SECTION 03: THE THYROID GLAND
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
By the end of Section 03, you should be able to:
Describe the synthesis of thyroid hormone and outline the importance of iodine. •
Describe the effects of thyroid hormones on metabolism and the consequences of hypo- and hyperthyroidism. •
Understanding the control of thyroid hormone release, describe the various hormone levels during hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. •
Describe the conditions that can lead to the formation of a goiter
📌 THYROID GLAND – QUICK NOTES
🔹 Location:
Found just below the larynx (voice box)
Sits on top of the trachea (windpipe)
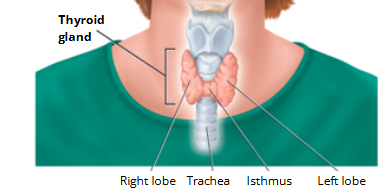
THYROID GLAND 🔹 Structure:
Has 2 lobes: Right lobe & Left lobe
Lobes are connected by a thin bridge called the isthmus
Looks like a butterfly in shape
THYROID GLAND 🔹 Function:
Produces and releases thyroid hormones
These hormones help control metabolism, energy, and growth
Both lobes work the same – no difference in function between them
THYROID GLAND 🔹 Inside the Gland:
Has a special internal organization (not shown in the image)
This structure helps it efficiently make and store hormones
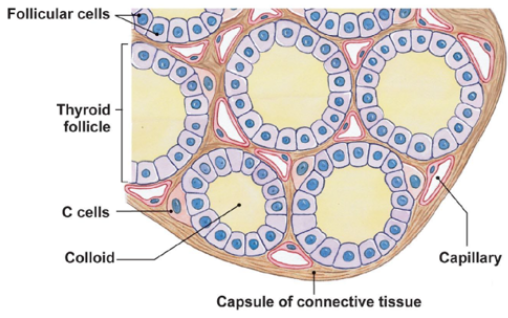
THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE 🔹 Follicular Cells
Main secretory cells of the thyroid
Form hollow spheres called thyroid follicles
Responsible for making thyroid hormones (T3 & T4)
THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE 🔹 Thyroid Follicles:
Appear like rings under a microscope
Each ring is made of follicular cells surrounding a center filled with colloid
📌 THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE🔹 Colloid:
Gel-like substance in the center of each follicle
Made mostly of a protein called thyroglobulin
Where thyroid hormones are made and stored
📌 THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE🔹 C Cells (Parafollicular Cells):
Found between the follicles
Make the hormone calcitonin (helps lower blood calcium)
Not involved in making thyroid hormones like T3/T4
📌 THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE 🔹 Capillaries:
Surround the follicles
Carry hormones into the bloodstream
📌 THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE 🔹 Capsule of Connective Tissue:
Outer layer that protects and holds the thyroid together
📌 THYROID GLAND – CELLULAR STRUCTURE image
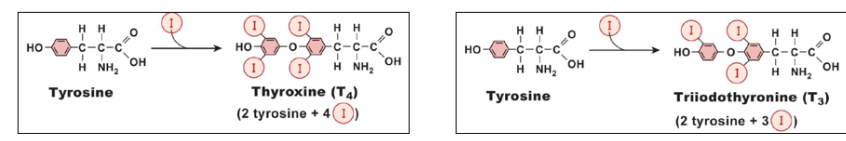
📌 THYROID HORMONES – QUICK NOTES 🔹 Made From:
Both hormones are made from the amino acid tyrosine
They both contain iodine (I)
🔹 T4 – Thyroxine (Tetraiodothyronine):
Made of: 2 tyrosine + 4 iodine
Makes up ~90% of thyroid hormones released
Less active form
Converted to T3 in target tissues for full effect
🔹 T3 – Triiodothyronine:
Made of: 2 tyrosine + 3 iodine
Makes up ~10% of thyroid hormones
More active form
Works faster and stronger than T4
🔹 Key Function (for both):
T3 and T4
Control metabolism, growth, development, and body temperature regulation
💡 Tip to Remember:
The number in the name tells you the number of iodine atoms!
T4 = 4 iodines
T3 = 3 iodines
IMPORTANCE OF IODINE🔹 Where It Comes From:
Iodine is taken in through the diet
In blood, it circulates as iodide (I⁻)
We need about 1 mg of iodine per week
IMPORTANCE OF IODINE 🔹 How the Thyroid Uses It:
Follicular cells take tyrosine + iodide from the blood
Used to make thyroid hormones (T3 and T4)
The thyroid gland is very good at collecting iodide
📌 IMPORTANCE OF IODINE – QUICK NOTES 🔹 Storage:
Thyroid stores extra hormone in the colloid (inside follicles)
Hormones are held bound to thyroglobulin until needed
This is unusual because most lipophilic hormones aren’t stored
🔹 Why Iodine Deficiency Is Rare in Canada:
Table salt has iodine added (iodized salt)
Most people get enough iodine from their food
🔹 Bonus Definition:
Iodide (I⁻): The form of iodine found in the blood (oxidation state -1)
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES – 🔹 Step 1: Thyroglobulin Production
Inside the follicular cell, the ER + Golgi make thyroglobulin (Tg)
Tg is sent into the colloid (middle of the follicle)
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 2: Iodide Trapping
Iodide (I⁻) from the blood is pulled into the cell using a Na⁺/I⁻ cotransporter
Na⁺ moves down its gradient, helping I⁻ move against its gradient
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES🔹 Step 3: Iodide Moves Into Colloid
Iodide travels from inside the cell into the colloid space
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 4: Iodide Organification
The enzyme TPO (thyroperoxidase) turns iodide (I⁻) into reactive iodine (I⁰)
Iodine attaches to tyrosine on the Tg molecule
1 iodine = MIT (Monoiodotyrosine)
2 iodines = DIT (Diiodotyrosine)
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 5: Hormone Formation (Coupling Reaction)
MIT + DIT → T3 (Triiodothyronine)
DIT + DIT → T4 (Thyroxine)
❌ No MIT + MIT (This combo does not form hormones)
T3 & T4 stay attached to Tg in the colloid until needed
SYNTHESIS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Bonus: Hormone Release (Not numbered in slide but shown in image)
When needed, Tg with T3 and T4 is taken back into the follicular cell
Inside the cell:
Tg is broken down by lysosomes
Free T3 and T4 are released into the blood
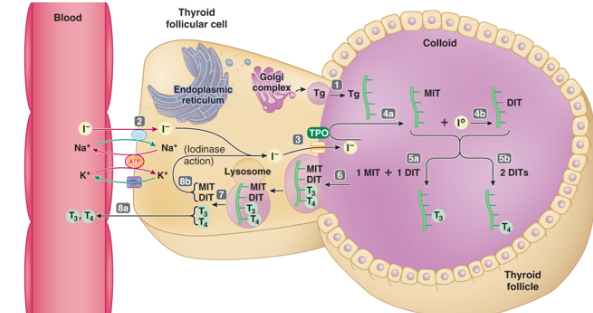
RELEASE OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 1: Colloid is Taken In
Follicular cells take in part of the colloid (which contains Tg + T3/T4)
This happens through phagocytosis (cell “eating”)
Forms vesicles inside the cell
RELEASE OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 2: Digestion by Lysosomes
Lysosomes (cell “digesters”) fuse with the vesicle
They use enzymes to break down thyroglobulin (Tg)
This releases:
T3 (active)
T4 (less active)
MIT and DIT (recycled, not released)
RELEASE OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 Step 3: T3 & T4 Enter Bloodstream
T3 and T4 are lipophilic (fat-loving), so they easily cross the cell membrane
Enter the bloodstream and bind to plasma proteins for transport
Main one: Thyroid-binding globulin
RELEASE OF THYROID HORMONES 💡 Reminder:
Only T3 and T4 get released into blood
MIT and DIT stay inside the cell and get reused
ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 General Info:
Acts on almost all body tissues
Slow effects (can take hours)
Long-lasting (effects stay even after hormone levels drop)
ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 1. Metabolic Rate & Heat Production
Increases basal metabolic rate (body's basic energy use)
Raises oxygen use + energy use
Makes body produce more heat (thermogenesis)
ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 2. Intermediary Metabolism
Affects how the body uses fuel (like glucose and protein)
Low hormone levels:
→ promotes glycogen storage + protein buildingHigh hormone levels:
→ promotes glycogen breakdown + protein breakdown
ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 3. Sympathomimetic Effect
Makes cells more responsive to catecholamines (like adrenaline)
How? → Increases number of receptors for catecholamines
📌 ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 4. Cardiovascular Effects
Increases heart rate + contraction strength → raises cardiac output
Increases blood flow + blood volume
❌ No effect on blood pressure
ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 🔹 5. Growth
Helps release growth hormone (GH) + insulin-like growth factor (IGF)
Supports new protein building + bone growth
Essential for normal growth in children
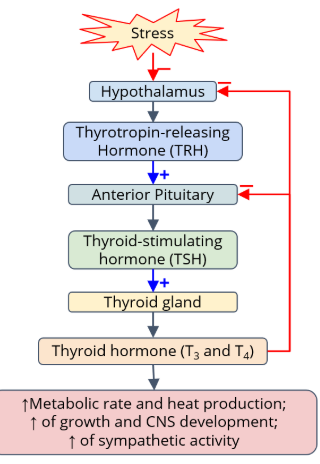
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis - What starts the process?
Trigger:
Stress (or low thyroid hormone levels)
Effect:
Stimulates the hypothalamus.
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis - What does the hypothalamus do?
Secretes:
TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone)
Target:
Anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis - What does the anterior pituitary do?
Secretes:
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone)
Target:
Thyroid gland
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis What does the thyroid gland do?
Releases:
Thyroid hormones: T₃ and T₄
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis What do T₃ and T₄ do in the body?
Effects:
↑ Metabolic rate and heat production
↑ Growth and CNS development
↑ Sympathetic activity (fight or flight)
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis How is the system controlled?
Negative feedback:
High T₃ and T₄ levels signal the hypothalamus and pituitary to stop releasing TRH and TSH
Prevents too much thyroid hormone
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis What happens if TSH is missing or too much?
No TSH → Thyroid shrinks
Too much TSH → Thyroid grows (enlarges follicles)
What is Hypothyroidism?
Definition:
A condition where the thyroid gland doesn't make enough T₃ and T₄ (thyroid hormones).
Also called:
Low thyroid or underactive thyroid
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism (general idea)
Fatigue
Weight gain
Cold intolerance
Slowed metabolism
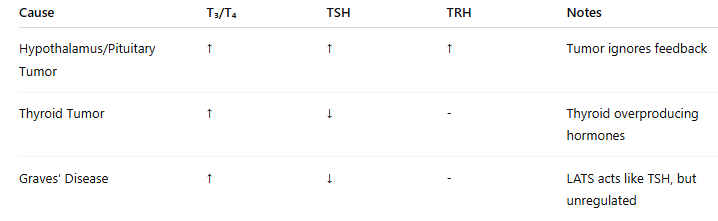
Hypothyroidism Cause #1 — Primary Failure of the Thyroid Gland
What happens?
Thyroid itself is damaged (e.g. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease)
Hormone levels:
↓ T₃ and T₄
↑ TSH (because there’s no negative feedback!)
Hypothyroidism Cause #2 — Secondary Failure
What happens?
The hypothalamus or pituitary doesn’t work properly → ↓ TRH or ↓ TSH → ↓ T₃ and T₄
Hormone levels:
↓ T₃ and T₄
↓ TRH and/or ↓ TSH (depends on where the problem is)
Hypothyroidism Cause #3 — Low Iodine in Diet
What happens?
Iodine is needed to make T₃ and T₄, so not enough iodine = not enough thyroid hormone
Hormone levels:
↓ T₃ and T₄
↑ TSH (same as primary failure—no negative feedback)
Most common cause worldwide!
Definition Recap
🧪 Primary failure = Problem in the thyroid gland itself
🧠 Secondary failure = Problem in hypothalamus or pituitary (the control centers)
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism - Why do symptoms happen?
Thyroid hormones (T₃ & T₄) control:
Metabolism
Growth
Nervous system function
So when they’re low, everything slows down.
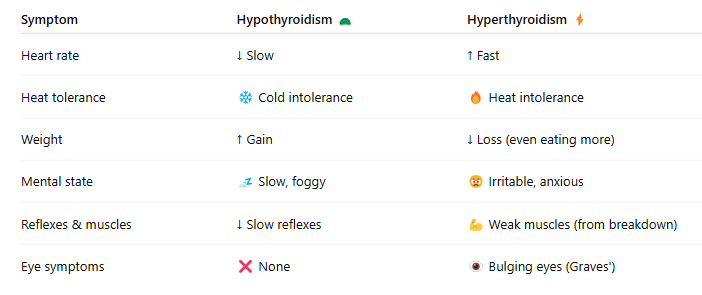
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
🧊 Cold intolerance
⏳ Slower reflexes
💭 Reduced mental alertness
😴 Easily fatigued
❤ Slow, weak heart rate
⚖ Weight gain (due to ↓ basal metabolic rate)
What is Cretinism?
🍼 Congenital hypothyroidism = Born with low thyroid hormone
🧠🧍♀ Results in:
Dwarfism (short stature)
Intellectual disability
💡 Because thyroid hormones are essential for growth and brain development
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Definition:
A condition where the thyroid makes too much T₃ and T₄
Everything in the body speeds up
Hyperthyroidism Cause #1 — Secondary Failure (Tumors in Hypothalamus or Pituitary)
What happens?
A tumor in the hypothalamus (↑ TRH) or pituitary (↑ TSH) causes constant stimulation of the thyroid
Hormone levels:
↑ T₃ and T₄
↑ TRH and/or ↑ TSH
❌ No negative feedback control (tumor ignores it)
Hyperthyroidism Cause #2 — Thyroid Tumor
What happens?
Tumor in the thyroid gland itself → overproduces T₃ and T₄
Hormone levels:
↑ T₃ and T₄
↓ TSH (because of negative feedback from high T₃ and T₄)
Hyperthyroidism Cause #3 — Graves’ Disease (Most Common Cause)
What happens?
An autoimmune disease
The body makes LATS (long-acting thyroid stimulator)
LATS mimics TSH and overstimulates the thyroid
But LATS ignores negative feedback
Hormone levels:
↑ T₃ and T₄
↓ TSH
❌ LATS is not regulated
Quick Recap — Hyperthyroidism Causes & Hormones
Hyperthyroidism Why do symptoms happen?
🌀 Too much T₃ and T₄ = Everything in the body speeds up
⚡ High metabolism, high energy use, overactive systems
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
❤ Increased heart rate
🔥 Excessive heat production (feel hot/sweaty)
💪 Muscle weakness (from protein breakdown)
😠 Mood swings (irritable, anxious from ↑ CNS activity)
⚖ Weight loss (even with more eating)
📈 Elevated basal metabolic rate
Hyperthyroidism Special Symptom — Graves’ Disease
👀 Exophthalmos = Bulging eyes
Caused by fluid buildup from water-retaining carbs behind the eyes
Most commonly seen in Graves’ disease
Hyperthyroidism vs Hypothyroidism (Quick Compare)
What is a Goiter?
🦠 Goiter = Enlarged thyroid gland
👀 Often visible in the neck
📈 Caused by too much TSH stimulation → increases size and number of thyroid follicles
When Does a Goiter Form?
A goiter forms any time TSH is high, even if thyroid hormones (T₃/T₄) are low or high.
Goiter in Hypothyroidism
🧪 Primary hypothyroidism (e.g. Hashimoto’s or iodine deficiency):
↓ T₃/T₄
↑ TSH (due to lack of negative feedback)
✅ Goiter present
Goiter in Hyperthyroidism
💉 Graves’ disease:
LATS (autoantibody) acts like TSH and overstimulates the thyroid
TSH is ↓, but LATS still causes thyroid growth
✅ Goiter present
🧠 Pituitary tumor (secondary hyperthyroidism):
↑ TSH from tumor → overstimulates thyroid
✅ Goiter present
When is Goiter Not Present?
Thyroid tumor: ↑ T₃/T₄ but ↓ TSH (because of negative feedback)
❌ No goiter — TSH is lowSecondary hypothyroidism: Low TSH & TRH due to pituitary/hypothalamus issue
❌ No goiter — no TSH to stimulate thyroid
Summary Table — Goiter or Not?

What causes a goiter?
A goiter forms when the thyroid is overstimulated by TSH (or anything acting like TSH like LATS)
⬆ TSH or LATS = Goiter
⬇ or 🚫 TSH = No Goiter
Goiter in Hypothyroidism – Primary Failure
🧠 What happens?
Thyroid can't make T₃/T₄ → No negative feedback → TSH increases
✅ Goiter Present
Goiter in Hypothyroidism – Secondary Failure
🧠 What happens?
Problem in pituitary or hypothalamus → ↓ TRH and/or ↓ TSH → ↓ T₃/T₄
❌ No Goiter (not enough TSH to stimulate growth)
Goiter in Hypothyroidism – Iodine Deficiency
🧠 What happens?
No iodine = No T₃/T₄ → TSH rises due to lack of feedback
✅ Goiter Present
Goiter in Hyperthyroidism – Pituitary or Hypothalamic Tumor
🧠 What happens?
Tumor makes too much TRH or TSH → ↑ T₃/T₄ AND ↑ TSH
✅ Goiter Present
Goiter in Hyperthyroidism – Thyroid Tumor
🧠 What happens?
Tumor makes lots of T₃/T₄ → Negative feedback ↓ TSH
❌ No Goiter (low TSH = no stimulation)
Goiter in Graves’ Disease
🧠 What happens?
LATS antibody mimics TSH → Constant stimulation of thyroid
✅ Goiter Present
Activity