Cardiology Diagnostics: Serum Studies and PCI
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
AST
enzyme present in tissues of high metabolic activity
-heart, liver, and skeletal muscle cells have higher concentrations of this when compared to kidney, pancreatic, and red blood cells
36, pregnancy, liver
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST/SGOT)
-Peak elevation: 24-__ hours, clearing from the body after that
-Interfering factors: __________, pyridoxine deficiency (decreases), DKA, _____ disease (increases), and uremia (increases)
-Females tend to have slightly lower levels than males
5, total, hemolysis
Lactic Dehydrogenase (LDH)
-Enzyme found in many types of cells like heart, liver, RBCs, kidneys, skeletal muscle, brain, and lungs
-_ isoenzymes
-LDH measures ______, meaning throughout the whole body
-Interfering factors = _________ of sample and strenuous exercise
LDH1, 2, 3
LDH isoenzyme most specific for the heart, where elevation is indicative of myocardial injury
-not as useful as troponin or CK-MB
-peaks in _-_ days
LDH 2
LDH isoenzyme associated with the reticuloendothelial system, where elevation is indicative of pulmonary injury or disease
oxygen, myocardium, 6, trauma
Myoglobin
-Myoglobin is an ________ binding protein found in cardiac and skeletal muscle, which provides early index of damage to the _______________
-Peak at 4-_ hours
-Interfering factors include IM injection, _______, inflammation or ischemic changes to non-cardiac skeletal muscle
-Can occur in the urine, turning it red
3, 18, surgery, pregnancy
Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK)
-Predominantly found in heart muscle, skeletal muscle, and the brain. There are _ isoenzymes (CK-BB, CK-MB, CK-MM)
-Peak at __ hours but will stay elevated if damage is not resolved
-Interfering factors include IM injections, strenuous exercise, recent _______, and early _________
CK-MB, 12-24
CPK isoenzyme specific for myocardial cells, which helps to quantify the degree of MI and timing (onset)
-Peaks at __-__ hours but elevates in 3-6 hours
-Rises only in MI
CK-MM
CPK isoenzyme predominantly found in skeletal muscle, varying according to a person’s muscle mass
CK-BB
CPK isoenzyme predominantly found in brain / lung
disease, MI, 12, 24, dialysis
Cardiac Troponins: Troponin I/T
-Biochemical markers for cardiac ________, specific for cardiac muscle injury
-Utilization = evaluation of a patient with unstable angina, detection of reperfusion associated with coronary recanalization, estimation of __ size, detection of perioperative MI, severity of pulmonary emboli, and ventricular strain due to CHF
-Peak = I at __ hours, T at 12-__ hours
-Interfering factors = ________
peptides, renin, failure, BNP, older
Natriuretic Peptides
-Neuroendocrine ________ that oppose the activity of the ____-angiotensin system
-Utilized to identify and stratify patients with heart _________
-___ is the most specific subtype for cardiac issues
-Interfering factors are ________ age, cardiac surgery 1 month post op
lipid, vascular, familial, risk, pregnancy
Total Cholesterol
-Main _____ associated with arteriosclerotic _________ disease. It’s required for the synthesis of steroids, sex hormones, bile acids, and cellular membranes
-Used to screen for ________ lipid disorders, establish the ____ of cardiovascular disease, and evaluate lipid disorders
-Interfering factors include ___________, post oophorectomy, and post menopausal state
HDL
“healthy” cholesterol
-high density lipoproteins
-cholesterol minimal component
LDL
“lousy” cholesterol
-low density lipoproteins
-75% of cholesterol bound to LDL
Triglycerides
form of fat in the blood stream that constitutes most of the fat in the body
-part of the lipid panel test
-identifies the risk of developing coronary heart disease
-interfering factors include ingestion of fatty meals or alcohol and pregnancy
400
If a patient’s triglycerides are above ____ on a non-fasting panel, you need to repeat with a fasting panel
amino acid, coronary, malnutrition, renal, B
Homocysteine
-Intermediate ______ ____ formed during the metabolism of methionine
-Important predictor of __________, cerebral, and peripheral vascular disease. Can also be used for evaluation of ___________
-Interfering factors are increased age, ______ impairment, men/them, Vitamin _ deficiency, and smoking
Aortic arch
#1
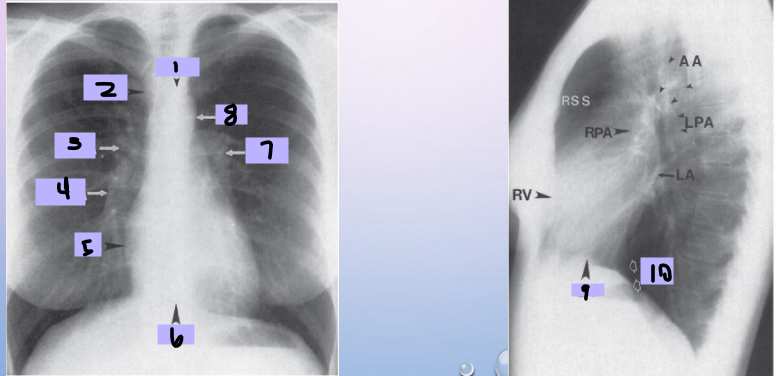
Superior vena cava
#2
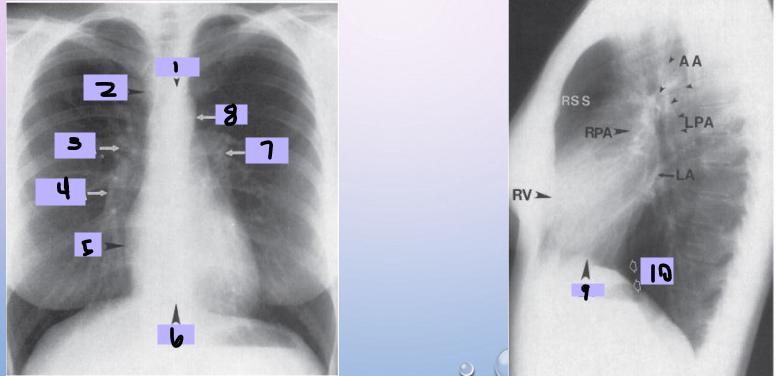
Right pulmonary artery
#3
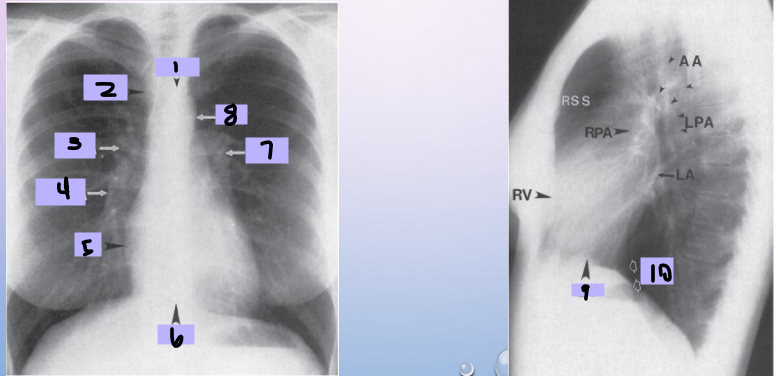
Right descending pulmonary artery
#4
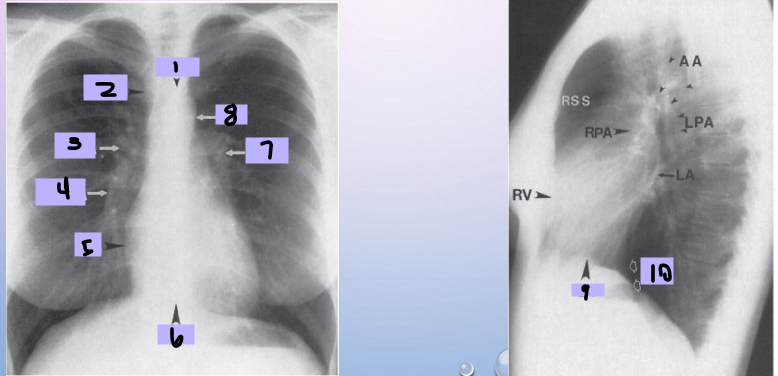
Right atrium
#5
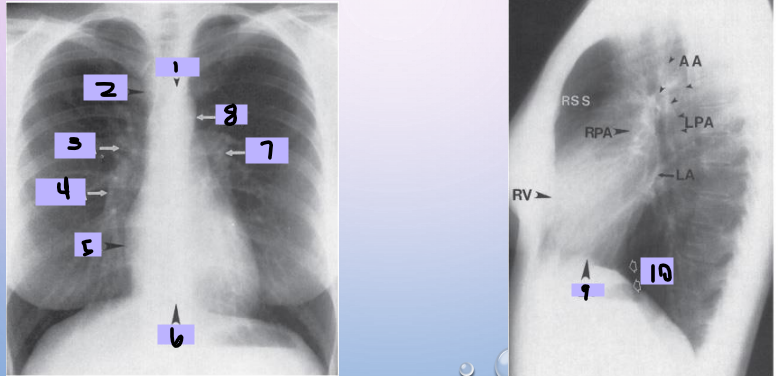
Right ventricle
#6
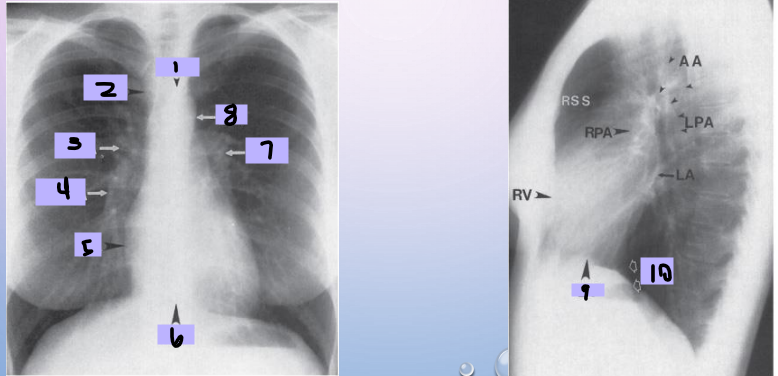
Left pulmonary artery
#7
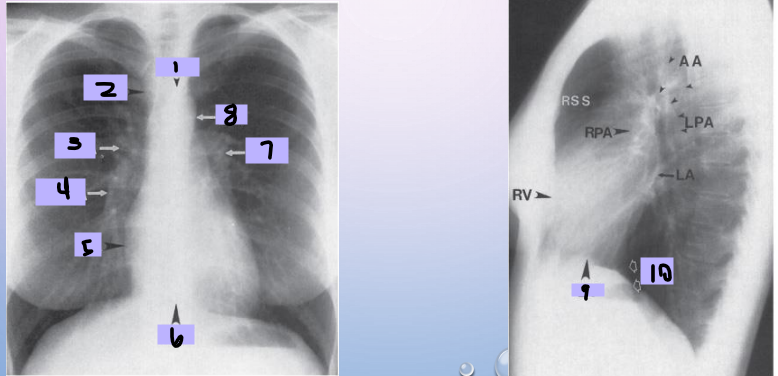
Descending aorta
#8
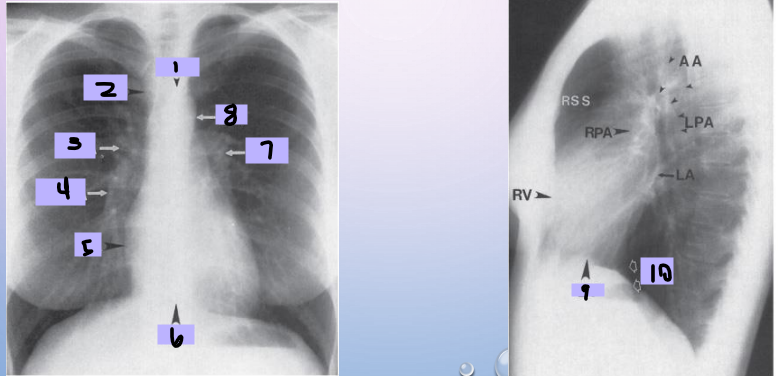
Left ventricle
#9
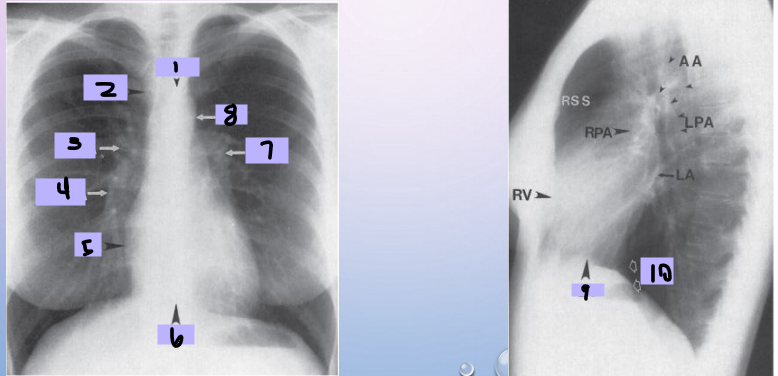
Inferior vena cava
#10
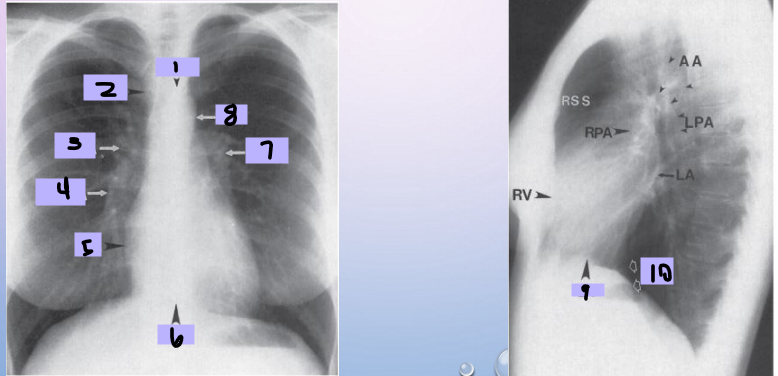
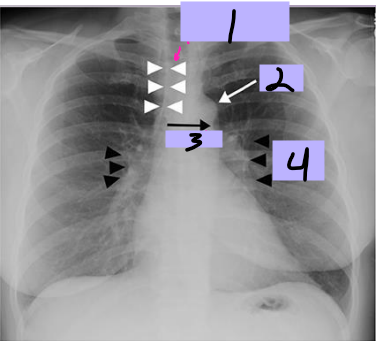
Paratracheal stripe
#1
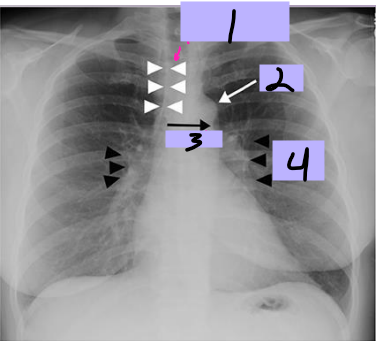
Aortic knob
#2
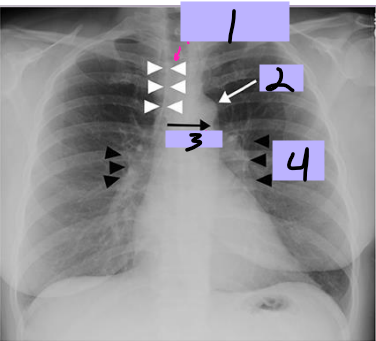
AP window
#3
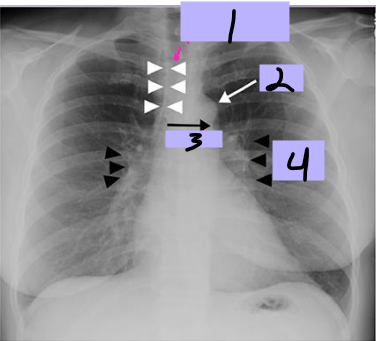
Hila
#4
nonsurgical, flow, circulation, structural, balloon
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
-Minimally invasive ___________ procedure performed to improve blood ____ in one or more segments of coronary ___________
-Can be used for evaluation/interventional treatment for ___________ heart disease like adult congenital heart disease or valvular heart disease
-Most commonly used revascularization procedure
-Primarily involves the use of ________ angioplasty + intracoronary stenting
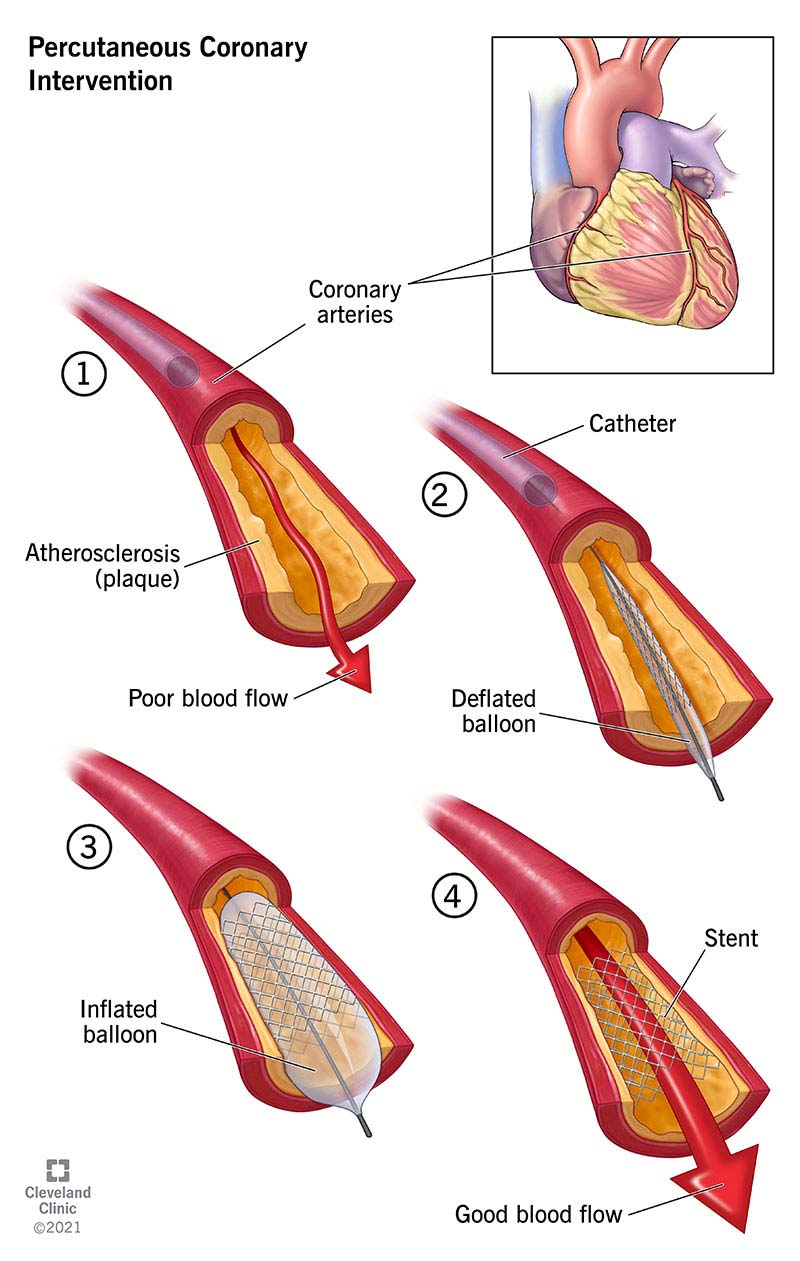
catheter, artery, blockage, widen, increase, stent
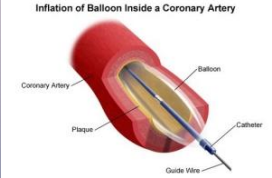
Balloon Angioplasty
-A specifically designed _________ is placed in a peripheral ______, and a tiny balloon is guided through the artery to a _________ within coronary circulation
-Balloon is inflated to _____ the opening and _______ blood flow to the heart. Part of PCI
-_____ is often placed during procedure to keep artery open after the balloon is deflated and removed