phs quiz 6
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
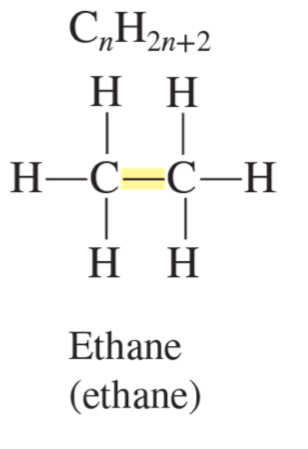
alkane formula
CnH2n+2
ethane (ethane)
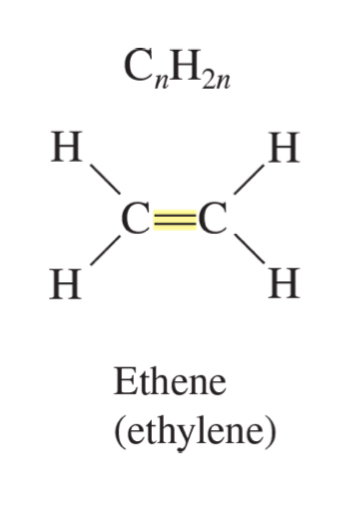
alkene formula
CnH2n
ethene (ethylene)
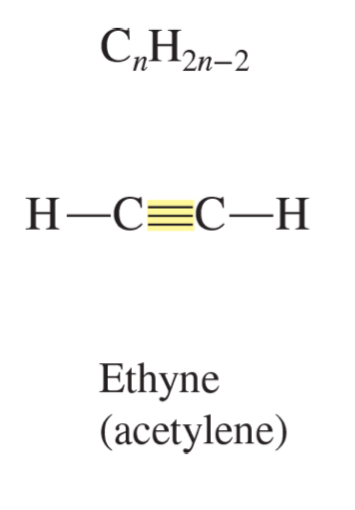
alkyne formula
CnH2n-2
ethyne (acetylene)
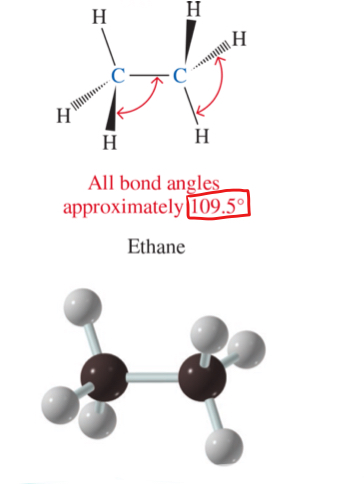
3D structure of ethane (alkane)
all bond angles approximately 109.5°
3D structure of ethene (alkene)
all bond angles approximately 120°
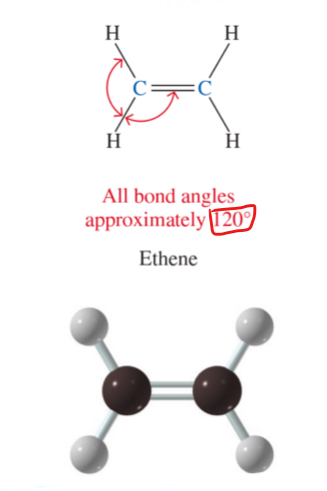
3D structure of ethyne (alkyne)
all bond angles approximately 180°
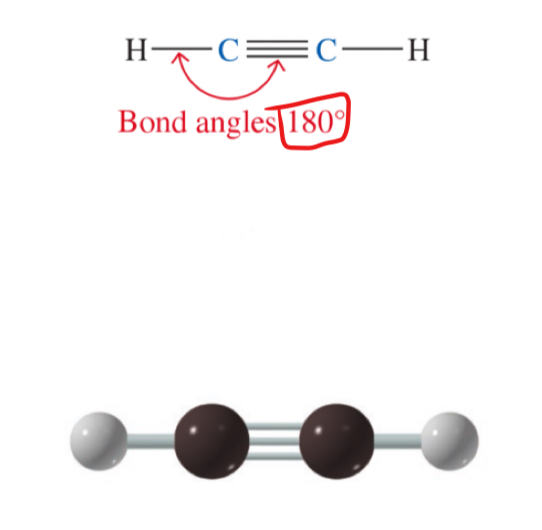
a long-chain alkane (pentane)
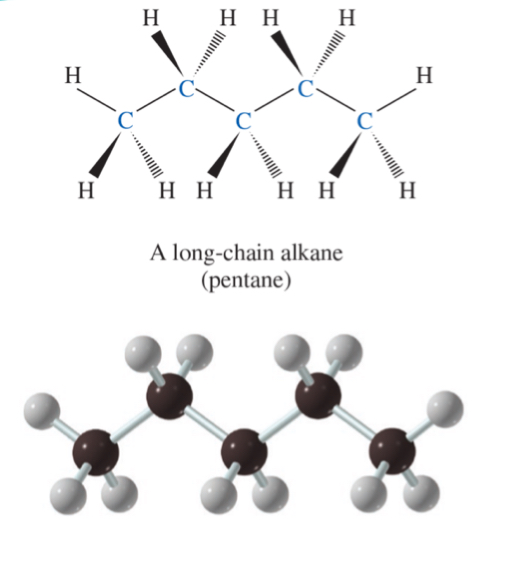
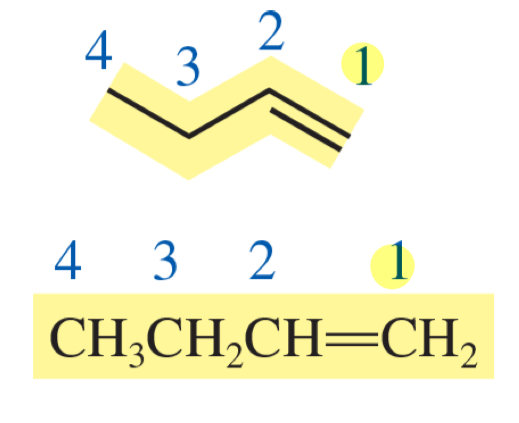
a long-chain alkene (pent-1-ene)
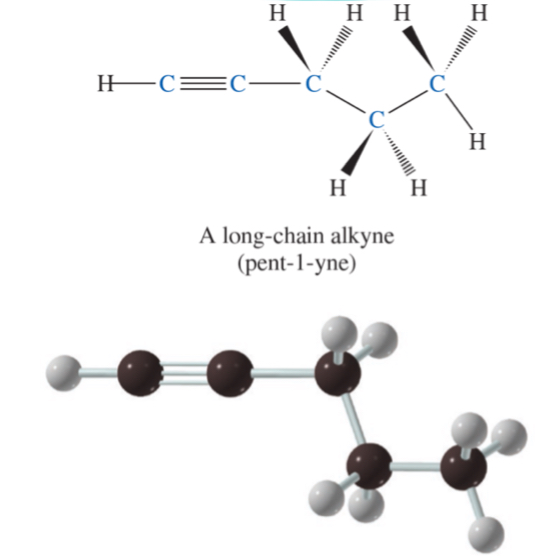
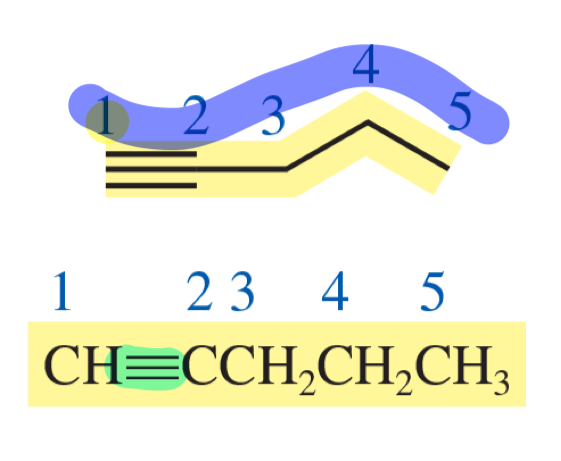
a long-chain alkyne (pent-1-yne)
ethane
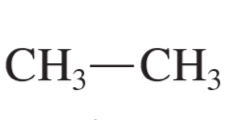
ethene
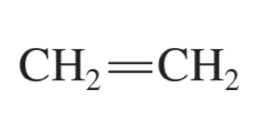
ethyne
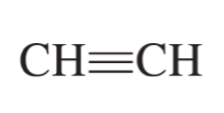
propane
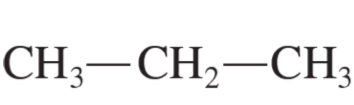
prop-1-ene

prop-1-yne
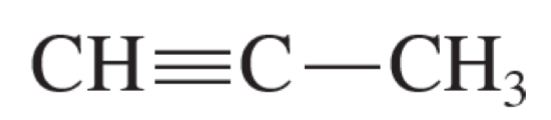
but-1-ene
pent-1-yne
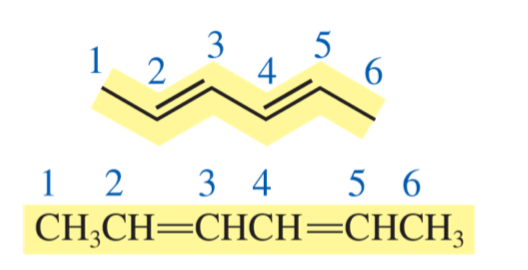
hexa-2, 4-diene
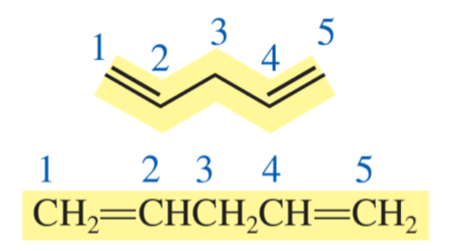
penta-1, 4-diene
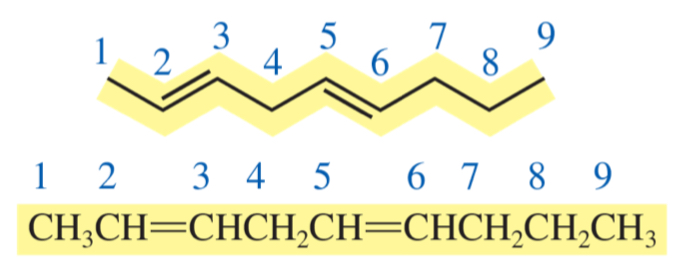
nona-2, 5-diene
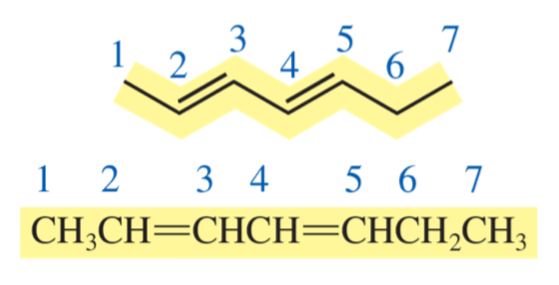
hepta-2, 4-diene
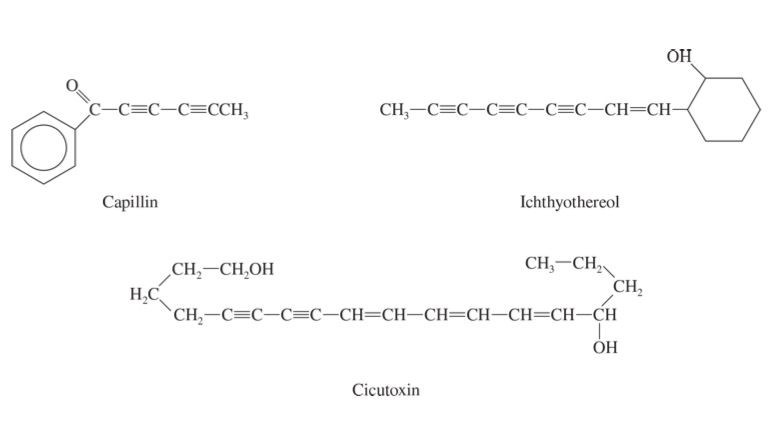
toxic alkynes
for plant defense
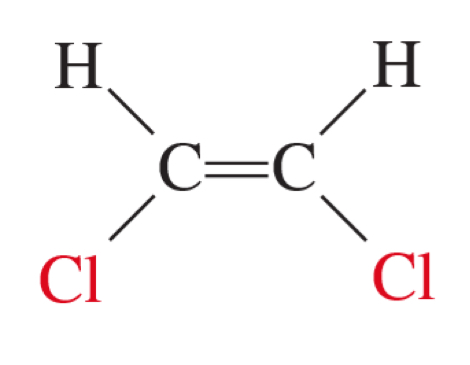
geometric isomer
cis and trans conformation
cis-1, 2-dichloroethene
on the same side
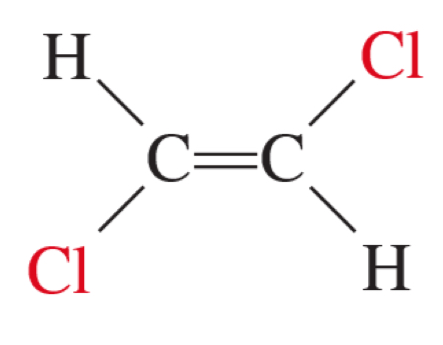
trans-1, 2-dichloroethene
on opposite side
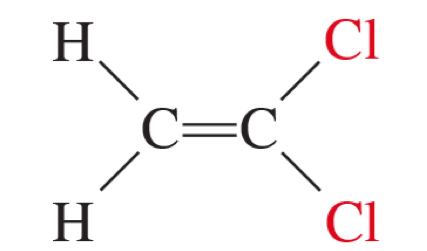
neither cis nor trans
alkenes in nature
flavor by polyenes
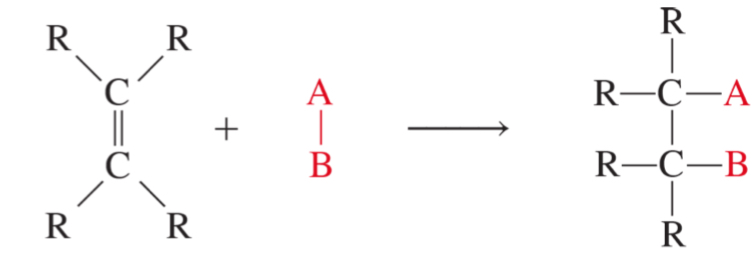
addition reaction
two molecules add together to form a new molecule
the major alkene addition reactions
hydrogenation
halogenation
hydration
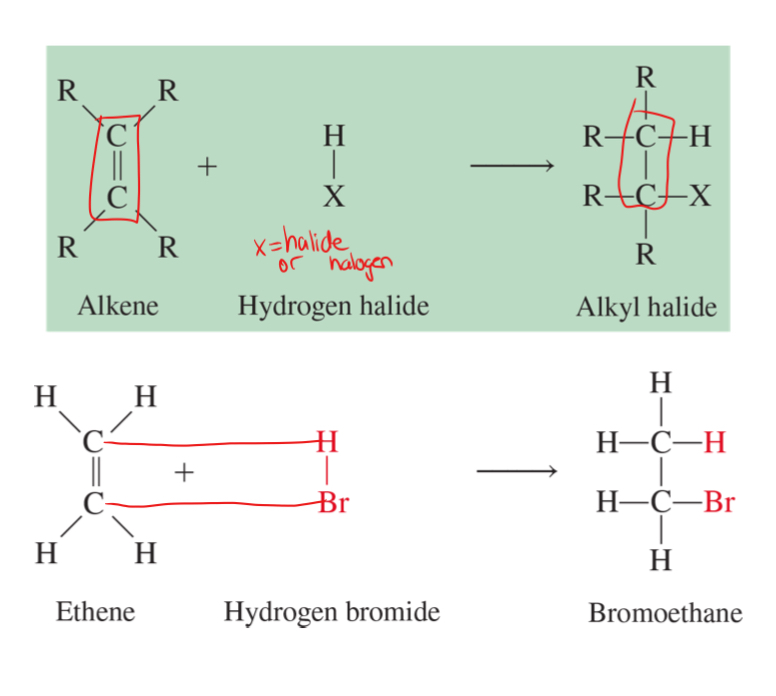
hydrohalogenation
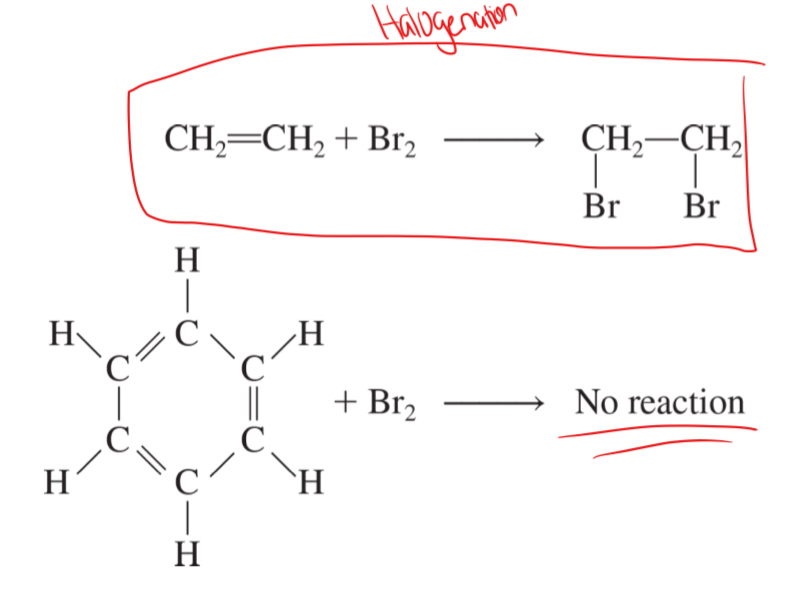
halogenation
the addition of halogen atoms to a double or triple bond
H2, Cl, I, F, Br
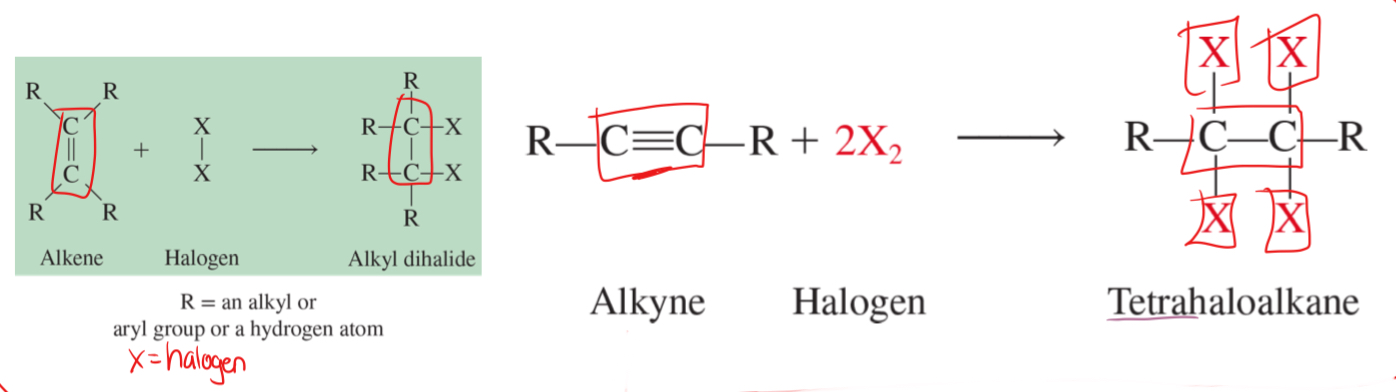
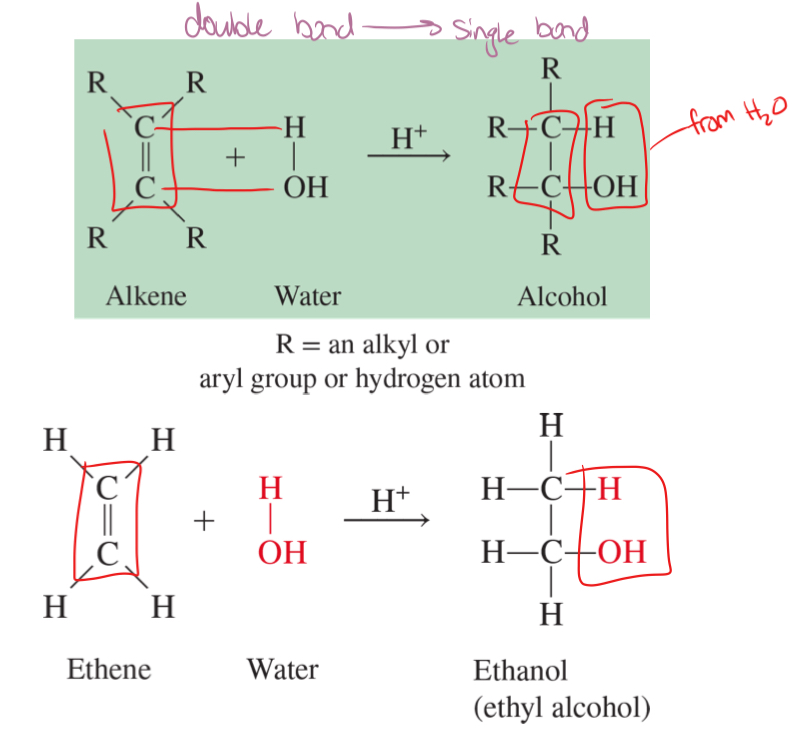
hydration
the addition of a water molecule to an unsaturated bond
hydrohalogenation
the addition of a hydrogen halide molecule to an unsaturated bond
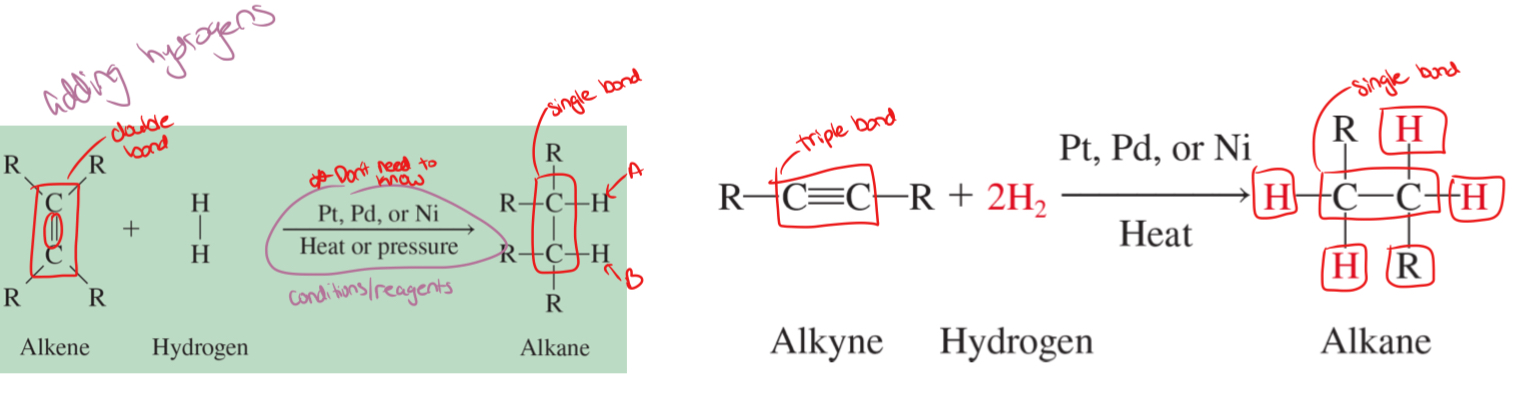
addition reaction of alkene
R= an alkyl or aryl group or a hydrogen atom
hydrogenation
adding hydrogen to a double or a triple bond
oil to fat conversion
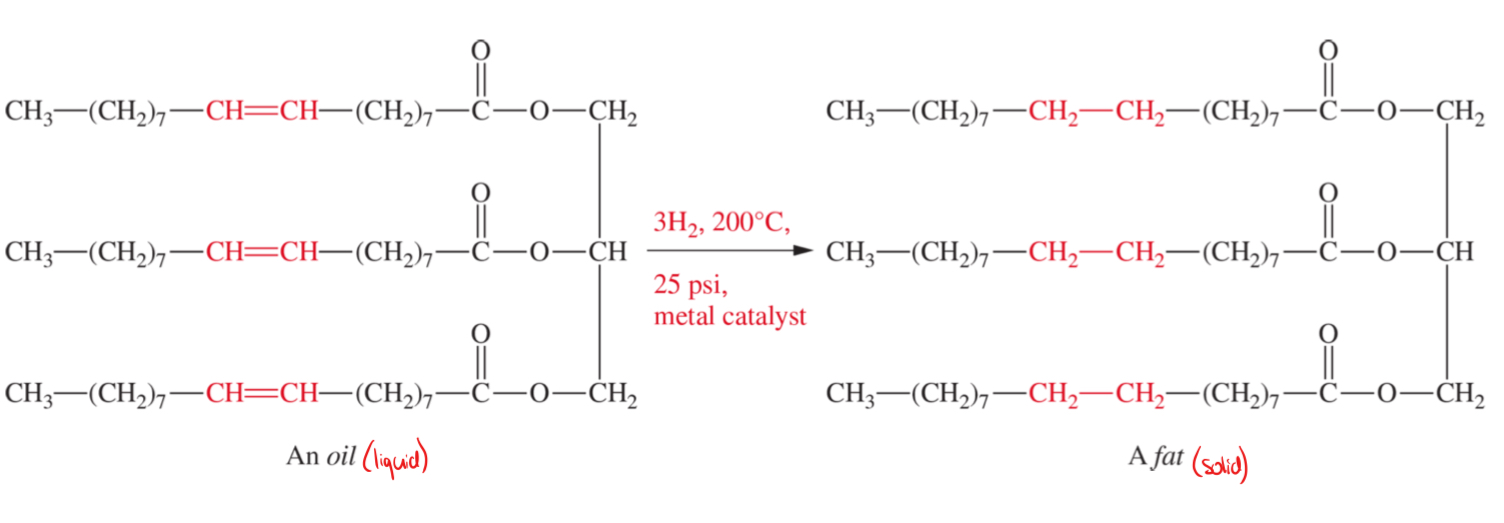
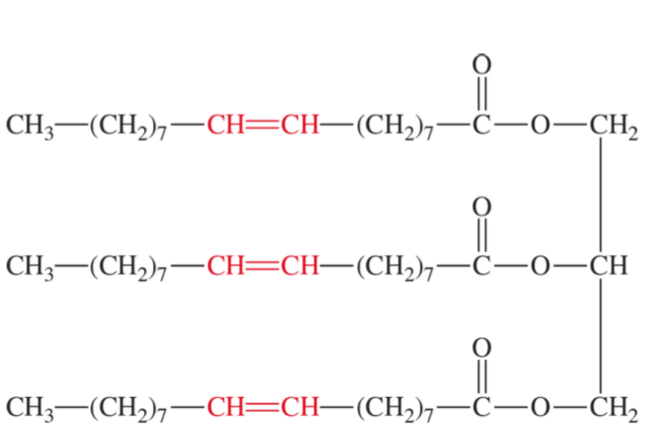
oil (liquid)
more double bonds makes it more oil-like
unsaturated fatty acids
double bonds
fat (solid)
less double bonds makes it more fat-like
saturated
single bonds
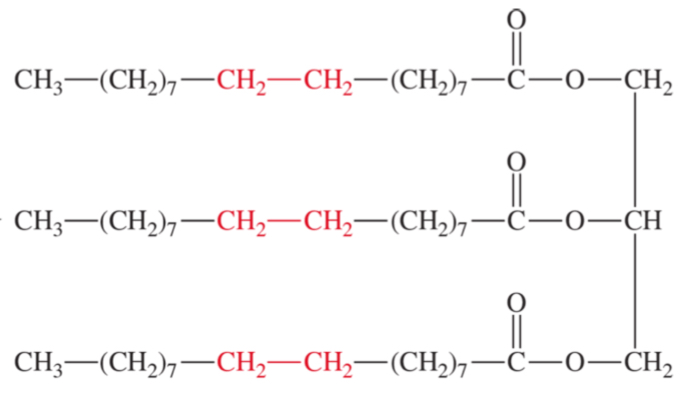
saturated (single bonds) fatty acids
fats (solids)
palmitic acid
stearic acid
arachidic acid
unsaturated (double bonds) fatty acids
liquid (oil)
palmitoleic acid
oleic acid
linoleic acid
linolenic acid
arachidonic acid
saturated fatty acids: carbon chain length
palmitic acid: 16
stearic acid: 18
arachidic acid: 20
unsaturated fatty acids: carbon chain length
palmitoleic acid: 16
oleic acid: 18
linoleic acid: 20
linolenic acid: 20
arachidonic acid: 20
saturated fatty acids: number of double bonds
palmitic acid: 0
stearic acid: 0
arachidic acid: 0
unsaturated fatty acids: number of double bonds
palmitoleic acid:1
oleic acid: 1
linoleic acid: 2
linolenic acid: 3
arachidonic acid: 4
saturated fatty acids: melting point (C)
palmitic acid: 63
stearic acid: 70
arachidic acid: 77
unsaturated fatty acids: melting point (C)
lower melting point
palmitoleic acid: 0
oleic acid: 16
linoleic acid: 5
linolenic acid: -11
arachidonic acid: -50
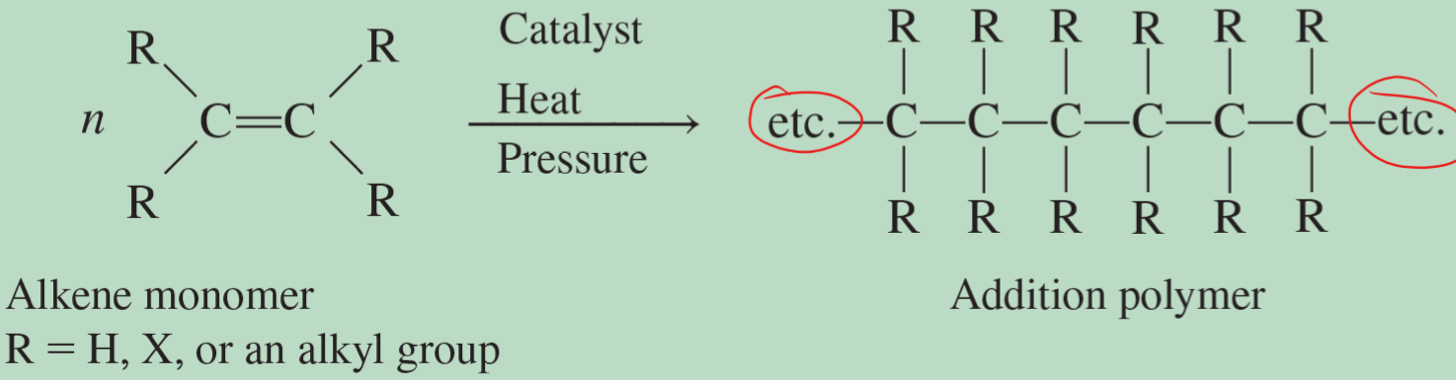
polymer and addition polymer
building blocks of plastic
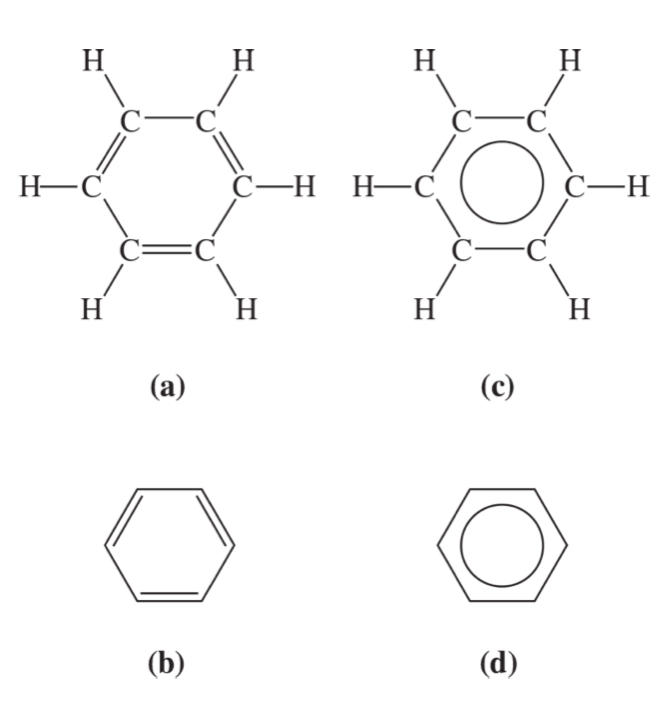
aromatic hydrocarbons
containing benzene ring of its derivatives
high chemical stability
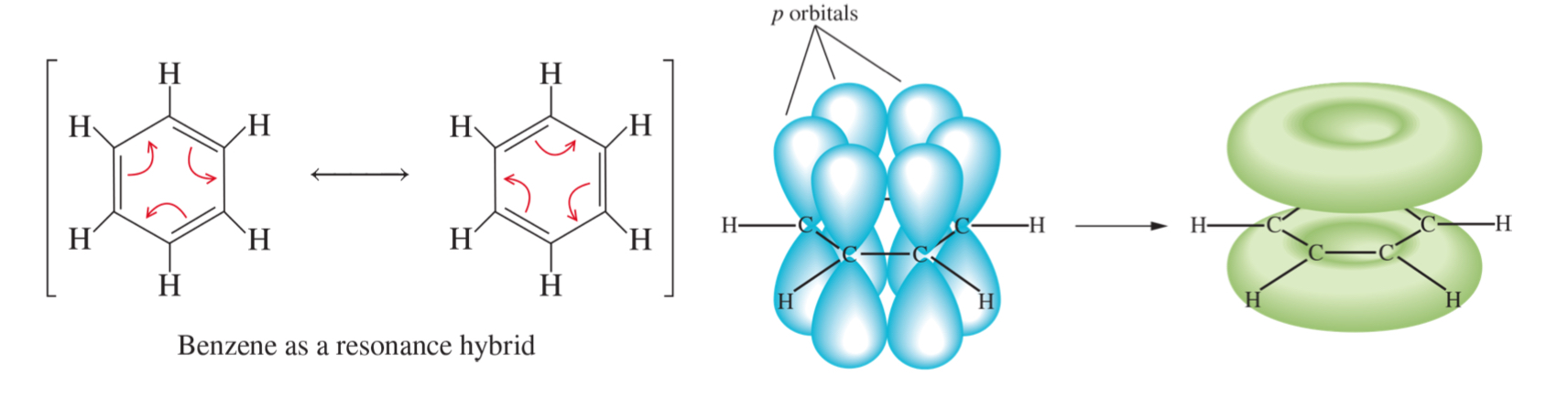
resonance
gives rise to stability
resonance and stability
benzene is stable because of these
benzene structures
mother chain (benzene) + substituents
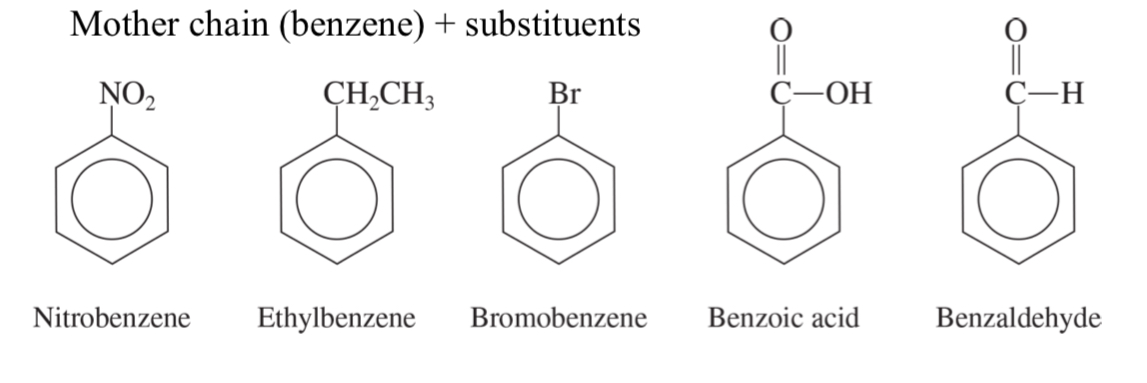
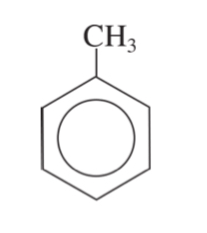
toluene
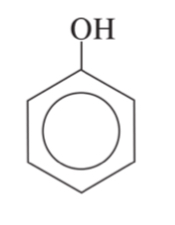
phenol
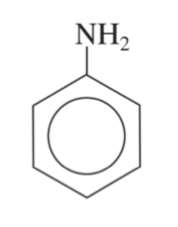
aniline
how to generate an alcohol using an alkene
has C OH bond
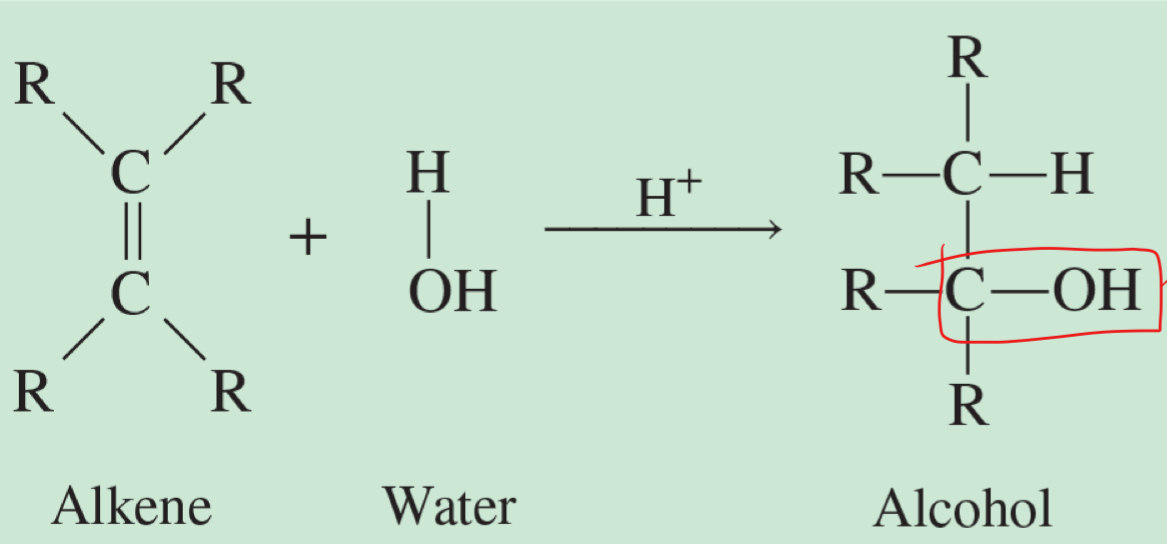
alcohol
R-O-H
R = carbon-containing group (alkyl group)
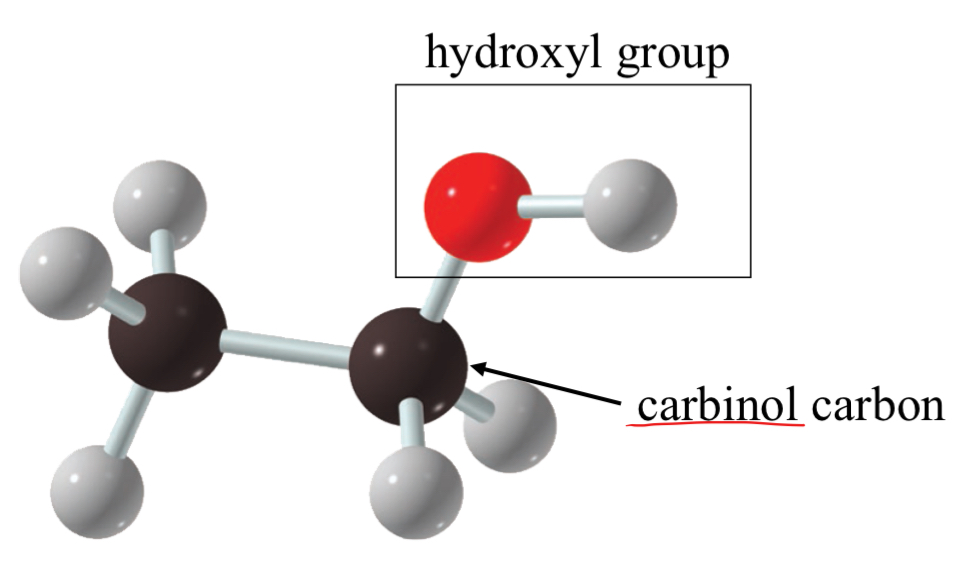
methyl alcohol
methanol
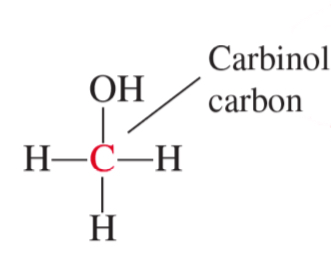
1° alcohol
primary
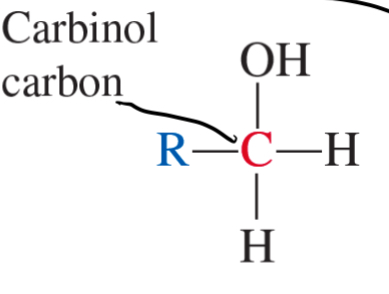
2° alcohol
secondary

3° alcohol
tertiary
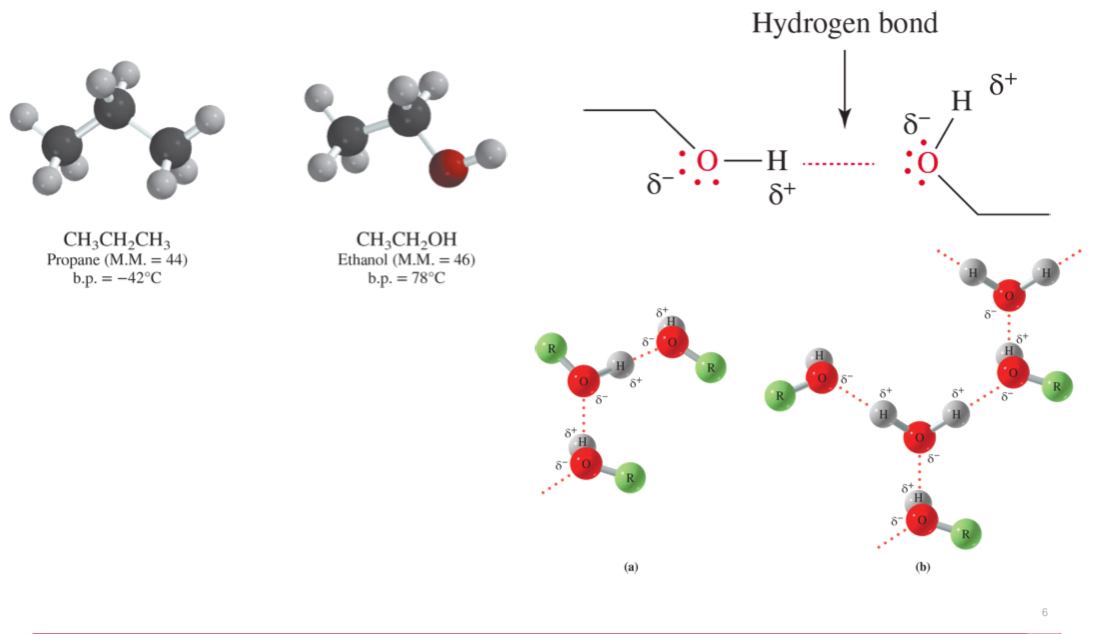
hydrogen bonding in alcohol
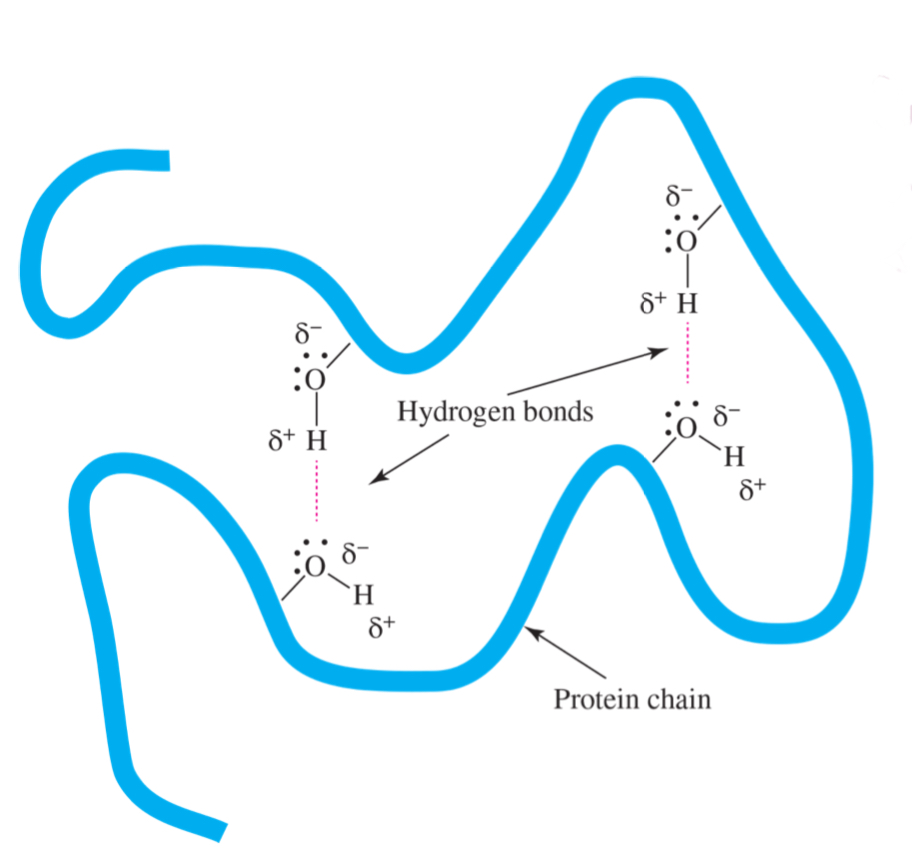
hydrogen bonding in OH group in biomolecules
can bond with others including themselves
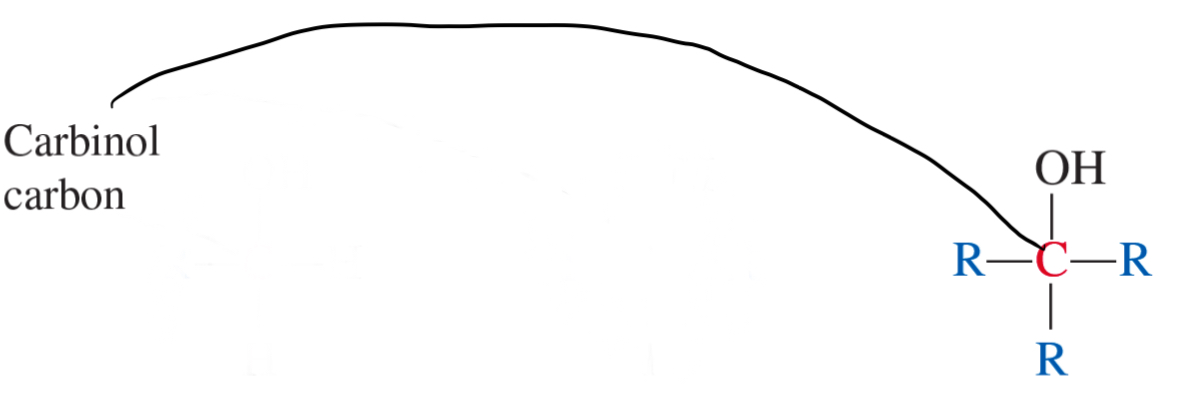
nomenclature of alkane/alkene/alkyne
identify the longest carbon chain containing the functional group
use -ane/ -ene/ -yne as the ending for alkane/ alkene/ alkyne
number the parent chain to give the double or triple bond the lowest number