Viruses, Viroids, and Prions: Structure, Classification, and Replication L.5
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What are viruses?
Inert particles that are incapable of metabolism and replication, and are obligate intracellular parasites.
How are viruses classified based on the cells they infect?
Into two groups: those that infect prokaryotic cells and those that infect eukaryotic cells.
What are bacteriophages?
Viruses that infect bacteria, serving as models for molecular biology and virus-host relationships.
How do bacteriophages help in controlling bacterial populations?
They can kill bacteria, limiting their populations in nature and controlling bacterial growth in foods.
What is the size range of most viruses?
Most viruses are about 100-1000-fold smaller than the cells they infect, with the smallest being about 10nm in diameter.
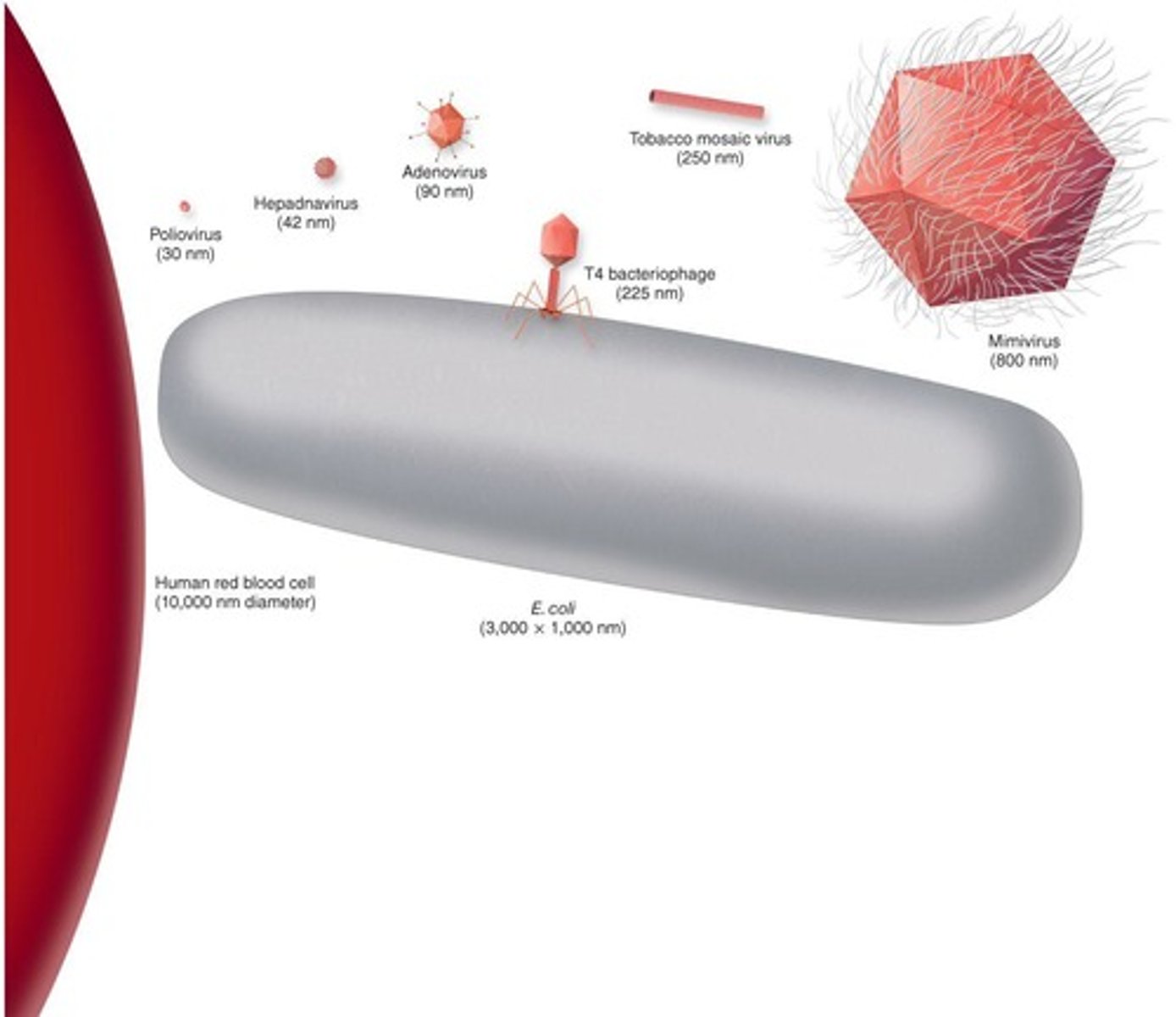
What type of microscope is needed to visualize viruses?
Viruses can only be visualized with an electron microscope.
What is the structure of a virus?
Viruses contain either DNA or RNA surrounded by a protective protein coat called a capsid.
What distinguishes naked viruses from enveloped viruses?
Naked viruses have no additional covering other than the capsid, while enveloped viruses have a lipid membrane surrounding the capsid.
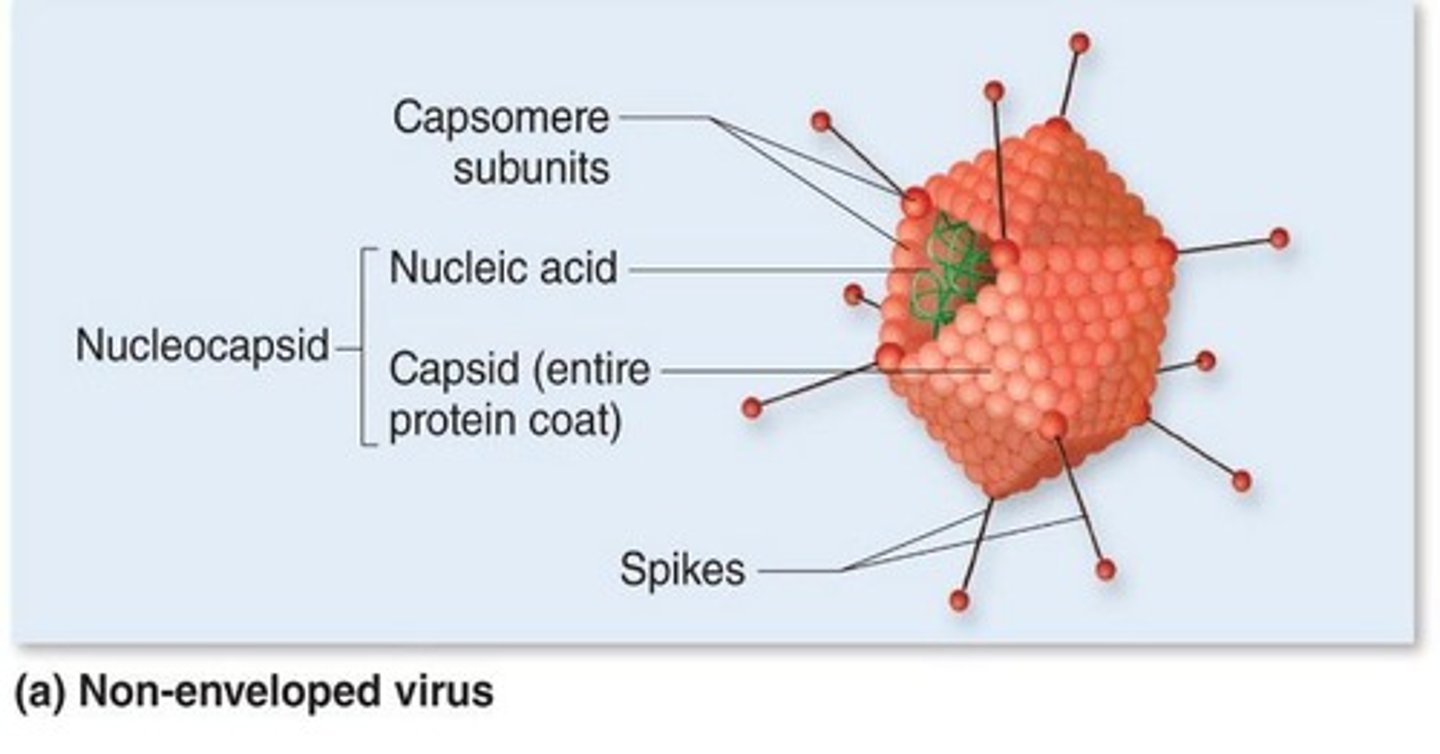
What are attachment proteins or spikes?
Proteins that bind the virus to host cells and project from the envelope or capsid.
What are the three different shapes of virions?
Icosahedral, helical (rod-shaped), and complex (intricate and irregular structures).
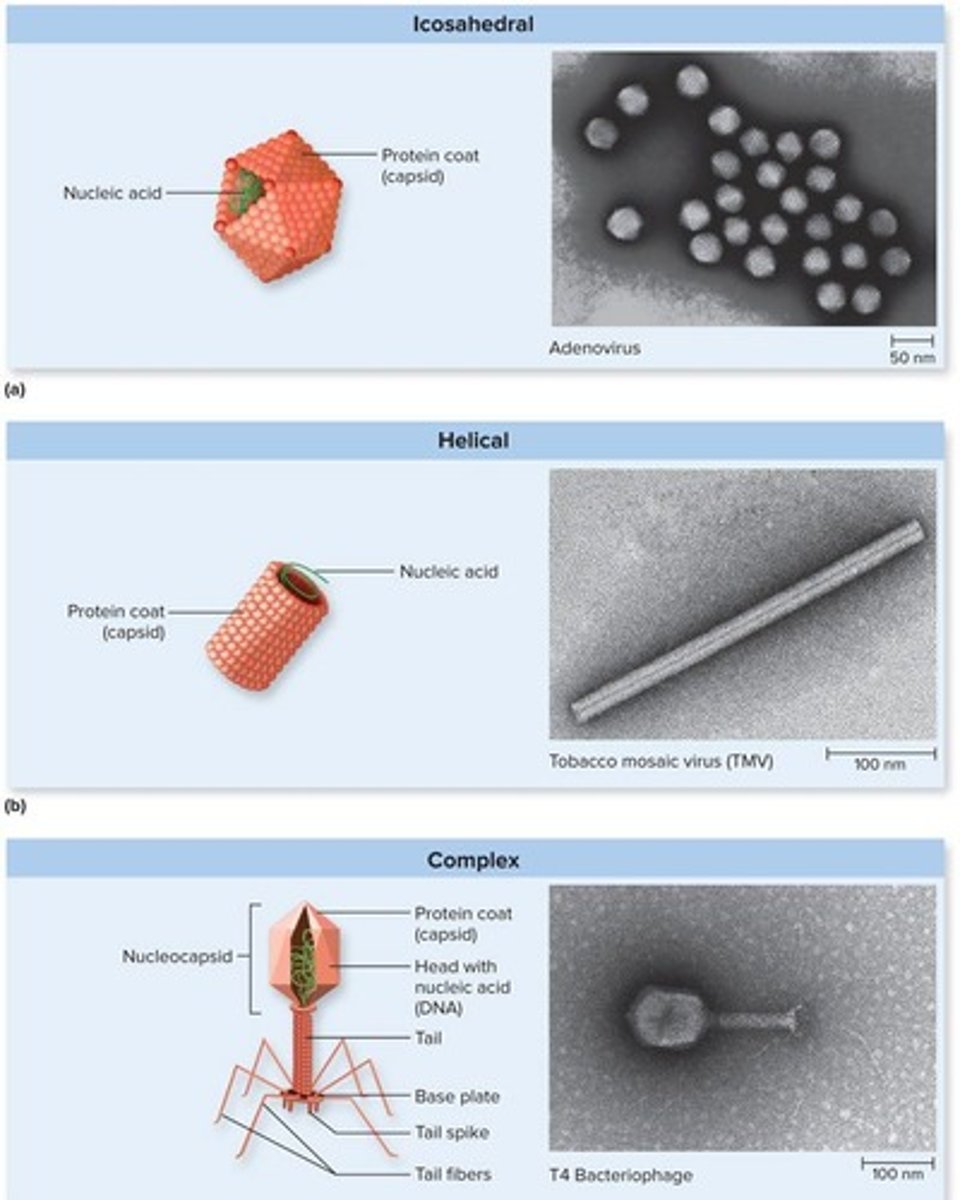
How are animal viruses classified?
Based on genome structure, virus particle structure, and the presence or absence of a viral envelope.
What is a segmented virus?
An RNA virus that has more than one RNA molecule, such as the influenza virus.
What is the significance of the family names of viruses?
Virus families end in -viridae and are italicized, while genera names end with -virus and are not italicized.
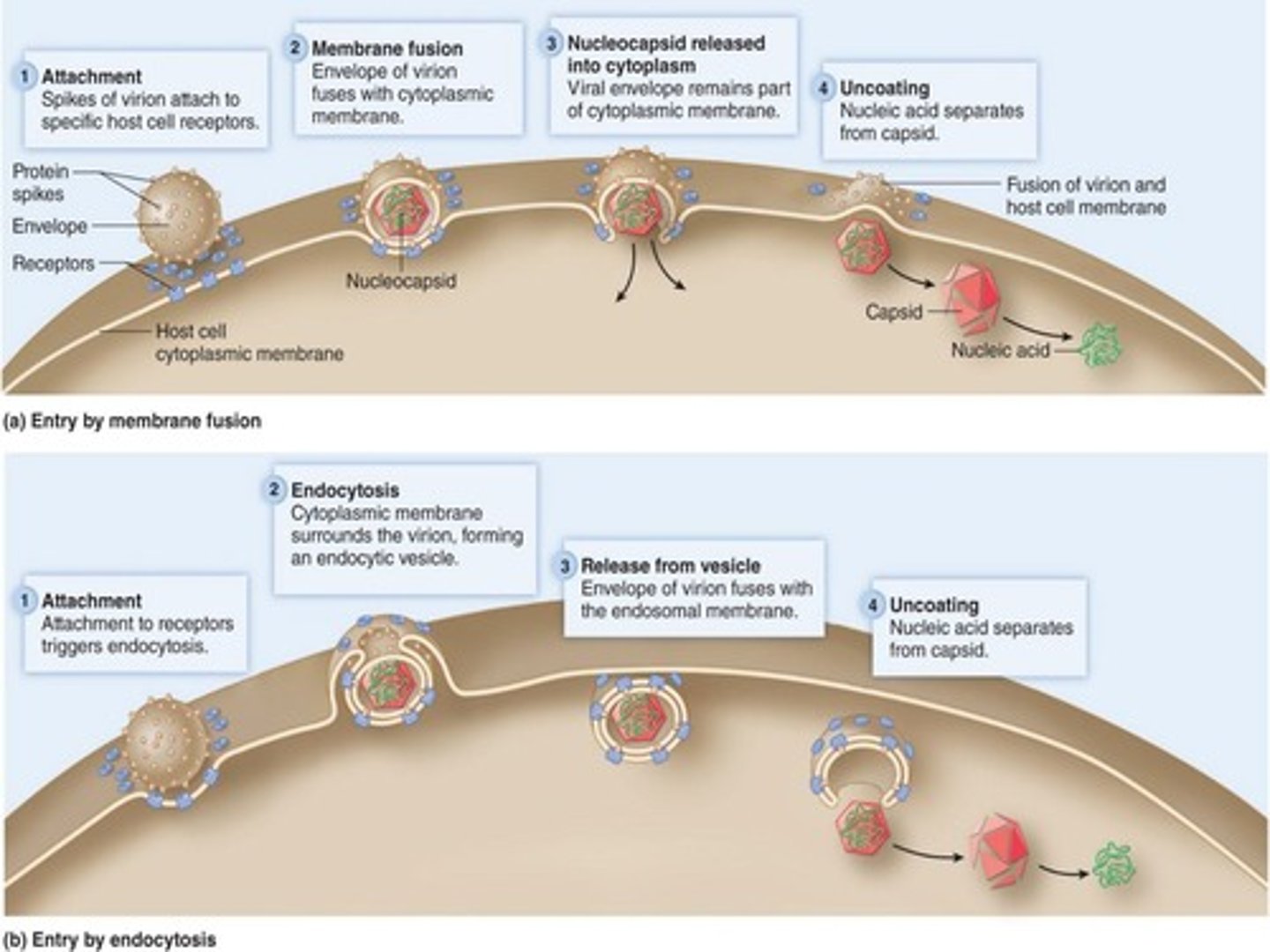
What is the generalized infection cycle of animal viruses?
It consists of five steps: attachment, entry and uncoating, synthesis of viral proteins and genome replication, assembly, and release.
What occurs during the attachment phase of virus replication?
Virus attachment proteins bind to host cell receptors on the cell membrane.
What are the two mechanisms for entry of enveloped viruses?
Membrane fusion and endocytosis.
What happens during the synthesis of viral proteins?
Viral genes are expressed to produce structural and catalytic proteins required for replication.
What is the assembly phase in virus replication?
The protein capsid is formed, and the genome along with necessary enzymes are packaged within it.
How are most enveloped viruses released from host cells?
By budding, acquiring the envelope from the plasma membrane.
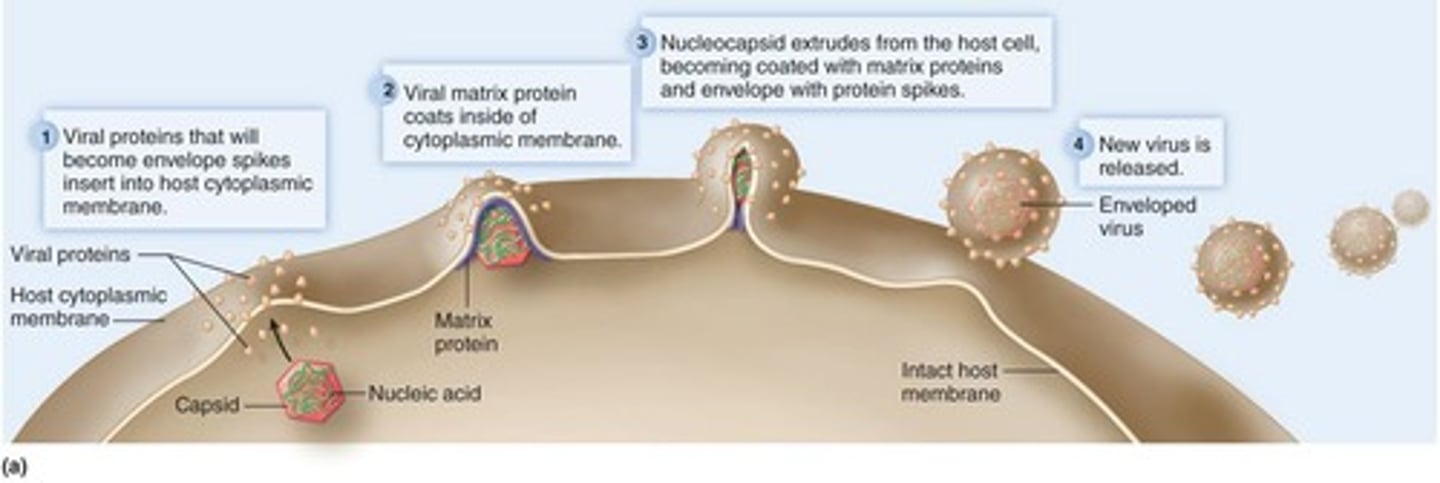
What triggers the release of naked viruses?
Naked viruses are released when the host cell dies.
What are acute infections characterized by?
Sudden onset of symptoms, relatively short duration, and productive infection leading to cell death.
What is an example of an acute infection?
Influenza, mumps, measles, and poliomyelitis.

What is the role of the immune response in viral infections?
The immune response can eliminate the virus and may lead to long-lasting immunity.
What is apoptosis in the context of viral infections?
A normal cellular process that may be triggered by viruses prior to the release of viral particles.
How can viruses be transmitted from one host to another?
Through shedding in feces, urine, genital secretions, blood, or respiratory secretions.
What are examples of acute infections?
Influenza, mumps, measles, and poliomyelitis.
What characterizes persistent infections?
They can continue for years, with or without symptoms.
What are the two categories of persistent infections?
Chronic infections and latent infections.
What is a chronic infection?
Characterized by continuous production of low levels of viral particles, e.g., hepatitis B.
How can chronic infections be transmitted?
A person can transmit the virus even in the absence of symptoms.
What is a latent infection?
The viral genome remains silent but can reactivate to cause a productive infection.
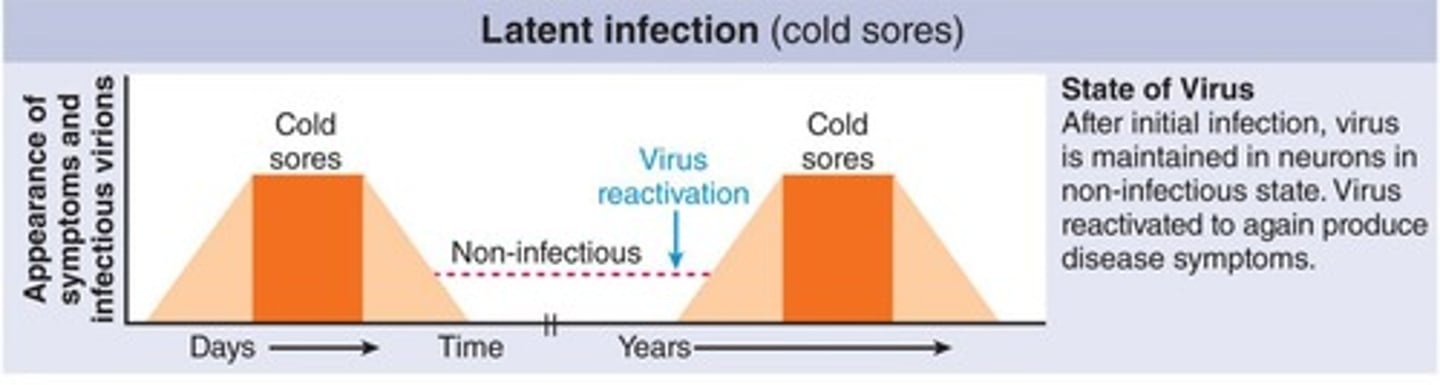
What is a provirus?
A silent viral genome that can integrate into the host genome or exist independently.
Give an example of a virus that can cause latent infections.
Herpes simplex type I virus (HSV-1).
What is the cytopathic effect?
Distinct morphological alterations in infected cells due to viral replication.
What is a plaque assay?
A method to quantify viruses by counting clear zones formed by lysis of infected cells.
What does ID50 represent?
Infective dose, the dilution at which 50% of hosts are infected.
What does LD50 represent?
Lethal dose, the dilution at which 50% of hosts are killed.
What is hemagglutination?
The clumping of red blood cells by some animal viruses.
What are prions?
Infectious agents composed only of protein, causing slow, fatal diseases.

What is the general term for diseases caused by prions?
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs).
What is PrPC?
Normal prion protein found in uninfected cells, especially neurons.
What is PrPsc?
Disease-causing prion protein that is resistant to protease digestion.
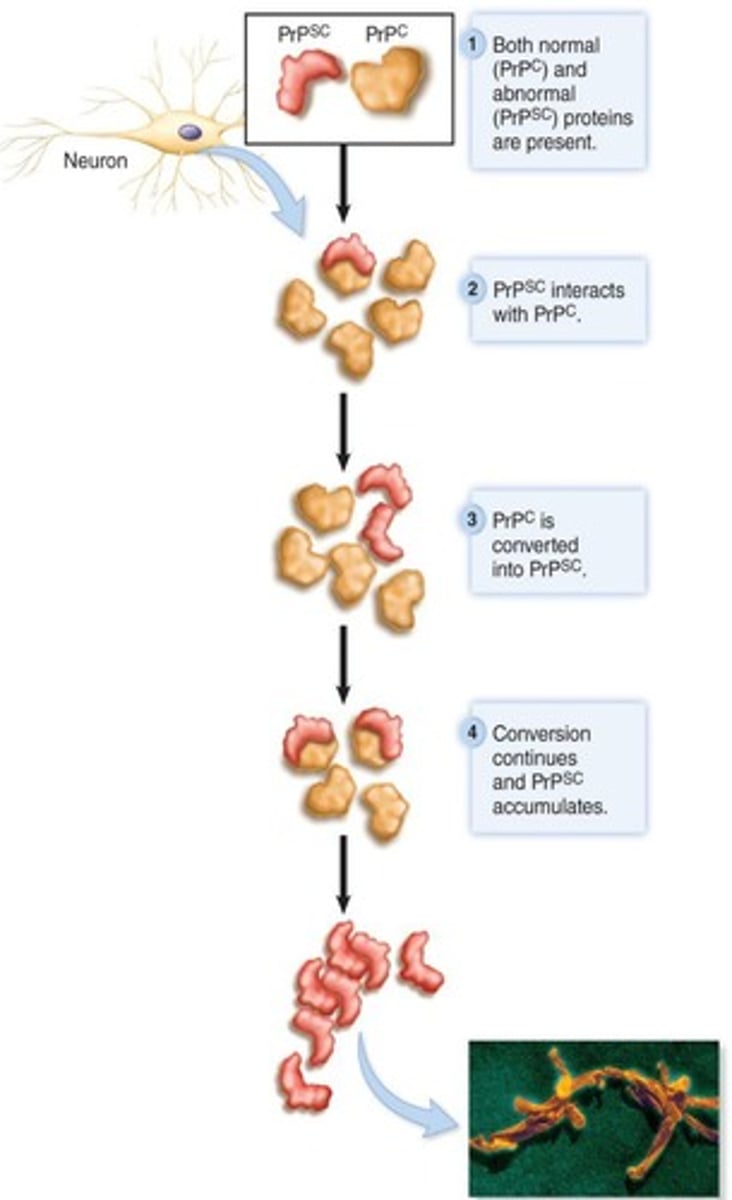
How do prions replicate?
By converting normal host proteins (PrPC) into disease-causing prion proteins (PrPsc).
What is a characteristic of prion transmission?
Usually transmitted only within the same species due to amino acid sequence differences.
What disease is associated with mad cow disease in humans?
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
What is the significance of chronic wasting disease (CWD)?
It spreads among deer populations but has not been shown to transmit to humans.
What is the role of cell or tissue culture in virology?
Used to cultivate viruses as they can only grow inside living cells.
What is the importance of inclusion bodies in virus identification?
They are distinct regions formed in infected cells that indicate viral replication.
What is the primary method for quantifying viruses?
Plaque assay is the most precise and commonly used method.
What types of cells can be used to study virus growth?
Living animals, embryonated chicken eggs, and human or animal cells.
What distinguishes infective from non-infective virions?
Electron microscopy can be used to count and distinguish them.
What is the effect of viral infections on cell cultures?
They can cause morphological changes, such as cell detachment or lysis.