Assessment 1: The Elements of Music
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
How can we define music?
“…sounds heard over time in succession”.
What are the 4 properties of sound?
pitch
intensity (loudness)
duration
timbre
Sound is produced through vibrations. The rates of vibrations are called….
frequencies
What’s a fundamental pitch?
A basic pitch that produces a series of harmonics (also known as partials or overtones).
What are harmonics (also known as partials and overtones)?
The various “partial” sounds generated by a vibrating medium in addition to the fundamental pitch.
What’s a tone?
A musical sound that is “pure,” is one that has no partials (does not exist in nature).
What’s a noise?
A sound that is so rich in overlapping partials that the fundamental pitch is obscured.
Pitches are notated on a series of lines and spaces called a(n)…
staff
The oval-shaped symbols on the lines and spaces that indicate pitch and rhythm are called…
notes
What can one do if one needs to indicate pitches that are too high or too low to fit on the lines and spaces of a staff?
Use ledger lines to accommodate notes outside of the staff’s range.
What are the two main clefs?
Treble and Bass
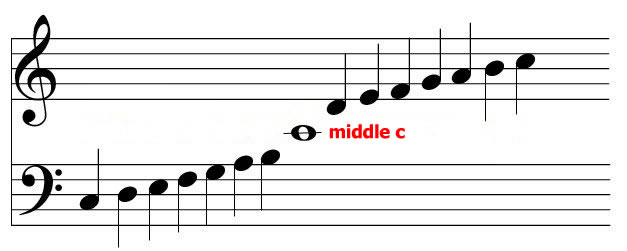
Which note occupies the first ledger line below the treble staff and above the bass staff?
Middle C
What are the symbols or signs that are used to indicate if a pitch is slightly higher or lower than a basic pitch? How are these signs canceled out?
Sharp (#) is slightly higher, flat (♭) is slightly lower
Both can be canceled out by a natural (♮)
Notes that are raised or lowered throughout a large part of a composition are indicated using a(n)…
key signature
What’s an accidental?
A sharp, flat, or natural that indicates a momentary departure from the key signature by raising or lowering a note.
A melody is made up of melodic portions called ______ that end in a pause known as a(n) _____.
phrases; cadence
What’s an interval?
The distance between two pitches
What does it mean to say that sounds are in unison?
They are the exact same pitch; an interval of the same pitch.
How do dissonant intervals sound?
Dissonant intervals sound harsh compared to consonant intervals
i.e. two adjacent pitches and sevenths
How do consonant intervals sound?
Consonant intervals sound more pleasant
i.e. thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, and octaves
What’s a conjunct melody?
A melodic motion by half step or whole step.
What’s a disjunct melody?
a melodic motion by skip or leap.
The home note of a piece is called…
the tonic
What are the two types of scales used in most Western music?
Major and Minor
there are 12 major scales and 12 minor scales
What is the pattern of whole steps and half steps used to make up the major scale?
Half steps occur between the third and fourth pitches, and between the seventh and eighth.
Whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half
How does the major scale sound?
Bright and cheerful
What is the pattern of whole steps and half steps used to make up the minor scale?
The main distinguishing feature of the minor scale is its third pitch, which is always one half-step lower than the corresponding third pitch of the major scale.
Whole, half, whole, whole, half, whole, whole
How does the minor scale sound?
Dark and somewhat melancholy
What is the pattern of whole steps and half steps used to make up the chromatic scale?
Division of an octave into 12 half steps
List and define at least four different types of notes that indicate different rhythmic values.
Whole Note: longest value (𝅝)
Half Note: two equals one whole note (𝅗𝅥𝅗𝅥)
Quarter Note: two equals one half note (𝅘𝅥𝅘𝅥)
Eighth Note: two eighth notes equal one quarter note (𝅘𝅥𝅮𝅘𝅥𝅮 or ♫)
What does adding a dot do to the note’s rhythmic value?
The dot extends the note by adding half of its value
i.e. the whole note is held for 6 beats instead of 4
What does adding a tie do to notes’ rhythmic values?
Join two notes to produce a rhythmic value equal to the sum of the individual values.
What is a triplet?
Groups of three notes marked by the numeral 3, indicating that they have the same duration as two notes of the same value.
What are rests?
Silence in music
Tempo refers to…
the speed of a musical composition.
Allegro means…
fast
Adagio means…
slow
What is the function of a metronome?
To keep time of a piece by emitting regular beats.
What is a beat?
The fundamental pulse in a musical composition; the basic subdivision within the measure lines of a composition.
A stress or emphasis on a beat is called a(n)…
accent
What is the difference between a downbeat and an upbeat?
A downbeat is the accented beat at the beginning of a measure.
An upbeat is the weak beat that precedes a downbeat; the last note of a measure.
What is syncopation?
A rhythmic device in which normally unaccented beats are accented.
What is the function of musical measures?
Organize rhythms into equal segments of time.
The beginning of each beat pattern in a measure is marked by a naturally felt…
accent
How are measures defined?
Measures are the basic temporal division of Western music, periodically indicated by vertical measure lines.
What are the 3 basic types of meter?
Duple meter: two beats per measure
Triple meter: three beats per measure
Compound meter: subdivide beats into smaller groupings of three.
What does time signature show?
The meter of a composition
How is the top number different from the bottom number of a time signature?
The top number of a time signature indicates how many beats each measure has.
The bottom number indicates the rhythmic value assigned to each beat.
Which time signature is known as common time?
4/4
What are the three basic musical textures, and how are they different from each other?
Monophony: a type of music with a single melodic line.
Polyphony: A texture in which two or more independent musical lines are contraposed.
Homophony: A texture characterized by a single melodic line supported by block-like chords; often a melody supported by chords.
What is counterpoint?
The art of setting separate musical lines against each other.
How is an imitative counterpoint different from a non-imitative counterpoint?
Imitative Counterpoint: Counterpoint that makes extensive use of imitation between the voices.
Non-imitative Counterpoint: Counterpoint in which the different parts are relatively independent and do not imitate one another.
A canon is also known as a(n)…
round
Harmony is the art of using combinations of three or more simultaneously sounding pitches called ___.
chords
Which musical texture uses harmony?
Homophony
What is a triad?
A chord consisting of three pitches, constructed by adding pitches a third and a fifth above a fundamental pitch.
What is meant by the term harmonic progression?
A dissonant harmony progresses to a consonant harmony that “resolves” the tension of the dissonance.
What is tonality?
A system of musical organization that depends on a network of harmonic relationships, all centered on consonant triads.
Define dynamics.
The relative loudness or softness of a pitch.
What are some common dynamic markings, and what do they mean?
Forte: loud
Piano: soft
Mezzo Piano: half soft
Mezzo Forte: half loud
Fortissimo: very loud
A gradual change from a soft to loud dynamic is known as a(n) ____, while the opposite is known as a(n) ___.
crescendo; decrescendo
What is timbre?
The quality of sound that differentiates one instrument from another.
Affected by size and material of the instrument and how the instrument is played—how loudly or softly and whether in a high or low register.
What are the three common female vocal ranges? Indicate them from highest to lowest.
Soprano, mezzo soprano, alto/contralto
What are the three common male vocal ranges? Indicate them from highest to lowest.
Tenor, baritone, bass
What are the five groups of musical instruments based on how they produce sound?
Idiophones
Membranophones
Aerophones
Chordophones
Electrophones
Idiophones
made of solid materials that produce sounds when struck, rubbed, or shaken.
the cymbal, gong, and xylophone
Membranophones
instruments with tautly stretched membranes that vibrate to produce sounds.
timpani (kettledrums), bass drum, and snare drum.
Aerophones
instruments that use columns of air to produce sounds.
woodwinds, brass, and the organ
Chordophones
instruments with strings
guitar, harp, violin, and piano
Electrophones
instruments that generate sound electronically.
modern electronic organ, synthesizers, and computer programs.
What are the four groups of Western instruments that are often used to define orchestral families?
Woodwinds
Brass
Strings
Percussion
Woodwinds
aerophones generally made of wind (flutes, piccolo, oboe, English horn, clarinet, bass clarinet, bassoon, and contrabassoon).
Brass
aerophones made of metal (trumpet, French horn, trombone, and tuba).
Strings
chordophones (violin, viola, cello, and double bass).
Percussion
made up of membranophones and idiophones (timpani, xylophone, and tubular bells—and instruments that produce indefinite sounds—for example, cymbals, gongs, and triangle).
How can the piano be classified?
Idiophone and Chordophone (hammers hit the strings)
What is range in music?
the distance from the lowest to the highest pitch an instrument can play
What is chamber music?
Music intended to be performed in an intimate setting or with a small ensemble.
Compositions for nine or fewer musicians.
How is a chamber orchestra different from an orchestra?
A chamber orchestra is smaller than an orchestra.
Chamber Orchestra
A small orchestra suitable for performing chamber music.
Orchestra
A large ensemble of instrumental performers; a contemporary orchestra typically has about one hundred performers.
What is the function of a conductor, and which type of ensemble typically uses one?
To keep time and conduct the orchestra.
Orchestras typically use conductors.
What are some types of vocal ensembles?
duos, trios, quartets, and choruses
What is a mixed ensemble?
Ensembles that join together vocal and instrumental musicians.
Jazz ensemble
Rock ensemble
What is meant by musical form?
The structural organization of a composition.
The overarching plan that holds a piece together.
Binary Form:
A musical form in two basic parts (AB), often repeated; there may be some similarities between the two, but essentially our brain processes the music as dividing into two portions. Often repeats as A, A, B, B.
Ternary Form:
There are three sections, of which the third is a repetition, either exact or modified, of the first. Often repeated as A, B, A.
How is theme and variations form constructed?
A composition using a particular musical form will typically have certain elements that return to form a theme.
The theme, presented at the beginning of the composition, and sometimes repeated at the end, as if completing a musical circle.
The variations (there can be as many as the composer decides) provide the variety by altering details or some aspect of the theme, such as its melodic shape, rhythm, meter, or harmonic accompaniment.