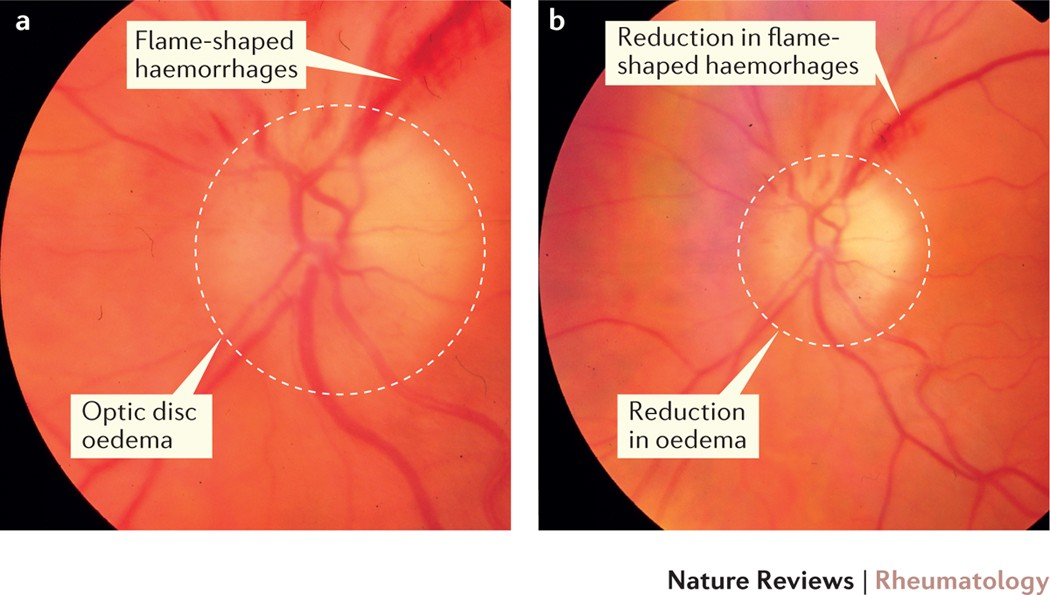
ESR, CRP, alk phos, biopsy, giant, halo
Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis
Labs
-Elevated ___, ___, and ___ ____
-CBC shows normochromic normocytic anemia
Definitive Diagnosis
-Temporal artery ______ is the gold standard
Transmural inflammatory infiltrate comprised of lymphocytes, macrophages, ± _____ cells
-Temporal artery CDUS
+ _____ sign of temporal arteries, which can also be diagnostic
corticosteroids, predisone, methylprednisone, methotrexate
Giant Cell Arteritis Management
-Initiate therapy ASAP
-First line therapy = high dose ____________
No symptoms of ischemic organ damage = ________
Signs/Symptoms of ischemic organ damage = ___________ for 3 days and then prednisone taper
-Additional therapy = tocilizumab or ____________
narrowing, lumen, stroke, atherosclerosis, asymptomatic
Carotid Artery Stenosis: General Info
-________ of carotid artery ____, may be symptomatic or asymptomatic
-TIA/_____ is the worst consequence of this
-Most cases due to ___________
-Prevalence of __________ disease is low
age, male, stroke, angiography, carotid
Carotid Artery Stenosis Classification and Risk Factors
Classification
-Symptom status
-Degree of stenosis, most pts are 60%
Risk Factors
-Advanced ___, ____ sex, family history, CAD, PAD, smoking, diet, obesity, DM, HTN
-Major risk factor for ischemic _____
Imaging Modalities
-Duplex US, MR angiography, contrast enhanced MRA, CTA
-Cerebral __________ is the gold standard for imaging _______ arteries
cessation, statin, CEA, elderly, asymptomatic, 70
Carotid Artery Stenosis Management/Screening
Management
-Medical Therapy
Smoking _________
BP control; < 140/90 mmHg
______ therapy
Antiplatelet therapy
-Invasive Therapy
Carotid endarterectomy (___), preferred in most patients
Stenting has better results in the elderly
-Routine Screening
Not recommended in ___________ patients
-When to Refer
Patients with > __% stenosis
Symptomatic patients (immediately)
malformation, increase, head
Arteriovenous Malformation: General Info
-Type of vascular ________
-Rare, associated with ________ morbidity and mortality
-Can affect any organ, but the _____ and neck are the most common sites
birth, proportionately, predictable, 2nd-3rd, stroke
Arteriovenous Malformation
-Developmental vascular malformation, present at ______
-Grow ___________ with the individual
-________ growth pattern, with tendency to progress in the ___-___ decades of life
-Thought to expand in response to certain stimuli
-Complications = hemorrhagic ____, intraparenchymal hemorrhage, epilepsy, headache, and neurological defects
telangiectasia, mass, thrill, bruit
Arteriovenous Malformation Clinical Manifestations
Physical Exam
-___________ / macular stains
-Faint, red-purple, ill-defined cutaneous ____
-Slightly compressible
-+ palpable pulsations or _____
-+ audible ____
-Stages I - IV, based on progression
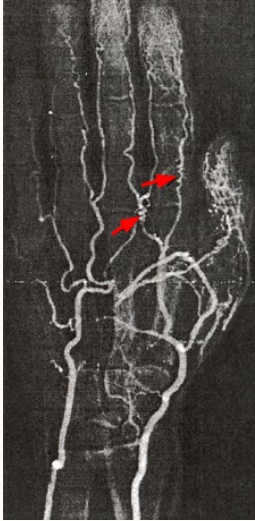
ultrasound, classifies, failure
Arteriovenous Malformation Diagnosis
-________ (US): identifies AV malformation and useful for follow-up
-Catheter-based angiography: _________ AV malformation
-ECHO: recommended for evaluation of heart _______ or right heart strain
early, pain, compression, resection, palliative
Arteriovenous Malformation Management
-______ diagnosis is critical for improving the patient’s quality of life
-Multidisciplinary team-based approach
-Asymptomatic/isolated AV malformations = conservative therapy
____ management
Physical therapy
__________ therapy
-Symptomatic Lesions = vascular intervention/surgery
Embolization, surgical _________, sclerotherapy
_________/goal oriented care may be the only option for complex/diffuse disease