ch 4-6 microbio, unit one
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
microbial growth
an increase in the number of cells in a population
binary fission
one cell divides into two identical cells. This is an exponential process
1 - 2 - 4 - 8 - 16

streak plate
A sterilized inoculating loop is dipped in solution containing organisms.
The loop is passed across 1/3 of the plate in parallel streaks.
The loop is then sterilized (with fire).
The loop is passed across the next 1/3 of the plate, touching the first 1/3 of the plate only at the start.
The loop is sterilized again.
The loop is passed across the last 1/3 of the plate, again only touching the 2nd 1/3 of the plate at the start.
advantages of agar
Not degraded by most bacteria
Not destroyed at high temperatures (can be sterilized)
Solid up to 95°C
Lag Phase
when cells are added to a media they must begin synthesizing macromolecules and obtaining nutrients to divide. No growth in this phase
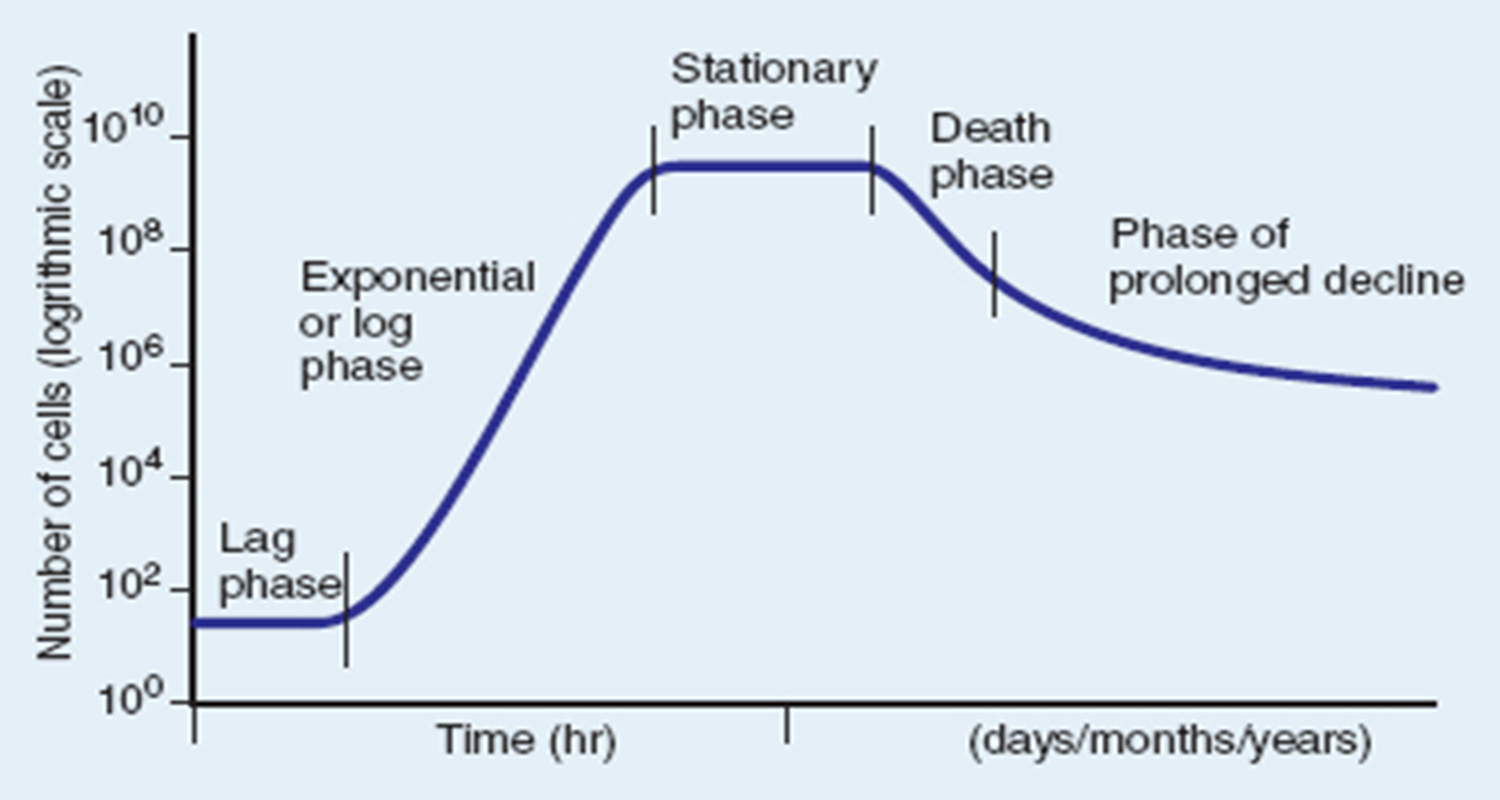
Log Phase or exponential phase
cells divide at a constant rate, which is exponential.
This is when the generation time is calculated.
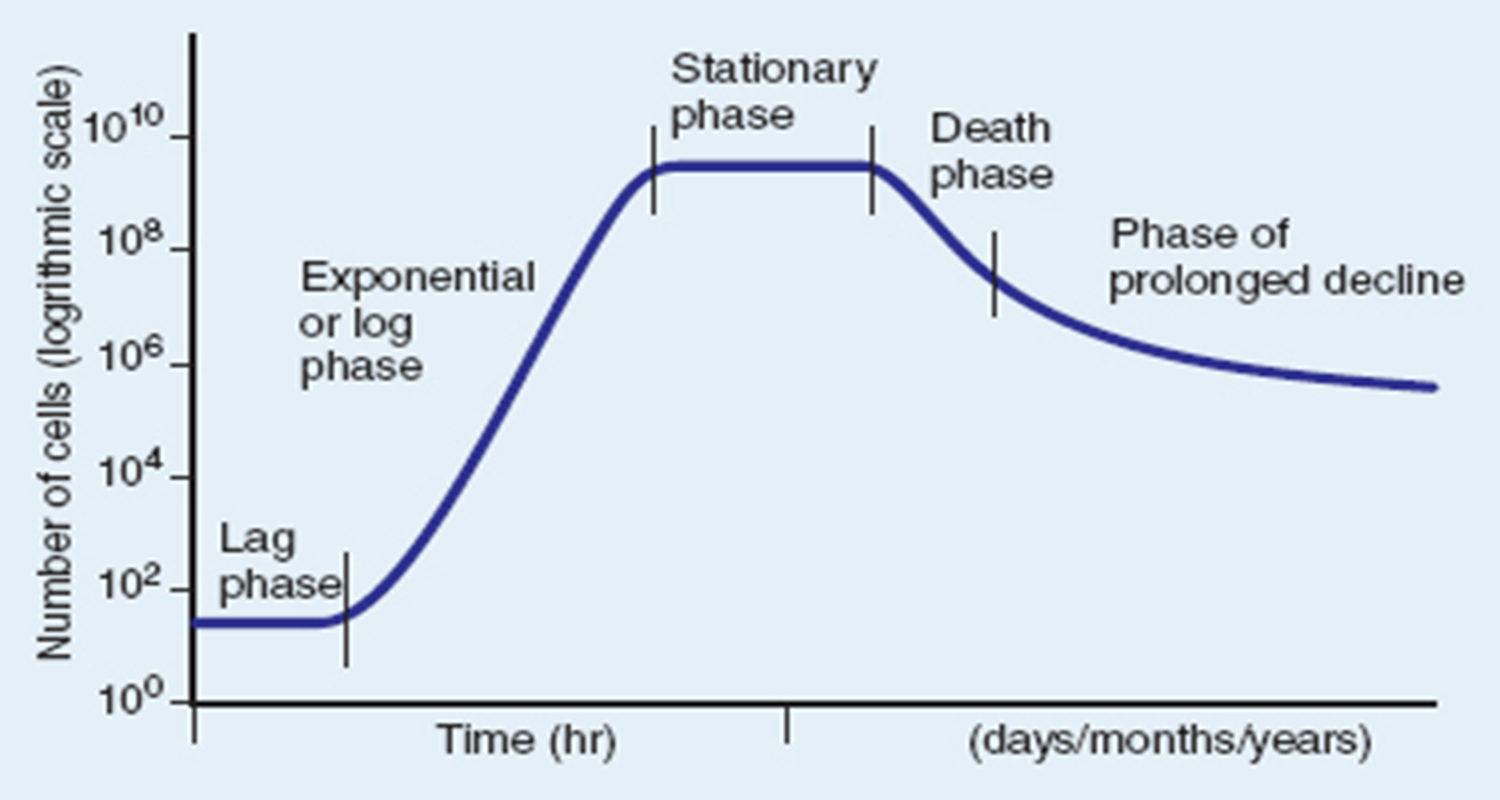
Stationary Phase
as nutrients diminish, the rate of growth decreases to the point that it equals the rate of death.
birth=deathrate
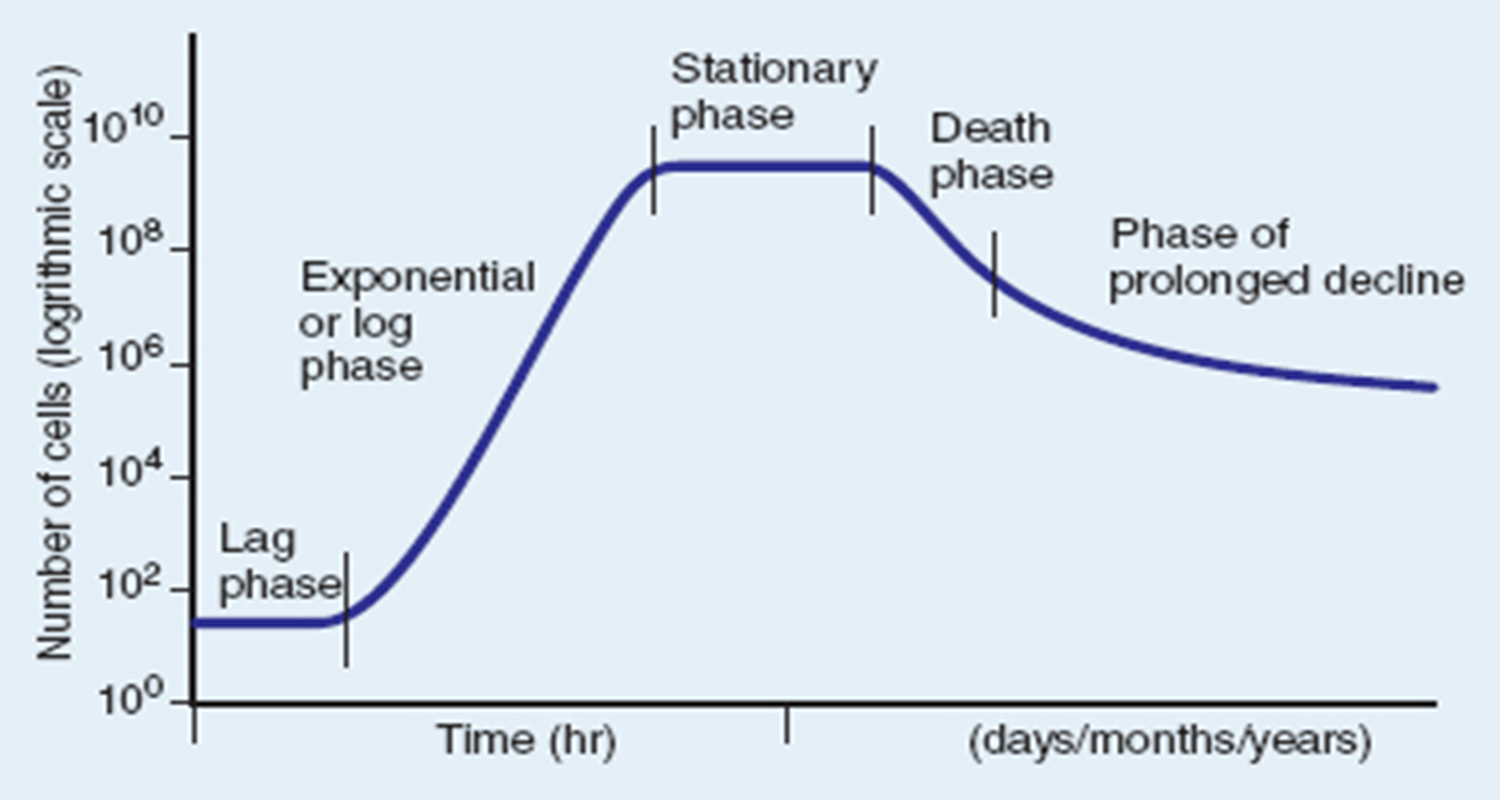
Death Phase
nutrients are depleted to a point that the constant rate of cell death is greater than that of cell growth.
cell death > growth
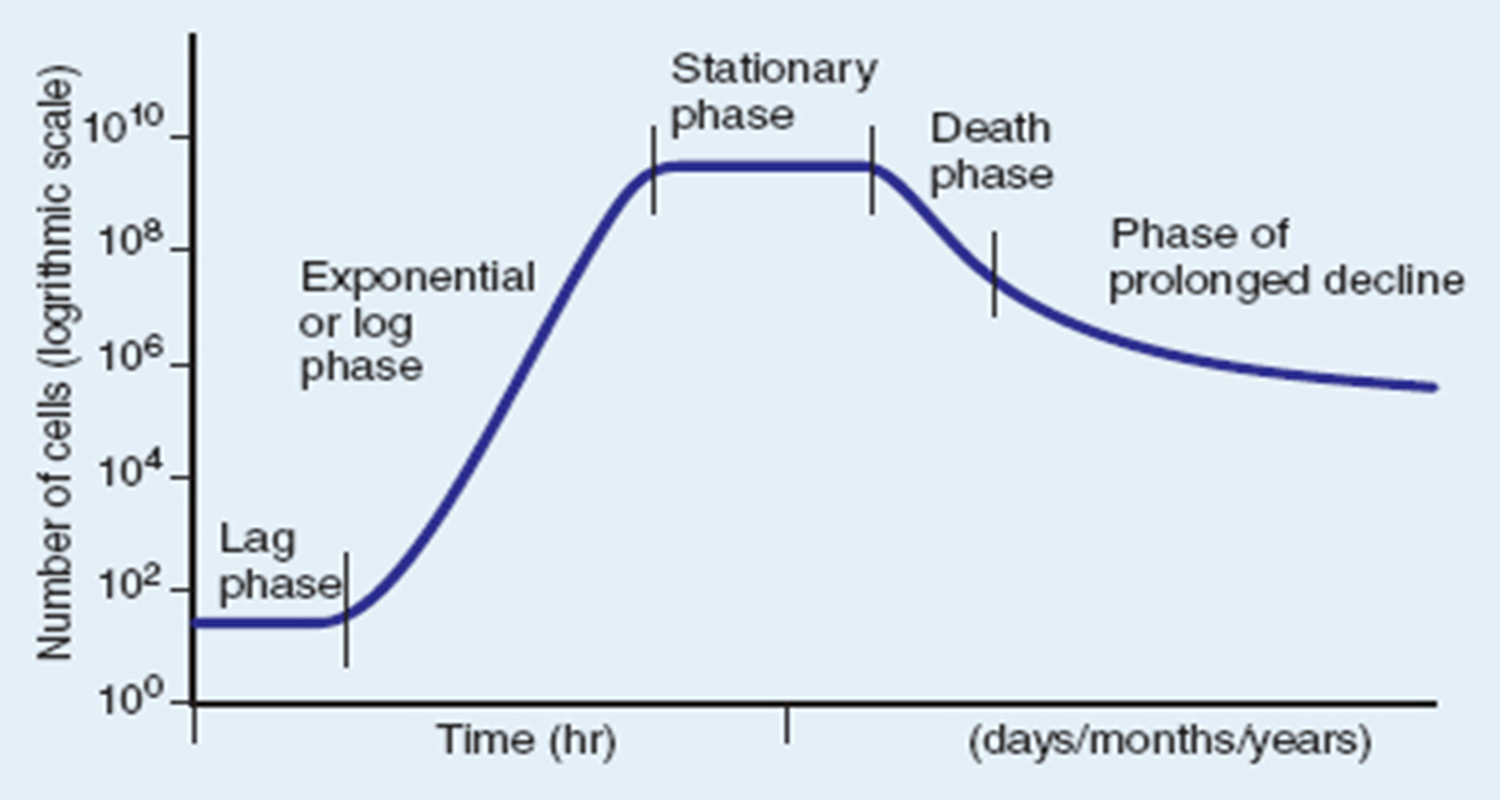
Prolonged Decline
the final 1% of cells will continue to decline in number at a slower rate, lasting days to years.
The “fittest” cells survive the longest.

closed system
nutrients are not renewed and waste is not removed
organisms display a predictable growth pattern
agar is an example of this
open system or continuous culture.
Cells kept in a state of continuous growth if nutrients are continuously added and waste products are removed.
Growth on agar plate
Cells at the outer most part of the colony are most likely to be found in the log phase
Those in the very center are most likely in the death phase.
In between are cells in the stationary phase.

Psychrophile
optimum temperature between -5 – 15°C
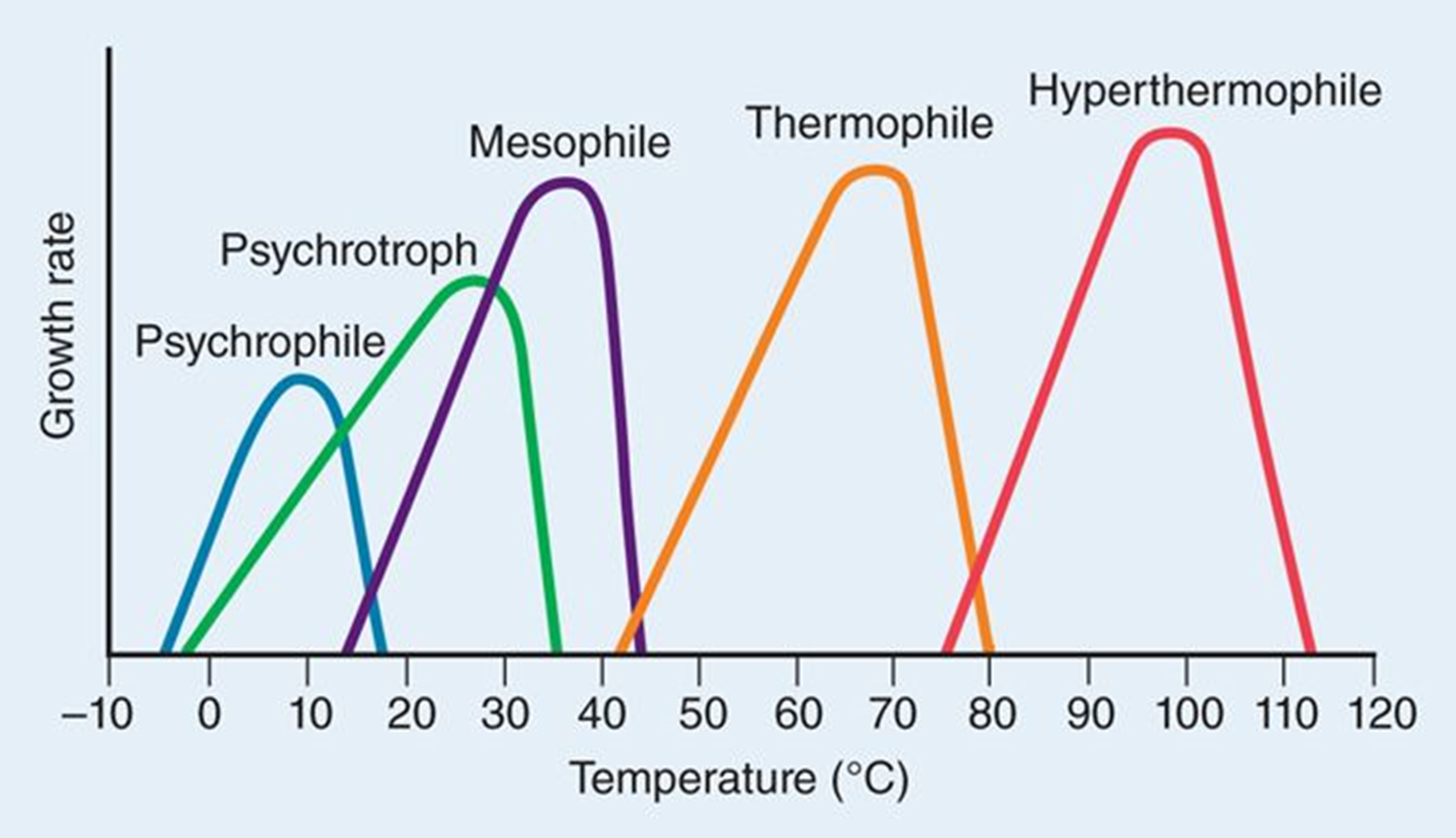
Mesophile
optimum temperature between 25 – 45°C
infect human and cause disease
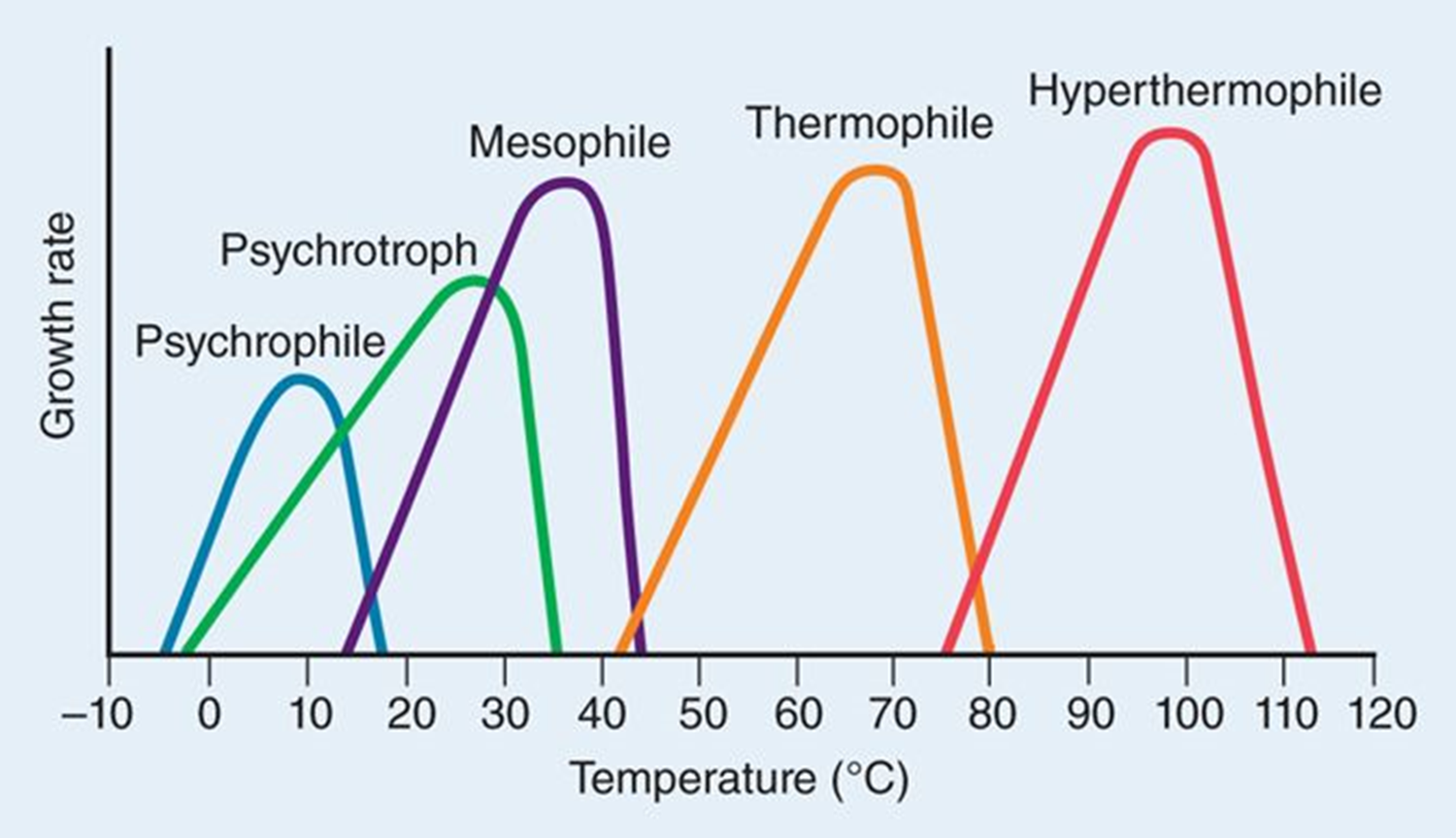
Thermophile
optimum temperature between 45 – 70 °C
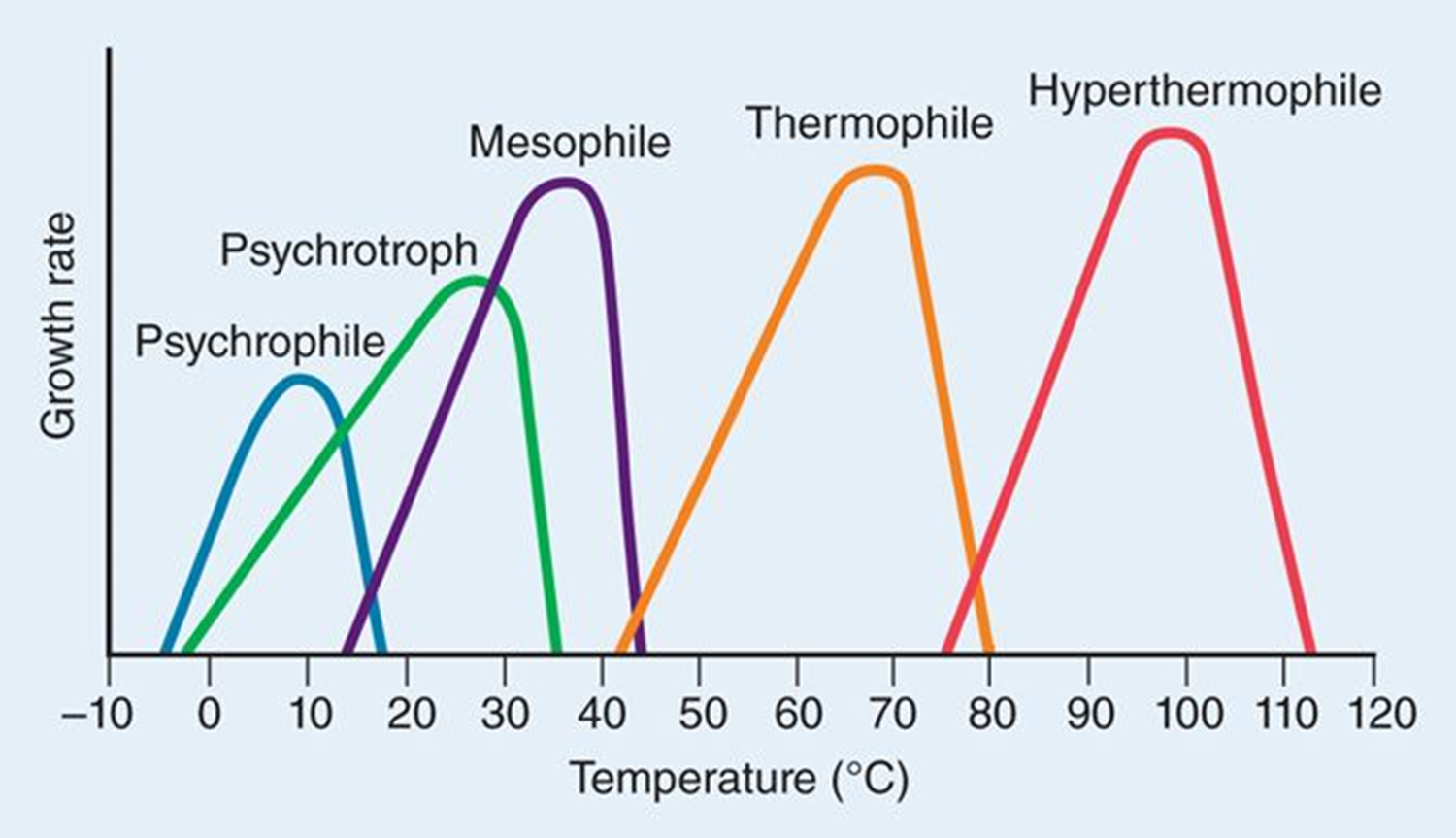
Hyperthermophile
optimum temperature 70°C or greater
mostly archaea
proteins resistant to denaturing from heat
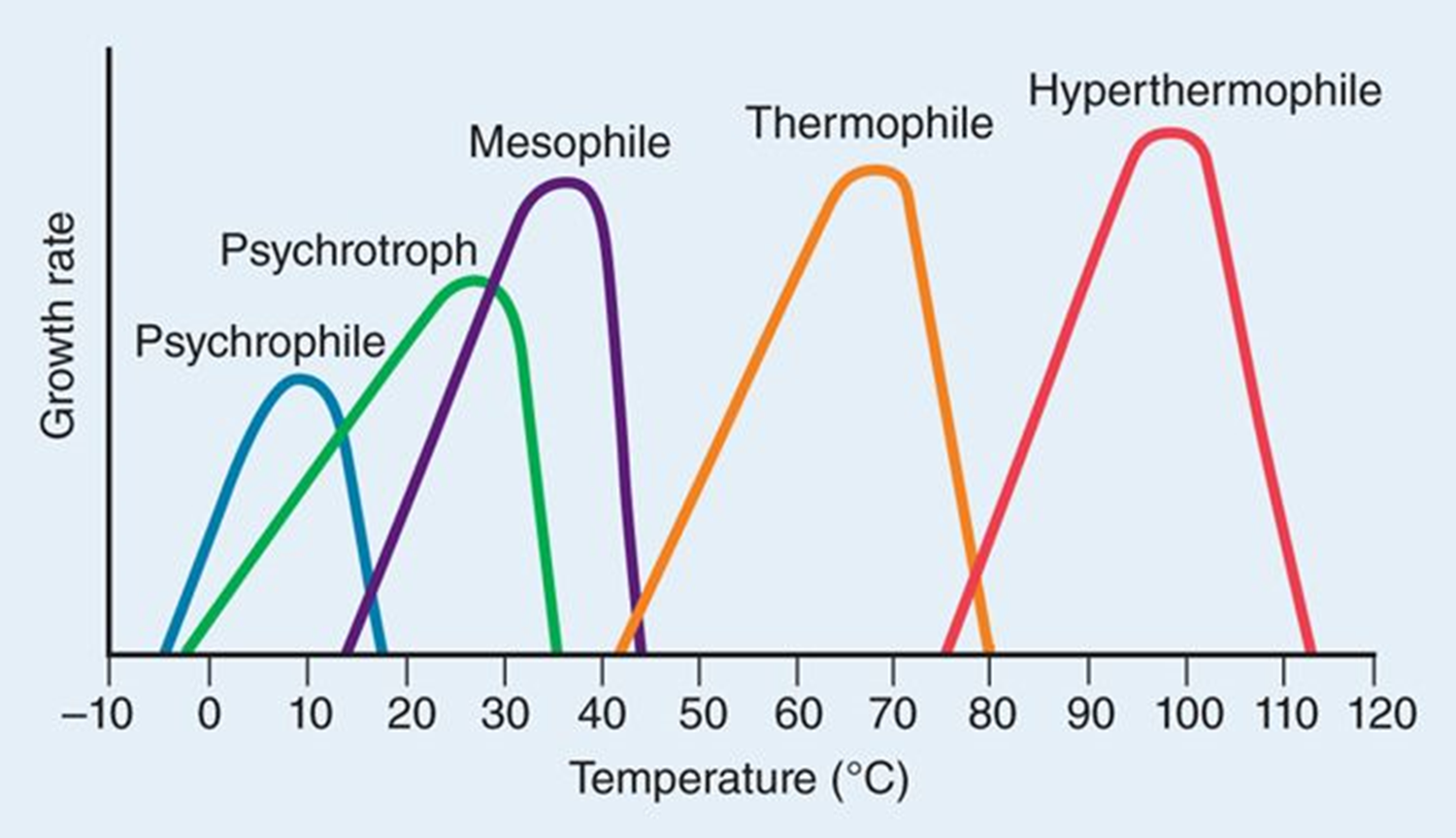
Temperature
Mycobacterium leprae and Treponema pallidum(syphilis) prefer cooler regions of body ex feet, hands, fingers
Immune system triggers fever to kill or reduce bacterial growth
Obligate anaerobes
Cannot multiply in the presence of oxygen, or are killed by O2 toxic derivatives (superoxide and hydrogen peroxide).
lack the enzymes superoxide dismutase (needed to convert superoxide to hydrogen peroxide) and catalase (needed to convert hydrogen peroxide to water and O2).
C botulinum and C tetani
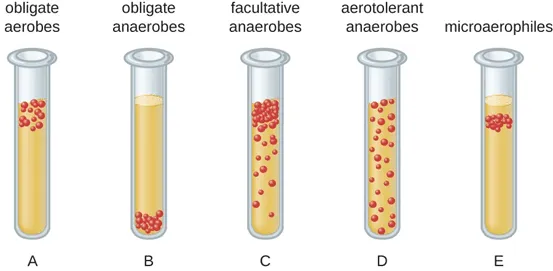
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Able to grow in the presence of oxygen, but do not use it to produce energy
ex Streptococcus pyogenes
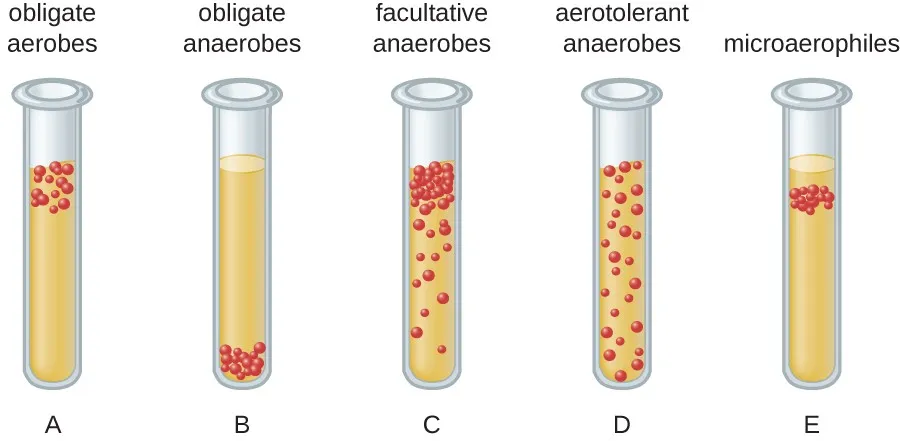
Facultative Anaerobes
Do not require O2 to grow
However, if oxygen is present these organisms switch to aerobic respiration and grow FASTER
ex e coli
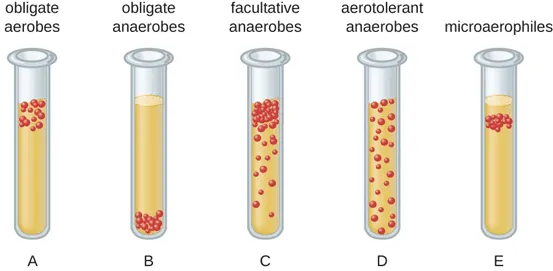
Microaerophiles
Require small amounts of O2 in order to grow
Growth is inhibited by higher concentrations of oxygen
Example: Helicobacter pylori
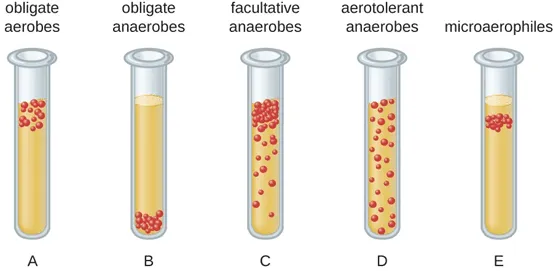
Obligate Aerobes
Have an absolute requirement for O2 in order to grow
pH
Most bacteria live and grow in a pH range of 5-8, and grow best at a pH at 7 (neutrophiles)
Acidophiles
prefer pH below 5.5
Alkalophiles
prefer pH above 8.5
neutrophiles
prefer pH of 7
Helicobacter pylori is an ex
neutralizes stomach acid in its vicinity by releasing the enzyme urease
halotolerant
bacteria able to resist loss of water and grow in high salt environments
ex Staphylococcus aureus
Autotrophs
use inorganic carbon (CO2) to produce organic compounds through carbon fixation
Heterotrophs
use organic molecules as their carbon source
phototroph
Organisms that harvest energy from sunlight are
chemotrophs
organisms that obtain energy by breakdown(oxidizing) chemical compounds are
can be organic(organo)
inorganic(litho)

chemo organotrophs
breakdown (oxidize) organic chemical compounds
chemolithotrophs
breakdown(oxidizing) of chemical compounds that are inorganic
Complex media
nutrient-rich growth mediums with an unknown, variable chemical composition
contains a variety of ingredients
These generally contain meat extract or other cells (example: Blood agar)
Chemically defined media
a growth broth/agar with a precisely known composition, using pure, identified chemicals (salts, sugars, amino acids, vitamins) for exact nutrient control
These are used to study the nutritional requirements of bacteria.
exact composition

Selective Media
inhibit the growth of organisms other than the one being sought
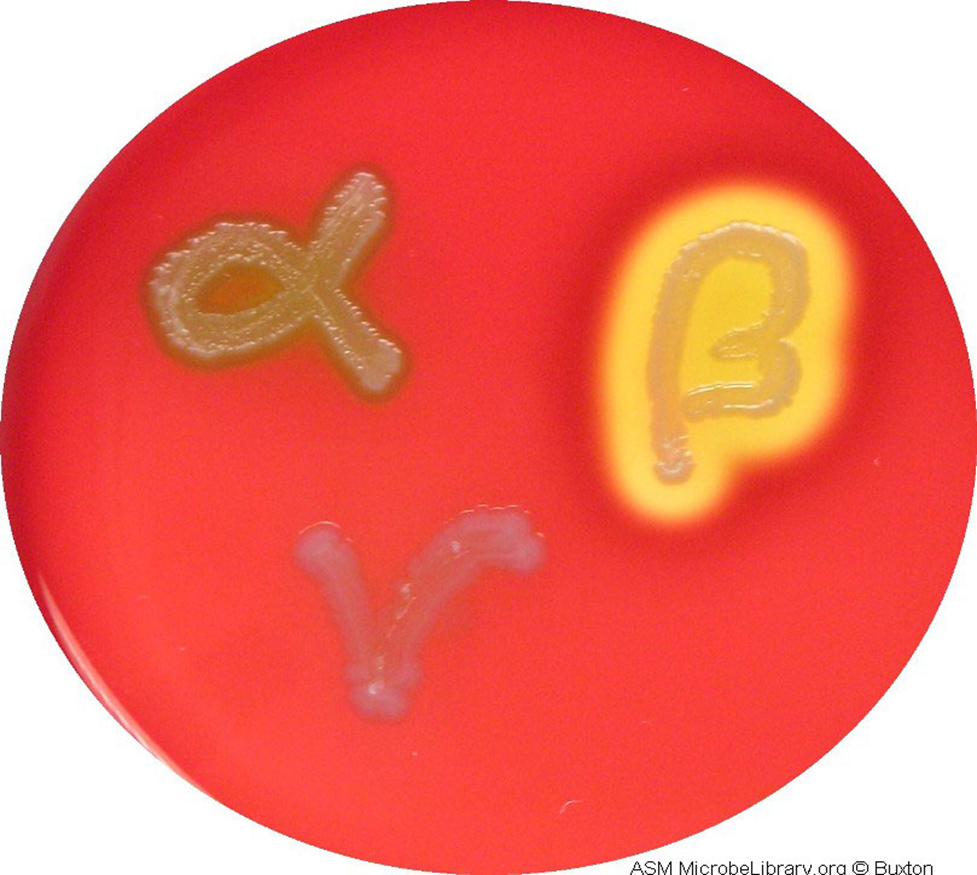
Differential Media
contain a substance that certain bacteria change in a recognizable way, changes color
Example: Blood agar contains RBCs that are lysed by Streptococcus pyogenes to produce clear zones on the red plate.

Direct Cell Counts
Total number of cells, living AND dead
Direct Microscopic Count
using a microscope to count cells
Coulter Counter
using electrical current to count cells
Flow Cytometer
using light to count cells
cells pass through laser
Viable Cell Counts
Total number of cells that are able to grow (living cells)
Plate Count
Small number of cells are plated on agar, and the number of colonies is counted (each colony represents one cell from original sample)
Membrane Filtration
Cells are collected with a membrane filter from dilute water.
The cells are then plated and colonies are counted (similar to plate count).
Most Probable Number
Statistical estimate of cell number. Not precise.
Turbidity (cloudiness)
more turbidity= more cell growth or cell count
The amount of scattered light in a broth is measured using a spectrophotometer.
As the number of cells increases, the amount of light that passes through the broth decreases.
This requires a very large number of cells to make a broth turbid.
total weight
This is tedious and time consuming, but is most effective for measuring growth in organisms that do not readily separate into individual cells (filamentous organisms)
Measuring Biomass
counting the mass or size of the population in general
Keep in mind that if the mass of a sample doubles, then the number of the cells doubled
Sterile
completely free of all viable microbes (bacteria, virus, etc.)
Disinfect
eliminate most or all pathogens on a material
Bacteriostatic
prevents bacterial growth, does not kill bacteria
Antiseptic
a disinfectant that is non-toxic enough to be used on skin
Moist heat
Denatures proteins
very effective at killing bacteria
Boiling
kills most microorganisms in 5 minutes. Notable exception: endospores
MOIST HEAT
Pasteurization
brief heating used to reduce the number of spoilage organisms and to kill disease-causing organisms.
Used for milk, juice, wine, and other products that are damaged by boiling. Example: milk is heated to 72°C (160°F) for 15 seconds.
MOIST HEAT
Autoclaving
heat water in an enclosed vessel.
As steam is produced, the pressure in the vessel increases beyond atmospheric pressure and allows for the temperature to reach >100°C
MOIST HEAT
Dry Heat
not as effective as moist heat. Requires longer times and higher temperatures
Incineration
fire oxidizes cell components to ashes
dry heat
Dry heat ovens
oxidizes cell components and denatures proteins.
Often used for laboratory glassware
Dry heat
filtration
removes microbes from fluid or air
Radiation
damage to cell dependent upon wavelength
Ionizing radiation- destroys DNA and cytoplasmic membrane. Used to sterilize heat-sensitive materials and items that have been packaged.
Ultraviolet light- damages DNA, but penetrates poorly. Used to destroy microbes in the air, drinking water, and on surfaces
Pressure
extremely high pressure may denature proteins and alter permeability of cell membrane.
Used to extend the shelf life of certain commercial foods
Alcohols
coagulates enzymes and proteins, and damages lipid membranes
Kill vegetative bacteria and fungi. Not effective against endospores and some viruses.
Relatively non-toxic and inexpensive
disinfectant
Aldehydes
Inactivate proteins and nucleic acids
Can kill all forms of microbial life, including endospores and viruses
Irritating to the respiratory tract, skin and eyes
Ethylene Oxide Gas
Commonly used to sterilize medical devices
Destroys all microbes by reacting with proteins
Carcinogenic
Halogens
Chlorine and Iodine are common disinfectants that act by oxidizing/denature proteins and other cell components
Chlorine is used to disinfect inanimate objects, surfaces, and drinking water. Too irritating to use on skin
Iodine can be used as an antiseptic on the skin, but is not as effective against endospores
Metals
Metal containing compounds, such as silver nitrate, bind to proteins and interfere with their function
Can not be used medically because of toxicity to humans
Act as preservatives in industry
Peroxygens
Powerful oxidizing agents that can be used as sterilants
Readily biodegradable and less toxic to humans than ethylene oxide and aldehydes
Lower concentrations of hydrogen peroxide can be used as antiseptic on skin
preservation of perishable products
Weak organic acids may be added to food (bread, cheese, juice) to prevent microbial growth
Nitrate is added to cured meats (cold cuts, bacon, smoked fish) in order to prevent the growth of Clostridium botulinum
Refrigeration slows enzyme activity and bacterial growth, with the exception of Psychrophilic organisms
Freezing preserves food by stopping microbial growth
dry preservation
Adding sugar and salt draws water out of cells, dehydrating them. Used in jams/jellies and cured meats.
Desiccation, or the removal of water, is used to produce jerkies.
Lyophilization (freeze-drying) is used to preserve coffee, milk, meats, and vegetables. This stops microbial growth but does not kill bacteria or fungi.
Oxidation
a process in which an electron is removed from a molecule. This often results in breaking a chemical bond
Reduction
a process in which an electron is gained by a molecule.
This often results in creating a chemical bond
Metabolism
the sum total of chemical reactions used for biosynthetic and energy-harvesting processes
Anabolism- processes that uses energy (ATP) to synthesize and assemble subunits of macromolecules; biosynthesis
Catabolism- processes that harvest energy released during the breakdown of compounds to synthesize ATP
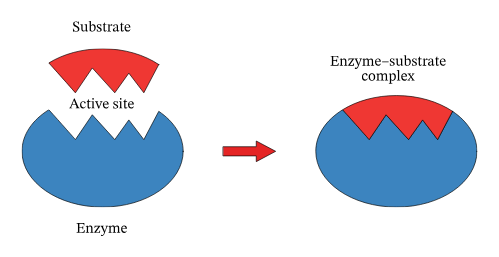
Enzymes
biological catalysts, accelerating the conversion of one substance, the substrate, into another, the product. reaction happen faster
Reaction rates are increased because ____ lower the activation energy of the reaction. This is the energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction.
active site
a specific groove or pocket where a substrate binds and a chemical reaction is catalyzed
Organic cofactor (coenzyme)
derived from vitamins
help enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions, acting as temporary carriers for atoms or electrons
inorganic cofactor
metals like magnesium, zinc, copper, and other trace elements
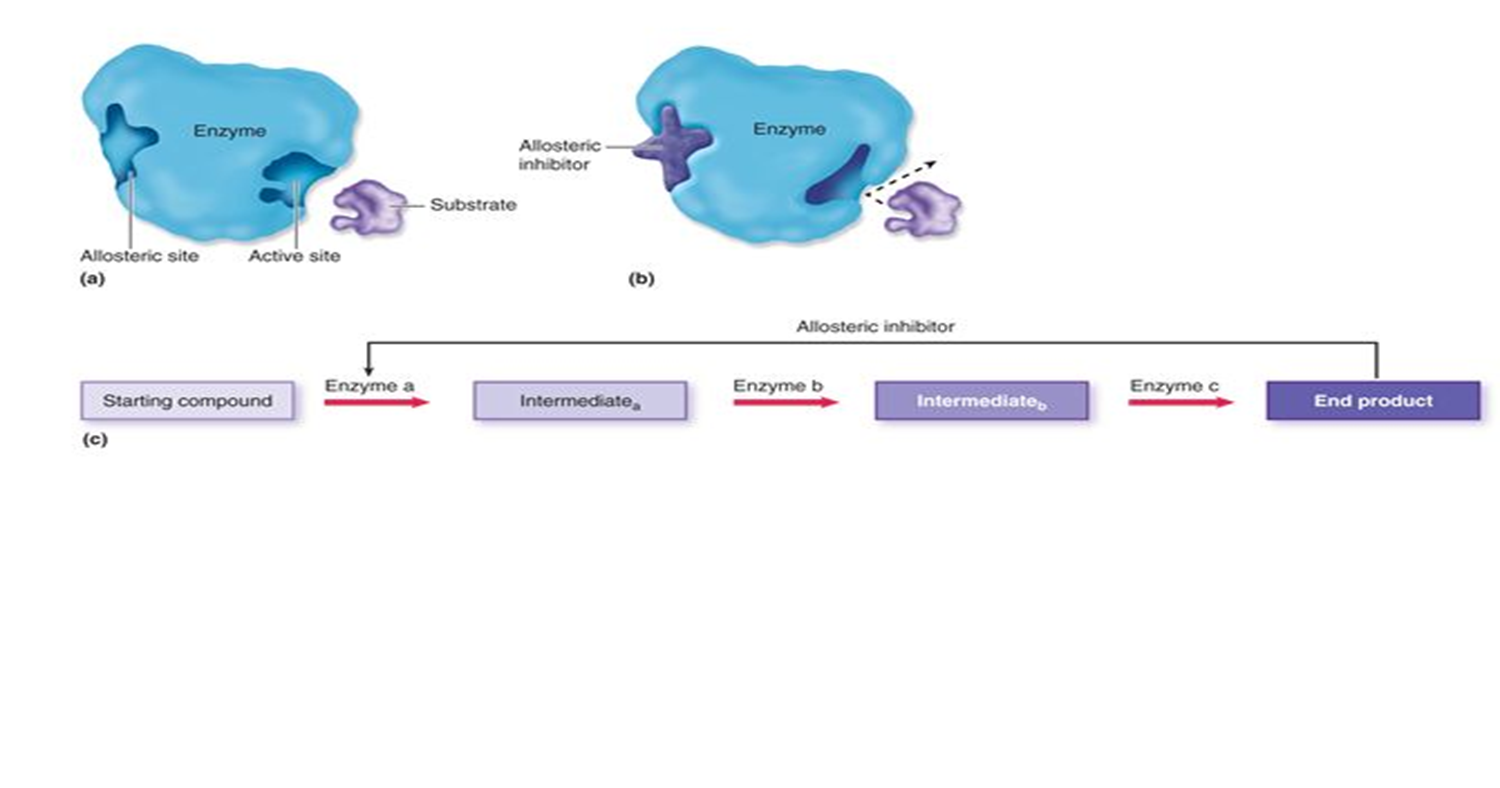
allosteric regulation
process in which a molecule binds to the back of enzyme and changes activity by decreasing or increasing activity
a molecule binds away from the active site, which can include both inhibition (like noncompetitive) and activation, affecting enzyme activity.
not a substrate
makes product when we need it, stops when we have it(feedback mech)
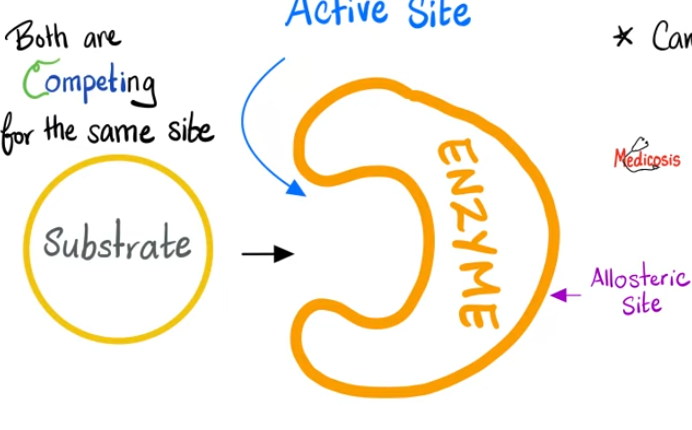
Competitive Inhibition
A molecule that is similar in structure binds at the active site of the enzyme and blocks the substrate from entering.
binds to active site
looks similar to substrate
blocks substrate from binding
competes with substrate
Non-Competitive Inhibition
A molecule binds elsewhere on the enzyme( the back), changing its shape and preventing the substrate from entering the active site.
form of allosteric inhibition where the inhibitor binds to an allosteric site (the back of enzyme)
Always reduces enzyme activity (inhibits).
not competing with substrate
Ionizing radiation
destroys DNA and cytoplasmic membrane.
Used to sterilize heat-sensitive materials and items that have been packaged.
Ultraviolet light
damages DNA, but penetrates poorly.
Used to destroy microbes in the air, drinking water, and on surfaces
Catalase
Definition: An enzyme that decomposes hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) into water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂). H2O2 → H2O + O2
Function: Protects cells from oxidative damage caused by H₂O₂.
Microbial Use: Common in aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria; used in the catalase test to differentiate species (e.g., Staphylococcus spp. vs. Streptococcus spp.).
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
Definition: An enzyme that converts superoxide radicals (O₂⁻) into hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) and oxygen (O₂). O2- —> H2O2 + O2
Function: Protects cells from damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Microbial Use: Found in aerobic and facultative anaerobes; important in pathogens for surviving host immune responses.
Peroxidase
Definition: An enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) to water (H₂O) using an electron donor. H2O2—> H2O
Function: Protects cells from oxidative stress without releasing oxygen gas.
Microbial Use: Common in aerobic and facultative anaerobes; plays a role in pathogen defense against host immune responses.
Bactericidal
kills bacteria
phile
factors optimal for bacteria growth
tolerant
do not require a particular environmental factor
not negatively affected factor
ex halotolerant (can grow in salt environment but does not need salt)
Chemoorganoheterotroph
uses organic molecules for energy and for carbon
Chemoorgano- energy source
heterotroph- carbon source
Photoautotroph
uses light for energy and makes its own organic molecules from CO2
Photo- energy
autotroph- carbon source