Conservation Bio Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/295
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
296 Terms
1
New cards
Anna Conservation Focus
increased natural disasters and invasives because European settler foresting practices. High mammalian extinctions.chall
2
New cards
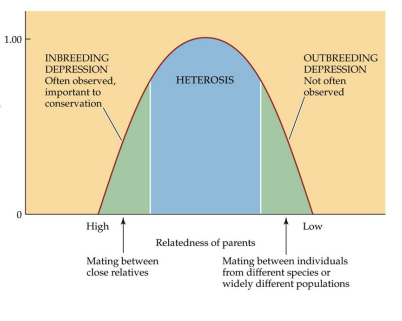
Outbreeding depression
lowered fitness that sometimes occurs when individuals of different subspecies or distinct populations mate and produce offspring
3
New cards
as population size declines, random effects become ___ influential in determining the fate of populations
more
4
New cards
Demographic stochasticity
random variation in birth and death rates among individuals over time in small populations
\
* Leads to increased annual variation in population growth rate (and therefore population size) over time
* May lead to skewed sex ratios in the population
* Effects are most pronounced in very small (
\
* Leads to increased annual variation in population growth rate (and therefore population size) over time
* May lead to skewed sex ratios in the population
* Effects are most pronounced in very small (
5
New cards
Total number of individuals in a species =
sum of all individuals from each distinct population
6
New cards
protecting _____ is the key to preserving species
populations
7
New cards
species extinction probability is related to both __ and __ of remaining populations
number and size
8
New cards
as populations are reduced in ____ and , populations are more likely to go extinct__
number and area
9
New cards
Population Decay
precursor to extinction
* delcines in population size
* local population extinctions
* geographic range contraction
* delcines in population size
* local population extinctions
* geographic range contraction
10
New cards
biological annhilation
population decay increases confidence of 6th extinction occurrence
11
New cards
Populations are spatially structured
i.e. big horn sheep -→ metapopulation
12
New cards
Metapopulation
network of subpopulations linked by movement of individuals among them
\
local dynamics of each subpopulation are independent
\
local dynamics of each subpopulation are independent
13
New cards
metapopulation persistence is determined by __ and _ of subpopulations
local extinction and recolonization
14
New cards
Metapopulations picture
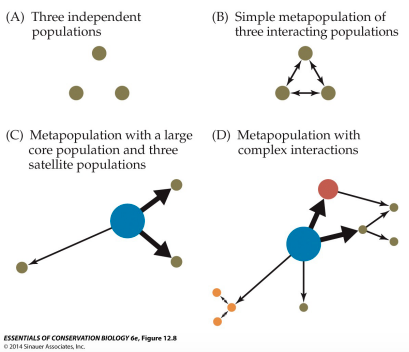
15
New cards
Source-sink theory
* Model population dynamics in the context of heterogeneous habitats patches
* Habitat quality varies from patch to patch
* Variation in habitat quality affects demographic (births & deaths)
* Habitat quality varies from patch to patch
* Variation in habitat quality affects demographic (births & deaths)
16
New cards
Source
* good habitat quality
* natality > mortality
* r > 0
* demographic excess
* net emigration
* natality > mortality
* r > 0
* demographic excess
* net emigration
17
New cards
Sink
* lower habitat quality
* mortality > natality
* r < 0
* demographic deficit
* net immigration
\
smaller isolated patches are sink habitats
* mortality > natality
* r < 0
* demographic deficit
* net immigration
\
smaller isolated patches are sink habitats
18
New cards
Conservation implications
* The “population” is the key unit of management and conservation focus
* Maintaining more and larger populations reduces extinction risk
* Local extirpation / elimination of local populations should be prevented
* Conserving source populations in high quality habitat is a particularly important conservation measure
* Maintaining more and larger populations reduces extinction risk
* Local extirpation / elimination of local populations should be prevented
* Conserving source populations in high quality habitat is a particularly important conservation measure
19
New cards
Large populations are less or more likely to go extinct?
less
20
New cards
the smaller the population, the ___ the extinction risk
greater
21
New cards
population size and extinction probability are ___ correlated
inversely
22
New cards
Problems of small populations
* Loss of genetic variation (genetic drift)
* Demographic stochasticity
* Environmental stochasticity
In general, the smaller the population becomes, the more influential of random processes become in determining population dynamics
* Demographic stochasticity
* Environmental stochasticity
In general, the smaller the population becomes, the more influential of random processes become in determining population dynamics
23
New cards
Minimum Viable Population
number of individuals necessary to ensure the long-term survival of a species
\
example: 99% chance of remaining extant for 1,000 years
* considers full range of environmental conditions
* requires detailed demographic study of populations
\
example: 99% chance of remaining extant for 1,000 years
* considers full range of environmental conditions
* requires detailed demographic study of populations
24
New cards
Population Viability Analysis
analytical technique that combines demographic analysis and environmental variation in predicting the probability of population persistence over time (and sometimes under different management scenarios)
* Risk assessment that incorporates demographic and environmental stochasticity
* Simulation approach: run model many times, report probability ranges
* Risk assessment that incorporates demographic and environmental stochasticity
* Simulation approach: run model many times, report probability ranges
25
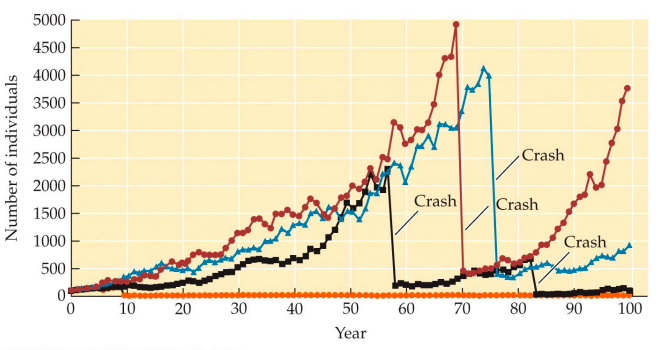
New cards
PVA output
each line, or population trajectory, represents on simulation
\
* they all have crashes and then population increase
\
* they all have crashes and then population increase
26
New cards
Minimum Dynamic Area
area of suitable habitat necessary for maintaining MVP
* puts MVP in spatial context
* estimated by studying spatial ecology and home range characteristics of target species
\
Useful in reserve design/planning, particularly when status of species populations are unknown.
* puts MVP in spatial context
* estimated by studying spatial ecology and home range characteristics of target species
\
Useful in reserve design/planning, particularly when status of species populations are unknown.
27
New cards
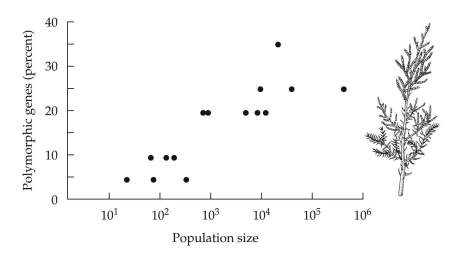
Is there a positive or negative association between genetic variation and population size?
positive
28
New cards
measures of genetic variation
* % polymorphic loci
* alleles per locus
* % heterozygosity
* alleles per locus
* % heterozygosity
29
New cards
Heterozygosity level is lower or higher with smaller population sizes?
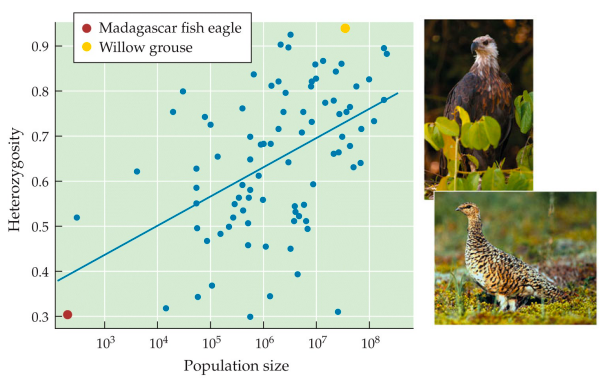
30
New cards
Genetic drift
change in allele frequencies and loss of genetic variation in a small population due to the random sampling of the gametes in sexual reproduction
31
New cards
All ___ populations are subject to genetic drift
finite
32
New cards
Genetic drift can alter __*___and cause the loss of___*__
allele frequencies; genetic variation
33
New cards
the magnitude of genetic drift is ___ to the population size
inversely proportional
34
New cards
when the population is _______*, genetic drift has a*__ ______ influence on allele frequencies than selection__
small; greater
35
New cards
What can counter the effects of drift?
Immigration
\
* with 1 immigrant per generation, population retains 90% initial heterozygosity
\
* with 1 immigrant per generation, population retains 90% initial heterozygosity
36
New cards
True or false. Natural mutation rates are not sufficient to counter effects of drift
true
37
New cards
Rate of loss of genetic variation is a function of __
effective population size
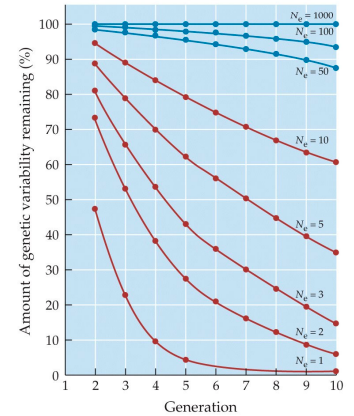
38
New cards
Effective population size (Ne)
“the number of breeding individuals in an idealized population that would show the same amount of dispersion of allele frequencies under random genetic drift or the same amount of inbreeding as the population under consideration“ (Wright 1938)
\
* smaller than actual population size
* not all individuals are reproductively mature
* not all reproductively mature individuals breed each year
* mating is not random/some individuals may have >1 mate
\
* smaller than actual population size
* not all individuals are reproductively mature
* not all reproductively mature individuals breed each year
* mating is not random/some individuals may have >1 mate
39
New cards
Factors that reduce effective population size
* Wide variation in reproductive output among individuals
* Mating system and/or unequal sex ratio
* Population fluctuations and bottlenecks
* Mating system and/or unequal sex ratio
* Population fluctuations and bottlenecks
40
New cards
Effective population size example
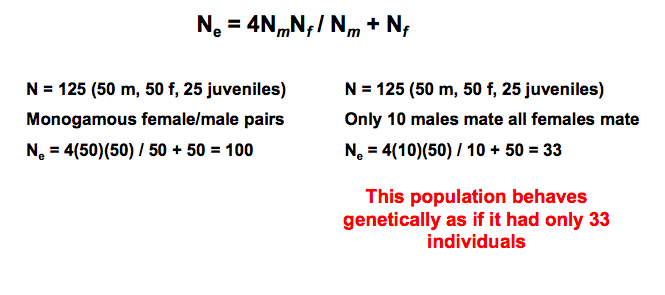
41
New cards
Does sex ratio affect effective population size?
yes.
\
overexploitation can alter sex ratios in wild populations
\
overexploitation can alter sex ratios in wild populations
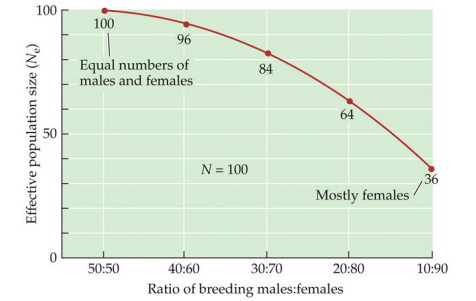
42
New cards
Population bottleneck
radical, short-term reduction in population size leading to lowering of N e and loss of genetic variation
* Greatest when N < 10 individuals for several generations
* Greatest when N < 10 individuals for several generations
43
New cards
founder effect
reduced genetic variability present when a new population is established by a small number of individuals
44
New cards
consequences of reduced genetic variability
* Inbreeding depression
* Loss of evolutionary flexibility
* (Outbreeding depression)
* Loss of evolutionary flexibility
* (Outbreeding depression)
45
New cards
Inbreeding
mating of close relatives; offspring alleles are identical by descent
46
New cards
Inbreeding coefficient (F)
ranges from 0 (no inbreeding) to 1 (complete inbreeding, all alleles identical by descent)
47
New cards
Inbreeding depression
the decline in fitness observed in inbred progeny relative to completely outbred individuals
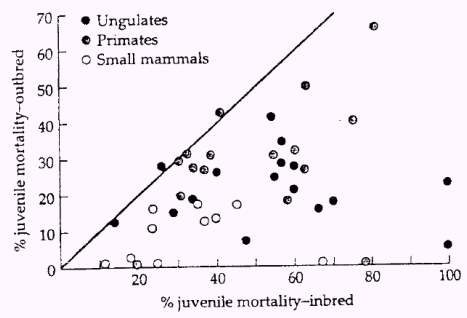
48
New cards
Loss of evolutionary flexibility
* Rare alleles and unique combinations of alleles may confer selective advantages for future set of environmental conditions
* Loss of genetic variability → limits potential response (plasticity) to changing future conditions
* Example: plant response to increasing concentrations of atmospheric gases or toxic metals in soil
* Loss of genetic variability → limits potential response (plasticity) to changing future conditions
* Example: plant response to increasing concentrations of atmospheric gases or toxic metals in soil
49
New cards
vulnerability to demographic stochaticity
* Species with naturally variable birth and death rates (e.g., annual plants, insects)
* Species with inherently low birth rates (populations take longer to recover after a decline)
* Species with inherently low birth rates (populations take longer to recover after a decline)
50
New cards
Allee effect
inability of a species’ social structure or reproductive system to function once a population falls below a certain density or number of individuals
51
New cards
Allee effect examples
* Minimum group size for hunting success (e.g., wild dogs) or anti-predator defense (e.g., musk ox)
* Declines in nesting success of colonial nesting birds (e.g., passenger pigeons and seabirds)
* Difficulty finding mates at low population densities (e.g., tigers)
* Disruption of plant/animal pollination interactions
* Declines in nesting success of colonial nesting birds (e.g., passenger pigeons and seabirds)
* Difficulty finding mates at low population densities (e.g., tigers)
* Disruption of plant/animal pollination interactions
52
New cards
Environmental stochasticity
random variation in the biological and/or physical environment that increase the risk of extinction in small populations
\
* single, catastrophic events may cause local extinctions
\
* single, catastrophic events may cause local extinctions
53
New cards
biological environmental stochasticity
fluctuation in population size of competitors, predators, or pathogens
54
New cards
Physical environmental stochasticity
variation in precipitation or disturbance events (fire, floods, etc.)
55
New cards
___ stochasticity is generally more important than __ stochasticity in increasing probability of extinction and may affect species with relatively larger population sizes
environmental; demographic
56
New cards
Extinction vortex
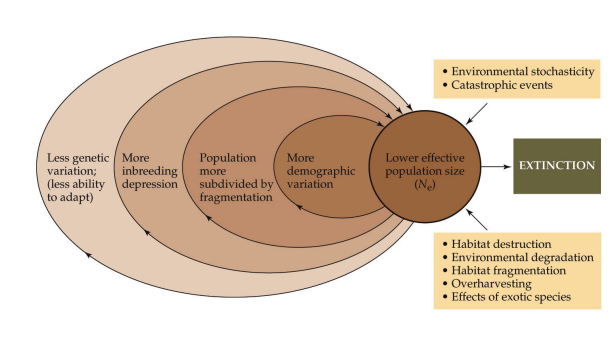
57
New cards
genetic restoration
the elimination or reduction of deleterious alleles and recovery to normal levels of genetic variation for a population in poor genetic health by the introduction of individuals from a genetically healthy population
\
* florida panther
\
* florida panther
58
New cards
Florida panther major threats
* Habitat loss and fragmentation
* Road mortality
suffered from inbreeding depression
* Road mortality
suffered from inbreeding depression
59
New cards
florida panther management option 1
Remove kittens from Florida population for captive breeding and release program.
60
New cards
florida panther management option 1 advantage
* maintain subspecies integrity
* can select/breed individuals with or without specific traits
* can select/breed individuals with or without specific traits
61
New cards
florida panther management option 1 disadvantage
* Risk that reintroduced animals won’t be released or survive in the wild.
62
New cards
florida panther management option 2
Artificially restore gene flow into Florida population by introducing Texas pumas (Puma concolor stanleyana)
63
New cards
florida panther management option 2 advantage
* **Potential to purge deleterious traits**
* **Continued incentive for habitat conservation**
* **Continued incentive for habitat conservation**
64
New cards
florida panther management option 2 disadvantage
Risk of outbreeding depression
65
New cards
Which primary THREATS to biodiversity do protected areas address directly?
overexploitation and habitat loss
66
New cards
Tropical rainforest hotspots
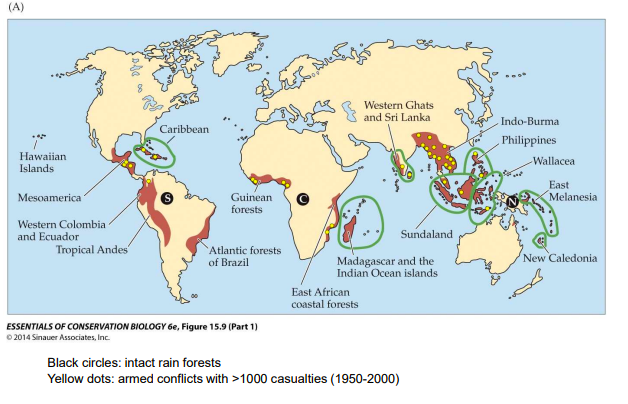
67
New cards
Mediterranean & Temperate hotspots
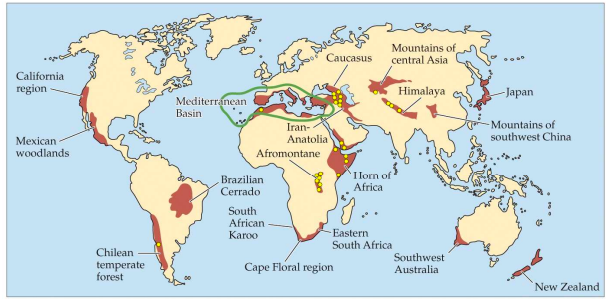
68
New cards
reserve selection: biodiversity hotspots
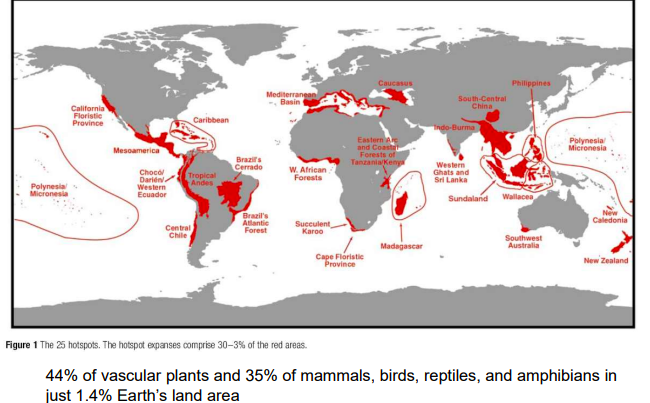
69
New cards
peak of species richness in USA
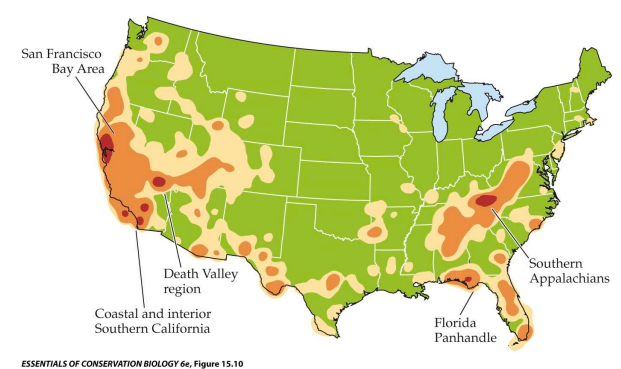
70
New cards
Where does this leave biodiversity coldspots?
* There is no single solution to reserve design/selection
* All areas need biodiversity and functioning ecological systems (regardless of their species richness)!
* All areas need biodiversity and functioning ecological systems (regardless of their species richness)!
71
New cards
___ are the highest converted biome
temperate grasslands
72
New cards
Gap analysis
using geographic information systems to select areas of reserve
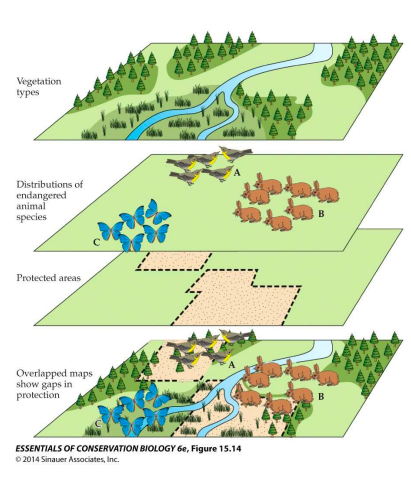
73
New cards
gap species
one not well protected in any part of its range
74
New cards
conceptual model of gap analysis
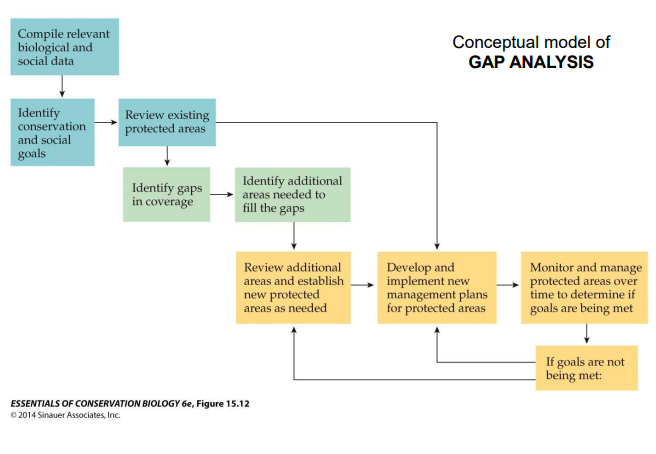
75
New cards
principles of reserve design
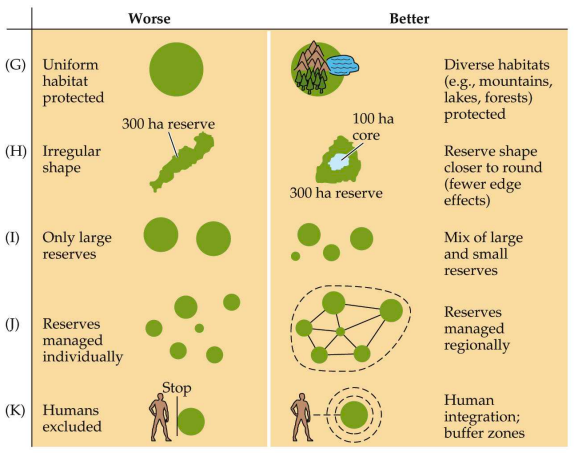
76
New cards
Four R’s of reserve design
* representation
* preserving all types
* redundancy
* multiple examples of each habitat types
* resiliency
* conserve an area that can recover after disturbances
* reality
* always going to be an impact of a reserve design
* sometimes have to relocate people
* sometimes receive donations or land to conserve
* preserving all types
* redundancy
* multiple examples of each habitat types
* resiliency
* conserve an area that can recover after disturbances
* reality
* always going to be an impact of a reserve design
* sometimes have to relocate people
* sometimes receive donations or land to conserve
77
New cards
general pattern of a biosphere reserve
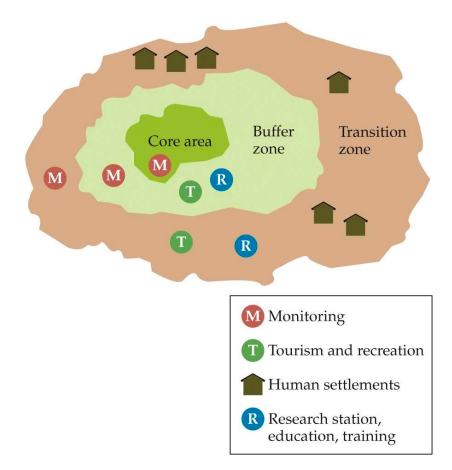
78
New cards
Core areas
complete protection in national parks
79
New cards
Buffer zones
sustainable forestry and agriculture
80
New cards
Terrestrial protected areas reduce
deforestation
81
New cards
Protected status affects
deforestation rates
82
New cards
paper parks
areas of land that are designated as protected areas on paper but lack the resources and management necessary to actually provide protection to the wildlife and ecosystems within them
83
New cards
Empty forests
areas of forest that appear to be intact from the outside, but have lost most of their large animals due to hunting and other human activities. These forests may still have trees and smaller animals, but the loss of large animals can have significant ecological impacts.
84
New cards
Resources for ___ are critical for protected areas
enforcement
85
New cards
defaunation
the decline or extinction of animal populations in a particular habitat or ecosystem, often caused by human activities such as habitat destruction, hunting, and climate change.
86
New cards
genetic restoration outcomes
* Reduction in frequency of traits associated with inbreeding in hybrids
* Increased reproduction and survival
* Population increase to >100 within 10 years • Shift in population age distribution
* Increase measures of genetic diversity
* Evidence of range expansion into previously vacant habitats
* Increased reproduction and survival
* Population increase to >100 within 10 years • Shift in population age distribution
* Increase measures of genetic diversity
* Evidence of range expansion into previously vacant habitats
87
New cards
panther example: do purebred and hybrid panthers survive at different rates?
* Hybrid female survival > purebred
* No difference among males
* Hybrid kittens 3x more likely to reach adulthood than purebreds
* No difference among males
* Hybrid kittens 3x more likely to reach adulthood than purebreds
88
New cards
Isle Royale
* Critically low numbers of wolves remaining
* High levels of inbreeding
* Low immigration and expected extirpation of wolves
* Remote location and isolation from Mainland
* Declining frequency of ice bridge formation due to climate change
* Low probability of adequate natural colonization to “rescue” population
* High levels of inbreeding
* Low immigration and expected extirpation of wolves
* Remote location and isolation from Mainland
* Declining frequency of ice bridge formation due to climate change
* Low probability of adequate natural colonization to “rescue” population
89
New cards
NEPA
national environmental policy act
90
New cards
What does NEPA require? Isle Royale
that federal agencies (like the National Park Service) explore alternative actions and make their decision-making open to the public.
91
New cards
Actions considered: Isle Royale
A.) No action
B.) Immediate Limited Introduction
C.) Immediate Introduction with Potential Supplemental Introductions
D.) No Immediate Action with Allowance for Future Action
B.) Immediate Limited Introduction
C.) Immediate Introduction with Potential Supplemental Introductions
D.) No Immediate Action with Allowance for Future Action
92
New cards
Outcomes of alternative elements : Isle Royale
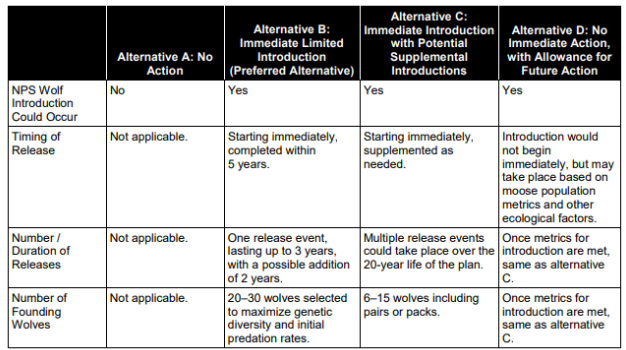
93
New cards
ex situ conservation
“off site” in captivity
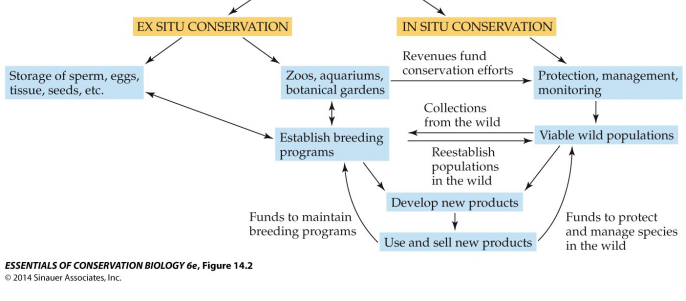
94
New cards
Population Establishment (3)
1. Reintroduction programs
2. Reinforcement/augmentation/restocking programs
3. Introduction programs
95
New cards
Reintroduction Programs
* involve release of individuals into an ecologically suitable site within their historic range
* Individuals may be captive-bred or collected from wild
* Establish new population within native environment
* Individuals may be captive-bred or collected from wild
* Establish new population within native environment
96
New cards
Reinforcement/augmentation/restocking programs
involve release of individuals into existing population to increase its size or alter gene pool
\
class examples:
* Florida panther (Puma concolor coryii) genetic restoration
* Isle Royale wolf (Canis lupus) rescue
* Kemp’s ridley sea turtle “headstarting”
* collect eggs and raise hatchlings in captivity before releasing
* “double-clutching” or chick fostering in endangered birds
* collect first eggs laid, female will produce and raise a second clutch
* incubate eggs and raise chicks in captivity
* Potentially doubles reproductive output of a rare female
\
class examples:
* Florida panther (Puma concolor coryii) genetic restoration
* Isle Royale wolf (Canis lupus) rescue
* Kemp’s ridley sea turtle “headstarting”
* collect eggs and raise hatchlings in captivity before releasing
* “double-clutching” or chick fostering in endangered birds
* collect first eggs laid, female will produce and raise a second clutch
* incubate eggs and raise chicks in captivity
* Potentially doubles reproductive output of a rare female
97
New cards
Introduction programs
* involve releasing animals or plants into ecologically suitable sites outside of historic range
* What conditions justify “introduction?
* What conditions justify “introduction?
98
New cards
Reintroduction of wild-caught individuals
* Individuals collected from closest healthy population and translocated to new site
* Screening to ensure genetically diverse “founder” population and select individuals adapted to a similar environment and climate
* Many successful examples:
* Gray wolf (Canis lupus) reintroduction into Greater Yellowstone ecosystem in late-1990’s
* White rhinoceros re-introductions in southern Africa
* Screening to ensure genetically diverse “founder” population and select individuals adapted to a similar environment and climate
* Many successful examples:
* Gray wolf (Canis lupus) reintroduction into Greater Yellowstone ecosystem in late-1990’s
* White rhinoceros re-introductions in southern Africa
99
New cards
Isle Royale is a __ release
hard
100
New cards
Yellowstone is a __ release
soft