organic reactions- CIE AS level chemistry 9701
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
alkene to alcohol
+ steam
H3PO4 catalyst
300°C
60atm
Alkene to Halogenoalkane
+ HBr
room temp
alkene to alkane
H2, Ni catalyst, 150°C
Alkene to dihalogenoalkane
+Br2
room temp
alkene to diol
+ cold dilute acidified KMnO4
e.g. CH3CH=CH2 +[O]+H2O --> CH3CH(OH)CH2OH
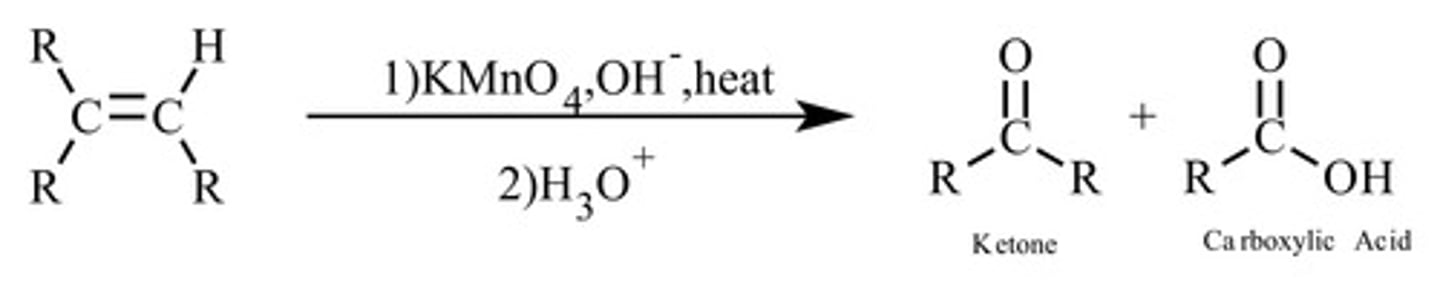
alkene and hot, concentrated KMnO4
double bond ruptured and constituent molecules oxidised
halogenoalkane to alcohol
+ NaOH (aq), heat under reflux
nucleophilic sub
primary halogenoalkanes= Sn2 mechanism
tertiary halogenoalkanes= Sn1 mechanism
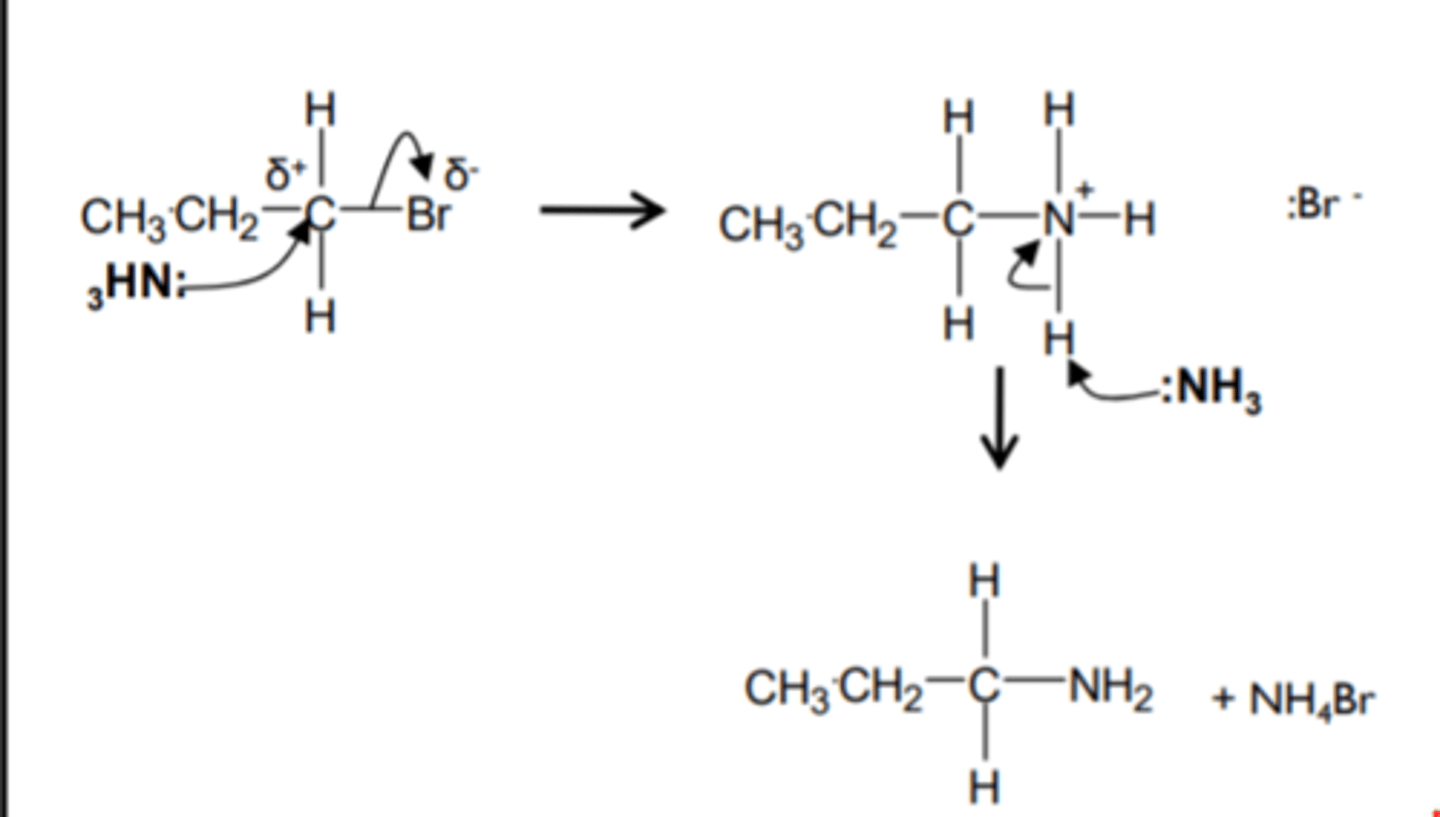
halogenoalkane to amine
+ excess conc NH3 (ethanolic)
heat and high pressure
nucleophilic sub
halogenoalkane to nitrile
+ KCN (ethanolic)
heat under reflux
nucleophilic sub
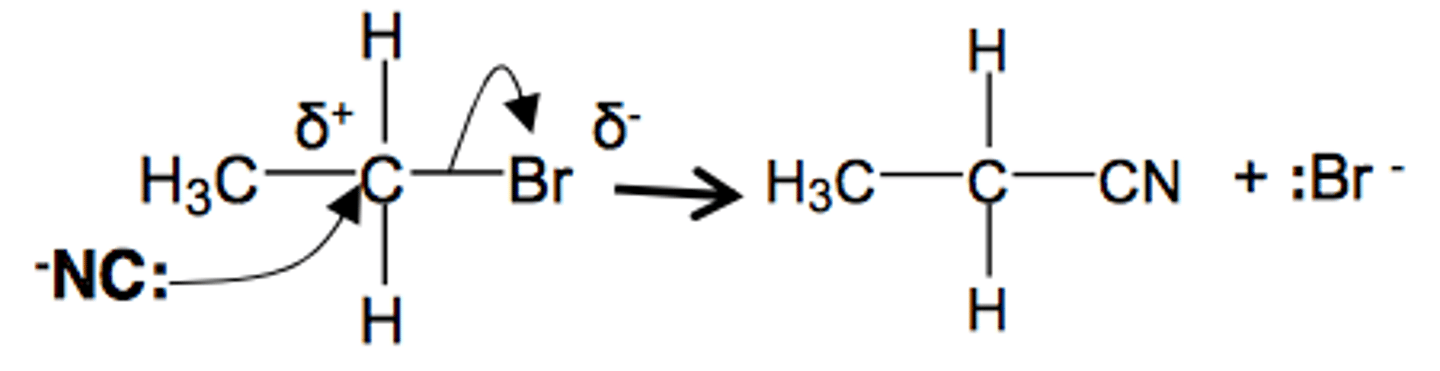
nitrile to amine
LiAlH4 in dry ether
Na in ethanol
H2 and nickel/platinum catalyst
halogenoalkane to alkene
NaOH (ethanolic)
heat under reflux
elimination reaction
alcohols to aldehydes
+KMnO4 (acidified) or K2Cr2O7 (acidified)
simple distillation
Alcohol to sodium alkoxide (and observations)
+ Na (produces H2)
effervescence
Na decreases in size
white solid formed (sodium alkoxide)
or + NaOH (produces H2O)
white solid formed (sodium alkoxide)
alcohols to carboxylic acids
+KMnO4 (acidified) or K2Cr2O7 (acidified)
heat under reflux
alcohols to chloroalkanes
ROH + PCl5 --> RCl +POCl3 + HCl
NaCl+ H2SO4 --> HCl (in situ) + NaHSO4
ROH + HCl --> RCl +H2O
ROH+ SOCl2 --> RCl + SO2 + HCl
all room temp
alcohol to bromoalkane
moist red 2P+ 3Br2 --> 2PBr3
3ROH + PBr3 --> 3RBr +H3PO3
NaBr + 50% H2SO4 --> NaHSO4 + HBr
ROH+ HBr --> RBr + H2O
both heat under reflux
alcohol to iodoalkane
moist red 2P + 3I2 --> 2PI3
3ROH + PI3 --> RI + H3PO3
alcohol to alkene
H3PO4/ conc H2S04/ Al2O3
heat
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
+ LiAlH4 in dry ether or + NaBH4 (aq) (both provide hydride ion)
room temp
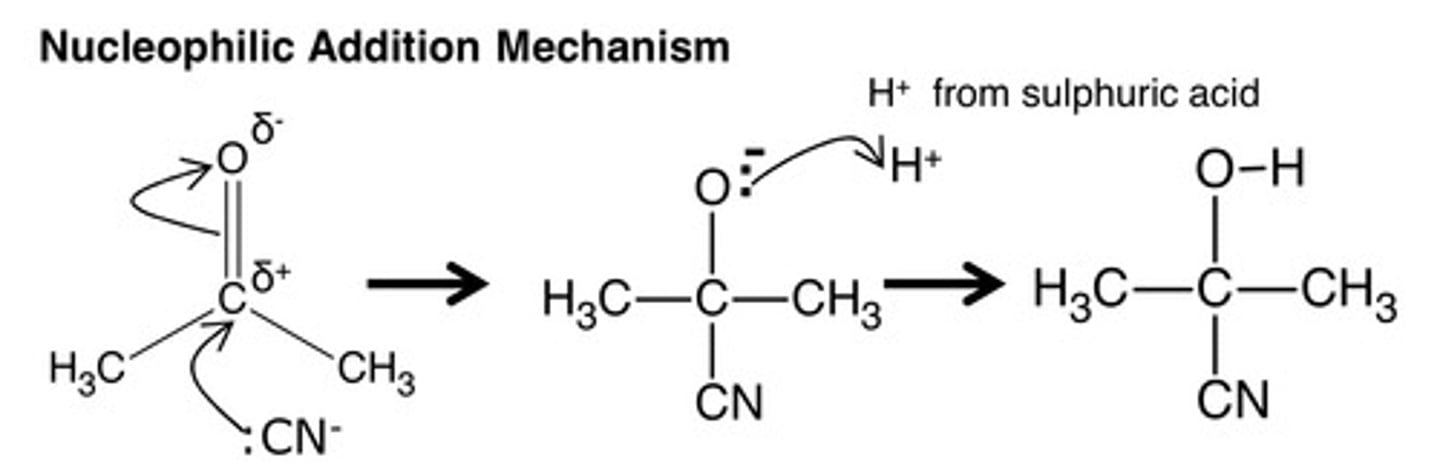
Aldehyde to Hydroxynitrile
KCN +H2SO4 --> HCN
catalyst: excess KCN
heat under reflux
HCN/KCN is toxic so perform in a fume cupboard
Nitriles to carboxylic acids
RCN + HCl + 2H2O --> RCOOH + NH4Cl
RCN +NaOH + H2O --> RCOONa + NH3
RCOONa + HCl/ H2SO4 --> RCOOH
both heat under reflux
hydroxynitriles to hydroxyamines
LiAlH4 in dry ether
or H2 and nickel catalyst
test for aldehydes/ketones
2,4-DNP (aka Brady's reagent)
yellow/orange solution, when reacts with aldehyde or ketone produces an orange ppt
nucleophilic addition- elimination reaction
iodoform test
reagents: I2 +NaOH (aq) + KI (aq)
detects:
ketones with a methyl group next to C=O
secondary alcohols with a methyl group next to C-O
ethanol
ethanal
reagent
if any of the above present, pale yellow crystals of iodoform (CHI3) are produced with antiseptic smell
e.g. propanone
RCOCH3(aq) + 3I2(aq) + 4NaOH(aq) ⇒ RCOONa(aq) + 3H2O(l) + 3NaI(aq) + CHI3(s)
test for carboxylic acids
add metal carbonate, bubble effervescence produced into limewater, if limewater is milky then presence of COOH
carboxylic acid to sodium alkyloate
+Na ;produces hydrogen effervescence)
+NaOH
+Na2CO3 ;produces CO2 effervescence, Na2CO3 decreases in size
carboxylic acid to alcohol
LiAlH4 in dry ether, room temp
CH3COOH + 4[H] --> CH3CH2OH + H2O
forming esters
carboxylic acid + alcohol, conc H2SO4 catalyst
heat
hydrolysis of esters
HCl catalyst (or any other strong acid)
if we wanted to hydrolyse it without it being an equillibrium reaction:
RCOOR + NaOH (aq) --> RCOONa + ROH
RCOONa + strong acid --> RCOOH + sodium salt
acid and alkali method both are heat under reflux